当前位置:网站首页>[weekly translation go] how to code in go series articles are online!!
[weekly translation go] how to code in go series articles are online!!
2022-07-04 21:28:00 【fifteen billion two hundred and thirty-one million one hundred 】
Gopher Hello, everyone , Starting from this week, we will publish regularly every week 《How-To-Code-in-Go》 Series of translated articles , contain 40 Learning the content .

《How-To-Code-in-Go》 The series of articles is the latest at this stage Go Language learning books , I hope everyone gopher We can persevere , Study every article carefully , Absorb the key points 、 The essence of , Let's cheer together , Common progress ! No one can fall behind ~
Antecedents feed ~
《How-To-Code-in-Go》 use Hugo Release . Welcome to pass issue Offer advice , It can also be done through pull requests To participate and contribute together .
installed hugo after , You need to synchronize the theme file first :
git submodule update --init --recursive
After synchronization , The following instructions can be executed in the root directory to test the website :
hugo server
Document in content/zh/docs Under the table of contents , After modification, you can go through pull requests Submit .
Today, let's study together Chapter one article :
How to be in Ubuntu 18.04 Installation on Go And setting the local programming environment
Go Introduction to language
Go Is a door in Google Language born after setbacks . Developers have to choose between two languages frequently , Or choose a language with high execution efficiency but long compilation time , Or choose a language that is easy to program but inefficient in production . Go Is designed to All three functions are provided at the same time : Quick compilation 、 Easy programming and efficient execution in production .
although Go Is a general programming language , It can be used for many different types of programming projects , But it Especially suitable for network / Distributed system project , Won “ Cloud language ” The reputation of the .Go Language focuses on helping modern programmers do more work through a powerful set of tools , Eliminate the debate about format by making it part of the language specification , And simplify deployment by compiling into a single binary .Go Easy to learn , There are very few keywords , This makes it the perfect choice for both beginners and experienced developers .
This tutorial will guide you through the command line to install Go And configuration Go Programming environment . This tutorial is specifically for Ubuntu 18.04 Installation process , But for others Debian Linux The same applies to distributions .
Installation premise
You need one to install Ubuntu 18.04 Computer or virtual machine , And have administrator access and network connection to the computer . You can Ubuntu 18.04 Version page Download this operating system .
First step : install Go
In this step , You passed Go Official download page Download the latest version to install Go.
So , You need to find the latest binary version of the compressed package URL . You should also pay attention to the next list SHA256 Hash value , Because you will use it to Verify the downloaded file .
You will complete the installation and setup through the command line , This is a non graphical way of interacting with computers . in other words , What you entered is text , And then get the feedback from the computer through the text , Instead of clicking a button .
Command line , That's what we know shell perhaps terminal , It can help you modify or automate many of the tasks you perform on your computer every day , This is a necessary tool for software developers . Although there are many terminal commands to learn , But these commands can make you do more powerful things . More information about the command line , Please check out Linux Terminal profile course .
stay Ubuntu 18.04 On , You can click on the top left corner of the screen Ubuntu Icon and enter terminal To find the terminal program . Click the terminal program icon to open the terminal . Or you can press and hold it on the keyboard at the same time “CTRL”、“ALT” and “T” Key to automatically open the terminal program .

After the terminal is opened , You can install it manually Go Binary system . Although you can use package management tools , such as apt-get, But manual installation can help you understand an effective Go Modification of any necessary configuration information in the workspace system .
download Go Before , Make sure you're in home (~) Catalog :
cd ~
According to the official Go Download the compressed package copied from the page URL, Use curl Command pull download :
curl -LO https://dl.google.com/go/go1.12.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
Next , Use sha256sum Command to verify the compressed package :
sha256sum go1.12.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
The hash value displayed by running the above command should be consistent with the hash value of the download page , If not , Then this compressed package is not a valid file , Need to download again .
Output
2a3fdabf665496a0db5f41ec6af7a9b15a49fbe71a85a50ca38b1f13a103aeec go1.12.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
Next , Extract the downloaded file and install it to the desired location of the system . It's usually in /usr/local Below directory :
sudo tar -xvf go1.12.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz -C /usr/local
So in /usr/local There is one under the catalogue go Catalog .
Be careful : Even though /usr/local/go It is the official recommended location , But some users may prefer or need different paths .
In this step , you are here Ubuntu 18.04 Downloaded and installed on the machine Go . Next you will configure Go The workspace .
The second step : Create your Go work area
installed Go after , You can create your coding workspace .Go The language workspace contains two directories under its root directory :
src: The directory contains Go The source file . The so-called source file is what you use Go File written in programming language . The source file is Go Compilers are built into executable binaries .bin: This directory contains Go Executable files for tool construction and installation . Executable files are binary files that run on your system and perform tasks . It is usually your source code or other downloaded Go Source code compiled program .
src Subdirectories may contain multiple version control repositories ( for example Git, Mercurial and Bazaar). This allows you to standardize the import code in your project . A specification import is an import that references a fully qualified package , for example github.com/digitalocean/godo .
When you introduce a third-party library , You can see something similar github.com, golang.org Or other directory , If you're using github.com Such a code warehouse , You will also put the project and source files in this directory . We will explore this concept later in this step .
The following is a typical workspace directory structure :
.
├── bin
│ ├── buffalo # command executable
│ ├── dlv # command executable
│ └── packr # command executable
└── src
└── github.com
└── digitalocean
└── godo
├── .git # Git repository metadata
├── account.go # package source
├── account_test.go # test source
├── ...
├── timestamp.go
├── timestamp_test.go
└── util
├── droplet.go
└── droplet_test.go
from 1.8 Start ,Go The default directory of the workspace is the user's home Catalog , with go subdirectories , Or is it $HOME/go Catalog . If you use it earlier than 1.8 Of Go edition , At present, it is considered that the best practice is to use $HOME/go Location .
Use the following command for your Go The workspace creates a directory structure :
mkdir -p $HOME/go/{bin,src}
-p The option is to tell mkdir Create all parent directories in the directory , Although they may not exist . Use {bin,src} by mkdir Create a set of parameters , And tell it to create bin Contents and src Catalog .
The above command will ensure that the following directory structure is in place :
└── $HOME
└── go
├── bin
└── src
stay Go 1.8 Before , You need to set a name $GOPATH Local environment variables for . $GOPATH Tell the compiler where to find the imported third-party source code , Also include any local source code you write . Although it is no longer explicitly required , But it is still considered a good practice , Because many third-party tools still rely on this variable .
You can add global variables to your ~/.profile To set your $GOPATH. You may want to base it on your shell Configure to add it to .zshrc or .bashrc In file .
First , Use nano Or open your favorite text editor ~/.profile:
nano ~/.profile
Set your $GOPATH :
~/.profile
export GOPATH=$HOME/go
When Go When compiling and installing tools , Will put them in $GOPATH/bin Catalog . For convenience , Usually, the /bin Add subdirectories to ~/.profile Medium PATH in :
~/.profile
export PATH=$PATH:$GOPATH/bin
This will allow you to run anywhere on the system through Go Any program compiled or downloaded by the tool .
Last , You need to go Binary files are added to PATH in . You can add /usr/local/go/bin To achieve :
~/.profile
export PATH=$PATH:$GOPATH/bin:/usr/local/go/bin
take /usr/local/go/bin Add to $PATH in , Can make all Go Tools can be used anywhere on the system .
To update your shell To configure , Please use the following command to load global variables :
. ~/.profile
You can use the echo Command and check its output , To verify your $PATH Updated or not :
echo $PATH
You will see your $GOPATH/bin Display in your home directory . If you are in root Identity login , You will see in the path /root/go/bin.
Output
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin:/root/go/bin:/usr/local/go/bin
You will see /usr/local/go/bin Of Go The path to the tool :
Output
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games:/snap/bin:/root/go/bin:/usr/local/go/bin
clear through Go To verify the installation :
go version
We should get output similar to the following :
Output
go version go1.12.1 linux/amd64
Now you have created the root directory of the workspace and set it $GOPATH environment variable , You can create your future projects according to the following directory structure . This example assumes that you use github.com As a warehouse :
$GOPATH/src/github.com/username/project
for example , If you are developing https://github.com/digitalocean/godo project , It will be stored in the following directory :
$GOPATH/src/github.com/digitalocean/godo
The project structure enables the project to pass go get Tool use . It also contributes to readability in the future . You can use go get Command and get godo Library to verify this :
go get github.com/digitalocean/godo
This will download godo Library and create it on your computer $GOPATH/src/github.com/digitalocean/godo Catalog . You can check whether the download is successful by listing the directory godo package :
ll $GOPATH/src/github.com/digitalocean/godo
You should see output like this :
>>>>>>> main
Outputdrwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Apr 5 00:43 ./
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Apr 5 00:43 ../
drwxr-xr-x 8 root root 4096 Apr 5 00:43 .git/
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 8 Apr 5 00:43 .gitignore*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 61 Apr 5 00:43 .travis.yml
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2808 Apr 5 00:43 CHANGELOG.md
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1851 Apr 5 00:43 CONTRIBUTING.md
.
.
.
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4893 Apr 5 00:43 vpcs.go
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4091 Apr 5 00:43 vpcs_test.go
In this step , You created a Go The workspace is configured with the necessary environment variables . Next you will use some code to test the workspace .
The third step : Create a simple program
Now you have set up the workspace , To create a “Hello, World!” The program! . This can verify whether the workspace configuration is correct , And give you a more familiar Go The opportunity of . Because we create a single Go Source file , Not the actual project , So we don't need to do this in the workspace .
In your home Catalog , Open a command line text editor , for example nano, Then create a new file :
nano hello.go
Write down your program in the new file :
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello, World!")
}
This code uses fmt Package and use Hello, World! Called as a parameter Println function . This will lead to the phrase Hello, World! Print to the terminal when the program is running .
Press CTRL and X Key to exit nano. When prompted to save the file , Press Y, Then press ENTER sign out .
sign out nano return shell after , Run the program :
go run hello.go
hello.go The program will make the terminal produce the following output :
Output
Hello, World!
In this step , You use a simple applet to verify whether it is configured correctly Go work area .
summary
Congratulations ! thus , You are already in Ubuntu The machine is equipped with Go Programming workspace , You can start writing projects !
That's all for today's study , If you have any questions or ideas, please leave a message or send a private message in the comment area to ask questions and Exchange . Need to know , You're not fighting alone ! Small G Has been ~
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

MP3是如何诞生的?
Foxit pdf editor v10.1.8 green version
华为ensp模拟器 给路由器配置DHCP
![Jerry's ad series MIDI function description [chapter]](/img/d7/348d85eb9f69ffd75612eeba56b16e.png)
Jerry's ad series MIDI function description [chapter]
B站视频 声音很小——解决办法

Huawei ENSP simulator configures DHCP for router
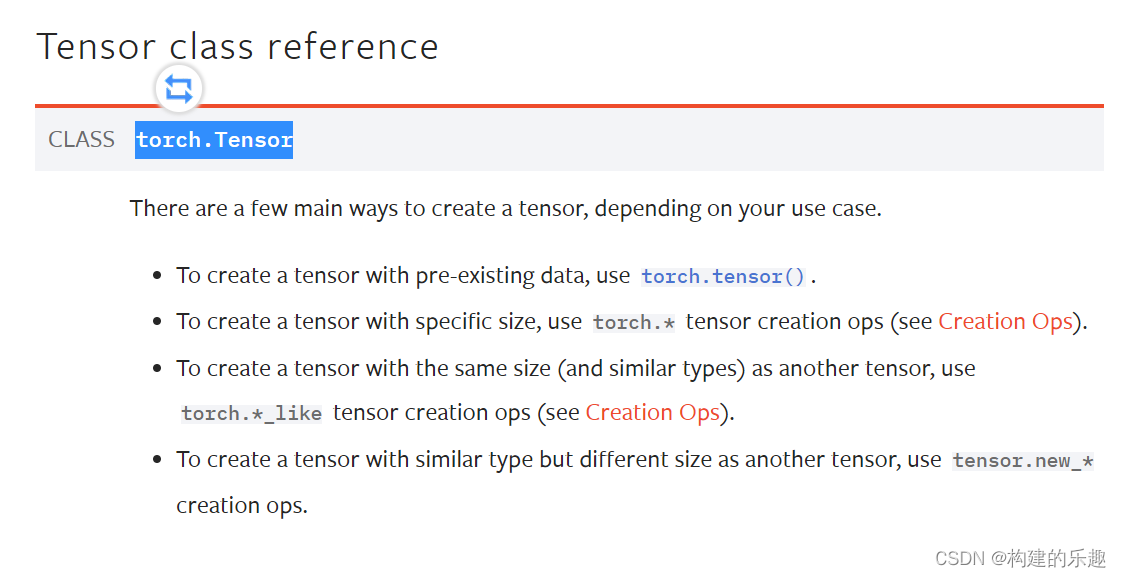
torch.tensor和torch.Tensor的区别
【optimtool.unconstrain】无约束优化工具箱
CAD中能显示打印不显示

Detailed explanation of multi-mode input event distribution mechanism
随机推荐
redis RDB AOF
Google colab踩坑
华为ensp模拟器 DNS服务器的配置
[buuctf.reverse] 151_[FlareOn6]DnsChess
LambdaQueryWrapper用法
y56.第三章 Kubernetes从入门到精通 -- 业务镜像版本升级及回滚(二九)
UTF encoding and character set in golang
2021 CCPC Harbin B. magical subsequence (thinking question)
Detailed explanation of multi-mode input event distribution mechanism
[solution] paddlepaddle 2 X call static graph mode
torch. Tensor and torch The difference between tensor
minidom 模塊寫入和解析 XML
仿ps样式js网页涂鸦板插件
Huawei ENSP simulator layer 3 switch
numpy vstack 和 column_stack
【C语言】符号的深度理解
Flutter在 release版本,打开后随机白屏不显示内容
TweenMax表情按钮js特效
js 3D爆炸碎片图片切换js特效
Can be displayed in CAD but not displayed in print