writing | Li Xudong ( flower : Xiang Xu )
Technical expert of ant group
Ant middleware R & D , Focus on SOFARegistry And its surrounding infrastructure development and optimization
this paper
2098
word read
8
minute
| Preface |
MOSN Used Subset Algorithm as its label matching routing load balancing method . This paper mainly introduces Subset Principle , Including under the super large-scale cluster MOSN Of Subset Some performance bottlenecks encountered and the optimization algorithm used .
First ,
Why optimize Subset Well ?
Overall speaking , Performance bottlenecks are often exposed gradually due to the increase of cluster size . In the super large colony of ants , The address list pushed by the registry will cause some overhead to the application .
In a large-scale pressure test I participated in , The number of machines for core applications is very large , When it comes to release or operation and maintenance , Its address list will be pushed to all applications that call it .
and MOSN Will receive this address list to rebuild its own route . When the address list is very large ,MOSN to update cluster The performance bottleneck of is gradually exposed , A higher CPU skin needling , Memory rose in a short time ,gc The frequency has also increased significantly .
Through the flame diagram below , We can see the effect on an application during this pressure test MOSN Of pprof:
-
Alloc:

-
CPU:

from pprof You can see , Whether it's CPU still alloc The cost of , structure SubsetLoadBalancer Are obviously taking the lead , Therefore, it is urgent to optimize the construction of this part .
Finally, through exploration and optimization ,
We can reduce SubsetLoadBalancer During construction 95% Of CPU Expenses and 75% Of alloc expenses .
Let's review the process and ideas of this optimization .
PART. 1--Subset Introduction to basic principles
In a cluster , Usually machines have different labels , So how do you route a request to a set of machines with a specified tag ?
MOSN The method is to pre group the machines under a service according to the machine tag combination , Form multiple subsets . At the time of request , According to the metadata The information can quickly query the subset that the request should match .
As shown in the figure below , You can see that there are 4 Nodes :

The tag matching rule will be based on zone 、mosn_aig 、mosn_version this 3 Fields to match the route , According to this 3 individual key The following matching paths are obtained by combining the sorting of :

The corresponding matching tree is as follows :

Suppose you need to access {zone: zone1, mosn_aig: aig1}, Then the search order after sorting is mosn_aig:aig1 -> zone:zone1, Find the [h1, h2].
That's all Subset Introduction to the basic principles of .
PART. 2--MOSN Yes Subset The construction of
There are two parameters that need to be input first :
-
List of machines with labels hosts, such as [h1, h2, h3, h4];
-
For matching subSetKeys, Here's the picture :

Then let's bring our thoughts , Then read the source code MOSN Of SubsetLoadBalancer How to build this tree .
The core idea is as follows :
-
Go through each one host Of labels and subSetKeys Recursion to create a tree ;
-
For each node of the tree , It's all traversed once hosts list , Filter out the matching nodes kvs Of subHosts, Each node creates a child load balancer.
Let's look at the source code diagram :

The overall build complexity is O
(M
N
K)
(M: Subset The number of tree nodes ,N: Hosts Number , K: Matching Keys)
PART. 3-- Build performance bottleneck analysis
Through the production of profile analysis , We found that SubsetLoadBalancer Of createSubsets stay CPU and alloc The proportion in the flame diagram is high . So let's start writing benchmark, To optimize the performance of this part .
Our input parameter is :
-
subSetKeys:

-
8000 individual hosts
( Every hosts There are 4 individual label, Every label Corresponding 3 Kind of value)
:

next , Let's see CPU and alloc_space The occupancy of .
-
CPU:

-
alloc_space:
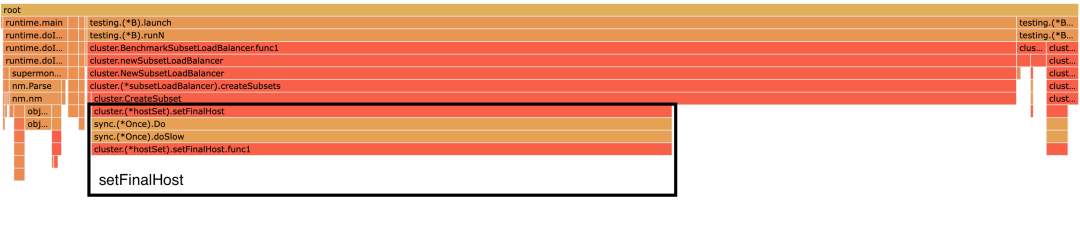
From the above two flame diagrams , We can see that HostMatches and setFinalHost It takes up a lot of CPU_time and alloc_space. Let's look at it first HostMatches:

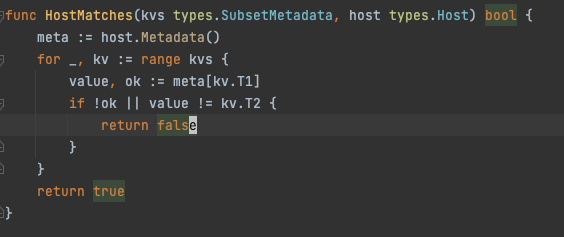
Its function is to judge a host Whether it exactly matches the given key value pair , And judge this host Whether to match this matching tree node .
Its overhead mainly lies in the excessive number of executions :treeNodes * len(hosts) , So when the cluster gets larger , The running cost here will increase significantly .
Then let's take a look at setFinalHost:


His main logic is to follow IP Deduplication , It also comes with copy. If we were SubsetLoadBalancer The top layer of the , Then its arbitrary Subset You don't need to do it again . therefore , Here you can change it to no weight .
PART. 4-- Optimized construction of inverted index
stay HostMatches In so many matches , There is actually a lot of repetition , For example, yes. host label One of them kv Judge equals, The build process is repeated quite a lot .
Therefore, the optimization idea can be based on avoiding this part of repeated overhead , Starting from the pre built inverted index . The specific steps are as follows :
1.
Enter two parameters :
-
subSetKeys:

-
hosts:

2.
Traverse once hosts, For each kv We use it bitmap Building inverted index :

3.
according to subSetKeys And inverted index kvs, Build a match tree , Because the index is de duplicated and hosts Number independent , This operation cost is very low ;
4.
For each node of the tree , Use the... In the inverted index bitmap Do the intersection to quickly get all the matches kv Of hosts The index of bitmap;
5.
Use bitmap Stored in the index from hosts Take out the corresponding subHosts Builder load balancer, Also note that... Is not required here setFinalHosts Deduplication .
Based on the above ideas and processes, new Subset preIndex Building algorithms , Can be in MOSN Corresponding Pull Request Page view details :
https://github.com/mosn/mosn/pull/2010
Share and add benchmark The address where the test was conducted :
https://github.com/mosn/mosn/blob/b0da8a69137cea3a60cdc6dfc0784d29c4c2e25a/pkg/upstream/cluster/subset_loadbalancer_test.go#L891


You can see the construction method compared with the previous one , The construction speed is fast
20
times ,alloc_space Reduced
75%
. meanwhile ,alloc There was a small increase in the number of times , This is due to the need to build an additional inverted index .
Let's take a look at gc:

We can find out , Compared to the previous build , Less memory during runtime , and CPU Less memory is reclaimed , meanwhile gc The duration of parallel scanning increased slightly ,STW Time becomes shorter .
Last , Test it in different hosts The degree of optimization under the number , You can see in the hosts When the number is large
(>100)
, The new construction algorithm will be significantly better than the old construction algorithm .

PART. 5-- summary
We see in mass production environments , Some previously unnoticed performance bottlenecks are often exposed , But through pressure measurement , We can find and optimize these problems in advance .
at present , The build algorithm has been incorporated into MOSN master, As MOSN default SubsetLoadBalancer Construction mode .
In this optimization process , We used some common optimization methods , Such as : Inverted index 、bitmap. It's not hard to see. , Although the basis of these optimization methods is common , But also achieved the ideal optimization effect , I hope it can help you .
Learn more about
MOSN Star once :
https://github.com/mosn/mosn
原网站版权声明
本文为[InfoQ]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
https://yzsam.com/2022/173/202206221009459262.html