当前位置:网站首页>Things about the kotlin collaboration process - pipeline channel
Things about the kotlin collaboration process - pipeline channel
2022-06-12 21:54:00 【Laysm0507】
Flow It is called cold flow , Since there is cold flow , Then there is heat flow , The Conduit Channel It's heat flow .Channel Is a concurrent secure queue , It is mainly used to handle the communication between processes 
Sender and receiver are two different processes , It is through this pipeline that data is sent and transferred between the two , One send, One receive
val channel = Channel<String>{
}
viewModelScope.launch {
channel.send("123")
}
viewModelScope.launch {
val receive = channel.receive()
if(receive == "123"){
Log.e(TAG," received ")
}
}
Channel Created a channel , Used to send a string , So, Xie Cheng 1 Sent 1 After data , In the process 2 Received this parameter in , So as to continue to perform subsequent operations
The Conduit Channel
1 Channel The capacity of
since Channel It's a queue , Then there will be capacity , By default capacity = 1
public fun <E> Channel(
capacity: Int = RENDEZVOUS,
onBufferOverflow: BufferOverflow = BufferOverflow.SUSPEND,
onUndeliveredElement: ((E) -> Unit)? = null
): Channel<E> =
when (capacity) {
RENDEZVOUS -> {
if (onBufferOverflow == BufferOverflow.SUSPEND)
RendezvousChannel(onUndeliveredElement) // an efficient implementation of rendezvous channel
else
ArrayChannel(1, onBufferOverflow, onUndeliveredElement) // support buffer overflow with buffered channel
}
meanwhile , There is also a cache BufferOverflow Used to store received data , When the cache is full ,send Will hang up , Until the cache has new space ; Again , If the cache is empty ,receive Will hang up
2 Channel Iteration
Channel There are iterators , By getting the iterator of the pipe , You can get the collected data , Can replace receive
viewModelScope.launch {
(1..3).asFlow().collect {
channel.send("123")
}
}
viewModelScope.launch {
val iterator = channel.iterator()
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Log.e(TAG," received ${
iterator.next()}")
}
}
3 Channel Builder for
In the foreword , One kind of builder is used Channel You can build a pipeline directly , And then there is 2 A way to build a process pipeline for producers or consumers
3.1 produce
produce Used to generate a ReceiveChannel, This pipeline can be used to receive data , It is equivalent to creating a producer , It's the same thing CorotinueScope An extension function of , It is equivalent to creating a coroutine , At the same time, a pipe is created
val channel= viewModelScope.produce<String> {
send("123")
}
viewModelScope.launch {
val receive = channel.receive()
if(receive == "123"){
Log.e(TAG," received ")
}
}
3.2 actor
And produce contrary ,actor It's a SendChannel, The channel used to send data , Data can be received in the scope of the collaboration
val channel = viewModelScope.actor<String> {
val receive = receive()
if (receive == "123") {
Log.e(TAG, " received ")
}
}
viewModelScope.launch {
channel.send("123")
}
4 Channel The closing of the
Because the sending and receiving of data are all executed in the process , When the cooperation process is completed ,Channel It's closed , This is a natural closure
If Active call Channel Of close Method ,Channel Will immediately stop sending new elements ,Channel Properties of isClosedForSend Return immediately true
val channel = viewModelScope.actor<String>(Dispatchers.Main) {
while (true){
val receive = receive()
if (receive == "123") {
Log.e(TAG, " received ")
}
}
}
viewModelScope.launch {
(1..5).asFlow().collect {
delay(500)
channel.send("123")
}
}
delay(1000)
Log.e(TAG, " Ready to close the pipe ")
channel.close()
When 1s After the bell , Closed the channel , This is the time , Will immediately stop sending data , The receiving end throws an exception ClosedReceiveChannelException It indicates that the current channel is closed and cannot receive data
5 await Multiplexing
Multiplexing is a concept in network , The bandwidth or capacity of the transmission medium is often greater than the demand of a single transmission signal , It is desirable to transmit multiple signals simultaneously on one channel
stay Channel in , Just one pipe , Then I hope that the receiver can receive multiple data sources , Instead of just sending one String data , Just receive one String data
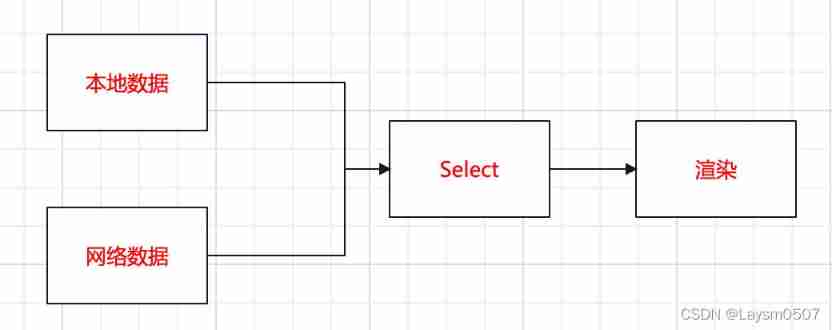
The above is a scene , When requesting data , Tend to have 2 Two data sources , From the cloud or locally , But the speed of data acquisition is inconsistent ,Select The function is to make a choice , See which end of the data comes fastest , Then take whose data to render
fun getLocal() = viewModelScope.async {
delay(2000)
" This is local data "
}
fun getNet() = viewModelScope.async {
delay(1000)
" This is the data of the network "
}
5.1 The traditional way
If according to which api The speed of the returned data determines which data to render , It can't be done just through a coordination process ,getLocal and getNet It's asynchronous , So when you get the data , Only after the slowest return , To get all the data , So you can only turn it on 2 Collaborators cheng , Listen to the respective data return separately
5.2 select
So in select Function , There is no need to open up two processes to achieve 2 The effects of these processes
viewModelScope.launch {
val result = select<Response<String>> {
getLocal().onAwait{
Response(it)}
getNet().onAwait{
Response(it)}
}
Log.e("TAG","${
result.t}")
}
Look, there is no use of await, It is onAwait function , Equivalent to the select A callback is registered in , Either way await Return the data first , Just call back the data
class Response<T>(var t:T)
This uses a coroutine , It's done 2 What a collaborative process can do
5.3 many Channel Reuse
Be similar to await Reuse , There are multiple channels to send data , It is detected which channel has sent data , Just print the data
fun CoroutineScope.channel1() = produce<String> {
delay(200)
send("123")
}
fun CoroutineScope.channel2() = produce<String> {
delay(400)
send("123456")
}
viewModelScope.launch {
val result = select<Response<String>> {
channel1().onReceive {
Response(it) }
channel2().onReceive {
Response(it) }
}
Log.e("TAG", "${
result.t}")
}
This is still the same as await It's a bit like , Not used receive, It USES onReceive Callback
5.4 SelectClause Type resolution
Since all the above are used select function , So what events can be select Well ?
from SelectBuilder Can be seen in ,SelectClause0、SelectClause1、SelectClause2 All types of events can be select
public interface SelectBuilder<in R> {
/** * Registers a clause in this [select] expression without additional parameters that does not select any value. */
public operator fun SelectClause0.invoke(block: suspend () -> R)
/** * Registers clause in this [select] expression without additional parameters that selects value of type [Q]. */
public operator fun <Q> SelectClause1<Q>.invoke(block: suspend (Q) -> R)
/** * Registers clause in this [select] expression with additional parameter of type [P] that selects value of type [Q]. */
public operator fun <P, Q> SelectClause2<P, Q>.invoke(param: P, block: suspend (Q) -> R)
/** * Registers clause in this [select] expression with additional nullable parameter of type [P] * with the `null` value for this parameter that selects value of type [Q]. */
public operator fun <P, Q> SelectClause2<P?, Q>.invoke(block: suspend (Q) -> R): Unit = invoke(null, block)
/** * Clause that selects the given [block] after a specified timeout passes. * If timeout is negative or zero, [block] is selected immediately. * * **Note: This is an experimental api.** It may be replaced with light-weight timer/timeout channels in the future. * * @param timeMillis timeout time in milliseconds. */
@ExperimentalCoroutinesApi
public fun onTimeout(timeMillis: Long, block: suspend () -> R)
}
SelectClause0 event : Events with no return value . for example join, Corresponding onJoin Namely SelectClause0 event , Is a parameterless constructor
fun CoroutineScope.co1() = launch {
delay(100)
Log.e(TAG,"co1 finish")
}
fun CoroutineScope.co2() = launch {
delay(10)
Log.e(TAG,"co2 finish")
}
no return value , Namely Unit type
select<Unit> {
co1().onJoin{
print("co1 finish")}
co2().onJoin{
print("co2 finish")}
}
SelectClause1 event : So it's like await,receive There is a return value , Then it's the corresponding onAwait and onReceive, Get the return value through callback
SelectClause2 event : The corresponding event has a return value , And you need an extra parameter , for example Channel Of send function , Need to send a data , Corresponding onSend You need to send a data
select<Unit?> {
launch {
delay(200)
channel1().onSend("2000"){
print("send in $it")
}
}
launch {
delay(100)
channel2().onSend("1000"){
print("send in $it")
}
}
}
6 Flow Multiplexing of
For example, the previous example , Get data from local and network , You need to open two coroutines to get data , In fact, it can be done through merge The operator , Combine two streams into one stream output
viewModelScope.launch {
listOf(::getLocal,::getNet)
.map {
kFunction0 ->
// Function executed
kFunction0.invoke()
}.map {
function ->
flow {
emit(function.await())
}
}.merge().collect {
Log.e(TAG," result :$it")
}
}
7 Concurrency security of concurrency
and Java Like multithreading , The concurrency of multiple processes also brings security problems
The solution :Channel、Mutex( Lock )、 Semaphore, etc , and Java The processing method in is consistent
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Xingda easy control modbustcp to profibusdp

SQL调优指南笔记13:Gathering Optimizer Statistics

CVPR 2022 | 应对噪声标签,西安大略大学、字节跳动等提出对比正则化方法

PCB package download website recommendation and detailed usage

SQL tuning guide notes 15:controlling the use of optimizer statistics

MySQL architecture and basic management (II)

Ansible基础和常用模块(一)

Turing prize winner: what should I pay attention to if I want to succeed in my academic career?

Preliminary use of jvisualvm

Oracle LiveLabs实验:Introduction to Oracle Spatial Studio
随机推荐
MySQL体系结构及基础管理(二)
Npoi create word
Oracle SQL Developer的代码输入框中推荐使用的中文字体
有向图深拷贝
What is the difference between a user thread and a daemon thread?
Ansible playbook和Ansible Roles(三)
SQL tuning guide notes 12:configuring options for optimizer statistics gathering
经济学人聚焦WTO MC12:数字经济或成重要议题
MySQL master-slave replication
ICML2022 | GALAXY:極化圖主動學習
SQL调优指南笔记14:Managing Extended Statistics
Data batch writing
Ansible summary (VI)
SQL调优指南笔记16:Managing Historical Optimizer Statistics
How do complex systems detect anomalies? North Carolina UNCC and others' latest overview of graph based deep learning anomaly detection methods in complex distributed systems describes the latest prog
同花顺能开户吗,在APP上可以直接开通券商安全吗 ,证券开户怎么开户流程
六月集训(第12天) —— 链表
Yyds dry goods inventory solution sword finger offer: the first non repeated character in the character stream
Oracle LiveLabs实验:Introduction to Oracle Spatial Studio
Oracle数据库中查询执行计划的权限