当前位置:网站首页>2020080 simulation competition [horizontal and vertical coordinates do not affect each other, cactus minimum cut, combined meaning translation formula]
2020080 simulation competition [horizontal and vertical coordinates do not affect each other, cactus minimum cut, combined meaning translation formula]
2022-06-11 07:29:00 【Master. Yi】
T1 We met a master
Title Description
X ∗ Y X*Y X∗Y Circular mesh of ( The left and right are connected , The upper and lower edges are connected ).
give n n n The lower left and upper right points of a rectangle are aligned , Each rectangle can be placed in one of four ways :
seek n n n The maximum area that a rectangle can cover at the same time .
Examples :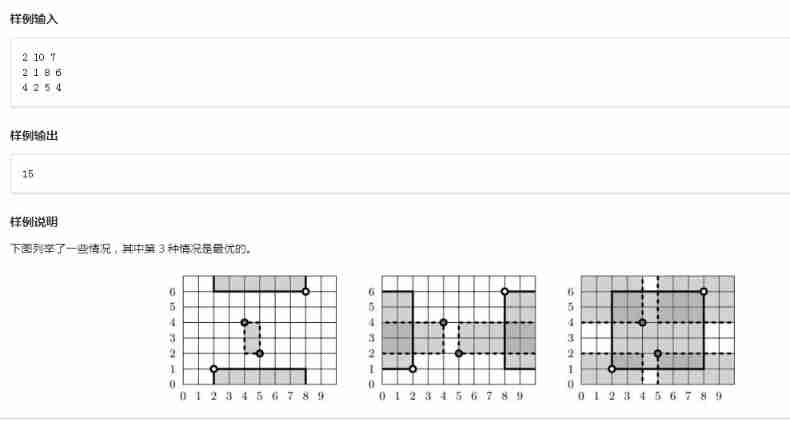
Topic analysis
At first glance, it seems very impossible to do .
Think about / After the violence I feel this rectangle is very beautiful . Exactly 4 Ways of planting , Horizontal and vertical coordinates 2 Kind of .
This enlightens us to put Look at the horizontal and vertical coordinates separately , Then multiply the two best answers .
Then the problem becomes one-dimensional , Each rectangle becomes a line segment , Divide the number axis into many segments .
So each segment has a state , Is the line segment corresponding to each rectangle inside or outside .
Those in the same state can be accessed at the same time .
Then give this 01 Set a hash value in the string , Segments with the same hash value are added up , Take the maximum length .
Scan from left to right , It can be used map, The faster way is to get each hash value and then sort by hash value .
Code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 500005
#define y1 y_1
#define LL long long
#define ULL unsigned long long
#define rep(i,j,k) for(int i=(j),LIM=(k);i<=LIM;i++)
using namespace std;
char cb[1<<20],*cs,*ct;
#define getc() (cs==ct&&(ct=(cs=cb)+fread(cb,1,1<<20,stdin),cs==ct)?0:*cs++)
void read(int &a){
char c;while(!isdigit(c=getc()));
for(a=c-'0';isdigit(c=getc());a=a*10+c-'0');
}
int n,X,Y,x1[maxn],y1[maxn],x2[maxn],y2[maxn];
ULL pw[maxn];
struct node{
int x; ULL v;
bool operator < (const node &p)const{
return x<p.x;}
}q[maxn*2]; int cnt;
map<ULL,int>val;
int solve(){
ULL H=0; val.clear();
int ret=0;
sort(q+1,q+1+cnt);
rep(i,0,cnt-1){
H+=q[i].v;
ret=max(ret,val[H]+=q[i+1].x-q[i].x);
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
freopen("master.in","r",stdin);
freopen("master.out","w",stdout);
read(n),read(X),read(Y);
rep(i,1,n) read(x1[i]),read(y1[i]),read(x2[i]),read(y2[i]);
rep(i,pw[0]=1,n) pw[i]=pw[i-1]*137;
q[cnt=1]=(node){
X,0};
rep(i,1,n) q[++cnt]=(node){
x1[i],pw[i]},q[++cnt]=(node){
x2[i],-pw[i]};
int ansx = solve();
q[cnt=1]=(node){
Y,0};
rep(i,1,n) q[++cnt]=(node){
y1[i],pw[i]},q[++cnt]=(node){
y2[i],-pw[i]};
int ansy = solve();
printf("%lld\n",1ll*ansx*ansy);
}
T2 ok take off
Title Description
A cactus , There's border power , set up f ( s , t ) f(s,t) f(s,t) by s → t s\to t s→t The minimum cut , seek ∑ 1 ≤ s < t ≤ n f ( s , t ) ⊕ s ⊕ t \sum_{1\le s<t\le n}f(s,t)\oplus s\oplus t ∑1≤s<t≤nf(s,t)⊕s⊕t
n ≤ 1 0 5 , w i ≤ 1 0 6 n\le 10^5,w_i\le 10^6 n≤105,wi≤106
Topic analysis
Consider the tree first , Obviously, the smallest edge is taken first to separate the two sides , Then a recursive , But this is not easy to achieve , You can add edges from large to small, and then merge them with a union , Because the number should take XOR , Separate the binary bits , Record the... In the connected block k k k Position as 0/1 The number of points , Then, according to the edge weight clause k k k Statistics weight of bit .
Cactus words , If the minimum cut falls on the ring , Then the two sides must be cut off , also The smallest edge of a ring must be cut , Then delete the smallest edge , Add its weight to the other edges of the ring , The minimum cut does not change .
So it becomes the case of trees .
Complexity O ( n log V ) O(n\log V) O(nlogV)
Code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 100005
#define maxm 400005
using namespace std;
char cb[1<<20],*cs,*ct;
#define getc() (cs==ct&&(ct=(cs=cb)+fread(cb,1,1<<20,stdin),cs==ct)?0:*cs++)
void read(int &a){
char c;while(!isdigit(c=getc()));
for(a=c-'0';isdigit(c=getc());a=a*10+c-'0');
}
int T,n,m;
int fir[maxn],nxt[maxm],to[maxm],w[maxm],tot=1;
void line(int x,int y,int z){
nxt[++tot]=fir[x],fir[x]=tot,to[tot]=y,w[tot]=z;}
int dfn[maxn],low[maxn],tim,stk[maxn*2],top;
struct edge{
int x,y,w;
bool operator < (const edge &p)const{
return w>p.w;}
}e[maxn]; int cnt;
void tarjan(int u,int ff){
dfn[u]=low[u]=++tim;
for(int i=fir[u],v;i;i=nxt[i]) if((v=to[i])!=ff){
if(!dfn[v]){
stk[++top]=i;
tarjan(v,u),low[u]=min(low[u],low[v]);
if(dfn[u]<low[v]) e[++cnt]=(edge){
u,v,w[i]},top--;
else if(dfn[u]==low[v]){
int mn=1e9,id;
for(int t=-1,j=top;t!=i;) t=stk[j--],mn>w[t]&&(mn=w[t],id=t);
for(int t=-1;t!=i;) t=stk[top--],id!=t&&(e[++cnt]=(edge){
to[t^1],to[t],w[t]+mn},0);
}
}
else if(dfn[v]<dfn[u]) stk[++top]=i,low[u]=min(low[u],dfn[v]);
}
}
int f[maxn],s[maxn][21][2];
int find(int x){
return !f[x]?x:f[x]=find(f[x]);}
int main()
{
freopen("okfly.in","r",stdin);
freopen("okfly.out","w",stdout);
read(T);
while(T--){
read(n),read(m);
memset(fir,0,(n+1)<<2),tot=1;
memset(dfn,0,(n+1)<<2),tim=top=0;
cnt=0;
for(int i=1,x,y,z;i<=m;i++) read(x),read(y),read(z),line(x,y,z),line(y,x,z);
tarjan(1,0);
long long ans=0;
sort(e+1,e+1+cnt);
//for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) cout<<e[i].x<<' '<<e[i].y<<' '<<e[i].w<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
f[i]=0;
for(int j=0;j<=20;j++) s[i][j][0]=s[i][j][1]=0,s[i][j][i>>j&1]++;
}
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++){
int x=find(e[i].x),y=find(e[i].y);
for(int k=0;k<=20;k++){
int w=e[i].w>>k&1;
for(int l=0;l<2;l++) ans+=1ll*s[x][k][l]*s[y][k][l^w^1]*(1<<k);
}
f[y]=x;
for(int k=0;k<=20;k++) s[x][k][0]+=s[y][k][0],s[x][k][1]+=s[y][k][1];
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
}
T3 This bowl doesn't go well with the restaurant
Title Description
The length is n n n Sequence a i a_i ai, n ≤ 200 , 1 ≤ a i ≤ 1000 n\le 200,1\le a_i\le 1000 n≤200,1≤ai≤1000
For a permutation p p p, Make b i = a p i , s i = ∑ j = 1 i b j b_i=a_{p_i}, s_i=\sum_{j=1}^ib_j bi=api,si=∑j=1ibj, Contribution: 1 ∏ i = 2 n s i \frac 1{\prod_{i=2}^ns_i} ∏i=2nsi1
Find the sum of the contributions of all permutations .
Topic analysis
This article blog Very good .
Introduce the hard way ( Not so much ):
Make m = ∑ a i m=\sum a_i m=∑ai
consider m m m A labeled ball , The first i i i There are... In different colors a i a_i ai individual , Arrange randomly .
Then the ball with the largest number in each color has the greatest probability of being located 1 ∏ a i \frac 1{\prod a_i} ∏ai1 .( Probability times n ! n! n! That's the number of schemes , So it's easier to understand later )
Consider an arrangement p p p, Indicates the order of the maximum positions of each color ( Thereafter, the maximum number is required to be in the maximum position ), So the probability of forming this arrangement is 1 ∏ i = 1 n s i \frac 1{\prod_{i=1}^n s_i} ∏i=1nsi1 ( p n p_n pn Indicates maximum )
And now we want to ∑ p 1 ∏ i = 2 n s i \sum_p \frac 1{\prod_{i=2}^ns_i} ∑p∏i=2nsi1, The color equivalent to the smallest in the largest position does not require the largest number to be in the largest position .
So let's enumerate the colors x x x, The remaining colors only need to meet the maximum number in the maximum position , And the maximum position is greater than x x x The maximum position of , Find the generation probability of the placement that meets the conditions .
The first limit only needs to be divided by the last one ∏ i ≠ x a i \prod_{i\neq x} a_i ∏i=xai, The second limit determines how many colors have a maximum position less than x x x The maximum position of the , Suppose this color set is S S S, So contribution is ( − 1 ) ∣ S ∣ ∗ a x a x + ∑ i ∈ S a i (-1)^{|S|}*\frac {a_x}{a_x+\sum_{i\in S}a_i} (−1)∣S∣∗ax+∑i∈Saiax, The last item is x x x The probability that the color will be in the maximum position .
enumeration ∑ a i \sum a_i ∑ai To calculate , Then you just need to know ∑ a i \sum a_i ∑ai Corresponding ∑ ( − 1 ) S \sum (-1)^S ∑(−1)S, It's just a backpack , It can be written as a generating function ( 1 − x a i ) (1-x^{a_i}) (1−xai), Remove the corresponding item when calculating a certain color .
Complexity O ( n ∗ m ) = O ( n 2 max a i ) O(n*m)=O(n^2\max a_i) O(n∗m)=O(n2maxai)
Code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define maxn 205
#define maxm 205*1005
using namespace std;
const int mod = 998244353;
int n,a[maxn],m,F[maxm],G[maxm],inv[maxm],Inv=1,ans;
int main()
{
freopen("restaurant.in","r",stdin);
freopen("restaurant.out","w",stdout);
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]);
F[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=(m+=a[i]);j>=a[i];j--)
F[j]=(F[j]-F[j-a[i]])%mod;
inv[0]=inv[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=m;i++) inv[i]=1ll*(mod-mod/i)*inv[mod%i]%mod;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) Inv=1ll*Inv*inv[a[i]]%mod;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int s=0;
for(int j=0;j<=m-a[i];j++) G[j]=(F[j]+(j>=a[i]?G[j-a[i]]:0))%mod, s=(s+1ll*G[j]*inv[j+a[i]])%mod;
s=1ll*s*a[i]%mod*a[i]%mod*Inv%mod;
ans=(ans+s)%mod;
}
printf("%d\n",(ans+mod)%mod);
}
边栏推荐
- Post-processing of ffmpeg miscellaneous notes
- What is the lifecycle of automated testing?
- MS office level II wrong question record [7]
- Server parameter adjustment record
- 【AtCoder2376】Black and White Tree(博弈)
- 多线程复习总结之解析Volatile关键字
- 【POJ3691】DNA repair (AC自动机+DP)
- [STL source code analysis] summary notes (7): ingenious deque
- [Oracle database] mammy tutorial day02 use of database management tool sqlplus
- Experience record of rural housing integration script
猜你喜欢

Summary of classic interview questions
![[STL source code analysis] summary note (2): overview of containers](/img/66/60fba564ae6020dfb503c7fdf78529.jpg)
[STL source code analysis] summary note (2): overview of containers

Mobile console Gobang (first draft of detailed design)
![[STL source code analysis] summary notes (7): ingenious deque](/img/da/8ec42bfdbbf1b5bd1c2e396c2213e2.jpg)
[STL source code analysis] summary notes (7): ingenious deque
10 advanced concepts that must be understood in learning SQL

CMAP of Matplotlib

Modular notes

如果要存 IP 地址,用什么数据类型比较好?99%人都会答错!
1、 Sqlserver2008 installation (with password), database creation, C form project test

群晖DS918创建m.2 固态硬盘SSD读写缓存
随机推荐
[analysis of STL source code] summary notes (3): vector introduction
MS office level II wrong question record [8]
Sdl-3 YUV playback
QT custom control library creation
Multi thread review summary parsing volatile keyword
[analysis of STL source code] summary notes (6): Design of iterator and magical traits
【CF】 A. New Year Candles
[STL source code analysis] summary notes (1): Opening
Ffmpe a small demo to understand 80% of common APIs
[Oracle database] mammy tutorial day03 Sorting Query
Nosqlzoo question brushing-1
R language Parallel Computing practice tutorial
Server parameter adjustment record
Cartland number application
C language judging big end and small end [consortium or pointer] big end and small end conversion
Mybags puls will report an error invalid bound statement (not found) when writing an SQL statement in the XML file:
Calculate the day of the week for a specific month, year and day
C memory alignment
MFC auxiliary CString string splicing
Djikstra solves the shortest circuit with negative weight