1. Use Arrays.asList Precautions for
1.1 A pit you might tread in
Let's start with Arrays.asList Use :
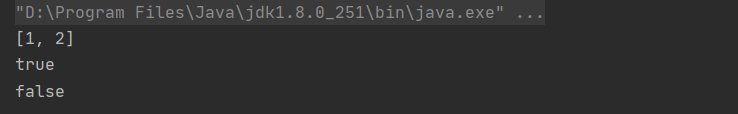
List<Integer> statusList = Arrays.asList(1, 2);
System.out.println(statusList);
System.out.println(statusList.contains(1));
System.out.println(statusList.contains(3));
The output result is shown in the figure below :
then , Go to statusList Add elements to it 3, As shown below :
statusList.add(3);
System.out.println(statusList.contains(3));
Expected results , It should be output true, But it was actually thrown out java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException abnormal :
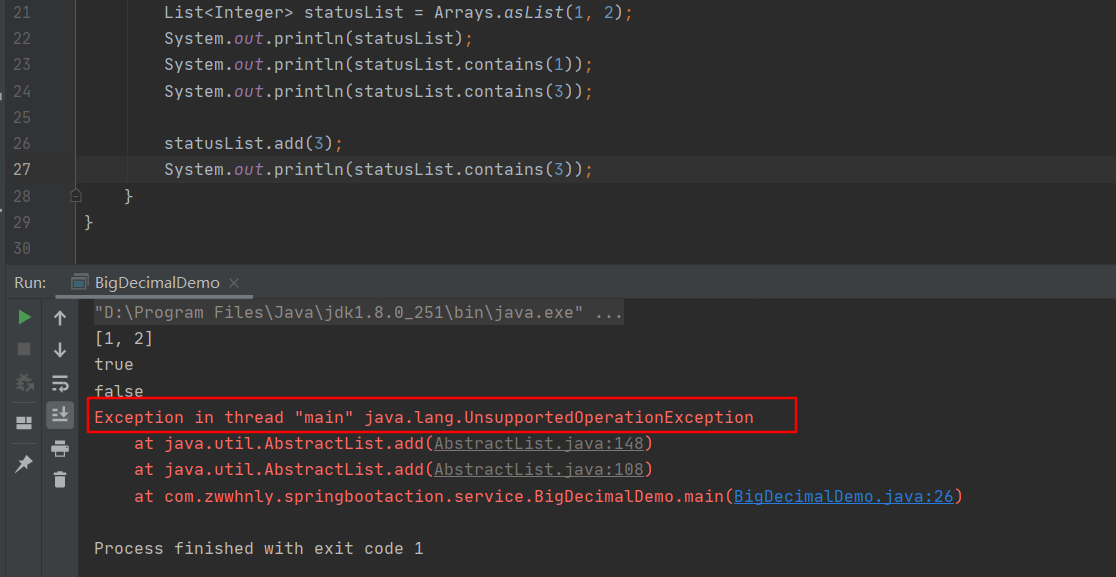
I can't help but wonder , Just add an element , Why did you throw such an exception , It's not scientific .
1.2 Cause analysis
With this question , Let's take a look at Arrays Static methods provided by class asList Source code :

The return is ArrayList, Familiar with , Is there any , But take a closer look , You'll find this ArrayList It's not something we use very often ArrayList, Because we usually use ArrayList It's located in java.util Under bag :
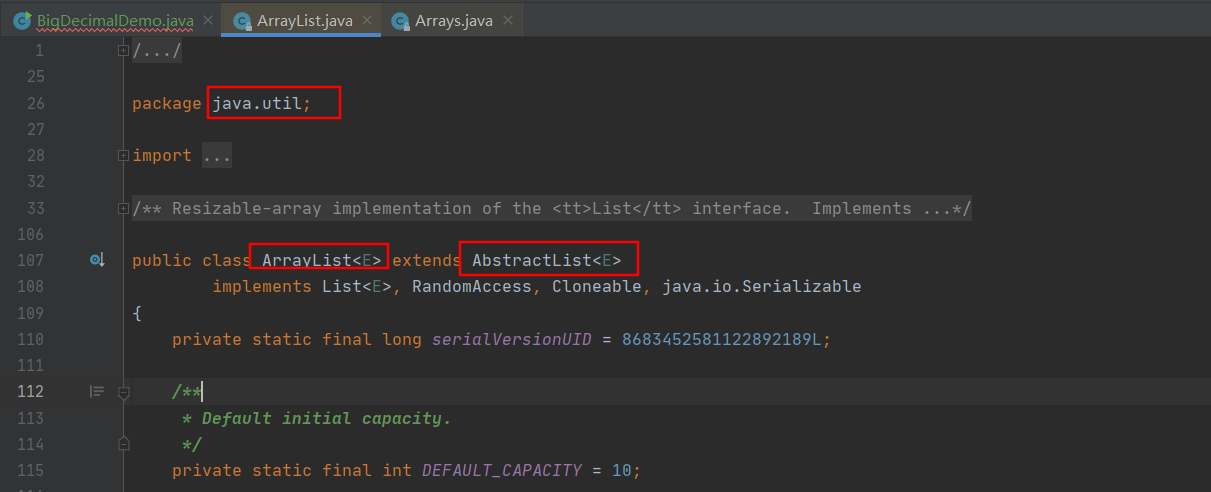
But here ArrayList nevertheless Arrays The inner class of a class :

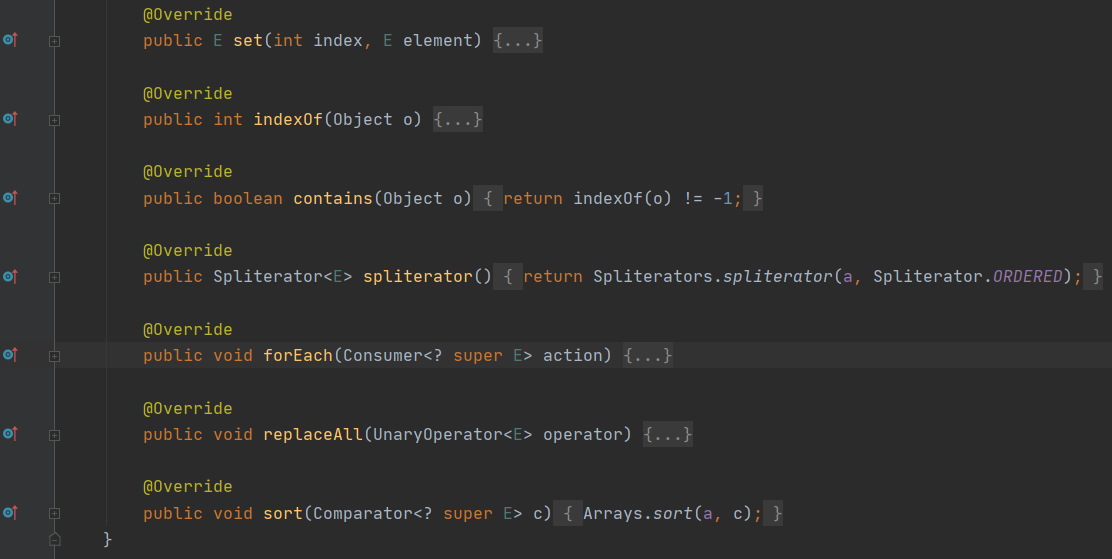
It also inherited AbstractList class , Rewriting a lot of methods , For example, the one we used above contains Method , But it didn't rewrite add Method , So we're calling add Method java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException abnormal .
On this point , stay 《 Alibaba Java Development Manual 》 In Taishan version , It is also mentioned that :
Use tool class Arrays.asList() When converting an array to a collection , You can't use it to modify collection related methods , its add/remove/clear Method will throw UnsupportedOperationException abnormal .

So we are using Arrays.asList You should pay attention to , Avoid trampling .
1.3 summary
Arrays.asList Methods can be used in some simple situations , For example, to quickly declare a collection , Determine whether a value is within the allowable range :
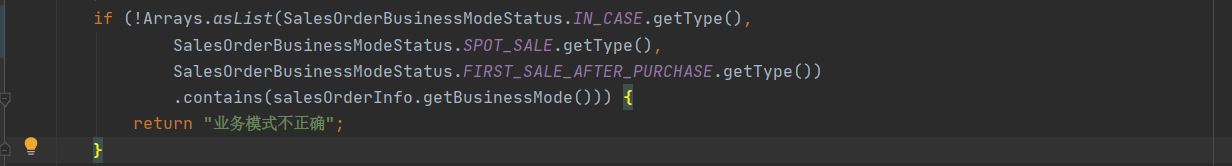
But don't call after declaration add And so on to modify the set , Otherwise it will be reported java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException abnormal .
2. Use ArrayList Of subList Precautions for
Let's start with subList Simple use :
List<String> bookList = new ArrayList<>();
bookList.add(" Distant Savior ");
bookList.add(" betrayal ");
bookList.add(" The world of heaven ");
bookList.add(" life ");
bookList.add(" Ordinary world ");
List<String> luyaoBookList = bookList.subList(3, 5);
System.out.println(bookList);
System.out.println(luyaoBookList);
The results are shown in the following figure :
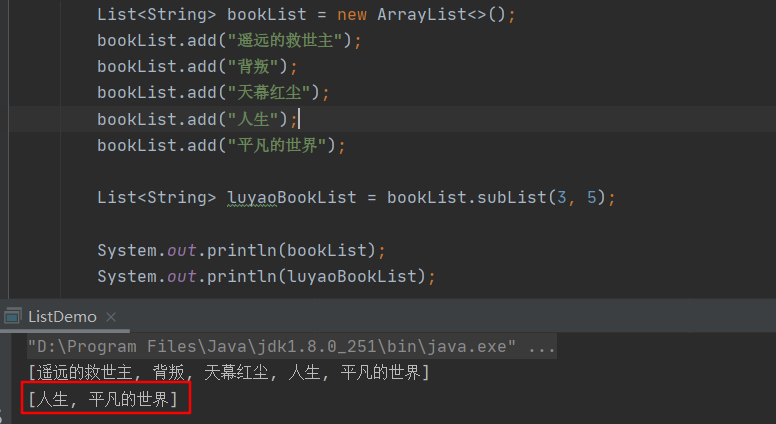
As you can see from the results ,subList The return is bookList Index from fromIndex( contain ) To toIndex( It doesn't contain ) Element collection for .
It's simple to use , It's easy to understand , However, there are still several points to pay attention to , Otherwise, it will cause program errors or exceptions :
- Modify the value of the original set element , It affects subsets
- Modify the structure of the original set , Can cause
ConcurrentModificationExceptionabnormal - Modify the value of a subset element , Will affect the original set
- Modify the structure of the subset , Will affect the original set
The above points are in 《 Alibaba Java Development Manual 》 This is what the Taishan version describes :

2.1 Modify the value of the original set , It affects subsets
such as , Let's modify the original set bookList The value of an element in ( Non structural modification ):
List<String> bookList = new ArrayList<>();
bookList.add(" Distant Savior ");
bookList.add(" betrayal ");
bookList.add(" The world of heaven ");
bookList.add(" life ");
bookList.add(" Ordinary world ");
List<String> luyaoBookList = bookList.subList(3, 5);
System.out.println(bookList);
System.out.println(luyaoBookList);
// Modify the value of the original set
bookList.set(3," Lu yao - life ");
System.out.println(bookList);
System.out.println(luyaoBookList);
The running results are as follows :

It can be seen that , Although we only modified the original set bookList Value , But it affects subsets luyaoBookList.
2.2 Modify the structure of the original set , Can cause ConcurrentModificationException abnormal
such as , Let's go back to the original bookList Add an element to ( Structural modification ):
List<String> bookList = new ArrayList<>();
bookList.add(" Distant Savior ");
bookList.add(" betrayal ");
bookList.add(" The world of heaven ");
bookList.add(" life ");
bookList.add(" Ordinary world ");
List<String> luyaoBookList = bookList.subList(3, 5);
System.out.println(bookList);
System.out.println(luyaoBookList);
// Add elements to the original collection
bookList.add(" The morning begins at noon ");
System.out.println(bookList);
System.out.println(luyaoBookList);
The running results are as follows :

It can be seen that , When we add elements to the original set ( Structural modification ) after , When traversing subsets , It happened. ConcurrentModificationException abnormal .
matters needing attention : The above exception does not occur when adding elements , But after adding elements , What happens when traversing a subset .
On this point , stay 《 Alibaba Java Development Manual 》 This is what the Taishan version describes :

2.3 Modify the value of the subset , Will affect the original set
such as , We modify subsets luyaoBookList The value of an element in ( Non structural modification ):
List<String> bookList = new ArrayList<>();
bookList.add(" Distant Savior ");
bookList.add(" betrayal ");
bookList.add(" The world of heaven ");
bookList.add(" life ");
bookList.add(" Ordinary world ");
List<String> luyaoBookList = bookList.subList(3, 5);
System.out.println(bookList);
System.out.println(luyaoBookList);
// Modify the value of the subset
luyaoBookList.set(1," Lu yao - Ordinary world ");
System.out.println(bookList);
System.out.println(luyaoBookList);
The running results are as follows :
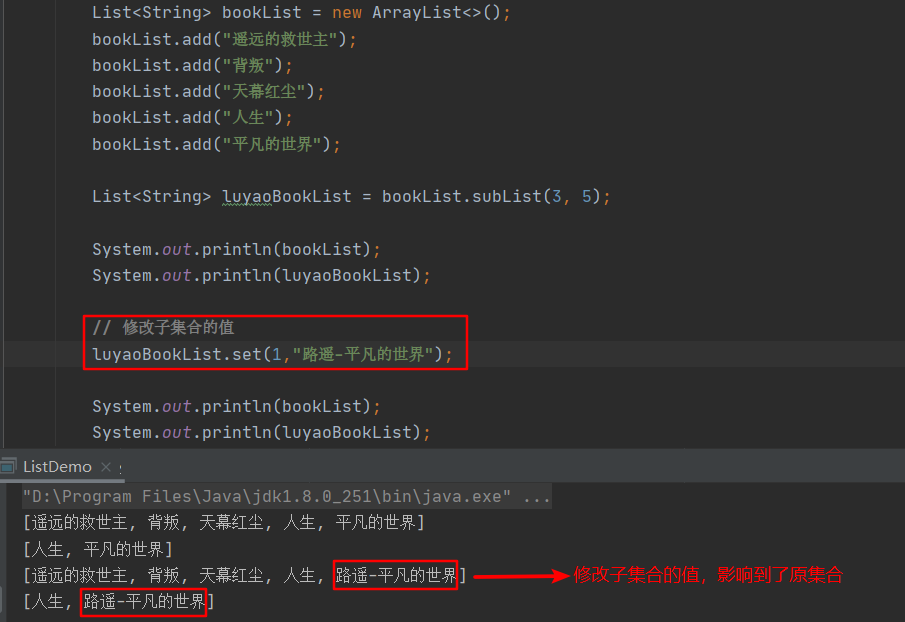
It can be seen that , Although we only modified the subset luyaoBookList Value , But it affects the original set bookList.
2.4 Modify the structure of the subset , Will affect the original set
such as , Let's go to the subset luyaoBookList Add an element to ( Structural modification ):
List<String> bookList = new ArrayList<>();
bookList.add(" Distant Savior ");
bookList.add(" betrayal ");
bookList.add(" The world of heaven ");
bookList.add(" life ");
bookList.add(" Ordinary world ");
List<String> luyaoBookList = bookList.subList(3, 5);
System.out.println(bookList);
System.out.println(luyaoBookList);
// Add elements to the subset
luyaoBookList.add(" The morning begins at noon ");
System.out.println(bookList);
System.out.println(luyaoBookList);
The running results are as follows :

It can be seen that , When we add elements to a subset ( Structural modification ) after , It affects the original set bookList.
2.5 Cause analysis
First , Let's take a look at subList Method comments , Find out what it does :
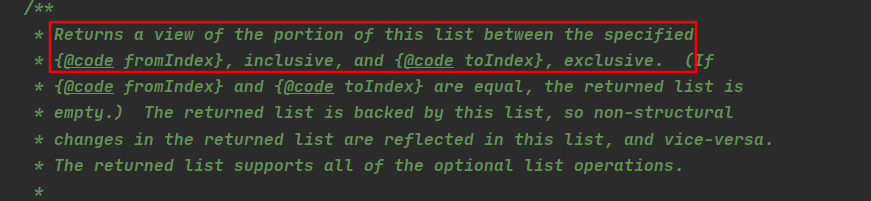
Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified {@code fromIndex}, inclusive, and {@code toIndex}, exclusive.
Translation means :
Returns the specified {@code fromIndex}( contain ) and {@code toIndex}( exclude ) Between the list parts of the view .
then , Let's take a look at the source code :
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
subListRangeCheck(fromIndex, toIndex, size);
return new SubList(this, 0, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
You can see , It calls for SubList Class constructor , The source code of the constructor is shown in the figure below :
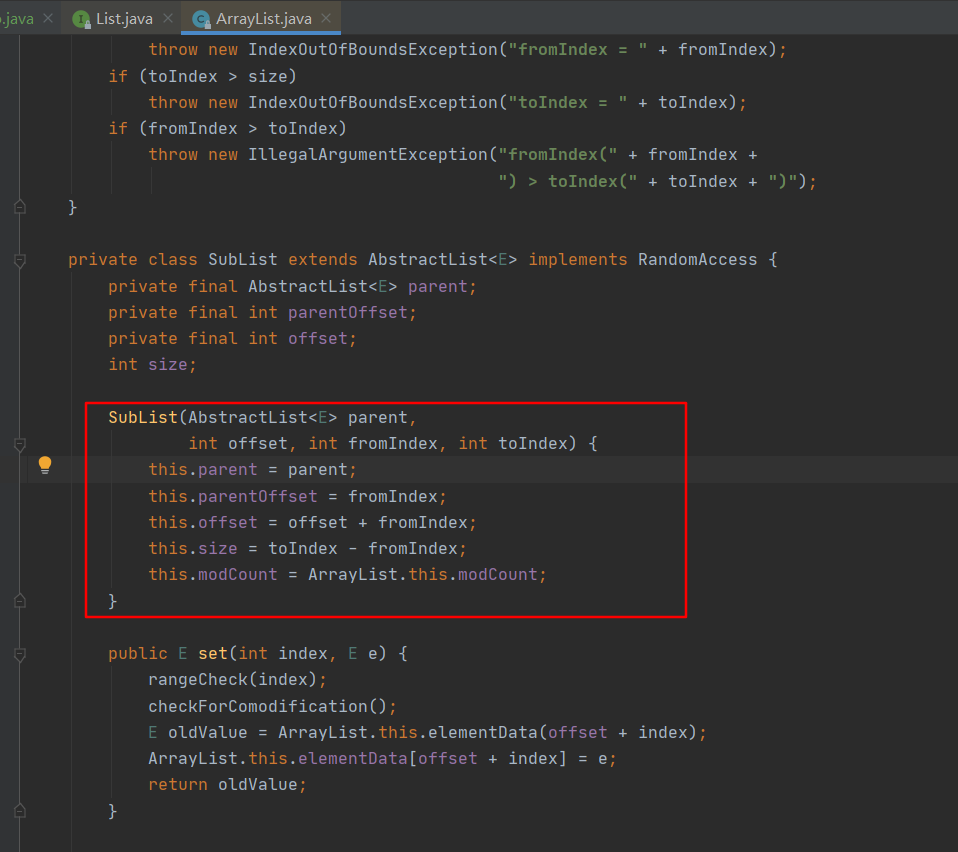
It can be seen that ,SubList Class is ArrayList The inner class of , The constructor does not recreate a new ArrayList, So modify the values of the elements of the original set or subset , It will affect each other .
2.6 summary
ArrayList Of subList Method , It returns a subset of the original set ( View ), Unstructured modification of the values of elements in any set , Will influence each other , When modifying the original set structurally , Will be submitted to the ConcurrentModificationException abnormal , When modifying subsets structurally , Will affect the original set , So pay attention to the use of , Avoid program errors or exceptions .
3. Reference resources
Use caution ArrayList Medium subList Method
《 Alibaba Java Development Manual 》 Taishan Edition

![[论文阅读笔记] A Multilayered Informative Random Walk for Attributed Social Network Embedding](/img/3d/657a60600219ce6cfc514ad1b1bb49.jpg)