当前位置:网站首页>Mmdetection build_ Optimizer module interpretation
Mmdetection build_ Optimizer module interpretation
2022-06-10 17:47:00 【Wu lele~】
List of articles
Preface
Previous article build_dataset,build_dataloader,build_model Have made a detailed introduction , and optimizer As “ Alchemy ” The last condition of , This article will introduce mmdetection How to build the optimizer .
1、 Overall process
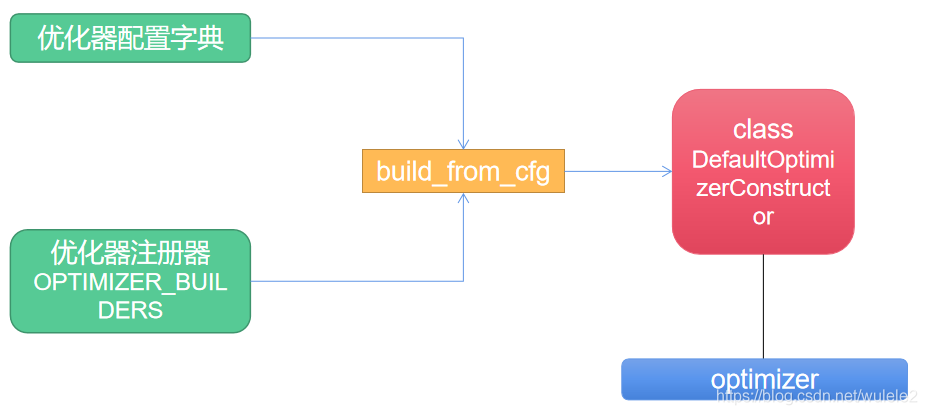
Overall process and construction model The process is similar to . First mmdetection Set up an optimizer register , It's registered DefaultOptimizerConstructor Optimizer class . And then with the help of build_from_cfg The function instantiates a from the optimizer configuration dictionary optimizer object . Next , The internal principles of each component will be described in detail .
2、 Optimizer configuration Dictionary
This article is still based on faster_rcnn_r50_fpn.py Take the default configuration file as an example . among , involve optimizer The fields of are as follows :
# optimizer
optimizer = dict(type='SGD', lr=0.00125, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0001)
It can be seen that the default is SGD Optimizer .
3、 Optimizer registrar
mmdetection Set up two registers :
OPTIMIZERS = Registry('optimizer')
OPTIMIZER_BUILDERS = Registry('optimizer builder')
3.1、 Registrar OPTIMIZERS
among ,OPTIMIZERS Some are added to the register pytorch Optimizer provided , Look at the picture below :
Here I will briefly introduce mmdetection The process of building this piece (mmcv/runners/optimizer/builder.py): adopt dir Methods through torch.optim, And then use it register_module()(_optim) To complete the registration .
def register_torch_optimizers():
torch_optimizers = []
for module_name in dir(torch.optim):
if module_name.startswith('__'):
continue
_optim = getattr(torch.optim, module_name)
if inspect.isclass(_optim) and issubclass(_optim,
torch.optim.Optimizer):
OPTIMIZERS.register_module()(_optim) # Here to OPTIMIZERS It's registered torch The default optimizer in .
torch_optimizers.append(module_name)
return torch_optimizers
TORCH_OPTIMIZERS = register_torch_optimizers()
3.2、 Registrar OPTIMIZER_BUILDERS
The other registrar mainly registers the following classes (mmcv/runner/optimizer/default_constructor.py), Here I just intercepted the class initialization part .
@OPTIMIZER_BUILDERS.register_module()
class DefaultOptimizerConstructor:
"""Default constructor for optimizers Args: model (:obj:`nn.Module`): The model with parameters to be optimized. optimizer_cfg (dict): The config dict of the optimizer. Positional fields are - `type`: class name of the optimizer. Optional fields are - any arguments of the corresponding optimizer type, e.g., lr, weight_decay, momentum, etc. paramwise_cfg (dict, optional): Parameter-wise options. Example 1: >>> model = torch.nn.modules.Conv1d(1, 1, 1) >>> optimizer_cfg = dict(type='SGD', lr=0.01, momentum=0.9, >>> weight_decay=0.0001) >>> paramwise_cfg = dict(norm_decay_mult=0.) >>> optim_builder = DefaultOptimizerConstructor( >>> optimizer_cfg, paramwise_cfg) >>> optimizer = optim_builder(model) Example 2: >>> # assume model have attribute model.backbone and model.cls_head >>> optimizer_cfg = dict(type='SGD', lr=0.01, weight_decay=0.95) >>> paramwise_cfg = dict(custom_keys={ '.backbone': dict(lr_mult=0.1, decay_mult=0.9)}) >>> optim_builder = DefaultOptimizerConstructor( >>> optimizer_cfg, paramwise_cfg) >>> optimizer = optim_builder(model) >>> # Then the `lr` and `weight_decay` for model.backbone is >>> # (0.01 * 0.1, 0.95 * 0.9). `lr` and `weight_decay` for >>> # model.cls_head is (0.01, 0.95). """
def __init__(self, optimizer_cfg, paramwise_cfg=None):
if not isinstance(optimizer_cfg, dict):
raise TypeError('optimizer_cfg should be a dict',
f'but got {
type(optimizer_cfg)}')
self.optimizer_cfg = optimizer_cfg
self.paramwise_cfg = {
} if paramwise_cfg is None else paramwise_cfg
self.base_lr = optimizer_cfg.get('lr', None)
self.base_wd = optimizer_cfg.get('weight_decay', None)
self._validate_cfg()
4、 Instance optimizer object
After having the configuration dictionary and registrar , Then you can instantiate the optimizer object . The entry to building the optimizer is mmdet/apis/trian.py In file , The code is as follows :
# build runner
optimizer = build_optimizer(model, cfg.optimizer)
Look here build_optimizer function :
def build_optimizer_constructor(cfg):
return build_from_cfg(cfg, OPTIMIZER_BUILDERS) # Complete the instance optimizer object
def build_optimizer(model, cfg):
optimizer_cfg = copy.deepcopy(cfg)
constructor_type = optimizer_cfg.pop('constructor', #optimizer_cfg There is no... In the dictionary "constructor" This key , Then return to DefaultOptimizerConstructor
'DefaultOptimizerConstructor')
paramwise_cfg = optimizer_cfg.pop('paramwise_cfg', None) # ditto
optim_constructor = build_optimizer_constructor( # It's actually calling theta build_from_cfg function
dict(
type=constructor_type,
optimizer_cfg=optimizer_cfg,
paramwise_cfg=paramwise_cfg))
optimizer = optim_constructor(model)
return optimizer
As you can see from the code ,build_optimizer Internal call build_optimizer_constructor function , And then called build_from_cfg Completed the instantiation of the class , In the code optim_constructor object . after , Here comes the interesting part . We just used the register earlier OPTIMIZER_BUILDERS, Without the use of a registrar OPTIMIZERS. So where is it called ? The calling code is :optimizer=optim_constructor(model).
Now look back 3.2 Section DefaultOptimizerConstructor class . Internally implemented __call__ Method . Intercept this part of the code :
def __call__(self, model):
if hasattr(model, 'module'):
model = model.module
optimizer_cfg = self.optimizer_cfg.copy()
# if no paramwise option is specified, just use the global setting
if not self.paramwise_cfg:
optimizer_cfg['params'] = model.parameters()
return build_from_cfg(optimizer_cfg, OPTIMIZERS)
# set param-wise lr and weight decay recursively
params = []
self.add_params(params, model)
optimizer_cfg['params'] = params
return build_from_cfg(optimizer_cfg, OPTIMIZERS)
With the help of build_from_cfg(optimizer_cfg,OPTIMIZERS) Completed the establishment of the real optimizer object .
summary
This paper mainly introduces mmdetection The process of building an optimizer in . Of course , There are many more code details to learn . in general , Due to the actual use of the optimizer , There will be a variety of flexible settings . If only with a single registrar OPTIMIZERS, It is bound to be inconvenient . and mmdetection after “ factory ”—OPTIMIZER_BUILDERS To give the optimizer flexibility ( For example, just optimize some parameters or add optimized parameters ). This design pattern is worth learning . If you have any questions, welcome +vx:wulele2541612007, Pull you into the group to discuss communication .
Expand reading materials
mmcv in Config Class introduction
mmcv And Registry Class introduction
mmdetection And dataset Class construction
mmdetection And dataloader Class construction
mmdetection And model structure
mmdetection Train yourself coco Data sets
边栏推荐
- Nacos注册中心
- Thread interview related questions
- 2022年茶艺师(中级)操作证考试题库及模拟考试
- Primekg: building a knowledge map to achieve precision medicine
- 单片机底层通信协议① —— 同步和异步、并行和串行、全双工和半双工以及单工、电平信号和差分信号
- 牛客网:表达式求值
- Is the fund of futures account safe?
- 训练时添加进度条的库--tqdm
- matplotlib plt. Specific usage of text() - labeling points in a drawing
- Fabric. JSON for JS compact output
猜你喜欢

Online communication skill network: a sparse model for solving multi task and multi-modal problems (Qingyuan talk, issue 19, tangduyu)

软件项目管理 6.10.成本预算

牛客网:两数之和

vscode常用插件与配置
2022年焊工(初级)试题模拟考试平台操作

Numpy numpy中np.set_printoptions()的用法——控制输出方式

THE LOTTERY TICKET HYPOTHESIS: FINDING SPARSE, TRAINABLE NEURAL NETWORKS论文笔记

Photoshop如何打开、编辑和导出Webp格式图片的方法

2022G1工业锅炉司炉考题及在线模拟考试

The children in the deep mountains are seeing the stars farther away
随机推荐
安全感
Solve the problem that idea is stuck in opening a project
C#_ Serial port communication project
《华为数据之道》读书笔记
Facebook AI | learning reverse folding from millions of prediction structures
几个对程序员的误解,害人不浅!
Detailed derivation of perspective projection transformation and related applications
See how advanced technology changes human life
It has become a unicorn since its establishment one year ago. Tencent didi is the "backer". This year's new unicorn is not simple
蓝桥杯_糊涂人寄信_递归
Numpy numpy中np.set_printoptions()的用法——控制输出方式
pands pd.DataFrame()函数详细解析
Mapbox GL development tutorial (11): loading line layers
Is the fund of futures account safe?
sense of security
vscode常用快捷键
Fabric. Keep the original level when JS element is selected
Leetcode String to integer(Atoi)
There is an urgent need to enrich the smart home product line. Can fluorite be crowded on the sweeping robot track?
Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. | Application of AI in small molecule drug discovery: an upcoming wave?