当前位置:网站首页>【ceph】mkdir|mksnap流程源码分析|锁状态切换实例
【ceph】mkdir|mksnap流程源码分析|锁状态切换实例
2022-06-26 14:56:00 【bandaoyu】
目录
Locker::process_request_cap_release
Server::rdlock_path_xlock_dentry
MDCache::predirty_journal_parents
Client----------------------op:mkdir-------------->MDS
mkdir就是创建目录,客户端并不直接创建目录,而是将mkdir的请求(op为CEPH_MDS_OP_MKDIR)发给MDS,然后MDS执行mkdir的操作,并返回创建的目录的元数据。客户端无非就是发送请求和处理回复。
例子 mkdir /mnt/ceph-fuse/test
一、mkdir Clientd端的处理
转自:cephfs:用户态客户端mkdir - https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/85624700
发送请求的流程

发送请求的内容
两类请求:MetaRequest,MClientRequest。
MetaRequest的大部分内容都是在make_request和send_request中填充,所以各种op填充的内容都差不多,只研究不同的地方。
struct MetaRequest {
private:
InodeRef _inode, _old_inode, _other_inode; // _inode为创建目录的父目录的inode指针
// 这里_inode->ino = 1
Dentry *_dentry; //associated with path, _dentry->dir是父目录的Dir,_dentry->name = "test"
public:
ceph_mds_request_head head; // head.op = CEPH_MDS_OP_MKDIR
filepath path, path2; // path.ino = 0x1(父目录的inode号), path.path = "test"
......
int dentry_drop, dentry_unless; // dentry_drop = CEPH_CAP_FILE_SHARED = "Fs",在send_request过程中,会释放掉父目录的Inode的caps的"Fs"权限
// dentry_unless = CEPH_CAP_FILE_EXCL = "Fx"
vector<MClientRequest::Release> cap_releases; // cap_releases.push_back(MClientRequest::Release(rel,""))。?
......
ceph::cref_t<MClientReply> reply; // the reply
//possible responses
bool got_unsafe; // 收到unsafe的回复时,got_unsafe为true
xlist<MetaRequest*>::item item; // 插入到session的requests链表中
xlist<MetaRequest*>::item unsafe_item; // 收到unsafe回复后,插入到session的unsafe_requests链表中。
xlist<MetaRequest*>::item unsafe_dir_item; // 收到unsafe回复且涉及到父目录操作(在父目录下创建/删除文件/目录),插入到父目录Inode的unsafe_ops链表中
xlist<MetaRequest*>::item unsafe_target_item; // 收到unsafe回复且请求需要获取目的inode信息,插入到自己Inode的unsafe_ops链表中
// 上述4个链表节点,都在收到safe回复后,会将链表节点从各自的链表中删除
InodeRef target; // target是创建的目录的Inode指针,从mds的回复中组装而成。
}
MClientRequest的内容是在通用函数build_client_request和send_request函数中填充的,所以大部分内容都差不多
class MClientRequest : public Message {
public:
mutable struct ceph_mds_request_head head; // head.op = CEPH_MDS_OP_MKDIR
// head.flags = CEPH_MDS_FLAG_WANT_DENTRY
// path arguments
filepath path, path2; // path.ino = 0x1(父目录的inode号), path.path = "test"
......
}
从代码可以看出,发送给mds的请求最重要的就是两个:
- op,不同的op,处理机制不同;
- filepath path,path.ino是父目录的inode号,path.path就是需要创建的目录名。
通过这两个,mds就知道在哪个目录下创建目录。
处理请求的流程

class MClientReply : public Message {
public:
// reply data
struct ceph_mds_reply_head head {};
/* client reply */
struct ceph_mds_reply_head {
__le32 op;
__le32 result;
__le32 mdsmap_epoch;
__u8 safe; /* true if committed to disk; 用来判断是否已经下刷了disk,或者不需要下刷时,safe就为1*/
__u8 is_dentry, is_target; /* true if dentry, target inode records are included with reply; is_dentry = 1, is_target = 1*/
}
bufferlist trace_bl; // trace_bl里面存着真正的信息,用于更新目的inode
}
最后"test"目录inode的cap.issued == "pAsxLsXsxFsx", cap.implemented == "pAsxLsXsxFsx"
后记
在linux中同一目录下的子目录和文件名是不能相同的,如test/目录下就不能有"test1"的目录和"text1"的文件。这是为啥,在看过lookup之后,就知道答案了,举例说明:比如我们要mkdir /test/test1: 先进行索引,即lookup 0x1/test,获得test的inode,这里假设test的inode号为0x2, 接下来再lookup 0x2/test1, 即获取test目录下"test1"的Dentry,然后从Dentry中获得Inode,假设在mkdir /test/test1之前,已经有了一个test1的文件,那么这时lookup 0x2/test1会获得test1文件的Inode,lookup返回的结果是0,这是mkdir就报错:文件或目录已存在。
二、mkdir MDS端的处理
现在就研究下MDS这边处理mkdir的流程。例子:mkdir /test/a
MDS对于来自客户端请求的通用处理

通用处理流程
在上面的图中可以看出,在正式处理mkdir请求之前,先处理了请求中附带的cap_realse消息,即函数Locker::process_request_cap_release;
Locker::process_request_cap_release
process_request_cap_release用来处理请求中ceph_mds_request_release& item,item中的caps就是客户端持有父目录的caps(caps知识:http://t.csdn.cn/KKQzA),比如mkdir /test/a,caps就是客户端持有a的父目录"test"目录的caps。客户端在发送mkdir请求时,会丢掉自己持有的"Fs"权限:客户端"test"的inode中caps为"pAsLsXsFs"。 丢掉"Fs",就是"pAsLsXs"。
process_request_cap_release的代码简略如下。
void Locker::process_request_cap_release(MDRequestRef& mdr, client_t client,
const ceph_mds_request_release& item, std::string_view dname)
{ // item就是从客户端那边传过来的,dname = ""(客户端传的时候,并没有给dname赋值)
inodeno_t ino = (uint64_t)item.ino; // ino = "test"的inode号
uint64_t cap_id = item.cap_id;
int caps = item.caps; // caps = "pAsLsXs"
int wanted = item.wanted; // wanted = 0
int seq = item.seq;
int issue_seq = item.issue_seq;
int mseq = item.mseq;
CInode *in = mdcache->get_inode(ino); // 获取"test"的CInode
Capability *cap = in->get_client_cap(client);
cap->confirm_receipt(seq, caps); // 将"test"的CInode的caps的_issued和_pending变成“pAsLsXs”
adjust_cap_wanted(cap, wanted, issue_seq); // 设置caps中的wanted
eval(in, CEPH_CAP_LOCKS);
......
}
void Locker::process_request_cap_release(MDRequestRef& mdr, client_t client,
const ceph_mds_request_release& item, std::string_view dname)
{ // item就是从客户端那边传过来的,dname = ""(客户端传的时候,并没有给dname赋值)
inodeno_t ino = (uint64_t)item.ino; // ino = "test"的inode号
uint64_t cap_id = item.cap_id;
int caps = item.caps; // caps = "pAsLsXs"
int wanted = item.wanted; // wanted = 0
int seq = item.seq;
int issue_seq = item.issue_seq;
int mseq = item.mseq;
CInode *in = mdcache->get_inode(ino); // 获取"test"的CInode
Capability *cap = in->get_client_cap(client);
cap->confirm_receipt(seq, caps); // 将"test"的CInode的caps的_issued和_pending变成“pAsLsXs”
adjust_cap_wanted(cap, wanted, issue_seq); // 设置caps中的wanted
eval(in, CEPH_CAP_LOCKS);
......
}
简单来讲就是将MDS缓存的"test"的CInode中的对应的客户端的caps与客户端保持一致 (客户端丢掉Fs,MDS缓存的"test"的CInode中的对应的客户端的caps也丢掉),即cap中的_issued和_pending变成"pAsLsXs"。这样做的目的就是在acquire_lock时避免向该客户端发送revoke消息。
Server::handle_client_mkdir
cap_release消息处理完后,通过Server::dispatch_client_request分发请求,根据op执行Server::handle_client_mkdir,处理过程可以分为7个重要的流程:
步骤说明和代码(本段末尾)如下:
1,获取"a"目录的CDentry以及需要加 上锁的元数据的 lock(锁头,放入rdlocks, wrlocks, xlocks),具体函数为Server::rdlock_path_xlock_dentry
2,加上锁,具体函数为Locker::acquire_locks,如果加 上锁不成功,即某些客户端持有的caps需要回收(其他客户端占着本次请求的某些caps?),就新建C_MDS_RetryRequest,加入"test"的CInode的waiting队列中,等待满足加锁条件后,再把请求拿出来处理。
3,如果加 上锁成功,则继续,新建"a"的CInode,具体函数为Server::prepare_new_inode
4,新建"a"的CDir,具体函数为CInode::get_or_open_dirfrag
5,更新"a"目录到"/"根目录的CDir和CInode中的元数据,填充"mkdir"事件,具体函数为MDCache::predirty_journal_parents
6,新建"a"的Capability,具体函数为Locker::issue_new_caps
7,记录"mkdir"事件,进行第一次回复,提交日志,具体函数为Server::journal_and_reply。
void Server::handle_client_mkdir(MDRequestRef& mdr)
{
MClientRequest *req = mdr->client_request;
set<SimpleLock*> rdlocks, wrlocks, xlocks;
// 获取"a"目录的CDentry以及需要加锁的元数据lock,填充rdlocks,wrlocks,xlocks,dn是"a"的CDentry
CDentry *dn = rdlock_path_xlock_dentry(mdr, 0, rdlocks, wrlocks, xlocks, false, false, false);
......
CDir *dir = dn->get_dir(); // dir是"test"的CDir
CInode *diri = dir->get_inode(); // diri是"test"的CInode
rdlocks.insert(&diri->authlock); // 将"test"的CInode的authlock加入rdlocks
// 去获取锁,由于有锁未获取到,所以直接返回
if (!mds->locker->acquire_locks(mdr, rdlocks, wrlocks, xlocks))
return;
......
}


Server::rdlock_path_xlock_dentry
该函数具体做的事如下
1,获取"a"的CDentry
2,rdlocks、wrlocks、xlocks 收集操作需要上锁的各种锁
rdlocks:"a"的CDentry中的lock
"/"、"test"的CInode的snaplocks(从根到父目录)
wrlocks:"test"的CInode的filelock和nestlock
xlocks:"a"的CDentry中的lock(simplelock)
代码如下
CDentry* Server::rdlock_path_xlock_dentry(MDRequestRef& mdr, int n, set<SimpleLock*>& rdlocks, set<SimpleLock*>& wrlocks, set<SimpleLock*>& xlocks,
bool okexist, bool mustexist, bool alwaysxlock, file_layout_t **layout)
{ // n = 0, rdlocks, wrlocks, xlocks都为空,okexist = mustexist = alwaysxlock = false,layout = 0
const filepath& refpath = n ? mdr->get_filepath2() : mdr->get_filepath(); // refpath = path: path.ino = 0x10000000001, path.path = "a"
client_t client = mdr->get_client();
CDir *dir = traverse_to_auth_dir(mdr, mdr->dn[n], refpath); // 获取"test"的CDir
CInode *diri = dir->get_inode(); // 获取"test"的CInode
std::string_view dname = refpath.last_dentry(); // dname = "a"
CDentry *dn;
if (mustexist) { ...... // mustexist = false
} else {
dn = prepare_null_dentry(mdr, dir, dname, okexist); // 获取“a”的CDentry
if (!dn)
return 0;
}
mdr->dn[n].push_back(dn); // n = 0, 即mdr->dn[0][0] = dn;
CDentry::linkage_t *dnl = dn->get_linkage(client, mdr); // dnl中的remote_ino = 0 && inode = 0
mdr->in[n] = dnl->get_inode(); // mdr->in[0] = 0
// -- lock --
for (int i=0; i<(int)mdr->dn[n].size(); i++) // (int)mdr->dn[n].size() = 1
rdlocks.insert(&mdr->dn[n][i]->lock); // 将"a"的CDentry中的lock放入rdlocks
if (alwaysxlock || dnl->is_null()) // dnl->is_null()为真
xlocks.insert(&dn->lock); // new dn, xlock,将"a"的CDentry中的lock放入xlocks
else ......
// 下面是将"test"的CDir中的CInode的filelock和nestlock都放入wrlocks
wrlocks.insert(&dn->get_dir()->inode->filelock); // also, wrlock on dir mtime
wrlocks.insert(&dn->get_dir()->inode->nestlock); // also, wrlock on dir mtime
if (layout) ......
else
mds->locker->include_snap_rdlocks(rdlocks, dn->get_dir()->inode); // 将路径上的CInode的snaplock全放入rdlocks中,即从"test"到“/”
return dn;
}
在prepare_null_dentry函数中会新生成"a"的CDentry,代码如下
CDentry* Server::prepare_null_dentry(MDRequestRef& mdr, CDir *dir, std::string_view dname, bool okexist)
{ // dir是"test"的CDir,dname = "a"
// does it already exist?
CDentry *dn = dir->lookup(dname);
if (dn) {......} // dn没有lookup到,所以为NULL
// create
dn = dir->add_null_dentry(dname, mdcache->get_global_snaprealm()->get_newest_seq() + 1); // 新建CDentry
dn->mark_new(); // 设置 state | 1
return dn;
}
即Server::prepare_null_dentry会先去父目录"test"的CDir的items中去找有没有"a"的CDentry,如果没有找到就新生成一个CDentry。研究MDS,不去研究元数据细节,很容易迷失。下面就是CDentry的类定义,其中可以看到CDentry是继承自LRUObject,因为CDentry是元数据缓存,得靠简单的LRU算法来平衡缓存空间。先研究其中的成员变量的含义
class CDentry : public MDSCacheObject, public LRUObject, public Counter<CDentry> {
......
// 成员变量如下
public:
__u32 hash; // hash就是"a"通过ceph_str_hash_rjenkins函数算出来的hash值
snapid_t first, last;
elist<CDentry*>::item item_dirty, item_dir_dirty;
elist<CDentry*>::item item_stray;
// lock
static LockType lock_type; // LockType CDentry::lock_type(CEPH_LOCK_DN)
static LockType versionlock_type; // LockType CDentry::versionlock_type(CEPH_LOCK_DVERSION)
SimpleLock lock; // 初始化下lock.type->type = CEPH_LOCK_DN,lock.state = LOCK_SYNC
LocalLock versionlock; // 初始化下lock.type->type = CEPH_LOCK_DVERSION,lock.state = LOCK_LOCK
mempool::mds_co::map<client_t,ClientLease*> client_lease_map;
protected:
CDir *dir = nullptr; // dir是父目录的CDir,即"test"的CDir
linkage_t linkage; // 里面保存了CInode,在mkdir时,由于CInode还没有创建,所以linkage_t里面的内容为空
mempool::mds_co::list<linkage_t> projected; // 修改CDentry中的linkage时,并不直接去修改linkage
// 而是先新建一个临时的linkage_t用来保存修改的值,并存放在peojected中
// 待日志下刷后,再将临时值赋给linkage,并删掉临时值
// 所以projected中存放linkage_t的修改值。
version_t version = 0;
version_t projected_version = 0; // what it will be when i unlock/commit.
private:
mempool::mds_co::string name; // 文件或目录名, name = "a"
public:
struct linkage_t { // linkage_t中主要存了CInode的指针
CInode *inode = nullptr;
inodeno_t remote_ino = 0;
unsigned char remote_d_type = 0;
......
};
}
接下来就是填充rdlocks,wrlocks,xlocks,然后根据填充的锁set数组,去拿锁,只有拿到需要的锁,才能去修改元数据。
Locker::acquire_locks
进行acquire_lock之前需要知道有哪些lock要去获取,如下

对"a"的CDentry的lock进行rdlock和xlock(这里有一个疑点,对lock 加上xlock后,其实就不需要再加rdlock,事实上接下来也只加了xlock),是因为在接下来会对"a"的CDentry里面的内容读写;
对"a"的父目录"test"的filelock和nestlock加 上wrlock,是因为接下来要对"test"的CInode的inode里面的dirstat和neststat进行修改;
对"test"的authlock加rdlock,是因为要读取"test"的权限相关的内容(mode、uid、gid等);
剩下的就是snaplock,这个与快照有关,这里暂不讨论快照。
这里解释下,为什么要加这些锁
1,对"test"的CInode的authlock加读锁,因为在Server::prepare_new_inode过程中会获取"test"的CInode的mode内容,如下
if (diri->inode.mode & S_ISGID) {
dout(10) << " dir is sticky" << dendl;
in->inode.gid = diri->inode.gid;
if (S_ISDIR(mode)) {
dout(10) << " new dir also sticky" << dendl;
in->inode.mode |= S_ISGID;
}
2,对"test"的CInode的filelock和nestlock加wrlock,是因为之后在MDCache::predirty_journal_parents过程中会修改"test"的CInode中inode_t的dirstat和rstat:dirstat受filelock保护,rstat受nestlock保护。
3,对"a"的CDentry加xlock,是因为之后要去给CDentry中的linkage_t填充内容(CInode指针之类)
4,在之后也会去对CInode的versionlock加wrlock,是因为要去修改CInode中inode_t的version;对"/"的CInode的nestlock也加wrlock。
Locker::acquire_locks函数代码有好几百行,我把它分了3个步骤。
第一个步骤是整理xlocks、wrlock和rdlocks,因为这三个锁容器里面,可能有重复的lock,所以要把所有的lock放入一个整体的set中(sorted)。
先遍历xlocks,将"a"的CDentry中的lock放入sorted中,将"a"的CDentry放入mustpin中,并且将"a"的CDentry的versionlock放入wrlocks中;
接下来遍历wrlocks,将"a"的CDentry的versionlock和"test"的CInode的filelock和nestlock放入sorted中,并且将"test"的CInode放入mustpin中;
遍历rdlocks,将"a"CDentry的lock,"test"CInode的authlock、snaplock,和"/"的CInode的snaplock放入sorted中,并将"/"的CInode加入mustpin中。
代码如下
bool Locker::acquire_locks(MDRequestRef& mdr, set<SimpleLock*> &rdlocks, set<SimpleLock*> &wrlocks, set<SimpleLock*> &xlocks,
map<SimpleLock*,mds_rank_t> *remote_wrlocks, CInode *auth_pin_freeze, bool auth_pin_nonblock)
{ // remote_wrlocks = NULL, auth_pin_freeze = NULL, auth_pin_nonblock = false
client_t client = mdr->get_client();
set<SimpleLock*, SimpleLock::ptr_lt> sorted; // sort everything we will lock
set<MDSCacheObject*> mustpin; // items to authpin
// xlocks,遍历xlocks,此时xlocks只有一个,就是“a”的CDentry的lock
for (set<SimpleLock*>::iterator p = xlocks.begin(); p != xlocks.end(); ++p) {
sorted.insert(lock); // 将"a"的CDentry中的lock放入sorted中
mustpin.insert(lock->get_parent()); // 将CDentry放入mustpin中
// augment xlock with a versionlock?
if ((*p)->get_type() == CEPH_LOCK_DN) {
CDentry *dn = (CDentry*)lock->get_parent(); // dn就是"a"的CDentry
if (mdr->is_master()) {
// master. wrlock versionlock so we can pipeline dentry updates to journal.
wrlocks.insert(&dn->versionlock); // 将"a"的CDentry中的versionlock放入wrlocks中
} else { ...... }
} ......
}
// wrlocks,遍历wrlocks,此时wrlocks里面有三个: "a"的CDentry的versionlock,
// “test”的CInode的filelock和nestlock
for (set<SimpleLock*>::iterator p = wrlocks.begin(); p != wrlocks.end(); ++p) {
MDSCacheObject *object = (*p)->get_parent();
sorted.insert(*p); // 将三个lock加入sorted中
if (object->is_auth())
mustpin.insert(object); // 将"test"的CInode加入mustpin中
else if ......
}
// rdlocks,rdlocks里面有4个lock:"a"CDentry的lock,
// "test"CInode的authlock、snaplock,"/"的CInode的snaplock
for (set<SimpleLock*>::iterator p = rdlocks.begin();p != rdlocks.end();++p) {
MDSCacheObject *object = (*p)->get_parent();
sorted.insert(*p); // 将4个lock加入sorted中
if (object->is_auth())
mustpin.insert(object); // 将"/"的CInode加入mustpin中
else if ......
}
......
}
综上述得:所以sorted中有7个lock:"a"的CDentry的lock和versionlock,"test"的CInode的filelock、nestlock、authlock、snaplock, 还有“/”目录的snaplock。
第二个步骤是auth_pin住元数据,通过第一步,可以知道要auth_pin的MDSCacheObject:"a"的CDentry,"test"的CInode,"/"的CInode。先遍历这三个,去看看是否可以auth_pin,即判断两个部分:auth、pin。如果当前MDS持有的MDSCacheObject不是auth结点,则需要发给auth的MDS去auth_pin,如果当前的MDSCacheObject处于被冻结,或冻结中,则不能auth_pin,加入等待队列,等待可以auth_pin;然后直接返回false。如果可以auth_pin,下面才去auth_pin,将MDSCacheObject中的auth_pins++,代码如下
bool Locker::acquire_locks(MDRequestRef& mdr, set<SimpleLock*> &rdlocks, set<SimpleLock*> &wrlocks, set<SimpleLock*> &xlocks,
map<SimpleLock*,mds_rank_t> *remote_wrlocks, CInode *auth_pin_freeze, bool auth_pin_nonblock)
{
......
// AUTH PINS
map<mds_rank_t, set<MDSCacheObject*> > mustpin_remote; // mds -> (object set)
// can i auth pin them all now?,看是否可以authpin
// 遍历mustpin,mustpin中含有三个元素:"a"的CDentry,"test"的CInode,"/"的CInode
marker.message = "failed to authpin local pins";
for (set<MDSCacheObject*>::iterator p = mustpin.begin();p != mustpin.end(); ++p) {
MDSCacheObject *object = *p;
if (mdr->is_auth_pinned(object)) {...... }// 即看mdr的auth_pins中是否有该MDSCacheObject,如果有,就表示已经auth_pin了
if (!object->is_auth()) { ...... } // 如果不是auth节点,将该CDentry/CInode加入mustpin_remote队列,在下面去auth_pin时,发MMDSSlaveRequest消息给auth的mds去处理
// 并将该CDentry/CInode加入waiting_on_slave后,直接返回
int err = 0;
if (!object->can_auth_pin(&err)) { // CDentry是否可以auth_pin,即看父目录("test")的CDir是否可以can_auth_pin
// "test"的CDir是否是auth,且是否被冻结frozen或者正在被冻结frozing
// 如果不能auth_pin,则add_waiter,并返回,等待下次唤醒重试。
//CInode是否可以auth_pin,得看CInode是否是auth,或者inode是否被冻结,或者正在被冻结,或者auth_pin被冻结;
// 看CInode的CDentry是否可以can_auth_pin
if (err == MDSCacheObject::ERR_EXPORTING_TREE) {
marker.message = "failed to authpin, subtree is being exported";
} else if (err == MDSCacheObject::ERR_FRAGMENTING_DIR) {
marker.message = "failed to authpin, dir is being fragmented";
} else if (err == MDSCacheObject::ERR_EXPORTING_INODE) {
marker.message = "failed to authpin, inode is being exported";
}
object->add_waiter(MDSCacheObject::WAIT_UNFREEZE, new C_MDS_RetryRequest(mdcache, mdr));
......
return false;
}
}
// ok, grab local auth pins
for (set<MDSCacheObject*>::iterator p = mustpin.begin(); p != mustpin.end(); ++p) {
MDSCacheObject *object = *p;
if (mdr->is_auth_pinned(object)) { ...... }
else if (object->is_auth()) {
mdr->auth_pin(object); // 开始auth_pin,即将object中的auth_pins++
}
......
}
第三个步骤,正式开始加锁,经过一系列操作,要加锁的lock变化了,如下

wrlocks中多了"a"的CDentry的versionlock。
sorted中有7个lock:"a"的CDentry的versionlock和lock, “/”目录的snaplock,"test"的CInode的snaplock、filelock、authlock、nestlock。
bool Locker::acquire_locks(MDRequestRef& mdr, set<SimpleLock*> &rdlocks, set<SimpleLock*> &wrlocks, set<SimpleLock*> &xlocks,
map<SimpleLock*,mds_rank_t> *remote_wrlocks, CInode *auth_pin_freeze, bool auth_pin_nonblock)
{
......
// caps i'll need to issue
set<CInode*> issue_set;
bool result = false;
// acquire locks.
// make sure they match currently acquired locks.
set<SimpleLock*, SimpleLock::ptr_lt>::iterator existing = mdr->locks.begin();
for (set<SimpleLock*, SimpleLock::ptr_lt>::iterator p = sorted.begin(); p != sorted.end(); ++p) {
bool need_wrlock = !!wrlocks.count(*p); // 先是"a"的CDentry的versionlock
bool need_remote_wrlock = !!(remote_wrlocks && remote_wrlocks->count(*p));
// lock
if (xlocks.count(*p)) {
marker.message = "failed to xlock, waiting";
// xlock_start "a"的CDentry的lock,lock状态由LOCK_SYNC --> LOCK_SYNC_LOCK --> LOCK_LOCK (simple_lock) --> LOCK_LOCK_XLOCK --> LOCK_PEXLOCK(simple_xlock)
// --> LOCK_XLOCK (xlock_start)
if (!xlock_start(*p, mdr)) // 先进行xlock
goto out;
dout(10) << " got xlock on " << **p << " " << *(*p)->get_parent() << dendl;
} else if (need_wrlock || need_remote_wrlock) {
if (need_wrlock && !mdr->wrlocks.count(*p)) {
marker.message = "failed to wrlock, waiting";
// nowait if we have already gotten remote wrlock
if (!wrlock_start(*p, mdr, need_remote_wrlock)) // 进行wrlock
goto out;
dout(10) << " got wrlock on " << **p << " " << *(*p)->get_parent() << dendl;
}
} else {
marker.message = "failed to rdlock, waiting";
if (!rdlock_start(*p, mdr)) // 进行rdlock
goto out;
dout(10) << " got rdlock on " << **p << " " << *(*p)->get_parent() << dendl;
}
}
......
out:
issue_caps_set(issue_set);
return result;
}
开始遍历sorted。
- 对"a"的CDentry的versionlock加wrlock,看是否可以wrlock,即是否已经xlocked,这里可以直接加wrlock。并没有涉及到锁的切换(versionlock 是locallock类型)。
bool can_wrlock() const {
return !is_xlocked();
}

- 对"a"的CDentry的lock (属于simplelock)加xlock,即进行xlock_start,最初锁的状态为LOCK_SYNC,而这种状态是不可以直接加xlock的,具体判断这里先不细讲,后面研究lock时,再扩展。
bool can_xlock(client_t client) const {
return get_sm()->states[state].can_xlock == ANY ||
(get_sm()->states[state].can_xlock == AUTH && parent->is_auth()) ||
(get_sm()->states[state].can_xlock == XCL && client >= 0 && get_xlock_by_client() == client);
}
从locks.cc中定义的simplelock数组中可以查的get_sm()->states[state].can_xlock == 0不满足上 xlock 条件(不等于0),所以要经过锁切换。

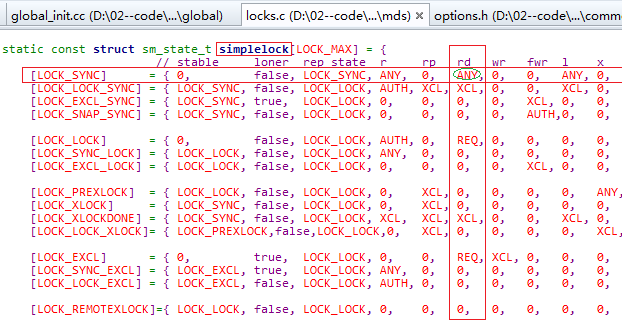
先经过Locker::simple_lock,将锁的状态切换为LOCK_LOCK(过程):LOCK_SYNC --> LOCK_SYNC_LOCK -->LOCK_LOCK。在LOCK_SYNC_LOCK -->LOCK_LOCK的切换过程中,需要判断是否满足条件:即该lock是否leased;是否被rdlocked;该CDentry是否在别的MDS上有副本,如果有,则需要发送LOCK_AC_LOCK消息给拥有副本的MDS,也去对它加锁。这里都满足,因为"a"目录是正在创建的。但是LOCK_LOCK也不能xlock,所以还需要继续切换,即通过Locker::simple_xlock,来切换锁:LOCK_LOCK --> LOCK_LOCK_XLOCK --> LOCK_PEXLOCK。切换成LOCK_PEXLOCK后就可以加xlock了。最后将锁状态切换为LOCK_XLOCK。
- 对"/"和"test"的CInode的snaplock (是simple_lock类型)加rdlock,它们锁的状态都是LOCK_SYNC,是可以直接加rdlock。这里没有涉及到锁的切换。
- 对"test"的CInode的filelock加wrlock,最初锁的状态为LOCK_SYNC,不满足加wrlock条件,需要通过Locker::simple_lock对锁进行切换。先将锁切换为中间状态LOCK_SYNC_LOCK,然后判断是否可以切换成LOCK_LOCK状态,在CInode::issued_caps_need_gather中,发现别的客户端拿了"test"目录inode的"Fs"权限(此时filelock的状态为LOCK_SYNC_LOCK,而这种状态的锁,只允许客户端持有"Fc",其他与"F"有关的权限都不允许),所以"test"的CInode的filelock不能切换成LOCK_LOCK状态。需要通过Locker::issue_caps去收回其他客户端持有的"Fs"权限。
void Locker::simple_lock(SimpleLock *lock, bool *need_issue)
{ //need_issue = NULL
CInode *in = 0;
if (lock->get_cap_shift()) // 由于lock的type是CEPH_LOCK_IFILE,所以cap_shift为8
in = static_cast<CInode *>(lock->get_parent());
int old_state = lock->get_state(); // old_state = LOCK_SYNC
switch (lock->get_state()) {
case LOCK_SYNC: lock->set_state(LOCK_SYNC_LOCK); break;
......}
int gather = 0;
if (lock->is_leased()) { ...... }
if (lock->is_rdlocked()) gather++;
if (in && in->is_head()) {
if (in->issued_caps_need_gather(lock)) { // in->issued_caps_need_gather(lock) = true
if (need_issue) *need_issue = true;
else issue_caps(in);
gather++;
}
}
......
if (gather) {
lock->get_parent()->auth_pin(lock);
......
} else { ...... }
}
issue_caps代码如下,即遍历"test"目录的CInode中client_caps中保存的各个客户端的Capability,此时通过get_caps_allowed_by_type算出客户端允许的caps为"pAsLsXsFc",而有客户端持有"pAsLsXsFs",所以发送CEPH_CAP_OP_REVOKE消息给客户端,让客户端释放"Fs"权限。
bool Locker::issue_caps(CInode *in, Capability *only_cap)
{
// allowed caps are determined by the lock mode.
int all_allowed = in->get_caps_allowed_by_type(CAP_ANY); // all_allowed = "pAsLsXsFc"
int loner_allowed = in->get_caps_allowed_by_type(CAP_LONER); // loner_allowed = "pAsLsXsFc"
int xlocker_allowed = in->get_caps_allowed_by_type(CAP_XLOCKER); // xlocker_allowed = "pAsLsXsFc"
// count conflicts with
int nissued = 0;
// client caps
map<client_t, Capability>::iterator it;
if (only_cap) ...... // only_cap = NULL
else it = in->client_caps.begin();
for (; it != in->client_caps.end(); ++it) {
Capability *cap = &it->second;
if (cap->is_stale()) continue; // cap如果过期,就不需要遍历
// do not issue _new_ bits when size|mtime is projected
int allowed;
if (loner == it->first) ......
else allowed = all_allowed; // allowed = all_allowed = "pAsLsXsFc"
// add in any xlocker-only caps (for locks this client is the xlocker for)
allowed |= xlocker_allowed & in->get_xlocker_mask(it->first); // allowed |= 0
int pending = cap->pending(); // pending = "pAsLsXsFs"
int wanted = cap->wanted(); // wanted = "AsLsXsFsx"
// are there caps that the client _wants_ and can have, but aren't pending?
// or do we need to revoke?
if (((wanted & allowed) & ~pending) || // missing wanted+allowed caps
(pending & ~allowed)) { // need to revoke ~allowed caps. // (pending & ~allowed) = "Fs"
// issue
nissued++;
// include caps that clients generally like, while we're at it.
int likes = in->get_caps_liked(); // likes = "pAsxLsxXsxFsx"
int before = pending; // before = "pAsLsXsFs"
long seq;
if (pending & ~allowed)
// (wanted|likes) & allowed & pending = "AsLsXsFsx" | "pAsxLsxXsxFsx" & "pASLsXsFc" & "pASLsXsFs" = "pASLsXs"
seq = cap->issue((wanted|likes) & allowed & pending); // if revoking, don't issue anything new.
else ......
int after = cap->pending(); // after = "pAsLsXs"
if (cap->is_new()) { ......
} else {
int op = (before & ~after) ? CEPH_CAP_OP_REVOKE : CEPH_CAP_OP_GRANT; // op = CEPH_CAP_OP_REVOKE
if (op == CEPH_CAP_OP_REVOKE) {
revoking_caps.push_back(&cap->item_revoking_caps);
revoking_caps_by_client[cap->get_client()].push_back(&cap->item_client_revoking_caps);
cap->set_last_revoke_stamp(ceph_clock_now());
cap->reset_num_revoke_warnings();
}
auto m = MClientCaps::create(op, in->ino(), in->find_snaprealm()->inode->ino(),cap->get_cap_id(),
cap->get_last_seq(), after, wanted, 0, cap->get_mseq(), mds->get_osd_epoch_barrier());
in->encode_cap_message(m, cap);
mds->send_message_client_counted(m, it->first);
}
}
}
return (nissued == 0); // true if no re-issued, no callbacks
}
发送完revoke cap消息后,在Locker::wrlock_start中,跳出循环,生成 C_MDS_RetryRequest,加入等待队列,等待lock状态变成稳态后,再把请求拿出来执行。
bool Locker::wrlock_start(SimpleLock *lock, MDRequestRef& mut, bool nowait)
{ // nowait = false
......
while (1) {
// wrlock?
// ScatterLock中sm是sm_filelock,states是filelock,而此时CInode的filelock->state是LOCK_SYNC_LOCK, filelock[LOCK_SYNC_LOCK].can_wrlock == 0, 所以不可wrlock
if (lock->can_wrlock(client) && (!want_scatter || lock->get_state() == LOCK_MIX)) { ...... }
......
if (!lock->is_stable()) break; // 由于此时filelock->state是LOCK_SYNC_LOCK,不是stable的,所以跳出循环
......
}
if (!nowait) {
dout(7) << "wrlock_start waiting on " << *lock << " on " << *lock->get_parent() << dendl;
lock->add_waiter(SimpleLock::WAIT_STABLE, new C_MDS_RetryRequest(mdcache, mut)); // C_MDS_RetryRequest(mdcache, mut))加入等待队列,等待“test”的CInode的filelock变为稳态
nudge_log(lock);
}
return false;
}
接下来客户端会回复caps消息op为CEPH_CAP_OP_UPDATE。MDS通过Locker::handle_client_caps处理caps消息
Locker::handle_client_caps
代码如下
void Locker::handle_client_caps(const MClientCaps::const_ref &m)
{
client_t client = m->get_source().num();
snapid_t follows = m->get_snap_follows(); // follows = 0
auto op = m->get_op(); // op = CEPH_CAP_OP_UPDATE
auto dirty = m->get_dirty(); // dirty = 0
Session *session = mds->get_session(m);
......
CInode *head_in = mdcache->get_inode(m->get_ino()); // head_in是"test"的CInode
Capability *cap = 0;
cap = head_in->get_client_cap(client); // 获取该client的cap
bool need_unpin = false;
// flushsnap?
if (cap->get_cap_id() != m->get_cap_id()) { ...... }
else {
CInode *in = head_in;
// head inode, and cap
MClientCaps::ref ack;
int caps = m->get_caps(); // caps = "pAsLsXs"
cap->confirm_receipt(m->get_seq(), caps); // cap->_issued = "pAsLsXs",cap->_pending = "pAsLsXs"
// filter wanted based on what we could ever give out (given auth/replica status)
bool need_flush = m->flags & MClientCaps::FLAG_SYNC;
int new_wanted = m->get_wanted() & head_in->get_caps_allowed_ever(); // m->get_wanted() = 0
if (new_wanted != cap->wanted()) { // cap->wanted() = "AsLsXsFsx"
......
adjust_cap_wanted(cap, new_wanted, m->get_issue_seq()); // 将wanted设置为0
}
if (updated) { ...... }
else {
bool did_issue = eval(in, CEPH_CAP_LOCKS); //
......
}
if (need_flush)
mds->mdlog->flush();
}
out:
if (need_unpin)
head_in->auth_unpin(this);
}
在handle_client_caps中将客户端的cap中的_issued和_pending改变为"pAsLsXs"后,开始eval流程,分别eval_any "test"的CInode的filelock,authlock,linklock和xattrlock。
bool Locker::eval(CInode *in, int mask, bool caps_imported)
{ //in是"test"目录的CInode指针,mask = 2496, caps_imported = false
bool need_issue = caps_imported; // need_issue = false
MDSInternalContextBase::vec finishers;
retry:
if (mask & CEPH_LOCK_IFILE) // 此时filelock的state为LOCK_SYNC_LOCK,不是稳态
eval_any(&in->filelock, &need_issue, &finishers, caps_imported);
if (mask & CEPH_LOCK_IAUTH) // 此时authlock的状态为LOCK_SYNC
eval_any(&in->authlock, &need_issue, &finishers, caps_imported);
if (mask & CEPH_LOCK_ILINK) // 此时linklock的状态为LOCK_SYNC
eval_any(&in->linklock, &need_issue, &finishers, caps_imported);
if (mask & CEPH_LOCK_IXATTR) // 此时xattrlock的状态为LOCK_SYNC
eval_any(&in->xattrlock, &need_issue, &finishers, caps_imported);
if (mask & CEPH_LOCK_INEST)
eval_any(&in->nestlock, &need_issue, &finishers, caps_imported);
if (mask & CEPH_LOCK_IFLOCK)
eval_any(&in->flocklock, &need_issue, &finishers, caps_imported);
if (mask & CEPH_LOCK_IPOLICY)
eval_any(&in->policylock, &need_issue, &finishers, caps_imported);
// drop loner?
......
finish_contexts(g_ceph_context, finishers);
if (need_issue && in->is_head())
issue_caps(in);
dout(10) << "eval done" << dendl;
return need_issue;
}
由于filelock的state为LOCK_SYNC_LOCK,不是稳态,所以去eval_gather, state状态的转换过程是LOCK_SYNC_LOCK --> LOCK_LOCK --> LOCK_LOCK_SYNC --> LOCK_SYNC,在mkdir的acquire_lock过程中,将LOCK_SYNC转换成LOCK_LOCK_SYNC,这里再将状态转换回来,转换成LOCK_SYNC。代码如下
void Locker::eval_gather(SimpleLock *lock, bool first, bool *pneed_issue, MDSInternalContextBase::vec *pfinishers)
{ // first = false
int next = lock->get_next_state(); // next = LOCK_LOCK
CInode *in = 0;
bool caps = lock->get_cap_shift(); // caps = 8
if (lock->get_type() != CEPH_LOCK_DN)
in = static_cast<CInode *>(lock->get_parent()); // 得到"test"的CInode
bool need_issue = false;
int loner_issued = 0, other_issued = 0, xlocker_issued = 0;
if (caps && in->is_head()) {
in->get_caps_issued(&loner_issued, &other_issued, &xlocker_issued, lock->get_cap_shift(), lock->get_cap_mask());
// 得到loner_issued = 0,other_issued = 0,xlocker_issued = 0
......
}
#define IS_TRUE_AND_LT_AUTH(x, auth) (x && ((auth && x <= AUTH) || (!auth && x < AUTH)))
bool auth = lock->get_parent()->is_auth();
if (!lock->is_gathering() && // gather_set为空,即其他mds并不需要获取锁,所以lock不处于gathering中,
(IS_TRUE_AND_LT_AUTH(lock->get_sm()->states[next].can_rdlock, auth) || !lock->is_rdlocked()) &&
(IS_TRUE_AND_LT_AUTH(lock->get_sm()->states[next].can_wrlock, auth) || !lock->is_wrlocked()) &&
(IS_TRUE_AND_LT_AUTH(lock->get_sm()->states[next].can_xlock, auth) || !lock->is_xlocked()) &&
(IS_TRUE_AND_LT_AUTH(lock->get_sm()->states[next].can_lease, auth) || !lock->is_leased()) &&
!(lock->get_parent()->is_auth() && lock->is_flushing()) && // i.e. wait for scatter_writebehind!
(!caps || ((~lock->gcaps_allowed(CAP_ANY, next) & other_issued) == 0 &&
(~lock->gcaps_allowed(CAP_LONER, next) & loner_issued) == 0 &&
(~lock->gcaps_allowed(CAP_XLOCKER, next) & xlocker_issued) == 0)) &&
lock->get_state() != LOCK_SYNC_MIX2 && // these states need an explicit trigger from the auth mds
lock->get_state() != LOCK_MIX_SYNC2
) {
if (!lock->get_parent()->is_auth()) { // 如果是副本,则发送消息给auth的mds, 让auth的mds去加锁
......
} else {
......
}
lock->set_state(next); // 将锁转换为LOCK_LOCK
if (lock->get_parent()->is_auth() && lock->is_stable())
lock->get_parent()->auth_unpin(lock);
// drop loner before doing waiters
if (pfinishers)
// 将之前的mkdir的C_MDS_RetryRequest取出,放入pfinishers中
lock->take_waiting(SimpleLock::WAIT_STABLE|SimpleLock::WAIT_WR|SimpleLock::WAIT_RD|SimpleLock::WAIT_XLOCK, *pfinishers);
...
if (caps && in->is_head()) need_issue = true;
if (lock->get_parent()->is_auth() && lock->is_stable()) try_eval(lock, &need_issue);
}
if (need_issue) {
if (pneed_issue)
*pneed_issue = true;
else if (in->is_head())
issue_caps(in);
}
}
在eval_gather中只是将LOCK_SYNC_LOCK转换成LOCK_LOCK,在Locker::simple_sync中将lock转换为LOCK_SYNC, 代码如下
bool Locker::simple_sync(SimpleLock *lock, bool *need_issue)
{
CInode *in = 0;
if (lock->get_cap_shift())
in = static_cast<CInode *>(lock->get_parent());
int old_state = lock->get_state(); // old_state = LOCK_LOCK
if (old_state != LOCK_TSYN) {
switch (lock->get_state()) {
case LOCK_LOCK: lock->set_state(LOCK_LOCK_SYNC); break; // 将state转换成LOCK_LOCK_SYNC
......
}
int gather = 0;
}
......
lock->set_state(LOCK_SYNC); // 将state转换成LOCK_SYNC
lock->finish_waiters(SimpleLock::WAIT_RD|SimpleLock::WAIT_STABLE); // 此时waiting之前被取出来了,所以waiting为空
if (in && in->is_head()) {
if (need_issue) *need_issue = true;
......
}
return true;
}
流程为

由于其他4个锁的状态都是LOCK_SYNC,不需要去转换状态,所以在eval_gather中并没有做实际的事情。接下来在finish_contexts中执行finishers中的回调函数,finishers存了之前的C_MDS_RetryRequest。即重新执行handle_client_mkdir
void C_MDS_RetryRequest::finish(int r)
{
mdr->retry++;
cache->dispatch_request(mdr);
}
流程为:

即重来一遍handle_client_mkdir,虽说是重来一遍,但由于之前request中保存了一些数据,所有有些过程不用重走。Server::rdlock_path_xlock_dentry与之前一样,就不重复分析,再来一遍Locker::acquire_locks
Locker::acquire_locks
之前讲了Locker::acquire_locks分为3个步骤:整理 (收集)xlocks、wrlock和rdlocks;auth_pin住元数据;开始 加 (上)锁。
前两个步骤之前已经研究了,所以直接从第三个步骤开始。上一次是在对"test"的filelock加wrlock时,没加成功,所以这里直接从对"test"的filelock加wrlock开始。将锁切换为中间状态LOCK_SYNC_LOCK后,CInode::issued_caps_need_gather中并没有发现别的客户端拿了"test"目录inode的与"F"有关的权限,所以直接将lock的状态设为LOCK_LOCK。代码如下
void Locker::simple_lock(SimpleLock *lock, bool *need_issue)
{
CInode *in = 0;
if (lock->get_cap_shift()) // 由于lock的type是CEPH_LOCK_IFILE,所以cap_shift为8
in = static_cast<CInode *>(lock->get_parent());
int old_state = lock->get_state(); // old_state = LOCK_SYNC
switch (lock->get_state()) {
case LOCK_SYNC: lock->set_state(LOCK_SYNC_LOCK); break;
......}
int gather = 0;
if (lock->is_leased()) { ...... }
if (lock->is_rdlocked()) ......;
if (in && in->is_head()) {
if (in->issued_caps_need_gather(lock)) { ... }
}
...
if (gather) { ...
} else {
lock->set_state(LOCK_LOCK);
lock->finish_waiters(ScatterLock::WAIT_XLOCK|ScatterLock::WAIT_WR|ScatterLock::WAIT_STABLE);
}
}
"test"的CInode的filelock状态为LOCK_LOCK时,就可以被加上wrlock了。加锁结束。
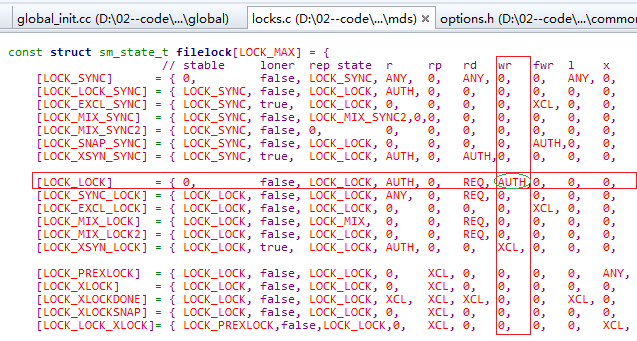
接下来是对"test"的CInode的authlock (属于SimpleLock )加rdlock。它的锁的状态是LOCK_SYNC,是可以直接加rdlock。这里没有涉及到锁的切换。
对"test"的CInode的nestlock(属于ScatterLock )加wrlock。而此时nestlock的状态已经是LOCK_LOCK,这个状态估计是之前的请求中加上的。可以直接加上wrlock。自此,acquire_lock过程完结。

总结:在acquire_lock中对7个lock("a"的CDentry的versionlock和lock, “/”目录的snaplock,"test"的CInode的snaplock、filelock、authlock、nestlock)加锁。锁的状态变化如下图

接下来就是生成"a"目录的CInode,处理函数Server::prepare_new_inode,
见下一篇。
接上一篇
Server::prepare_new_inode
生成CInode过程比较简单,分配一个inode号,以及填充其他的内容到CInode。代码如下
CInode* Server::prepare_new_inode(MDRequestRef& mdr, CDir *dir, inodeno_t useino, unsigned mode, file_layout_t *layout)
{ // dir是"test"的CDir,useino = 0,layout = NULL
CInode *in = new CInode(mdcache);
bool allow_prealloc_inos = !mdr->session->is_opening(); // allow_prealloc_inos = true
if (allow_prealloc_inos && mdr->session->info.prealloc_inos.size()) {
mdr->used_prealloc_ino = in->inode.ino = mdr->session->take_ino(useino); // prealloc -> used,拿出一个inode号
mds->sessionmap.mark_projected(mdr->session);
} else { ...}
...
in->inode.version = 1;
in->inode.xattr_version = 1;
in->inode.nlink = 1; // FIXME
in->inode.mode = mode;
memset(&in->inode.dir_layout, 0, sizeof(in->inode.dir_layout));
if (in->inode.is_dir()) {
// in->inode.dir_layout.dl_dir_hash = 0x2
in->inode.dir_layout.dl_dir_hash = g_conf()->mds_default_dir_hash;
}
in->inode.truncate_size = -1ull; // not truncated, yet!,超大的数字
in->inode.truncate_seq = 1; /* starting with 1, 0 is kept for no-truncation logic */
CInode *diri = dir->get_inode(); // diri是"test"的CInode
// diri->inode.mode = 040777,即“test”的mode, mode = 040755
if (diri->inode.mode & S_ISGID) { ...... }
else in->inode.gid = mdr->client_request->get_caller_gid();
in->inode.uid = mdr->client_request->get_caller_uid();
in->inode.btime = in->inode.ctime = in->inode.mtime = in->inode.atime = mdr->get_op_stamp();
in->inode.change_attr = 0;
const MClientRequest::const_ref &req = mdr->client_request;
if (!mds->mdsmap->get_inline_data_enabled() ||
!mdr->session->get_connection()->has_feature(CEPH_FEATURE_MDS_INLINE_DATA))
in->inode.inline_data.version = CEPH_INLINE_NONE;
mdcache->add_inode(in); // add, 将inode加入mdcache的inode_map中
return in;
}
CDentry和CInode都已经创建,接着就是创建CDir

=======================
CInode::get_or_open_dirfrag
代码如下,关于frag_t,这个作为dirfrags中的key,与目录分片有关,具体后面再研究。
CDir *CInode::get_or_open_dirfrag(MDCache *mdcache, frag_t fg)
{ // fg._enc = 0
// 由于CInode是刚刚新生成的,所以dirfrags为空,所以找不到fg对应的CDir
CDir *dir = get_dirfrag(fg); // dir = NULL
if (!dir) {
// create it. 生成新的CDir
dir = new CDir(this, fg, mdcache, is_auth());
add_dirfrag(dir); // 加入到CInode的dirfrags中
}
return dir;
}
创建目录后,需要去更改父目录中的元数据,即MDCache::predirty_journal_parents
MDCache::predirty_journal_parents
MDCache::predirty_journal_parents也是一个大函数,我把它分为两个步骤
1,更新目录"test","/"的CDir的fnode_t中的fragstat、rstat和CInode的inode_t中的dirstat、rstat(但是"/"的CInode的inode_t的rstat并不在这里更新)
2,记录"mkdir"事件中metablob,即lump_map中记录了"/"到“a”的dirlump,roots中记录了"/"的fullbit将这两个分别研究,第一步其实就是一个while循环遍历,遍历"test"、"/"的CDir。这里就先研究遍历"test"的CDir,代码如下
void MDCache::predirty_journal_parents(MutationRef mut, EMetaBlob *blob,CInode *in, CDir *parent,
int flags, int linkunlink,snapid_t cfollows)
{
bool primary_dn = flags & PREDIRTY_PRIMARY; // primary_dn = true
bool do_parent_mtime = flags & PREDIRTY_DIR; // do_parent_mtime = true
bool shallow = flags & PREDIRTY_SHALLOW; // shallow = false
// make sure stamp is set
if (mut->get_mds_stamp() == utime_t())
mut->set_mds_stamp(ceph_clock_now());
// build list of inodes to wrlock, dirty, and update
list<CInode*> lsi;
CInode *cur = in; // cur就是"a"目录的CInode指针
CDentry *parentdn = NULL;
bool first = true;
while (parent) { // parent 是"test"的CDir指针
// opportunistically adjust parent dirfrag
CInode *pin = parent->get_inode(); // pin就是"test"的CInode指针
// inode -> dirfrag
mut->auth_pin(parent); // auth pin "test"的CDir
mut->add_projected_fnode(parent); // 将"test"的CDir放入mdr的projected_fnode的list中
fnode_t *pf = parent->project_fnode(); // 获取"test"的CDir中的projected_fnode中的最后一个fnode_t
pf->version = parent->pre_dirty();
if (do_parent_mtime || linkunlink) {
// update stale fragstat/rstat?
parent->resync_accounted_fragstat();
parent->resync_accounted_rstat();
if (do_parent_mtime) {
pf->fragstat.mtime = mut->get_op_stamp(); // 修改“test”目录的pf->fragstat.mtime
pf->fragstat.change_attr++; // change_attr = 1
if (pf->fragstat.mtime > pf->rstat.rctime) {
pf->rstat.rctime = pf->fragstat.mtime;
}
}
if (linkunlink) {
if (in->is_dir()) {
pf->fragstat.nsubdirs += linkunlink; // pf->fragstat.nsubdirs += 1 = 1
} else { ... }
}
}
if (!primary_dn) {
// don't update parent this pass
} else if (!linkunlink && !(pin->nestlock.can_wrlock(-1) &&
pin->versionlock.can_wrlock())) { ...
} else {
if (linkunlink) {
assert(pin->nestlock.get_num_wrlocks() || mut->is_slave());
}
if (mut->wrlocks.count(&pin->nestlock) == 0) {
dout(10) << " taking wrlock on " << pin->nestlock << " on " << *pin << dendl;
mds->locker->wrlock_force(&pin->nestlock, mut);
}
...
parent->resync_accounted_rstat();
// 更新父目录"test"中的rstat,即rstat中rsubdirs + 1
project_rstat_inode_to_frag(cur, parent, first, linkunlink, prealm);
cur->clear_dirty_rstat();
}
bool stop = false;
...
// can cast only because i'm passing nowait=true in the sole user
MDRequestRef mdmut = static_cast<MDRequestImpl*>(mut.get());
...
if (!mut->wrlocks.count(&pin->versionlock))
// 对“test”的CInode的versionlock加锁
mds->locker->local_wrlock_grab(&pin->versionlock, mut);
pin->last_dirstat_prop = mut->get_mds_stamp();
// dirfrag -> diri
mut->auth_pin(pin);
mut->add_projected_inode(pin); // 将"test"的CInode加入projected_inodes中
lsi.push_front(pin);
pin->pre_cow_old_inode(); // avoid cow mayhem!
// pi是“test”的Inode_t, 这里会新建一个projected_inode_t,并插入CInode的projected_nodes中
inode_t *pi = pin->project_inode();
pi->version = pin->pre_dirty();
// dirstat
if (do_parent_mtime || linkunlink) {
bool touched_mtime = false, touched_chattr = false;
// 更新"test"的CInode的inode_t的dirstat中的nsubdirs,即nsubdirs = 1
pi->dirstat.add_delta(pf->fragstat, pf->accounted_fragstat, &touched_mtime, &touched_chattr);
pf->accounted_fragstat = pf->fragstat;
if (touched_mtime)
pi->mtime = pi->ctime = pi->dirstat.mtime;
if (touched_chattr)
pi->change_attr = pi->dirstat.change_attr;
...
}
// stop?
if (pin->is_base()) break;
parentdn = pin->get_projected_parent_dn(); // 得到"test"中的projected_parent中的CDentry
// rstat
parent->resync_accounted_rstat();
parent->dirty_old_rstat.clear();
//将"test"的CDir中的fnode_t的rstat新增的值,加入到"test"的CInode的inode_t中的rstat
project_rstat_frag_to_inode(pf->rstat, pf->accounted_rstat, parent->first, CEPH_NOSNAP, pin, true);//false);
pf->accounted_rstat = pf->rstat;
parent->check_rstats();
broadcast_quota_to_client(pin);
// next parent!
cur = pin; // cur变成了"test"
parent = parentdn->get_dir();// parent = "/"的CDir
linkunlink = 0;
do_parent_mtime = false;
primary_dn = true;
first = false;
}
...
}
遍历"/"的CDir,其实和遍历"test"的CDir差不多,只不过在while循环中,跳出循环了,所以没有更新到"/"的CInode的inode_t的rstat。
if (pin->is_base()) break
第二步是更新"mkdir"的EUpdate事件中的元数据
在handle_client_mkdir中,记录了"mkdir"的日志。
EUpdate *le = new EUpdate(mdlog, "mkdir");
日志中不仅要记录操作,也要记录修改的元数据,这些保存在le->metablob中,在MDCache::predirty_journal_parents中的代码如下
void MDCache::predirty_journal_parents(MutationRef mut, EMetaBlob *blob,CInode *in, CDir *parent,
int flags, int linkunlink,snapid_t cfollows)
{
...
blob->add_dir_context(parent);
blob->add_dir(parent, true);
for (list<CInode*>::iterator p = lsi.begin();
p != lsi.end();
++p) {
CInode *cur = *p;
journal_dirty_inode(mut.get(), blob, cur);
}
}
这里面的操作比较琐碎,直接跳出来看,看le->metablob中最后填充了什么元数据
class EMetaBlob {
public:
......
// lump_order中有"/"、"test"、"a"的CDir的dirfrag_t
list<dirfrag_t> lump_order;
// lump_map中存有{<"/"的CDir的dirfrag_t, "/"的dirlump>
// 其中dirlump中fnode("/"的CDir的fnode_t), dfull:fullbit("test")
// <"test"的CDir的dirfrag_t, "test"的dirlump>
// 其中dirlump中fnode("test"的CDir的fnode_t), dfull:fullbit("a")
// <"a"的CDir的dirfrag_t, "a"的dirlump>
// 其中dirlump中fnode("a"的CDir的fnode_t), dfull为空
map<dirfrag_t, dirlump> lump_map;
// roots中只有"/"的fullbit,fullbit中主要有inode_t
list<ceph::shared_ptr<fullbit> > roots;
public:
list<pair<__u8,version_t> > table_tids; // tableclient transactions
inodeno_t opened_ino; // "a"目录的inode号
...
}
可以看到lump_order存的是"/"、"test"、"a"的CDir的dirfrag_t,roots存的就是根目录的fullbit,这里面最重要的就是lump_map,lump_map存的是dirfrag_t和dirlump的键值对,dirlump如下,fnode来自于CDir,主要存的是目录下的文件和目录数,以及时间,大小。而dfull中存的是fullbit的指针集合,fullbit中最重要的就是inode_t
struct dirlump {
public
//version_t dirv;
fnode_t fnode;
__u32 state;
__u32 nfull, nremote, nnull;
private:
...
mutable list<ceph::shared_ptr<fullbit> > dfull;
...
}
之后就是Locker::issue_new_caps
Locker::issue_new_caps
这个很简单,就新建Capability保存在"a"目录CInode的client_caps中,并且给"a"目录CInode的lock设置锁状态。经过一番操作,"a"的CInode的各种锁状态如下

基本上请求处理完了,这个时候就得回复客户端。
Server::journal_and_reply
有两次回复,以下刷日志为分界。第一次回复处理函数是Server::early_reply。
void Server::early_reply(MDRequestRef& mdr, CInode *tracei, CDentry *tracedn)
{
...
MClientRequest *req = mdr->client_request;
entity_inst_t client_inst = req->get_source_inst();
MClientReply *reply = new MClientReply(req, 0); // 新建reply
reply->set_unsafe(); // reply中的head.safe = 0
mds->locker->set_xlocks_done(mdr.get(), req->get_op() == CEPH_MDS_OP_RENAME); //"a"的CDentry的lock的state = LOCK_XLOCKDONE
if (tracei || tracedn) {
if (tracei) mdr->cap_releases.erase(tracei->vino());
if (tracedn) mdr->cap_releases.erase(tracedn->get_dir()->get_inode()->vino());
// 填充reply,并给新建的"a"的cap中_issued和_pending赋值
set_trace_dist(mdr->session, reply, tracei, tracedn, mdr->snapid, req->get_dentry_wanted(), mdr);
}
reply->set_extra_bl(mdr->reply_extra_bl);
req->get_connection()->send_message(reply); // 发送消息
mdr->did_early_reply = true;
......
mdr->mark_event("early_replied");
}
early_reply中填充了reply的信息,包括"test","a"的inode信息,并给"a"的Capability赋上权限,根据filelock、authlock、linklock、xattrlock的状态算出来的权限信息是"pAsxLsXsxFsx"。
第一次回复完后,就得提交日志,以便日志落盘,在journal_and_reply函数入参中注册了回调new C_MDS_mknod_finish(this, mdr, dn, newi),当日志落盘成功后,会去执行回调C_MDS_mknod_finish::finish函数。submit_entry函数如下
void submit_entry(LogEvent *e, MDSLogContextBase *c = 0) {
Mutex::Locker l(submit_mutex);
_submit_entry(e, c);
submit_cond.Signal();
}
MDLog::_submit_entry函数如下
void MDLog::_submit_entry(LogEvent *le, MDSLogContextBase *c)
{
cur_event = NULL; // 将当前事件置空
LogSegment *ls = segments.rbegin()->second; // 获取LogSegment
ls->num_events++; // 事件数++
le->_segment = ls;
le->update_segment();
le->set_stamp(ceph_clock_now());
mdsmap_up_features = mds->mdsmap->get_up_features();
// 新建PendingEvent并加入pending_events中
pending_events[ls->seq].push_back(PendingEvent(le, c));
num_events++;
unflushed++; //
uint64_t period = journaler->get_layout_period(); // period = 4M
// start a new segment?
if (le->get_type() == EVENT_SUBTREEMAP ||
(le->get_type() == EVENT_IMPORTFINISH && mds->is_resolve())) {
} else if (ls->end/period != ls->offset/period || // 如果LogSegment中end和offset不在一个对象中
ls->num_events >= g_conf->mds_log_events_per_segment) { // 或者LogSegment中事件数>=1024个,就开始新的LogSegment
_start_new_segment();
} else if (g_conf->mds_debug_subtrees && le->get_type() != EVENT_SUBTREEMAP_TEST) { ...... }
}
接下来就是唤醒MDLog中的md_submit线程,去处理pending_events队列中的PendingEvent。关于MDLog如何下刷日志,这个暂不扩展,之后研究。
journal_and_reply最后一个操作就是drop_rdlocks,之前对"test"目录CInode的authlock和snaplock、"\"的CInode的snaplock加了rdlock,这里就是将读锁丢掉。为什么要去drop_rdlock,这是因为如果有别的请求要对该对象去加wrlock/xlock时,都会经过simple_lock,在simple_lock中要将锁切换成LOCK_LOCK,在这过程中,如果该对象已经被rdlock了,则不能加LOCK_LOCK,加锁失败,请求就无法往下执行;而之后丢掉rdlock,在symple_sync中将锁切换成稳态LOCK_SYNC后,再执行之前未加锁成功的请求。
C_MDS_mknod_finish
接下来研究回调C_MDS_mknod_finish的finish函数
代码如下,
void finish(int r) override {
// link the inode
// 1,取出并删除"a"的CDentry中projected的linkage_t元素,并给CDentry的linkage赋值(主要是赋上CInode的指针)
// 2,取出并删除"a"的CInode的projected_parent中的第一个元素,并给CInode的parent赋上CDentry
dn->pop_projected_linkage();
// be a bit hacky with the inode version, here.. we decrement it
// just to keep mark_dirty() happen. (we didn't bother projecting
// a new version of hte inode since it's just been created)
newi->inode.version--;
newi->mark_dirty(newi->inode.version + 1, mdr->ls);
newi->_mark_dirty_parent(mdr->ls, true);
// mkdir?
if (newi->inode.is_dir()) {
CDir *dir = newi->get_dirfrag(frag_t());
assert(dir);
dir->fnode.version--;
dir->mark_dirty(dir->fnode.version + 1, mdr->ls);
dir->mark_new(mdr->ls);
}
// 取出并删除CInode的projected_inodes中的第一个,并更新"test"、“/”的CInode的inode
// 取出并删除CDir的projected_fnodes中的第一个,并更新"test"、“/”的CDir的fnode
mdr->apply();
MDRequestRef null_ref;
// 如果"a"的CDentry有副本,则将"a"的inode,父目录的dirfrag和子树根的dirfrag发送 副本
get_mds()->mdcache->send_dentry_link(dn, null_ref);
...
// hit pop
get_mds()->balancer->hit_inode(mdr->get_mds_stamp(), newi, META_POP_IWR);
// reply
server->respond_to_request(mdr, 0);
}
get_mds()->balancer->hit_inode会去更新该目录的写热度,这个之后再研究。mkdir的最后一步就是respond_to_request --> Server::reply_client_request
Server::reply_client_request,代码如下
void Server::reply_client_request(MDRequestRef& mdr, MClientReply *reply)
{
...
snapid_t snapid = mdr->snapid;
CInode *tracei = mdr->tracei; // mdr->tracei就是"a"的CInode
CDentry *tracedn = mdr->tracedn; // mdr->tracedn就是"za"的CDentry
bool is_replay = mdr->client_request->is_replay(); // is_replay = false
bool did_early_reply = mdr->did_early_reply; // did_early_reply = true
entity_inst_t client_inst = req->get_source_inst();
int dentry_wanted = req->get_dentry_wanted(); //
if (!did_early_reply && !is_replay) { ... }
// drop non-rdlocks before replying, so that we can issue leases
mdcache->request_drop_non_rdlocks(mdr);
// reply at all?
if (client_inst.name.is_mds() || !session) { ...
} else { // send reply.
if (!did_early_reply && // don't issue leases if we sent an earlier reply already
(tracei || tracedn)) { ... } // 如果没有进行early_reply,则去将内容填充给回复
// We can set the extra bl unconditionally: if it's already been sent in the
// early_reply, set_extra_bl will have claimed it and reply_extra_bl is empty
reply->set_extra_bl(mdr->reply_extra_bl);
reply->set_mdsmap_epoch(mds->mdsmap->get_epoch());
req->get_connection()->send_message(reply); // 发送回复
}
// clean up request
mdcache->request_finish(mdr);
// take a closer look at tracei, if it happens to be a remote link
if (tracei && tracedn && tracedn->get_projected_linkage()->is_remote()) {
mdcache->eval_remote(tracedn);
}
}
在Server::reply_client_request中会调用request_drop_non_rdlocks,去drop wrlock,这些wrlock是在之前acquire_lock里加的wrlock。加上了wrlock,该元数据之后的其他会加rdlock的操作等,会被阻塞,这里丢掉wrlock,会触发之前阻塞的操作继续执行。
之后给客户端第二次回复,表明日志已经下刷。最后会调用request_finish去做收尾工作,这里面会去auth_unpin之前pin住的元数据。
边栏推荐
- TS常用数据类型总结
- Is it safe to open a stock account through the account opening link given by the broker manager? I want to open an account
- Principle of TCP reset attack
- Unity uses skybox panoramic shader to make panorama preview. There is a gap. Solution
- [cloud native] codeless IVX editor programmable by "everyone"
- R语言dplyr包bind_rows函数把两个dataframe数据的行纵向(竖直)合并起来、最终行数为原来两个dataframe行数的加和(Combine Data Frames)
- R language uses the aggregate function of epidisplay package to split numerical variables into different subsets based on factor variables, calculate the summary statistics of each subset, and use agg
- About selenium common. exceptions. Webdriverexception: message: an unknown server side error solution (resolved)
- The DOTPLOT function in the epidisplay package of R language visualizes the frequency of data points in different intervals in the form of point graphs, specifies the grouping parameters with the by p
- 1. accounting basis -- several major elements of accounting (general accounting theory, accounting subjects and accounts)
猜你喜欢

Function: crypto JS encryption and decryption

qt下多个子控件信号槽绑定方法

【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB单据受理-创建业务介绍

程序分析与优化 - 8 寄存器分配

刷题笔记(十九)--二叉树:二叉搜索树的修改与构造

【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB运维单据介绍

1.会计基础--会计的几大要素(会计总论、会计科目和账户)

Document 1

10 minutes to understand bim+gis fusion, common BIM data formats and characteristics

RestCloud ETL解决shell脚本参数化
随机推荐
Pod scheduling of kubernetes
R language dplyr package bind_ The rows function merges the rows of the two dataframes vertically. The final number of rows is the sum of the rows of the original two dataframes (combine data frames)
Redis cluster re fragmentation and ask command
One click analysis hardware /io/ national network performance script (strong push)
一键安装gcc脚本
RestCloud ETL与Kettle对比分析
Execution of commands in the cluster
Numpy basic use
Informatics Olympiad 1405: sum and product of prime numbers (thinking problem)
10 minutes to understand bim+gis fusion, common BIM data formats and characteristics
R language uses GLM function to build Poisson logarithm linear regression model, processes three-dimensional contingency table data to build saturation model, uses step function to realize stepwise re
R语言caTools包进行数据划分、scale函数进行数据缩放、class包的knn函数构建K近邻分类器
Bank of Beijing x Huawei: network intelligent operation and maintenance tamps the base of digital transformation service
Optimizing for vectorization
Optimizing for vectorization
Use of subqueries
Excel-VBA 快速上手(二、条件判断和循环)
Talk about the recent situation of several students from Tsinghua University
The tablestack function of the epidisplay package of R language makes a statistical summary table (descriptive statistics of groups, hypothesis test, etc.), does not set the by parameter to calculate
Authoritative announcement on the recruitment of teachers in Yan'an University in 2022