当前位置:网站首页>[STM32] actual combat 3.1 - drive 42 stepper motors with STM32 and tb6600 drivers (I)
[STM32] actual combat 3.1 - drive 42 stepper motors with STM32 and tb6600 drivers (I)
2022-07-07 10:55:00 【Goo Goo and melon】
Catalog
1 Expected effect of experiment
2.1.1 Set the subdivision and current through the dial switch
2.1.2 Common Yin and common Yang wiring method
2.2 Switching Mode Power Supply (AC turn DC transformer )& power cord
2.3.2 Speed subdivision control
2.3.3 Full step 、 half of step 、 Micro step driving principle
3 Software configuration and hardware wiring
3.1 STM32CubeMX Configuration of
3.1.1 Configure timer TIM2 edit
3.3 Subdivision and current regulation
6.1.3 Common faults and Countermeasures
6.2 42 Dimension drawing and internal structure of stepping motor
0 Reference source
Reference blog :
1、 utilize STM32F103 Accurately control the stepping motor _jl_mlh The blog of -CSDN Blog _stm32 Control stepping motor ;
Reference paper :
1、 Houyanxia . The working principle of hybrid stepping motor and its PLC control ;
1 Expected effect of experiment
Complete the forward rotation of the stepping motor ( No serial port control 、 Non removable power supply ).
2 Hardware learning
2.1 TB6600 Driver
The information provided by a treasure store is as follows : 
2.1.1 Set the subdivision and current through the dial switch



2.1.2 Common Yin and common Yang wiring method

Common Yin :
Driver —— stm32
DIR- And PUL- —— GND
DIR+ —— Direction pin
PUL+ —— Pulse pinGongyang :
Driver —— stm32
DIR+ And PUL+ —— +5V
DIR- —— Direction pin
PUL- —— Pulse pin
2.2 Switching Mode Power Supply (AC turn DC transformer )& power cord


2.3 42 Stepper motor

2.3.1 Basic knowledge
According to the information provided by the merchant :42 Step motor The number of phases is 2(A、B two-phase , The number of parallel branches per phase is 2, Each branch is connected in series 2 A coil )、 The step angle is 1.8°( Full step )、 The number of rotor teeth is 50.

Every beat There is only one phase The winding is energized , Four beats Form a cycle . Above picture , Stator B phase Electrify , magnetic pole 2 Of 5 Teeth and rotor Tooth to tooth ( Here's the picture 4), The analysis shows that , magnetic pole 6 Same as rotor Tooth to tooth , And the magnetic pole 4 and 8 yes Tooth to groove ( Here's the picture 2). Lateral A phase Winding magnetic pole 3 Of 5 Teeth and rotor teeth have 1/4 Dislocation of tooth pitch ( Here's the picture 3), namely 1.8°(360°/50/4).


When B Phase outage A When connected with electricity , magnetic pole 3 produce N Polarity , Attract the nearest S Pole rotor teeth , Make the rotor rotate clockwise 1.8°, Realization magnetic pole 3 And rotor Tooth to tooth , here magnetic pole 4 And rotor teeth 1/4 Dislocation of tooth pitch .
By analogy, if you continue to energize in the order of four beats , The rotor rotates clockwise step by step , Once every power on ( That is, every pulse ) The rotor turns 1.8°, Namely The step angle is 1.8°, It takes 360°/1.8° =200 Pulse . Consistent with the table .

【 Parameters and formulas can be found in the article : utilize STM32F103 Accurately control the stepping motor _jl_mlh The blog of -CSDN Blog 】
① Number of beats (N=km)—— The number of power on States contained in each cycle ( The number of pulses required for the motor to turn a pitch angle );
Single shot system (k=1)—— Number of beats = Phase number ; Two beat system (k=2)—— Number of beats = Twice the number of phases ;② Phase number (m)—— That is, inside the motor Number of coil groups . If you use Subdivision drive , be The number of phases will become meaningless , Just change the number of Subdivisions on the drive , You can change Step angle ;
③ Number of rotor teeth (Zr);
④ Step angle (θs)—— The stepper passes An electrical pulse The rotation angle of the rotor ;
⑤ speed (n)
2.3.2 Speed subdivision control
Motor's speed And Pulse frequency In direct proportion to , The motor turns angle And Number of pulses In direct proportion to . Therefore, the precise speed regulation can be achieved by controlling the number and frequency of pulses .

f: Pulse frequency ;θs: Step angle ;X: Subdivision values ;n: speed (rad/s).
If the step angle is known =1.8°, Subdivision values =32, Want to achieve 1rad/s Speed of ( One revolution per second ), Then the pulse frequency =1*32*360/1.8=6400, namely 6400 One pulse is one revolution , Consistent with the table given .

2.3.3 Full step 、 half of step 、 Micro step driving principle
【 This part is extracted from the article : Picture and text introduce the full step of stepping motor 、 half of step 、 Micro step driving principle 】
Full step drive ( Single shot full step drive and double shot full step drive ):

Half step drive :

The advantage of half step driving is to improve the resolution , But the disadvantage is that the torque is only driven in full step 70%, Of course , You can also optimize the current in the coil , To improve the half step driving torque .
Micro step drive :

The English on the picture is :With maximum power in phase A, phase B is at zero. The rotor will line up with phase A. As current to phase A decreases, it increases to phase B. The rotor will take small steps towards phase B until phase B is at its maximum and phase A is at zero. The process then continues around the other phases.
Translated roughly means :A The coil begins to have maximum current ,B The coil current is 0, The rotor points A coil . If A The coil current decreases slowly ,B The coil current increases slowly , The rotor will turn slowly B coil .
From a macro perspective ,A、B The current variation of the coil is close to the trigonometric function curve . The magnitude of each step of current change , Determines the size of the micro step movement . Although the more steps , The smoother the motion , But the torque will be reduced accordingly .

The change of current at each step , Determines the size of micro step movement , On the right is 1/4,1/8,1/16 Schematic diagram of Microstep current change .

Examples of micro step movement : In the figure 1 in ,A The coil is full of current , chart 2 in A The coil is connected with the maximum current 0.92 times , and B The coil is connected with the maximum current 0.38 times , Realization 22.5° rotate . Empathy , chart 3 in ,A and B The coil is connected with the maximum current at the same time 0.71 times , Can achieve 45° rotate .
The more steps , You can get The smoother The movement of , The less noise , It is not easy to lose step ( Lose step ), But the price is The torque is greatly reduced .
3 Software configuration and hardware wiring
3.1 STM32CubeMX Configuration of
【 See for basic configuration 【STM32】1— Zero basic hardware and software configuration & complete LED The twinkle of _ココの wonderful な My blog -CSDN Blog _stm32 Configuration software 】
Schematic diagram :

3.1.1 Configure timer TIM2 

Its output pin is PA0.
3.1.2 Configure pins PA1
Because I hope it turns forward , Then pull the level up :

3.2 Wiring mode of the driver
Adopt common female connection :

3.3 Subdivision and current regulation
Relevant see 2.1.1
4 Code writing
【 Code reference blog STM32 And TIM Timer drive 42 Stepper motor - Drive model TB6600_stm32 drive 42 Stepper motor 】
On the basis of automatic code generation, you need to main.c add :
Defining variables :
int count;Turn on PWM Interrupt and pull up the pin ( The latter can be omitted ):
HAL_TIM_PWM_Start_IT(&htim2,TIM_CHANNEL_1);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(DIR_GPIO_Port, DIR_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET); Count 1000 Stop after times :
void HAL_TIM_PWM_PulseFinishedCallback(TIM_HandleTypeDef *htim)
{
if(htim == &htim2)
{
if(count <1000)
{
count++;
}
else
{
HAL_TIM_PWM_Stop_IT(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_1);
count = 0;
}
}
}
The total code is as follows :
main.c:
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.c
* @brief : Main program body
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* Copyright (c) 2022 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software is licensed under terms that can be found in the LICENSE file
* in the root directory of this software component.
* If no LICENSE file comes with this software, it is provided AS-IS.
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "main.h"
#include "tim.h"
#include "gpio.h"
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
int count;
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Private typedef -----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PTD */
/* USER CODE END PTD */
/* Private define ------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PD */
/* USER CODE END PD */
/* Private macro -------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PM */
/* USER CODE END PM */
/* Private variables ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* Private function prototypes -----------------------------------------------*/
void SystemClock_Config(void);
/* USER CODE BEGIN PFP */
/* USER CODE END PFP */
/* Private user code ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
/* USER CODE END 0 */
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/* MCU Configuration--------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */
HAL_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* Configure the system clock */
SystemClock_Config();
/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */
/* USER CODE END SysInit */
/* Initialize all configured peripherals */
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_TIM2_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
HAL_TIM_PWM_Start_IT(&htim2,TIM_CHANNEL_1);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(DIR_GPIO_Port, DIR_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET);
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
}
/**
* @brief System Clock Configuration
* @retval None
*/
void SystemClock_Config(void)
{
RCC_OscInitTypeDef RCC_OscInitStruct = {0};
RCC_ClkInitTypeDef RCC_ClkInitStruct = {0};
/** Configure the main internal regulator output voltage
*/
__HAL_RCC_PWR_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_PWR_VOLTAGESCALING_CONFIG(PWR_REGULATOR_VOLTAGE_SCALE1);
/** Initializes the RCC Oscillators according to the specified parameters
* in the RCC_OscInitTypeDef structure.
*/
RCC_OscInitStruct.OscillatorType = RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSI;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSIState = RCC_HSI_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSICalibrationValue = RCC_HSICALIBRATION_DEFAULT;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLState = RCC_PLL_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLSource = RCC_PLLSOURCE_HSI;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLM = 8;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLN = 168;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLP = RCC_PLLP_DIV2;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLQ = 4;
if (HAL_RCC_OscConfig(&RCC_OscInitStruct) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Initializes the CPU, AHB and APB buses clocks
*/
RCC_ClkInitStruct.ClockType = RCC_CLOCKTYPE_HCLK|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_SYSCLK
|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK1|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.SYSCLKSource = RCC_SYSCLKSOURCE_PLLCLK;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.AHBCLKDivider = RCC_SYSCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB1CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV4;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB2CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV2;
if (HAL_RCC_ClockConfig(&RCC_ClkInitStruct, FLASH_LATENCY_5) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
void HAL_TIM_PWM_PulseFinishedCallback(TIM_HandleTypeDef *htim)
{
if(htim == &htim2)
{
if(count <1000)
{
count++;
}
else
{
HAL_TIM_PWM_Stop_IT(&htim2, TIM_CHANNEL_1);
count = 0;
}
}
}
/* USER CODE END 4 */
/**
* @brief This function is executed in case of error occurrence.
* @retval None
*/
void Error_Handler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN Error_Handler_Debug */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the HAL error return state */
__disable_irq();
while (1)
{
}
/* USER CODE END Error_Handler_Debug */
}
#ifdef USE_FULL_ASSERT
/**
* @brief Reports the name of the source file and the source line number
* where the assert_param error has occurred.
* @param file: pointer to the source file name
* @param line: assert_param error line source number
* @retval None
*/
void assert_failed(uint8_t *file, uint32_t line)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 6 */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the file name and line number,
ex: printf("Wrong parameters value: file %s on line %d\r\n", file, line) */
/* USER CODE END 6 */
}
#endif /* USE_FULL_ASSERT */
gpio.c:
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file gpio.c
* @brief This file provides code for the configuration
* of all used GPIO pins.
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* Copyright (c) 2022 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software is licensed under terms that can be found in the LICENSE file
* in the root directory of this software component.
* If no LICENSE file comes with this software, it is provided AS-IS.
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "gpio.h"
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
/* USER CODE END 0 */
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Configure GPIO */
/*----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/** Configure pins as
* Analog
* Input
* Output
* EVENT_OUT
* EXTI
*/
void MX_GPIO_Init(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
/* GPIO Ports Clock Enable */
__HAL_RCC_GPIOC_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOH_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();
/*Configure GPIO pin Output Level */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(DIR_GPIO_Port, DIR_Pin, GPIO_PIN_SET);
/*Configure GPIO pin : PtPin */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = DIR_Pin;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_LOW;
HAL_GPIO_Init(DIR_GPIO_Port, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
/* USER CODE END 2 */
tim.c:
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file tim.c
* @brief This file provides code for the configuration
* of the TIM instances.
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* Copyright (c) 2022 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software is licensed under terms that can be found in the LICENSE file
* in the root directory of this software component.
* If no LICENSE file comes with this software, it is provided AS-IS.
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Includes ------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include "tim.h"
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
/* USER CODE END 0 */
TIM_HandleTypeDef htim2;
/* TIM2 init function */
void MX_TIM2_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM2_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END TIM2_Init 0 */
TIM_ClockConfigTypeDef sClockSourceConfig = {0};
TIM_MasterConfigTypeDef sMasterConfig = {0};
TIM_OC_InitTypeDef sConfigOC = {0};
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM2_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END TIM2_Init 1 */
htim2.Instance = TIM2;
htim2.Init.Prescaler = 83;
htim2.Init.CounterMode = TIM_COUNTERMODE_UP;
htim2.Init.Period = 999;
htim2.Init.ClockDivision = TIM_CLOCKDIVISION_DIV1;
htim2.Init.AutoReloadPreload = TIM_AUTORELOAD_PRELOAD_ENABLE;
if (HAL_TIM_Base_Init(&htim2) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
sClockSourceConfig.ClockSource = TIM_CLOCKSOURCE_INTERNAL;
if (HAL_TIM_ConfigClockSource(&htim2, &sClockSourceConfig) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
if (HAL_TIM_PWM_Init(&htim2) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
sMasterConfig.MasterOutputTrigger = TIM_TRGO_RESET;
sMasterConfig.MasterSlaveMode = TIM_MASTERSLAVEMODE_DISABLE;
if (HAL_TIMEx_MasterConfigSynchronization(&htim2, &sMasterConfig) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
sConfigOC.OCMode = TIM_OCMODE_PWM1;
sConfigOC.Pulse = 500;
sConfigOC.OCPolarity = TIM_OCPOLARITY_HIGH;
sConfigOC.OCFastMode = TIM_OCFAST_DISABLE;
if (HAL_TIM_PWM_ConfigChannel(&htim2, &sConfigOC, TIM_CHANNEL_1) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM2_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END TIM2_Init 2 */
HAL_TIM_MspPostInit(&htim2);
}
void HAL_TIM_Base_MspInit(TIM_HandleTypeDef* tim_baseHandle)
{
if(tim_baseHandle->Instance==TIM2)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM2_MspInit 0 */
/* USER CODE END TIM2_MspInit 0 */
/* TIM2 clock enable */
__HAL_RCC_TIM2_CLK_ENABLE();
/* TIM2 interrupt Init */
HAL_NVIC_SetPriority(TIM2_IRQn, 0, 0);
HAL_NVIC_EnableIRQ(TIM2_IRQn);
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM2_MspInit 1 */
/* USER CODE END TIM2_MspInit 1 */
}
}
void HAL_TIM_MspPostInit(TIM_HandleTypeDef* timHandle)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
if(timHandle->Instance==TIM2)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM2_MspPostInit 0 */
/* USER CODE END TIM2_MspPostInit 0 */
__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();
/**TIM2 GPIO Configuration
PA0-WKUP ------> TIM2_CH1
*/
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_0;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_AF_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_LOW;
GPIO_InitStruct.Alternate = GPIO_AF1_TIM2;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStruct);
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM2_MspPostInit 1 */
/* USER CODE END TIM2_MspPostInit 1 */
}
}
void HAL_TIM_Base_MspDeInit(TIM_HandleTypeDef* tim_baseHandle)
{
if(tim_baseHandle->Instance==TIM2)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM2_MspDeInit 0 */
/* USER CODE END TIM2_MspDeInit 0 */
/* Peripheral clock disable */
__HAL_RCC_TIM2_CLK_DISABLE();
/* TIM2 interrupt Deinit */
HAL_NVIC_DisableIRQ(TIM2_IRQn);
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM2_MspDeInit 1 */
/* USER CODE END TIM2_MspDeInit 1 */
}
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
5 Final effect
42 Rotation of stepping motor
6 appendix
6.1 TB6600 Driver
The information provided by a treasure store is as follows :
6.1.1 Drive function

6.1.2 connection

6.1.3 Common faults and Countermeasures

6.2 42 Dimension drawing and internal structure of stepping motor


边栏推荐
- 软考中级有用吗??
- 一些线上学术报告网站与机器学习视频
- Différences entre les contraintes monotones et anti - monotones
- [daiy5] jz77 print binary tree in zigzag order
- The difference between monotonicity constraint and anti monotonicity constraint
- seata 1.3.0 四种模式解决分布式事务(AT、TCC、SAGA、XA)
- I plan to take part in security work. How about information security engineers and how to prepare for the soft exam?
- 如何顺利通过下半年的高级系统架构设计师?
- P1031 [noip2002 improvement group] average Solitaire
- Arduino board description
猜你喜欢
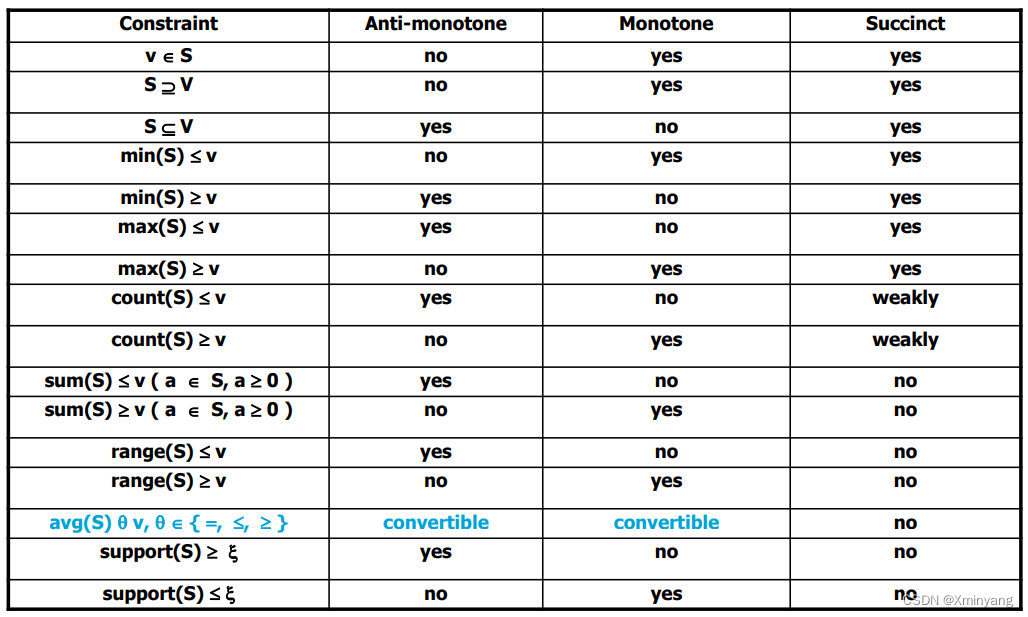
單調性約束與反單調性約束的區別 monotonicity and anti-monotonicity constraint
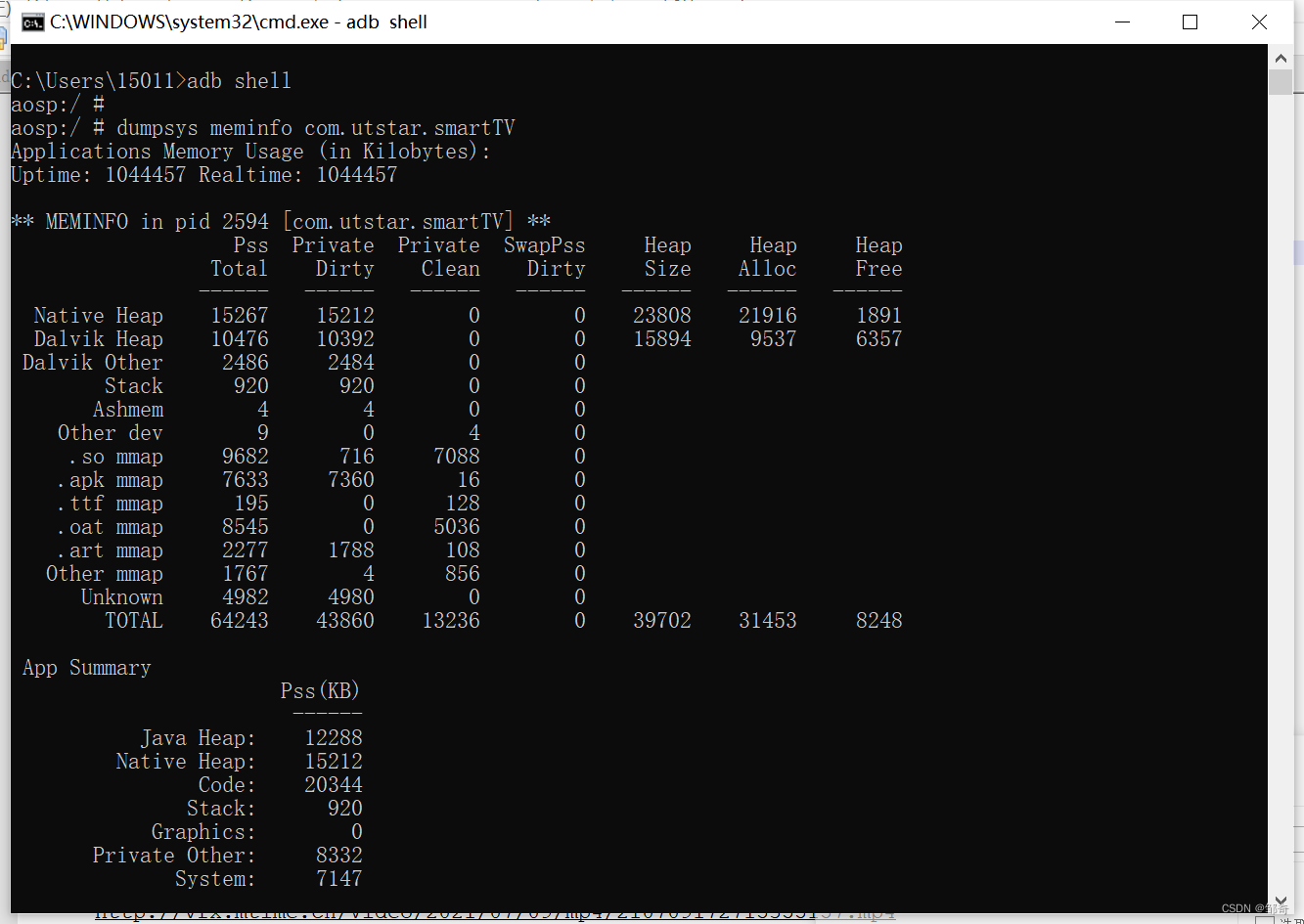
ADB utility commands (network package, log, tuning related)

Unity script visualization about layout code
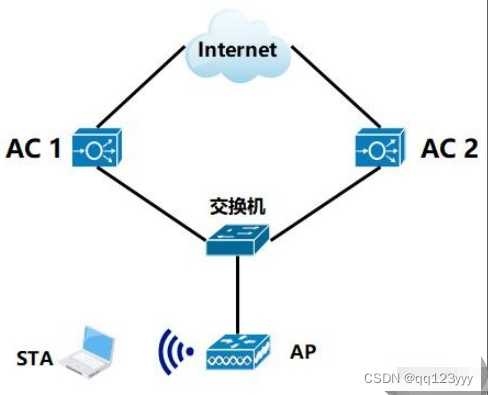
Network engineer test questions and answers in May of the first half of 2022
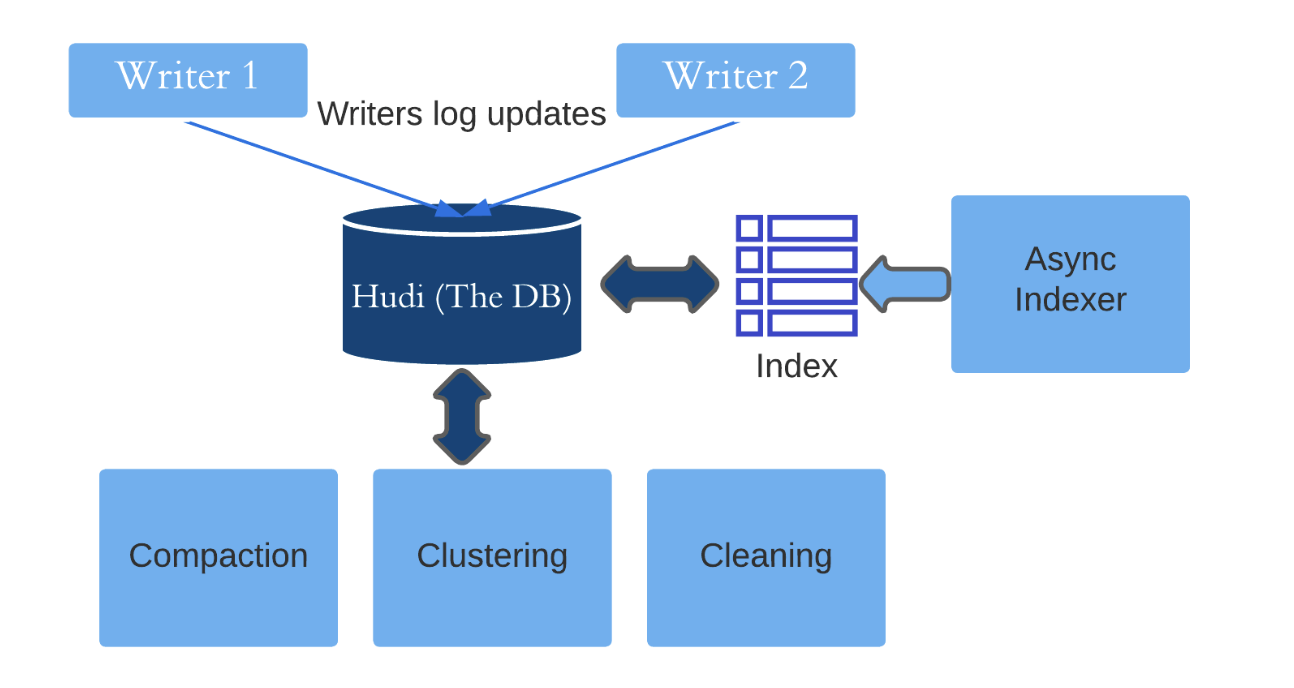
Deep understanding of Apache Hudi asynchronous indexing mechanism
Multithreaded asynchronous orchestration
![[actual combat] transformer architecture of the major medical segmentation challenges on the list --nnformer](/img/de/0cf12132216ffbde896a7b12022184.png)
[actual combat] transformer architecture of the major medical segmentation challenges on the list --nnformer
555 circuit details
![P1223 queuing for water /1319: [example 6.1] queuing for water](/img/09/29f19b32f0a3c82ddb3c30d5d0b16e.png)
P1223 queuing for water /1319: [example 6.1] queuing for water
Deeply analyze the main contents of erc-4907 agreement and think about the significance of this agreement to NFT market liquidity!
随机推荐
Deep understanding of Apache Hudi asynchronous indexing mechanism
香橙派OrangePi 4 LTS开发板通过Mini PCIE连接SATA硬盘的操作方法
施努卡:机器视觉定位技术 机器视觉定位原理
Galaxy Kirin desktop operating system installation postgresql13 (source code installation)
1323: [example 6.5] activity selection
深入理解Apache Hudi异步索引机制
2022.7.6DAY598
【推荐系统 02】DeepFM、YoutubeDNN、DSSM、MMOE
[homework] 2022.7.6 write your own cal function
Get pictures through opencv, change channels and save them
TypeScript 接口继承
Deeply analyze the main contents of erc-4907 agreement and think about the significance of this agreement to NFT market liquidity!
[système recommandé 01] rechub
VR development optimization
[recommendation system 01] rechub
在线硬核工具
IIC Basics
Prototype and prototype chain
Unity script visualization about layout code
Summary of router development knowledge



