当前位置:网站首页>Exploration of kangaroo cloud data stack on spark SQL optimization based on CBO
Exploration of kangaroo cloud data stack on spark SQL optimization based on CBO
2022-06-11 05:27:00 【Several stacks Seminar】

Reading guide :
Spark SQL Yes RBO and CBO Two optimization methods , Why do you choose to count stacks CBO As an optimization method ? How to land in the stack again ? What is the future optimization method choice , The content of this issue will show you how many stacks are in Spark SQL Exploration of optimization methods .
You can see
Spark SQL CBO Selection background
Spark SQL CBO Realization principle
Count the stack in Spark SQL CBO Exploration on
author / Fix the bamboo
edit / Hua Xia

Spark SQL CBO Selection background
Spark SQL There are two ways to optimize : One is rule-based optimization (Rule-Based Optimizer, Referred to as RBO); The other is cost based optimization (Cost-Based Optimizer, Referred to as CBO).
01
RBO It's traditional SQL Optimization techniques
RBO It is a relatively early and mature project SQL Optimization techniques , According to a series of optimization rules, it can optimize SQL Syntax expression for conversion , Finally, an optimal execution plan is generated .RBO It belongs to an empirical optimization method , Match in strict accordance with the established rules , So different SQL The writing method directly determines the execution efficiency . And RBO Not sensitive to data , When the table size is fixed , No matter how the intermediate result data changes , as long as SQL remain unchanged , The generated execution plans are all fixed .
02
CBO yes RBO Improve the optimization method of evolution
CBO It's right RBO Improve the optimization method of evolution , It can convert relational expressions according to optimization rules , Generate multiple execution plans , According to statistics (Statistics) And the cost model (Cost Model) calculated Minimum cost Physical execution plan for .
03
CBO And RBO Comparison of advantages
● RBO Optimization example
Let's take an example : Calculation t1 surface ( The size is :2G) and t2 surface ( The size is :1.8G)join Number of lines after
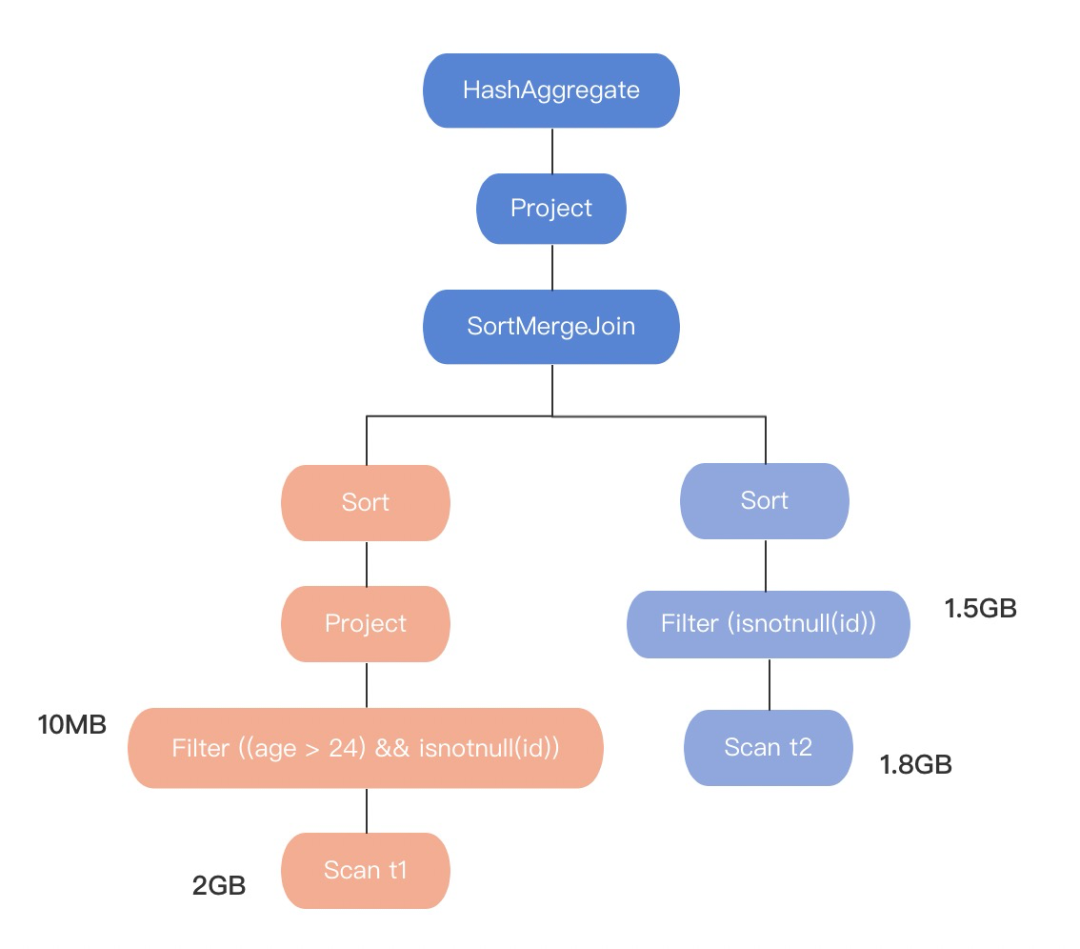
Above, :
SELECT COUNT(t1.id) FROM t1 JOIN t2 ON t1.id = t2.id WHERE t1.age > 24
be based on RBO The physical execution plan generated after optimization . In the picture we can see , Finally, the implementation plan is to select SortMergeJoin ⑴ Perform two tables join Of .
stay Spark in ,join There are three implementations of :
1.Broadcast Join
2.ShuffleHash Join
3.SortMerge Join
ShuffleHash Join and SortMerge Join Need to be shuffle, relative Broadcast Join It will cost a lot more , If you choose Broadcast Join The size of a table must be less than or equal to
spark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold Size ( The default is 10M).
And let's see , The execution plan in the figure above t1 surface , Original table size 2G After filtration 10M,t2 Table original table size 1.8G After filtration 1.5G. This explanation RBO Optimizer Do not care about changes in intermediate data , Only based on the original table size join The choice of SortMergeJoin As final join, Obviously, the execution plan is not optimal .
● CBO Optimization example
While using CBO The execution plan obtained by the optimizer is as follows :

It's not hard for us to see ,CBO The optimizer takes full account of intermediate results , Perceiving the change of intermediate results can Broadcast Join Conditions , Therefore, the final execution plan generated will select Broadcast Join To do two tables join.
● Other advantages
In fact, in addition to the rigid execution, it leads to the problem that the optimal solution cannot be obtained ,RBO also High learning cost The problem of : Developers need to be familiar with most optimization rules , Or write it out SQL Performance may be poor .
● CBO It's stacks Spark SQL Better choice for optimization
be relative to RBO,CBO No doubt it's a better choice , It makes Spark SQL The performance of has been improved to a new level ,Spark As one of the most important components in the bottom layer of the stack platform , It carries most of the tasks on the offline development platform , do Spark The optimization of will also promote the stack to be more efficient and easy to use . So several stacks are selected CBO Do research and exploration , This will further improve the performance of several stacks of products .

Spark SQL CBO Realization principle
Spark SQL To realize CBO The steps of are divided into two parts , The first part is the collection of statistical information , The second part is cost estimation :
Statistics collection
The collection of statistical information is divided into two parts : The first part is Original table information statistics 、 The second part is Information statistics of intermediate operators .
01
Original table information statistics
Spark in , By adding new SQL grammar ANALYZE TABLE For statistics Original table Information . The original table statistics are divided into Table level and Column level Two categories: , The specific implementation is as follows :
● Table level statistics
Through execution ANALYZE TABLE table_name COMPUTE STATISTICS Statement to collect , Statistical indicators include estimatedSize The size of the decompressed data 、rowCount Total number of data, etc .
● Column level statistics
Through execution ANALYZE TABLE table_name COMPUTE STATISTICS FOR COLUMNS column-name1, column-name2, …. Statement to collect .
Column level information is divided into basic column information and histogram , Basic column information Include column types 、Max、Min、number of nulls, number of distinct values, max column length, average column length etc. , Histogram It describes the distribution of data cloth .Spark Histogram statistics is not enabled by default , Additional parameters are required :spark.sql.statistics.histogram.enabled = true.
Original table The information statistics of is relatively simple , It is relatively complicated to calculate the statistical information of intermediate nodes , And different operators have different calculation rules , stay Spark There are many operators in , Interested students can see Spark SQL CBO Design document :
https://issues.apache.org/jira/secure/attachment/12823839/Spark_CBO_Design_Spec.pdf
02
Information statistics of intermediate operators
Here we take the common filter For example, operators , Look at the process of calculating operator statistics . Based on the previous section SQL SELECT COUNT(t1.id) FROM t1 JOIN t2 ON t1.id = t2.id WHERE t1.age > 24 Look at the generated syntax tree t1 The table contains the greater than operator filter Node statistics .

There are three situations to consider here :
The first one is
The constant value of filter condition is greater than max(t1.age), The return result is 0;
The second kind
The constant value of filter condition is less than min(t1.age), Then all return to ;
The third kind of
The filter condition constant is between min(t1.age) and max(t1.age) Between , When the histogram is not turned on The formula of filtered statistical information is after_filter = (max(t1.age) - Filter condition constant 24)/(max(t1.age) – min(t1.age)) * before_filter, If the histogram is not enabled, the task data distribution is uniform by default ; When histogram is turned on The statistical information formula after filtering is after_filter = height(>24) / height(All) * before_filter. Then the node min(t1.age) Equal to the filter condition constant 24.
cost estimation
After introducing how to count the statistics of the original table and how to calculate the statistics of the intermediate operator , With this information, we can calculate the cost of each node .
Before introducing how to calculate node cost, let's introduce some Cost parameters The meaning of , as follows :
Hr: from HDFS Read 1 The cost of bytes
Hw: from HDFS Write 1 The cost of bytes
NEt: stay Spark From any node in the cluster through the network 1 Byte to The average cost of the target node
Tr: The total number of data
Tsz: Average data size
CPUc: CPU cost
The node cost will be calculated from IO and CPU Consider two dimensions , The cost calculation rules of each operator are different , We go through join Operator to illustrate how to calculate the cost of the operator :
hypothesis join yes Broadcast Join, Large tables are distributed in n A node , that CPU The price and IO The cost calculation formula is as follows :
CPU Cost= Small table construction Hash Table Cost of + The cost of large table detection = Tr(Rsmall) * CPUc + (Tr(R1) + Tr(R2) + … + Tr(Rn)) * n * CPUc
IO Cost = Cost of reading small tables + Cost of small table broadcasting + Cost of reading large tables = Tr(Rsmall) * Tsz(Rsmall) * Hr + n * Tr(Rsmall) * Tsz(Rsmall) * NEt + (Tr(R1)* Tsz(R1) + … + Tr(Rn) * Tsz(Rn)) * Hr
But whatever operator , Cost calculation and the total number of data involved 、 Factors such as the average size of data are directly related , This is why we should first introduce how to count the information of the original table and the statistics of the intermediate operator .
Each operator calculates the cost according to the defined rules , The sum of the costs of each operator is the total cost of the entire implementation plan , Here we can consider a problem , Is the optimal execution plan obtained by enumerating the total cost of each execution plan one by one ? Obviously not , If the total cost is calculated once for each execution plan , I guess the day lily is going to be cold ,Spark The idea of dynamic programming is cleverly used , Get the best execution plan quickly .

Count the stack in Spark SQL CBO Exploration on
To understand the Spark SQL CBO After the implementation principle of , Let's think about the first question : The big data platform wants to support Spark SQL CBO Optimized words , What needs to be done ?
In the previous implementation principle, we mentioned ,Spark SQL CBO There are two steps in the implementation of , The first step is to Statistics collection , The second step is cost estimation . The collection of statistical information is divided into two steps : First step Original table information statistics 、 The second step Information statistics of intermediate operators . Here we find the answer to the first question : The platform needs to have Original table information statistics The function of .
After the first problem is solved , We need to think about the second question : When is the appropriate time to perform table information statistics ? In response to this question , We have tentatively conceived three solutions to information statistics :
● In every time SQL Before query , First, perform the primary table information statistics
The statistical information obtained in this way is more accurate , after CBO The optimized execution plan is also optimal , But the cost of information statistics is the greatest .
● Refresh table statistics regularly
Every time SQL Table information statistics is not required before query , Because of the uncertainty of business data update , So this way SQL The table statistics obtained during query may not be up-to-date , that CBO The optimized execution plan may not be optimal .
● Perform information statistics on the business party that changes the data
This method has the least cost for information statistics , Also can guarantee CBO The optimized execution plan is optimal , But it is the most intrusive to the business code .
It is not difficult to see the advantages and disadvantages of each of the three schemes , Therefore, the specific scheme for table information statistics depends on The architecture design of the platform itself .
The structure diagram of building data warehouse based on data stack platform is shown in the figure below :

First, through ChunJun Collect business database data to Hive ODS layer
And then through Hive perhaps Spark Data processing
Finally through ChunJun take Hive The data of the library is written to the business database for business processing
From the structure diagram, we can see that several stacks are useful to Hive、Spark and ChunJun Three components , And these three components can read and write Hive, Several stacks of multiple sub products ( Such as offline platform and real-time platform ) It is also possible to Hive To read and write , therefore If based on the scheme 3 The cost is very high .
programme 1 The price itself is already high , Before each query, make an information statistics , The time of information statistics should be included in the query time , If the amount of table data is large, the increase time may be more than ten minutes or even longer .
Comprehensive consideration , We chose More flexible and reasonable scheme 2 To perform table information statistics . although Spark SQL The statistics obtained at runtime may not be up to date , But in general RBO It's still very big Of Performance improvement .
Let's share , How the data stack collects the information of the original table :
We added the table information statistics function on the offline platform project management page , It ensures that different triggering strategies can be configured for each project according to its own conditions . Trigger policy can be configured to trigger by day or by hour , Triggering by day supports configuration to trigger from a certain time of the day , So as to avoid business peak . After configuration , At the time of triggering, the offline platform will automatically submit a project by project Spark Task to count item table information .
It is not implemented in the stack CBO Before supporting ,Spark SQL Can only be optimized by adjusting Spark Its own parameter implementation . This kind of tuning method has a high entry threshold , Users should be familiar with Spark Principle . Counting stack CBO The introduction of Greatly reduced The user's learning threshold , Users only need to be in Spark Conf In the open
CBO-spark.sql.cbo.enabled=true
Then you can configure table information statistics in the corresponding project SQL To optimize the .

Future outlook
stay CBO After continuous research on Optimization ,Spark SQL CBO Compare the whole RBO In terms of performance, it has been greatly improved . But this does not mean that the entire operating system has no room for optimization , The progress we have made will only encourage us to continue our further exploration , Try to take another step forward .
Finish right CBO After the initial support exploration , Several stacks looked at Spark 3.0 New features introduced in the ——AQE(Adaptive Query Execution).
AQE yes dynamic CBO How to optimize , Is in CBO On the basis of SQL Another performance improvement of optimization technology . As said before, ,CBO The current calculation still depends on the information statistics of the original table , And the outdated information statistics will give CBO Bring about no small impact .
If you optimize dynamically at run time SQL Implementation plan , You don't need to be like CBO In that case, you need to do table information statistics in advance . Several stacks are working on this new feature , It is believed that we will be able to introduce AQE, Make the stack a higher level in ease of use and high performance . I hope you will keep your attention , Several stacks are willing to grow with you .
+
Previous recommendation

The exploration and practice of several stacks on the integration of lake and warehouse
open
Source
hand over
flow
● ChunJun
https://github.com/DTStack/chunjun
https://gitee.com/dtstack_dev_0/chunjun
● Taier
https://github.com/DTStack/Taier
https://gitee.com/dtstack_dev_0/taier
● ChengYing
https://github.com/DTStack/chengying
https://gitee.com/dtstack_dev_0/chengying
● Molecule
https://github.com/DTStack/molecule
https://gitee.com/dtstack_dev_0/molecule

Kangaroo cloud open source technology framework exchange group
Nail group |30537511

Click on “ Read the original ”, Direct access to the open source community !

边栏推荐
- Yolov5 training personal data set summary
- Carrier coordinate system inertial coordinate system world coordinate system
- Opencv learning path (2-5) -- Deep parsing imwrite function
- 截取文件扩展名
- Some details about memory
- Huawei equipment is configured to access the virtual private network through GRE
- 【入门级基础】Node基础知识总结
- 力扣(LeetCode)161. 相隔为 1 的编辑距离(2022.06.10)
- Huawei equipment is configured with bgp/mpls IP virtual private network
- 2021 iccv paper sharing - occlusion boundary detection
猜你喜欢

es-ik 安装报错

WinForm (I) introduction to WinForm and use of basic controls

BERT知识蒸馏

22. Generate parentheses
Simple linear regression of sklearn series

Huawei equipment is configured with bgp/mpls IP virtual private network address space overlap

KD-Tree and LSH

jvm调优五:jvm调优工具和调优实战
![[NIPS2021]MLP-Mixer: An all-MLP Architecture for Vision](/img/89/66c30ea8d7969fef76785da1627ce5.jpg)
[NIPS2021]MLP-Mixer: An all-MLP Architecture for Vision

PCB走線到底能承載多大電流
随机推荐
35.搜索插入位置
Cascade EF gan: local focus progressive facial expression editing
Intercept file extension
MySQL nested sorting: first sort and filter the latest data, and then customize the sorting of this list
Paper reproduction: expressive body capture
How to apply for free idea with official documents
Using keras to build the basic model yingtailing flower
oh my zsh正确安装姿势
Opencv learning path (2-1) -- Deep parsing imread function
Basics of customized view
Analyzing while experimenting - memory leakage caused by non static inner classes
Analysis while experiment - a little optimization of memory leakage in kotlin
(十五)红外通信
English digital converter
Zed2 running vins-mono preliminary test
Yolov5 training personal data set summary
项目-智慧城市
MySQL string to array, merge result set, and convert to array
49. 字母异位词分组
Wxparse parsing iframe playing video