当前位置:网站首页>Based on OpenGL glaciers and firebird (illumination calculation model, visual, particle system)
Based on OpenGL glaciers and firebird (illumination calculation model, visual, particle system)
2022-08-02 22:02:00 【biyezuopinvip】
目录
一、 项目简介 3
- Introduction to functions and operations 3
- 代码简介 3
- Correspondence to course design requirements 4
二、 场景实现 4 - 冰川 4
- Sun and time change 5
- 天空 6
- 雾效 6
- 风 6
三、 粒子系统 7 - 粒子生成器 7
- 雪 7
- 雨 8
- 火鸟 8
- 火 10
四、 交互控制 10 - 相机 10
- 角色 11
- Implementation of the rest of the interaction 12
五、 辅助功能 13 - Loader.h 13
- Mesh.h 13
- Shader_m.h 13
六、 External helpers and libraries 13 - 核心模式,GLFW与GLAD 13
- GLM 13
- Learn OpenGL 13
- Blender 14
- Stb_image 14
- Mmsystem.h 14
七、项目感想 14
一、项目简介
1.Introduction to functions and operations
This project builds a glacier scene.
The scene includes an ice surface、天空.拥有白天、夜晚、黄昏/Three time periods at dawn,雨、雪、暴风、雾等天气.
There is a firebird in the scene,And some flames scattered all over the map.Firebird approaching blue flames,It can be detonated,The flames then turned red,Then it turns back to blue after a while.
The user can control the movement of the firebird、视角的转换、Time changes fast、Weather switching, etc.
Use the mouse to control the viewing angle,The scroll wheel zooms in and out.
使用WSControls the Firebird to move along the current viewing direction,ADControl the firebird to turn.
Use the number keys to toggle the weather:
1:晴天
2:雨天
3:No wind and snow
4:暴风雪
使用+、-Change the speed of time change
(Since the above are all sticky bonds,The button needs to be long-pressed to take effect)
2.代码简介
使用了OpenGL的核心模式,And use some external libraries and code.with the same name as the header filevsThe file is the vertex shader corresponding to the model,fsfor the fragment shader.
CG.cpp:主函数,Create window is included,创建、Draw all objects in the scene,Control system wind,接受用户输入,Control the weather and more.
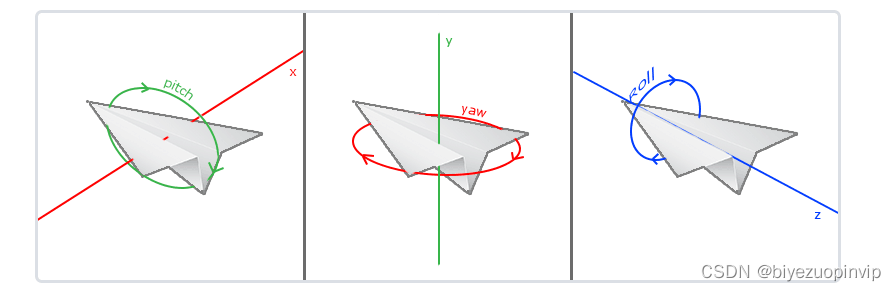
Camera.h:Responds to wheel and movement events of the user's mouse,转换视角.At the same time, the position and direction of the camera are modified according to the motion state of the bound object.
Character.h:Respond to the user's keyboardWASD输入,Change the movement state of the character.Control the character at the same time(火鸟)wings flapping、粒子效果等.
Fire.h:Controls the properties of the flames in the scene.Detects the distance to the protagonist,Control flame explosions.
Floor.h:Create glacial terrain.
Fog.h:Controls the range and variation of the fog.
Light.h:Controls the properties of the sun、移动.
Loader.h:读入模型.
Mesh.h:The model that will be read in withVAO、VBO绑定,加载纹理.
Particle.h:粒子生成器,Generates particles based on various attributes of the input.
Rain.h / Snow.h:control rain、Snow particle system.
Sky.h:Controls the properties of the sky.
Shader_m.h:加载着色器.
Stb_image.h:Read in an image as a texture.
Glad.c:在运行时查找opengl函数的具体位置.
The last three files are imported directly from outside,未作修改.此外,还使用了glfw、glm等库(详见“External helpers and libraries”).
3.Correspondence to course design requirements
(1)Scene modeling and rendering,Add lighting to the scene,Lighting can be interactively controlled(20分,According to the complexity of the scene、Rendering effect, etc)
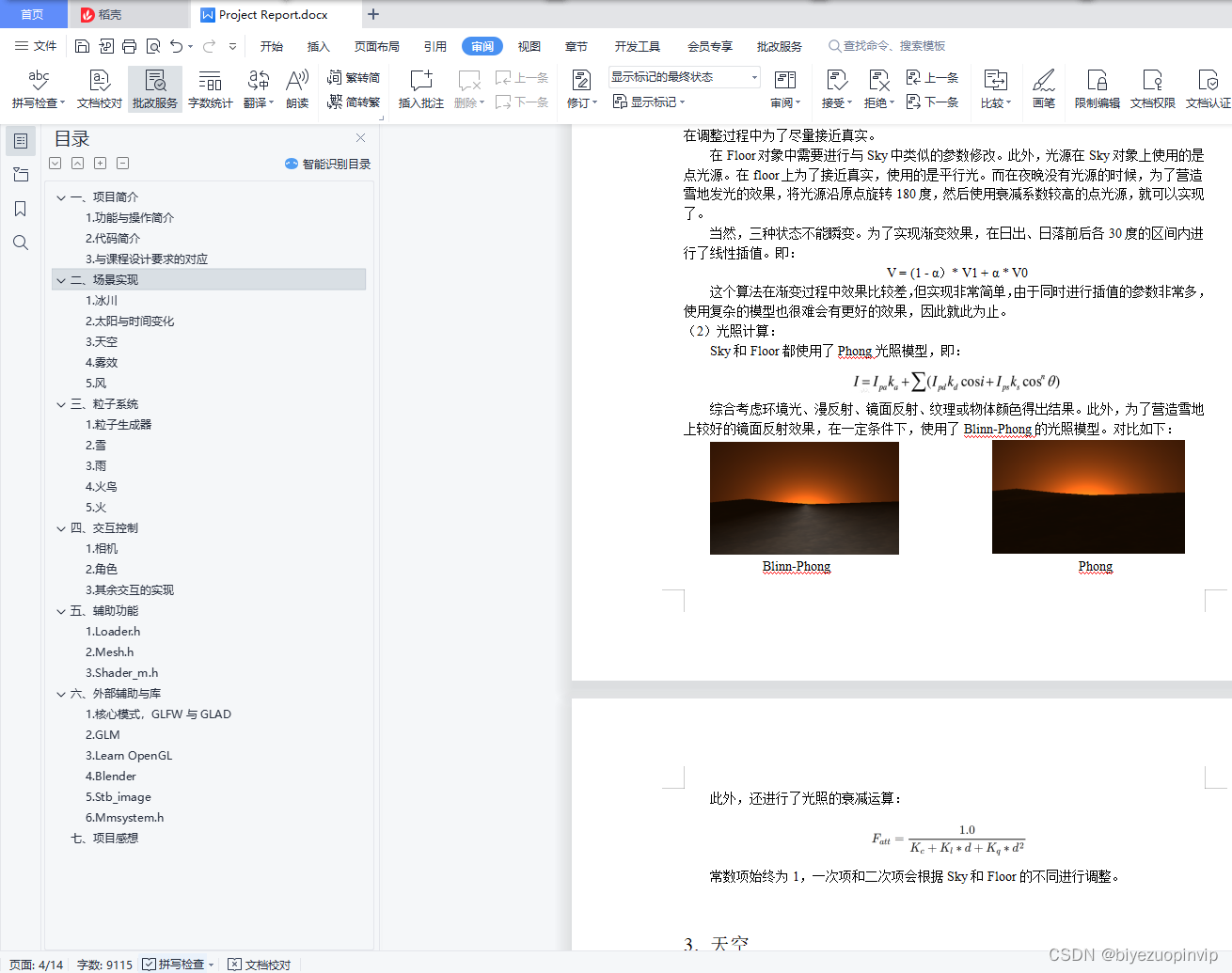
场景使用blender建模.Try external model import,But it didn't work well, so I gave up.The render has a render of the sun and sky、Rendering of fog effects, etc.
The sun in the scene、火焰、Firebirds have light.
Interactive control of lighting:The speed of time change can be controlled、Interacting with the flame changes the intensity of the flame light、颜色.
(2)Design and implement particle system special effects,There are physics simulations for particle motion,The 3D model of particles in the particle system can be switched in real time(30分,According to the special effect complexity of the particle system、计算模型、Algorithm efficiency, etc)
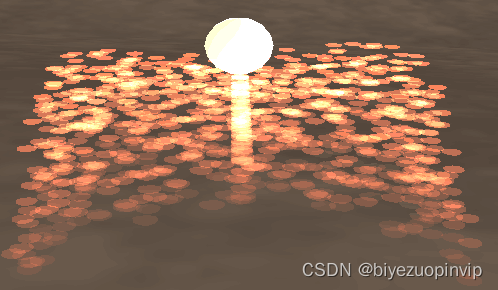
The particle system has rain、雪、火焰、Firebird wings.
雨、雪、Fire has a physical relationship to the wind in the scene,粒子的位置、速度、The acceleration uses the laws of physics.
It can be used when controlling the weather changes,Switch the 3D model of particles in the particle system in real time.
(3)Lighting of the 3D model of the particle、纹理映射(20分,The complexity of implementing the method in terms of the visual appearance of the particles、Implement performance scoring)
Particles use a 3D model,Snow particles and light sources in the scene have lighting calculations.Fire particles allow for computational efficiency,A light source is set in the position of the generator to create the effect of the example glowing.
火粒子、Snow particles have texture maps.
(4)Design and implement interactive control of particle systems(20分,According to the novelty of interaction、Natural and interactive response scoring)
The user can control the movement of the firebird、视角的转换、Time changes fast、Weather switching, etc.
本文来转载自:http://www.biyezuopin.vip/onews.asp?id=16550
#pragma once
#ifndef CAMERA_H
#define CAMERA_H
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <vector>
// Defines several possible options for camera movement. Used as abstraction to stay away from window-system specific input methods
/*enum Camera_Movement { FORWARD, BACKWARD, LEFT, RIGHT };*/
// Default camera values
const float YAW = -90.0f;
const float PITCH = 0.0f;
//const float SPEED = 2.5f;
const float SENSITIVTY = 0.1f;
const float ZOOM = 45.0f;
// An abstract camera class that processes input and calculates the corresponding Eular Angles, Vectors and Matrices for use in OpenGL
class Camera
{
public:
// Camera Attributes
glm::vec3 Position;
glm::vec3 Front;
glm::vec3 Up;
glm::vec3 Right;
glm::vec3 WorldUp;
// Eular Angles
float Yaw;
float Pitch;
// Camera options
//float MovementSpeed;
float MouseSensitivity;
float Zoom;
// Constructor with vectors
Camera(glm::vec3 position = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3 up = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), float yaw = YAW, float pitch = PITCH) : Front(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)), MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVTY), Zoom(ZOOM)
{
Position = position;
WorldUp = up;
Yaw = yaw;
Pitch = pitch;
updateCameraVectors();
}
// Constructor with scalar values
Camera(float posX, float posY, float posZ, float upX, float upY, float upZ, float yaw, float pitch) : Front(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)), MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVTY), Zoom(ZOOM)
{
Position = glm::vec3(posX, posY, posZ);
WorldUp = glm::vec3(upX, upY, upZ);
Yaw = yaw;
Pitch = pitch;
updateCameraVectors();
}
Camera(Character c) : MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVTY), Zoom(ZOOM)
{
Position = glm::vec3(c.GetPosition().x - c.GetDirection().x * 3.0f,c.GetPosition().y + 1.0f, c.GetPosition().z - c.GetDirection().z * 3.0f);
WorldUp = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
Front = glm::normalize(-Position + c.GetPosition() * 3.0f); //dst - src
Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Front, WorldUp));
Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Right, Front));
Yaw = -90.0f;
//std::cout << Yaw;
Pitch = -atan(1.0f / 3.0f) * 180.0f / Pi;
}
// Returns the view matrix calculated using Eular Angles and the LookAt Matrix
glm::mat4 GetViewMatrix()
{
return glm::lookAt(Position, Position + Front, Up);
}
// Processes input received from any keyboard-like input system. Accepts input parameter in the form of camera defined ENUM (to abstract it from windowing systems)
/* void ProcessKeyboard(Camera_Movement direction, float deltaTime) { float velocity = MovementSpeed * deltaTime; if (direction == FORWARD) Position += Front * velocity; if (direction == BACKWARD) Position -= Front * velocity; if (direction == LEFT) Position -= Right * velocity; if (direction == RIGHT) Position += Right * velocity; }*/
// Processes input received from a mouse input system. Expects the offset value in both the x and y direction.
void ProcessMouseMovement(float xoffset, float yoffset, Character c, GLboolean constrainPitch = true)
{
//std::cout << Front.x << std::endl;
xoffset *= MouseSensitivity;
yoffset *= MouseSensitivity;
Yaw += xoffset;
Pitch += yoffset;
// Make sure that when pitch is out of bounds, screen doesn't get flipped
if (constrainPitch)
{
if (Pitch > 89.0f)
Pitch = 89.0f;
if (Pitch < -89.0f)
Pitch = -89.0f;
}
// Update Front, Right and Up Vectors using the updated Eular angles
//Pitch = -atan(2.0f / 1.0f) * 180.0f / Pi;
updateCameraVectors();
float angle = atan(Front.z / Front.x);
if (Front.x < 0) angle -= Pi;
//else if (Direction.x < 0 && cameraDir.x > 0)angle += pi;
float x = cos(angle);
float z = sin(angle);
Position = glm::vec3(c.GetPosition().x - x * 3.0f, c.GetPosition().y + 1.0f, c.GetPosition().z - z * 3.0f);
}
// Processes input received from a mouse scroll-wheel event. Only requires input on the vertical wheel-axis
void ProcessMouseScroll(float yoffset)
{
if (Zoom >= 1.0f && Zoom <= 45.0f)
Zoom -= yoffset;
if (Zoom <= 1.0f)
Zoom = 1.0f;
if (Zoom >= 45.0f)
Zoom = 45.0f;
}
void MoveCameraByCharacter(Character c) {
//std::cout << c.GetDirection().x*c.GetDirection().x + c.GetDirection().z + c.GetDirection().z << std::endl;
Position = glm::vec3(c.GetPosition().x - c.GetDirection().x * 3.0f, c.GetPosition().y + 1.0f, c.GetPosition().z - c.GetDirection().z * 3.0f);
//double endAngle = atan((double)c.GetDirection().z / (double)c.GetDirection().x);
//double startAngle = atan((double)Front.z / (double)Front.x);
//std::cout << Xstart << " i " << Ystart << " j " << Xend << " x " << Yend << " y " << std::endl;
//防止180跳变
//if (Front.x > 0 && c.GetDirection().x < 0) endAngle += pi;
//else if (Front.x < 0 && c.GetDirection().x > 0)endAngle += pi;
//Direction = cameraDir;
//Yaw -= endAngle * 180.0f / Pi - startAngle * 180.0f / Pi;
//updateCameraVectors();
//std::cout << Yaw << std::endl;
//Front = c.GetDirection();
//WorldUp = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
//Front = glm::normalize(-Position + c.GetPosition()); //dst - src
//Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Front, WorldUp));
//Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Right, Front));
//Yaw = 0.0f;
//std::cout << Yaw;
//Pitch = -atan(2.0f / 1.0f) * 180.0f / Pi;
}
void RotateCameraByCharacter(Character c, bool isleft) {
Position = glm::vec3(c.GetPosition().x - c.GetDirection().x * 3.0f, c.GetPosition().y + 1.0f, c.GetPosition().z - c.GetDirection().z * 3.0f);
if(isleft)
Yaw -= c.rotateAcce;
else
Yaw += c.rotateAcce;
updateCameraVectors();
Front = glm::vec3(c.GetDirection().x * sqrt(1 - Front.y * Front.y), Front.y, c.GetDirection().z * sqrt(1 - Front.y * Front.y));
Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Front, glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f))); // Normalize the vectors, because their length gets closer to 0 the more you look up or down which results in slower movement.
Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Right, Front));
}
glm::vec3 GetHorizDir() {
return glm::vec3(Front.x* sqrt(1 - Front.y * Front.y), 0, Front.z* sqrt(1 - Front.y * Front.y));
}
private:
// Calculates the front vector from the Camera's (updated) Eular Angles
void updateCameraVectors()
{
// Calculate the new Front vector
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(Pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(Pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(Pitch));
Front = glm::normalize(front);
// Also re-calculate the Right and Up vector
Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Front, WorldUp)); // Normalize the vectors, because their length gets closer to 0 the more you look up or down which results in slower movement.
Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Right, Front));
}
};
#endif




边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
【C语言刷题】双指针原地修改数组(力扣原题分析)
想通过FC连接RDS mysql。是不是将FC服务角色添加rds权限后,就可以通过地址,端口建连了呢
Geoserver+mysql+openlayers2
register和volatile的区别
说一件事
实例034:调用函数
药品研发--工艺技术人员积分和职务考核评估管理办法
MySQL 事件调度
thinkphp框架5.0.23安全更新问题-漏洞修复-/thinkphp/library/think/App.php具体怎么改以及为什么要这么改
What are the useful real-time network traffic monitoring software
动态折线图,制作原来是这么简单
博云入选 Gartner 中国 DevOps 代表厂商
AtomicInteger详解
汇编实例解析--利用tcb,tss,全局tss,ldt管理任务实现任务切换
深度学习-学习笔记(持续更新)
去年,一道蚂蚁金服笔试题,还行,中等难度
为何国内年轻人都抢购iPhone,因为它更实惠也更亲民
I have 8 years of experience in the Ali test, and I was able to survive by relying on this understanding.
openlayers版本更新差别
Detailed explanation of AtomicInteger