当前位置:网站首页>IoU, GIoU, DIoU and CIoU in target detection
IoU, GIoU, DIoU and CIoU in target detection
2022-08-04 07:03:00 【Blood chef】
什么是IOU?
简单来说IOUIt is used to measure the degree of overlap between the predicted frame and the real frame in target detection.在图像分类中,There is a clear indicator准确率To measure the quality of the model classification model.其公式为:
a c c = P t r u e N N = 全 部 样 本 的 数 量 , P t r u e = 预 测 正 确 的 样 本 数 量 acc = \frac{P_{true}}{N} {\quad}{\quad}{\quad}{\quad}{\quad}{\quad}{\quad}N=the total number of samples,P_{true}=预测正确的样本数量 acc=NPtrueN=全部样本的数量,Ptrue=预测正确的样本数量
This formula is obviously not suitable for use in object detection.We know that in target detection, a rectangle is used to frame the detected object,And because the scale of the detected object is different,The predicted box is larger or smaller than the ground-truth box.Therefore, the metric must be scale-invariant,Then the great gods introduced a conceptIOU(交并比),Use the prediction box(A)和真实框(B)The intersection of is divided by the union of the two,其公式为:
I O U = A ∩ B A ∪ B IOU = \frac{A\cap B}{A\cup B} IOU=A∪BA∩B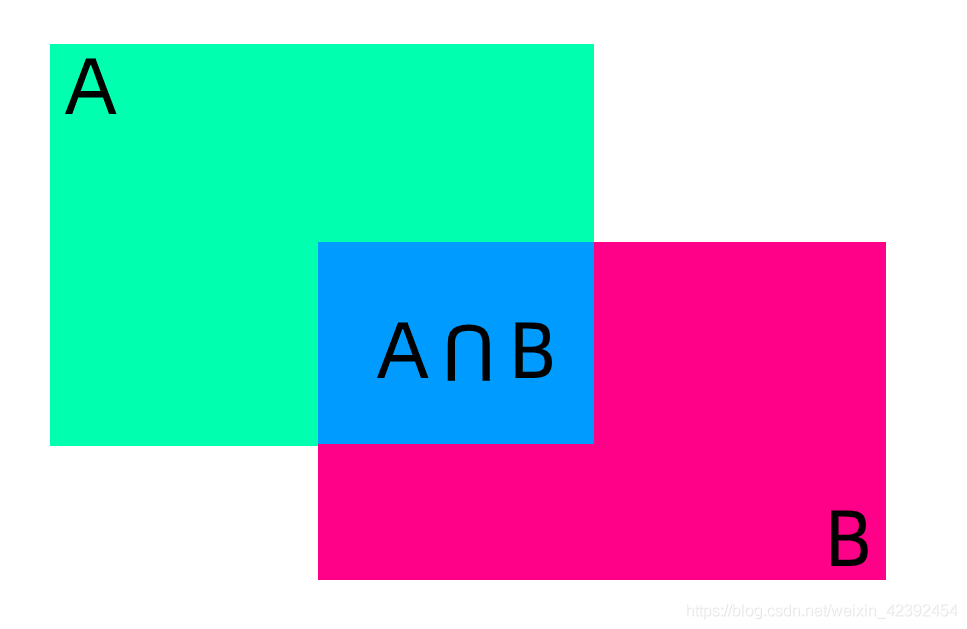
显而易见,IOUThe higher the value also indicatesA框与BThe higher the degree of frame overlap,代表模型预测越准确.反之,IOUThe lower the model, the worse the performance.
IOU应用场景
In addition to being an evaluation metric for object detection,IOU还有其他应用场景:
- 在anchor-basedmethod in target detection,根据IOUvalue to distinguish positive and negative samples.
- It can be directly regressed as a bounding boxloss函数进行优化.
- 在NMS(非极大值抑制)Filter on prediction boxes.
IOU的优缺点
普通IOU的优缺点很明显,优点:
- IOU具有尺度不变性
- 满足非负性
同时,由于IOUThe distance between boxes is not considered,So it workslossFunctions also have corresponding disadvantages:
- 在A框与BWhen the boxes do not overlapIOU为0,The distance between the two cannot be correctly reflected.
- IoU无法精确的反映两者的重合度大小.如下图所示,三种情况IOU都相等,但看得出来他们的重合度是不一样的,左边的图回归的效果最好,右边的最差.
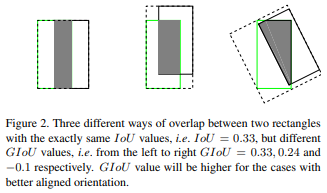
对IOU进行改进
普通IOUis insensitive to the distance between the two boxes,下面两张图中,The coordinates of the predicted box in the left picture are closer to the ground truth than the coordinates of the predicted box in the right picture.但两者的IOU皆为0,如果直接把IOU当作loss函数进行优化,则loss=0,没有梯度回传,So training is not possible.

GIOU
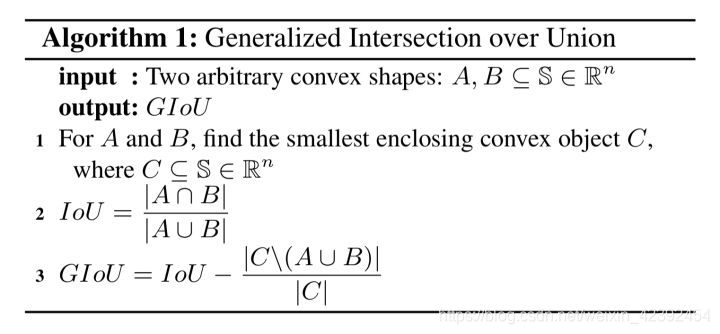
- 对于任意的两个A、B框,首先找到一个能够包住它们的最小方框,例如在上述场景 A 和 B 中,C 的形状分别为:


计算IOU
根据A、B,我们可以算出C的面积,有了Carea can be calculatedGIOU了:
G I O U = I O U − C − ( A ∪ B ) C GIOU = IOU - \frac{C - (A\cup B)}{C} GIOU=IOU−CC−(A∪B)
G I O U = − 1 + ( A ∪ B ) C ( I O U = 0 ) GIOU = -1 + \frac{(A\cup B)}{C} \quad\quad\quad(IOU=0) GIOU=−1+C(A∪B)(IOU=0)
而当IOU为0时,意味着A与Bvery far, A ∪ B C \frac{A\cup B}{C} CA∪B无限接近于0,GIOU趋近于-1,同理当IOU为1时,The two frames overlap, A ∪ B C \frac{A\cup B}{C} CA∪B为1.所以GIOU的取值为(-1, 1].
GIOU作为loss函数时,为 L = 1 − G I O U L=1-GIOU L=1−GIOU ,当A、BWhen the two boxes do not intersect A ∪ B A\cup B A∪B值不变,最大化 G I O U GIOU GIOUJust minimise C C C,This will cause the two boxes to move closer together.
DIoU
尽管GIoU解决了在IoUThe problem that the gradient cannot be calculated when used as a loss function,And added the minimum outer frame as a penalty item.But it still has some problems.The three images in the first row of the image below areGIoUPredict box convergence when iterating.The black box representsanchor,The blue box represents the prediction box,Green boxes represent real boxes.
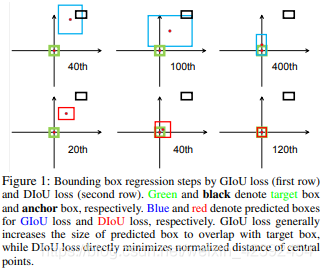
上图中可以看出,GIoUAt the beginning, the detection result method needs to be intersected with the target box,Only after that began to narrow down the test resultsGT重合,This brings about the problem of requiring more iterations to converge,Especially in the case of horizontal vs vertical boxes.此外,It's where one box contains another box,GIoUdegenerate intoIoU,Can't judge good or bad,见下图所示:
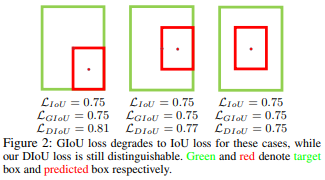
综合以上的问题,Another god proposedDIoU:
D I o U = ρ 2 ( A , B ) c 2 DIoU =\frac{\rho^2(A, B)}{c^2} DIoU=c2ρ2(A,B)
其中 d = ρ ( A , B ) d = \rho(A, B) d=ρ(A,B)是A框与BThe Euclidean distance of the coordinates of the center point of the box,而 c c cis the diagonal distance of the smallest box that encloses them.
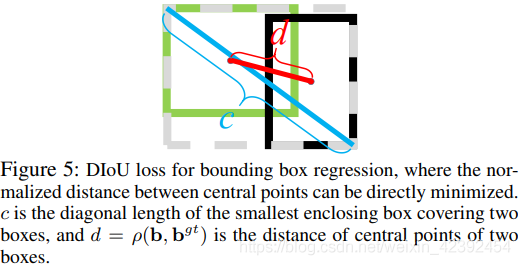
完整的DIoU Loss定义如下:
L D I o U = 1 − I o U + ρ 2 ( A , B ) c 2 L_{DIoU} = 1 - IoU + \frac{\rho^2(A, B)}{c^2} LDIoU=1−IoU+c2ρ2(A,B)
From formulas and schematics,我们可以看到,DIoU有几个优点:
- DIoU的惩罚项是基于中心点的距离和对角线距离的比值,避免了像GIoU在两框距离较远时,产生较大的外包框,Loss值较大难以优化(Because its penalty term is A ∪ B A \cup B A∪Bthan the area of the smallest outer frame).所以DIoU LossConvergence rate will be higher than GIoU Loss快.
- Even when one box contains another box,c值不变,但dValues can also be valid measures.
CIoU
同时DIoUThe authors take into account,When the center points of the two boxes coincide,c与d的值都不变.Therefore, the aspect ratio of the frame needs to be introduced at this time:
C I o U = ρ 2 ( A , B ) c 2 + α v CIoU = \frac{\rho^2(A, B)}{c^2} + \alpha v CIoU=c2ρ2(A,B)+αv
其中 α \alpha α是权重函数, v v vUsed to measure aspect ratio consistency:
α = v ( 1 − I o U ) + v \alpha = \frac{v}{(1 - IoU) + v} α=(1−IoU)+vv
v = 4 π 2 ( a r c t a n w g t h g t − a r c t a n w h ) 2 v = \frac{4}{\pi^2}(arctan \frac{w^{gt}}{h^{gt}} - arctan\frac{w}{h})^2 v=π24(arctanhgtwgt−arctanhw)2
最终CIoU Loss定义为:
C I o U = 1 − I o U + ρ 2 ( A , B ) c 2 + α v CIoU = 1 - IoU + \frac{\rho^2(A, B)}{c^2} + \alpha v CIoU=1−IoU+c2ρ2(A,B)+αv
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
自学网络安全你为什么一学就废?
网络安全求职指南
Database knowledge: SQLServer creates non-sa user notes
【HIT-SC-MEMO3】哈工大2022软件构造 复习笔记3
Logical Address & Physical Address
FCN——语义分割的开山鼻祖(基于tf-Kersa复现代码)
JUC锁框架——CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier和Semaphore
在线公众号文章内容转音频文件实用小工具
JUC并发容器——阻塞队列
华硕飞行堡垒系列无线网经常显示“无法连接网络” || 一打开游戏就断网
Uos统信系统 本地APT源配置
QT 显示窗口到最前面(非置顶)
nacos 返回 403 unknown user 太他么坑了 源码解析
解决腾讯云DescribeInstances api查询20条记录以上的问题
ZYNQ之FPGA LED 灯闪烁实验
自适应迁移学习核极限学习机用于预测
A semi-supervised Laplace skyhawk optimization depth nuclear extreme learning machine for classification
子空间结构保持的多层极限学习机自编码器(ML-SELM-AE)
SENet detailed explanation and Keras reproduction code
LeetCode刷题