当前位置:网站首页>Write a ten thousand word long article "CAS spin lock" to send Jay's new album to the top of the hot list
Write a ten thousand word long article "CAS spin lock" to send Jay's new album to the top of the hot list
2022-07-07 15:13:00 【Bulst】
Before the order
After many years , Jay finally released a new album ,《 The greatest work 》 Let's cross to 1920 year , I saw Margaret's green apple 、 Dali's surreal 、 Legs painted by Chang Yu 、 Monet's water lily 、 Xu Zhimo's Poems …
He said “ The greatest work ” It's not your own song , But the greatest works of art in the world .
Why write CAS Spin lock ? I looked at it recently Java Several ways to realize random numbers , Research research is to study quantum mechanics , So let's go back to the code , Look at the underlying implementation is used CAS, Just in time for Zhou Dong to sing , Just make a coincidence ~
Please subscribe to these free columns 【 Later, it will become a paid column 】, Listen to me. Thank you , Because of you , Warm the four seasons ~
《Java Is the core technology 》《 Middleware core technology 》
《 Core technology of microservice 》《 Cloud native core technology 》
List of articles
CAS The core principle
CAS namely Compare and Swap, Compare and exchange .
CAS It's an optimistic lock , The so-called optimistic lock is , Do not lock each time, but assume that there is no conflict to complete an operation , If the conflict fails, try again , Until we succeed .
【 As for other locks , We'll talk about it next , This article mainly explains CAS】
CAS An operation contains three operands —— Memory location V、 The original value of the expected A And the new value B.
If the value of the memory location matches the expected original value , Then the processor will automatically update the memory location value to the new value , otherwise , The processor does nothing .
i++ and ++i Is it atomic operation
Let's start with the answer : No .
Decompiled into bytecode files, it is easy to see this non atomic operation , First, getfield, And then again iadd.
i++ There are three steps :
- Remove from stack i
- i Self increasing 1
- take i Save to stack
++i
On a multi-core machine ,cpu Reading memory i It may also happen that the same value is read at the same time , This leads to two self accretions , Actually, it is only increased once .
++i How to achieve atomicity
【++i How to achieve atomicity 】
Code implementation
public final int incrementAndGet() {
// Dead cycle
for (;;) {
// The original value of the expected (A)
int current = get();
// The new value (B)
int next = current + 1;
// CAS operation
if (compareAndSet(current, next))
// If successful, the result is returned
return next;
}
}
Here we use CAS operation , Read the data from memory every time and then sum the data with +1 After the results go on CAS operation , If it succeeds, it returns the result , Otherwise try again until you succeed .
#compareAndSet utilize JNI To complete CPU The operation of instructions
/** * Atomically sets the value to the given updated value * if the current value {@code ==} the expected value. * * @param expect the expected value * @param update the new value * @return {@code true} if successful. False return indicates that * the actual value was not equal to the expected value. */
public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
Go deep into the #compareAndSwapInt Method , You will find that it is through JNI Method
public final native boolean compareAndSwapInt(Object var1, long var2, int var4, int var5);
What exactly does this method do ? Two things should be done .
- Current memory location V Whether it is equal to the expected original value A
- If equal to, the memory location V Update to the new value B, Come back anyway false
For clarity 、 Intuitively explain the problems here , Let's code it .
// 1. Current memory location V Whether it is equal to the expected original value A
if (V == A) {
// 2. If equal to, the memory location V Update to the new value B
V = B;
return true;
} else {
// Come back anyway false
return false;
}
There is a problem here , How to ensure the steps 1 And steps 2 What about atomicity ?
that , Our next question , Just explore compareAndSwapInt Realized. .
We mentioned above ,CAS By calling JNI Of code implementation .
JNI:Java Native Interface by JAVA Local call , allow java Call other languages ,JNI The method will eventually pass Jni.dvmCallJNIMethod() -> dvmPlatformInvoke() According to different cpu Architecture implementation to call , How to use it , Let's talk about next .
How to use Java call C++
Forget it , I'll write you a little demo, Let's first briefly understand how to use Java Call other languages .
First step :
Write a test class
package com.ossa.producer.jni;
/** * JNI Test class * * @author issavior */
public class JniUnit {
/** * Call local method */
public native void sayHello();
/** * Static blocks are used to load libraries ,jni.so We need to generate it manually , Put it under this path */
static {
System.load("/Users/issavior/java/mygit/ossa/ossa-service-producer/src/main/resources/jni.so");
}
/** * Program entrance * * @param args Parameters */
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JniUnit().sayHello();
}
}
The second step :
If it is Maven project , Can pass mvn Command to compile the Java file , If not , Just use javac Recompile, , I use mavan The way .
The third step :
stay class Under the path , perform javah command
[email protected] classes %
javah com.ossa.producer.jni.JniUnit
After that, it will generate jni The header file com_ossa_producer_jni_JniUnit.h:
/* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE - it is machine generated */
#include "jni.h"
/* Header for class com_ossa_producer_jni_JniUnit */
#ifndef _Included_com_ossa_producer_jni_JniUnit
#define _Included_com_ossa_producer_jni_JniUnit
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/* * Class: com_ossa_producer_jni_JniUnit * Method: sayHello * Signature: ()I */
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_ossa_producer_jni_JniUnit_sayHello
(JNIEnv *, jobject);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
Step four :
Write and implement c file jniUnit.c, Introduce the header file and method implementation just generated
#include "com_ossa_producer_jni_JniUnit.h"
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_ossa_producer_jni_JniUnit_sayHello
(JNIEnv * env, jobject obj){
printf("hello JNI");
}
From your $JAVA_HOME/include/ Contents and $JAVA_HOME/include/darwin/ Find jni.h and jni_md.h Copy the header to the current directory 【mac Words , The first thing you need to shift+command+. Open hidden file 】
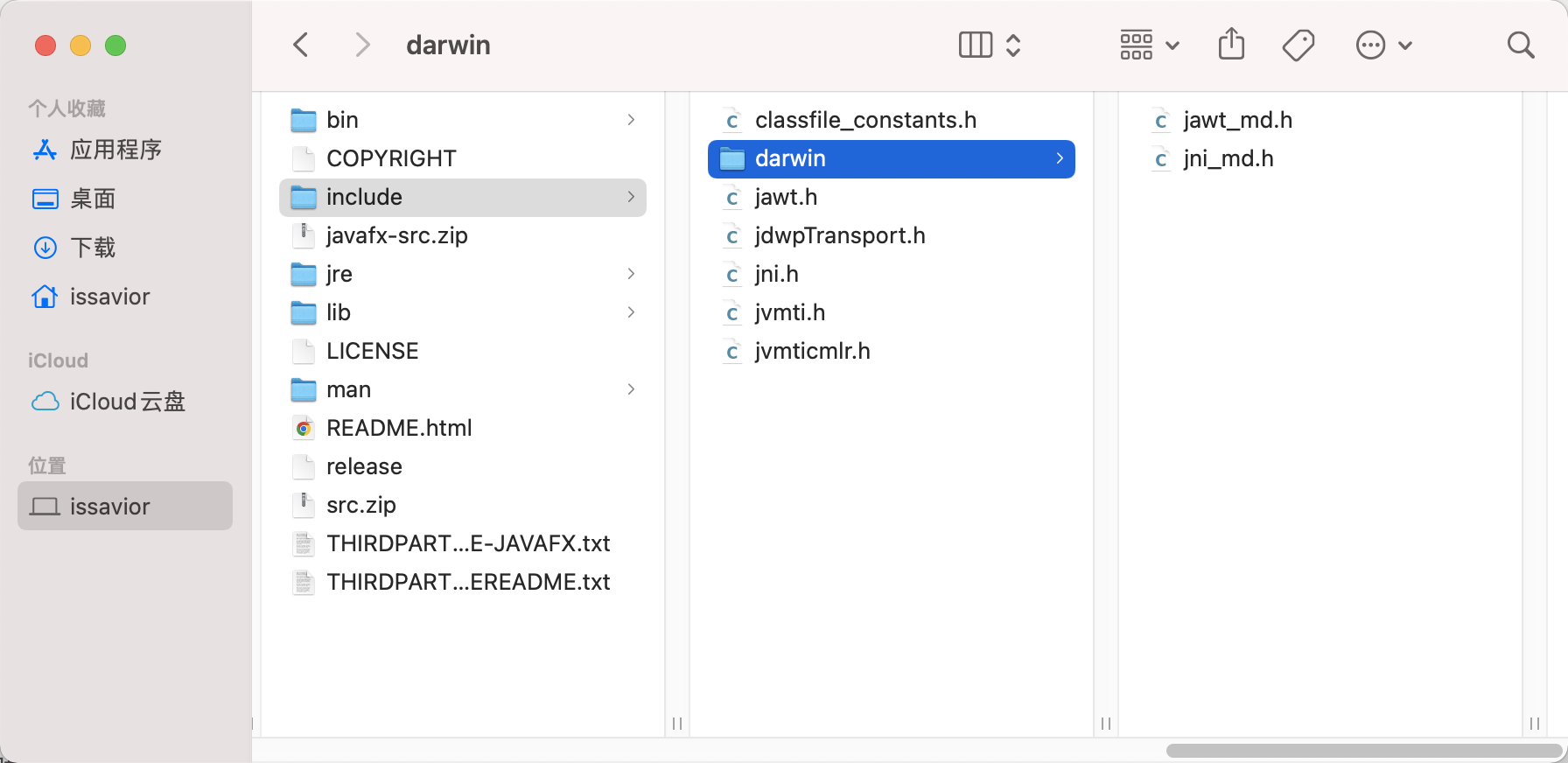
perform gcc -shared -fPIC -o jni.so jniUnit.c Compile to generate dynamic library
If this times the following error
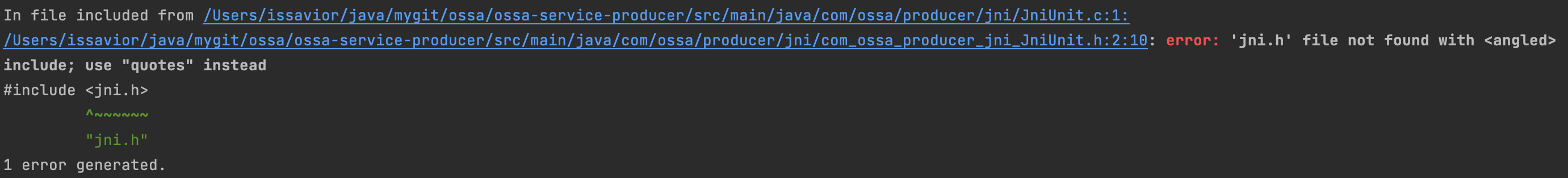
will com_ossa_producer_jni_JniUnit.h In file #include <jni.h> It is amended as follows #include "jni.h"
After the compilation is successful, the current directory will appear jni.so file , Put it in the specified directory .
Finally, test our JniUnit class , success !
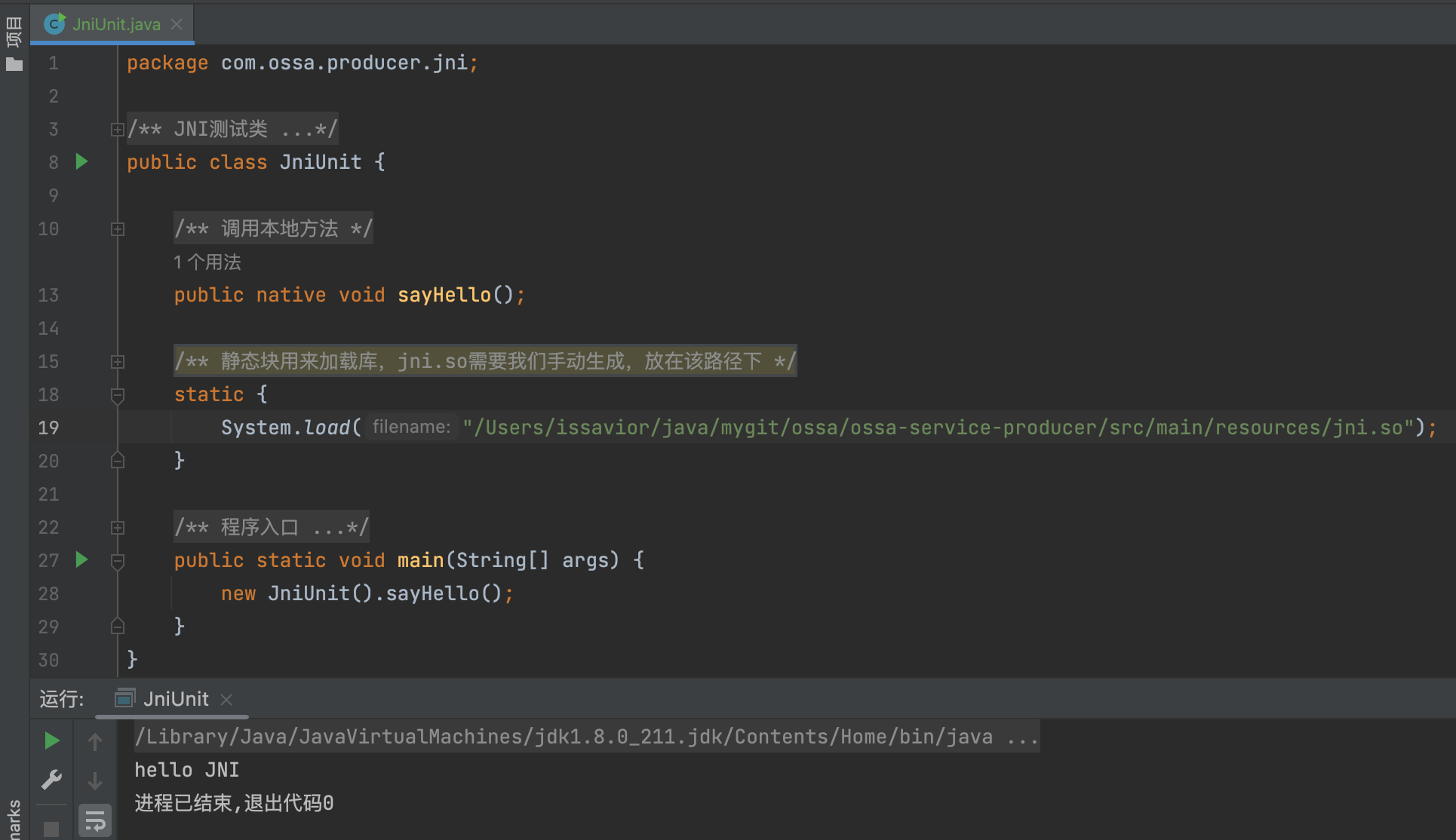
Here we are , I have personally led you to complete Java Small cases of calling other languages , So everyone is right native Methods have a deeper understanding , and compareAndSwapInt With the help of C To call CPU Underlying instructions (cmpxchg) To achieve .
cmpxchg It's an atomic instruction , This instruction is to lock the data bus , So it's thread safe .
Let's analyze its source code , So how to find the location of local method implementation ?
JNI Naming specification
Through the above case , We can know javah It can help us generate header files , Then you will find native The local method name of the method is generated according to certain rules . Therefore, you can set the corresponding local method name , Then search the source code .
according to JNI Local method name generation specification :
- The prefix for Java_
- Fully qualified class name ( Including the package name and the full path of the class ), In the middle to _ Division
- Method name
- For overloaded native Method , Follow the method name __ And parameter labels
We can infer that intern Local method name of method :
- With Java_ start
- The package name is converted to java_lang_String
- The method is called intern
- The result after splicing is Java_sun_misc_Unsafe_compareAndSwapInt
compareAndSwarpInt Source code analysis
stay unsafe.cpp In file , Can find compareAndSwarpInt The implementation of the :
UNSAFE_ENTRY(jboolean, Unsafe_CompareAndSwapInt(JNIEnv *env, jobject unsafe, jobject obj, jlong offset, jint e, jint x))
UnsafeWrapper("Unsafe_CompareAndSwapInt");
// take Java Object resolved to JVM Of oop( Normal object pointer )
oop p = JNIHandles::resolve(obj);
// According to object p And the address offset to find the address
jint* addr = (jint *) index_oop_from_field_offset_long(p, offset);
// // be based on cas Compare and replace , x Indicates the value that needs to be updated ,addr Express state Address in memory ,e Indicates expected value
return (jint)(Atomic::cmpxchg(x, addr, e)) == e;
UNSAFE_END
CAS shortcoming
CAS Although very efficient to solve the atomic operation , however CAS There are still three major problems .ABA problem
If a value turns out to be A, Turned into B, It's changed again. A, So use CAS Check that its value has not changed , But it actually changed .
ABA The solution to the problem is to use version number .
Append the version number to the variable , Each time the variable is updated, add one to the version number , that A-B-A Will become 1A-2B-3A.
from Java1.5 Start JDK Of atomic A class is provided in the bag AtomicStampedReference To solve ABA problem . This class of compareAndSet Method first checks whether the current reference is equal to the expected reference , And whether the current flag is equal to the expected flag , If all are equal , Then atomically set the reference and the value of the flag to the given update value .
// Static inner class , Encapsulates the Variable references and Version number
private static class Pair<T> {
final T reference; // Variable references
final int stamp; // Version number
private Pair(T reference, int stamp) {
this.reference = reference;
this.stamp = stamp;
}
static <T> Pair<T> of(T reference, int stamp) {
return new Pair<T>(reference, stamp);
}
}
private volatile Pair<V> pair;
/** * * @param initialRef Initial variable reference * @param initialStamp Version number */
public AtomicStampedReference(V initialRef, int initialStamp) {
pair = Pair.of(initialRef, initialStamp);
}
Common methods
// Constructors , Initialize reference and version number
public AtomicStampedReference(V initialRef, int initialStamp)
// Get the current reference value atomically
public V getReference()
// Get the current version number atomically
public int getStamp()
// Get the current reference value and version number atomically
public V get(int[] stampHolder)
// Update the reference value and version number at the same time in an atomic way
// When the expected reference value is not equal to the current reference value , operation failed , return false
// When the expected version number is not equal to the current version number , operation failed , return false
// On the premise that the expected reference value and the expected version number are equal to the current value at the same time
// When the new reference value and the new version number are equal to the current value , Not updated , Go straight back to true
// When the new reference value and the new version number are different and equal to the current value , At the same time, set the new reference value and the new version number , return true
public boolean weakCompareAndSet(V expectedReference,
V newReference,
int expectedStamp,
int newStamp)
// Update the reference value and version number at the same time in an atomic way
// When the expected reference value is not equal to the current reference value , operation failed , return false
// When the expected version number is not equal to the current version number , operation failed , return false
// On the premise that the expected reference value and the expected version number are equal to the current value at the same time
// When the new reference value and the new version number are equal to the current value , Not updated , Go straight back to true
// When the new reference value and the new version number are different and equal to the current value , At the same time, set the new reference value and the new version number , return true
public boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference,
V newReference,
int expectedStamp,
int newStamp)
// Atomically set the current value of the reference to the new value newReference
// meanwhile , Set the current value of the version number atomically as the new value newStamp
// Only one of the new reference value and the new version number is different from the current value , Just update
public void set(V newReference, int newStamp)
// Set the version number to the new value atomically
// Premise : Reference value remains unchanged
// When the expected reference value is different from the current reference value , operation failed , return fasle
// When the expected reference value is the same as the current reference value , Successful operation , return true
public boolean attemptStamp(V expectedReference, int newStamp)
// Use `sun.misc.Unsafe` Exchange two objects atomically
private boolean casPair(Pair<V> cmp, Pair<V> val)
Case study
If thread safe
/** * Program entrance * * @param args Parameters */
public static void main(String[] args) {
// The initial reference value is 【1】; The version number is 【1】
AtomicStampedReference<Integer> reference = new AtomicStampedReference<>(1, 1);
Integer reference1 = reference.getReference();
System.out.println(" Initial reference value " + reference1); // Initial reference value 1
// The expected initial reference value is 【1】;
// Update the reference to 2;
// The expected initial version number is 【1】;
// The updated version number is 2
boolean b = reference.weakCompareAndSet(1, 2, 1, 2);
// whether swap success
System.out.println(b); // true
// Get the reference value again
Integer reference2 = reference.getReference();
System.out.println(" Latest quoted value " + reference2); // Latest quoted value 2
}
If the thread is not safe
/** * Program entrance * * @param args Parameters */
public static void main(String[] args) {
// The initial reference value is 【1】; The version number is 【1】
AtomicStampedReference<Integer> reference = new AtomicStampedReference<>(1, 1);
Integer reference1 = reference.getReference();
System.out.println(" Initial reference value " + reference1); // Initial reference value 1
// The thread is not safe at this time , The expected reference value is 【2】;
// Update the reference to 2;
// The thread is not safe at this time , The expected version number is 【2】;
// The updated version number is 2
boolean b = reference.weakCompareAndSet(2, 2, 2, 2);
// whether swap success
System.out.println(b); // false
// Get the reference value again
Integer reference2 = reference.getReference();
System.out.println(" Latest quoted value " + reference2); // Latest quoted value 1
}
The cycle time is long and the cost is high
If CAS You don't succeed , It spins in place , If you spin for a long time, you will CPU Bring very large and unnecessary expenses .
Can destroy for Dead cycle , When more than a certain time or a certain number of times ,return sign out .
JDK8 Newly added LongAdder and ConcurrentHashMap Similar approach .
When multiple threads compete , Reduce the particle size , Split a variable into multiple variables , Achieve the effect of multiple threads accessing multiple resources , Last call sum Put it together .
although base and cells All are volatile Embellished , But this sum The operation is not locked , Probably sum The results are not so accurate .
Only one atomic operation of shared variables can be guaranteed
When operating on a shared variable , We can use cycles CAS The way to guarantee atomic operation , But when operating on multiple shared variables , loop CAS There is no guarantee of atomicity of operation , You can use the lock at this time , Or there's a clever way , It is to combine multiple shared variables into a shared variable to operate .
For example, there are two shared variables i=2,j=a, Merge ij=2a, And then use CAS To operate ij. from Java1.5 Start JDK Provides AtomicReference Class to ensure atomicity between reference objects , You can put multiple variables in one object CAS operation .
AtomicReference Of API
// When using a parameterless constructor to create AtomicReference When the object ,
// Need to call... Again set() Method is AtomicReference Inside value Specify the initial value .
AtomicReference()
// establish AtomicReference Object, and specify the initial value .
AtomicReference(V initialValue);
/** Update atomically AtomicReference Inside value value , among expect On behalf of the current AtomicReference Of value value ,update Is the new reference value to be set . This method returns a boolean Result , When expect and AtomicReference When the current values of are not equal , Modification will fail , The return value is false, If the modification is successful, it will return true. **/
compareAndSet(V expect, V update)
// Update atomically AtomicReference Inside value value , And back to AtomicReference The old value .
getAndSet(V newValue)
// Update atomically value value , And back to AtomicReference The old value , This method needs to pass in a Function Interface .
getAndUpdate(UnaryOperator<V> updateFunction)
// Update atomically value value , And back to AtomicReference Updated new value , This method needs to pass in a Function Interface .
updateAndGet(UnaryOperator<V> updateFunction)
// Update atomically value value , And back to AtomicReference Old value before update .
// This method needs to pass in two parameters , The first is the updated new value , The second is BinaryOperator Interface .
getAndAccumulate(V x, BinaryOperator<V> accumulatorFunction)
// Update atomically value value , And back to AtomicReference Updated value .
// This method needs to pass in two parameters , The first is the updated new value , The second is BinaryOperator Interface .
accumulateAndGet(V x, BinaryOperator<V> accumulatorFunction)
// obtain AtomicReference The current object reference value of .
get()
// Set up AtomicReference Latest object reference value , The update of this new value is immediately visible to other threads .
set(V newValue)
// Set up AtomicReference Object reference value of .
lazySet(V newValue)
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

全日制研究生和非全日制研究生的区别!
时空可变形卷积用于压缩视频质量增强(STDF)
![[server data recovery] data recovery case of raid failure of a Dell server](/img/5d/03bc8dcc6e554273b34a78c49a9eaf.jpg)
[server data recovery] data recovery case of raid failure of a Dell server
#yyds干货盘点# 解决名企真题:交叉线

暑期安全很重要!应急安全教育走进幼儿园

Promoted to P8 successfully in the first half of the year, and bought a villa!

Ctfshow, information collection: web10
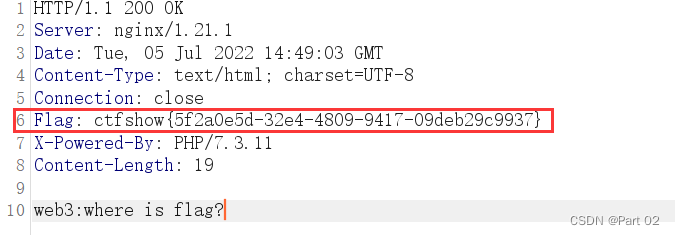
Ctfshow, information collection: Web3

CTFshow,信息搜集:web3
![[data mining] visual pattern mining: hog feature + cosine similarity /k-means clustering](/img/a4/7320f5d266308f6003cc27964e49f3.png)
[data mining] visual pattern mining: hog feature + cosine similarity /k-means clustering
随机推荐
Comparable and comparator of sorting
Shengteng experience officer Episode 5 notes I
【OBS】RTMPSockBuf_Fill, remote host closed connection.
FFmpeg----图片处理
CTFshow,信息搜集:web12
CPU与chiplet技术杂谈
写一篇万字长文《CAS自旋锁》送杰伦的新专辑登顶热榜
⼀个对象从加载到JVM,再到被GC清除,都经历了什么过程?
Concurrency Control & NoSQL and new database
Today's sleep quality record 78 points
最安全的证券交易app都有哪些
一个需求温习到的所有知识,h5的表单被键盘遮挡,事件代理,事件委托
#HPDC智能基座人才发展峰会随笔
Ctfshow, information collection: web10
[Yugong series] go teaching course 005 variables in July 2022
[follow Jiangke University STM32] stm32f103c8t6_ PWM controlled DC motor_ code
Bye, Dachang! I'm going to the factory today
TypeScript 发布 4.8 beta 版本
[make a boat diary] [shapr3d STL format to gcode]
Ctfshow, information collection: Web3