当前位置:网站首页>Introduction of UART, RS232, RS485, I2C and SPI
Introduction of UART, RS232, RS485, I2C and SPI
2022-07-03 00:22:00 【HDD615】
Basic knowledge
- serial communication : Multiple data passes through a data line , In turn
- Parallel communication : Multiple data passes through multiple data lines , One time transmission
- Simplex communication : Only receive data or send data ( The remote control 、 The radio )
- Half duplex communication : At the same time , Only receive data or send data ( Walkie-talkie )
- Full duplex communication : At the same time , It can receive data , You can also send data ( Telephone )
- Baud rate : Used to describe the communication speed during communication , Its unit is
bps(bit per second), I.e. transmission every secondbitThe number of
UART
UART(Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter), General asynchronous transceiver .
characteristic :
1、 There are two data cables (RXD、TXD)
2、 Serial 、 asynchronous communication
3、 Full duplex communication
4、 Point to point communication : Receiver and sender ( Two devices )application : In embedded systems , It is often used for communication between host and auxiliary equipment
Sequence diagram

A complete data transmission includes : Start bit 、 Data bits 、 Check bit ( not essential ) And stop bits
When transmitting data , High level ( Set up 1) I'm free
Start bit : Set low level (0), Indicates the beginning of communication
Data bits : Start communication after the start bit , To transmit data , First transmit the low order data , Then transmit the data in high order ( Data bits can be sent 5-8 position , Generally send 8 Bit data ( A byte ))
Check bit :( not essential ) Verify whether the data is sent correctly , Only errors can be checked , Can't fix , And after , Communication speed slows down
Stop bit : Set high level ( Set up 1), Indicates the end of a communication ( Occupy 1 position 、1.5 Bits or 2 position )UARTOnly one byte can be sent per communication , Cannot send cumulatively ( Avoid cumulative errors ); To send multiple bytes of data , You need to send a byte first , Then end the communication , Start communication again , Send next byteBecause it is asynchronous communication , There's no clock line , So pass Baud rate To distinguish between
01still0011Hardware connection diagram

In general ,SOC Will integrate
UARTcontroller , In the use of UART When communicating, you only need to set its internal related registers , Communication can be completed
USART
USART It's universal synchronization / Asynchronous transceiver ( With synchronous clock line USART_CK), It's just a way of agreement , It can be divided into RS232 The protocol and RS485 agreement .
UART Problems in serial communication :
1、 The electrical interface is not unified
2、 Poor anti-interference ability :UART Use it directly TTL The signal means 0 and 1, but TTL The anti-interference ability of the signal is very poor , It is easy to make mistakes during transmission
3、 Short communication distance : because TTL The anti-interference ability of the signal is poor , So its communication distance is also very short . Generally, it is only used for the communication between two different chips on a circuit board ( Onboard communication )
RS232 agreement :( Point to point communication )
1、 Based on serial port , So sequence diagram and UART The serial port is consistent
2、 Some changes have been made on the electrical layer , Unified electrical interface ( A standard connector is defined , The function of each pin of the connector is specified in the standard , The level of the signal is also specified )
3、 The anti-interference ability becomes stronger , The communication distance becomes longer ( Generally up to 15 rice )
4、 The electrical interface is DB-9, In general use RXD、TXD、GND These three lines
5、 The logic is 1 The level of is -5V To -15V; The logic is 0 The level of is +5V To +15V
Hardware connection :
RS232 The problem with the agreement :
1、 The signal level of the interface is high , A chip that can easily damage the interface circuit
2、 And TTL Level incompatibility , You need a level conversion chip to work with TTL Circuit connection
3、 Low communication speed
4、 Prone to common mode interference , Weak noise immunity
5、 Communication distance 15 rice , Still short
RS485 agreement
characteristic :( Half duplex communication )
1、 use Differential signal Data transfer ( Twisted pair ), The voltage difference between the two lines is +2V To +6V To express logic 0; The voltage difference between the two lines is -2V To -6V To express logic 1, Thus realizing long-distance communication (1500 rice ); And in the environment with large electronic noise , It can effectively transmit signals
2、 Allows multiple transceivers to be connected , Multi station capability , That is, a device network can be established
3、RS485 Level ratio of interface signal RS232 To reduce the , Therefore, it is not easy to damage the chip of the interface circuit
Hardware connection diagram ( Device network ,RS485 Multiple devices are mounted on the bus , Master slave mechanism reference I2C Bus )
120Ω Resistors are used to eliminate common mode interference on signal lines 
I2C
I2C Bus is a kind of serial 、 Sync 、 Multi host communication bus for half duplex communication , There are two data cables :SDA( cable )、SCL( Clock line ); The hardware structure is simple , Lower cost
application : Communication between different chips on the same circuit
characteristic :
1、I2C Bus is a kind of multi host bus , Connected to the I2C The devices on the bus are divided into master and slave ;
2、 The host has the right to initiate and end a communication , The slave can only be called by the host ;
3、 When multiple hosts on the bus enable the bus at the same time ,I2C It also has the function of conflict detection and arbitration to prevent errors ;
4、 Each is connected to I2C Devices on the bus , Have a unique address (7 position ), And each device can be used as a host ( There is only one host at a time ), It can also be used as a slave ; The addition and deletion of devices on the bus will not affect the normal operation of other devices ;
5、I2C The bus is in communication , The device that sends data on the bus is called a transmitter , The device that receives data is called a receiver
Hardware connection diagram  Communication process :
Communication process :
1、 Host send Start signal , Enable bus ( At this time, all devices on the bus can receive , And other devices will not enable the bus in this device )
2、 The host sends a byte of data indicating Slave address And subsequent bytes Direction of transmission ( Host computer —> Slave , Or slave —> host )
One byte of data : front 7 Bit is the slave address , The last bit is the direction of transmission ( yes 0 Represents the host —> Slave ,1 Represents the slave —> host )
3、 The addressed slave sends Answer signal Reply to the host , The check address of other devices is not their own address , And ignore
4、 The transmitter sends a byte of data
5、 The receiver sends a reply signal in response to the transmitter
The first 4、5 Step loop …
6、 When the communication is complete , Host send Stop signal Release the bus , One communication is completed
Start signal : When SCL At high power level ,SDA From high to low
Stop signal : When SCL At low power level ,SDA From low to high
Byte transfer and reply : The transmitter sends a byte of data ( Transmit the high order first , Then transmit the low order ); The receiver sends Response bit To respond to ,(1 Bit low level reply )
Synchronous signal :
During data transmission ,
When SCL by Low level period , The transmitter sends a bit of data to the data line , During this period, the signal on the data line is allowed to change
When SCL by High level period , The receiver reads a bit of data from the data line , During this period, the signal on the data line is not allowed to change ( because SCL by High level when , Signal changes on the data line will be considered Start signal perhaps Stop signal )
SPI
SPI(Serial Peripheral Interface) Is the abbreviation of serial peripheral interface , It's a high speed 、 full duplex 、 Synchronous serial communication bus ; There are at least four wires :MISO( Master input 、 Output from the device ),MOSI( Main device output 、 Input from the device ),SCLK( Clock line ),CS( Film selection line )SPI Work in master-slave mode , There is usually a master device and one or more slave devices
Hardware connection diagram
Each additional slave is connected , It is necessary to connect more than one film selection line , and I2C Address is used in different ways 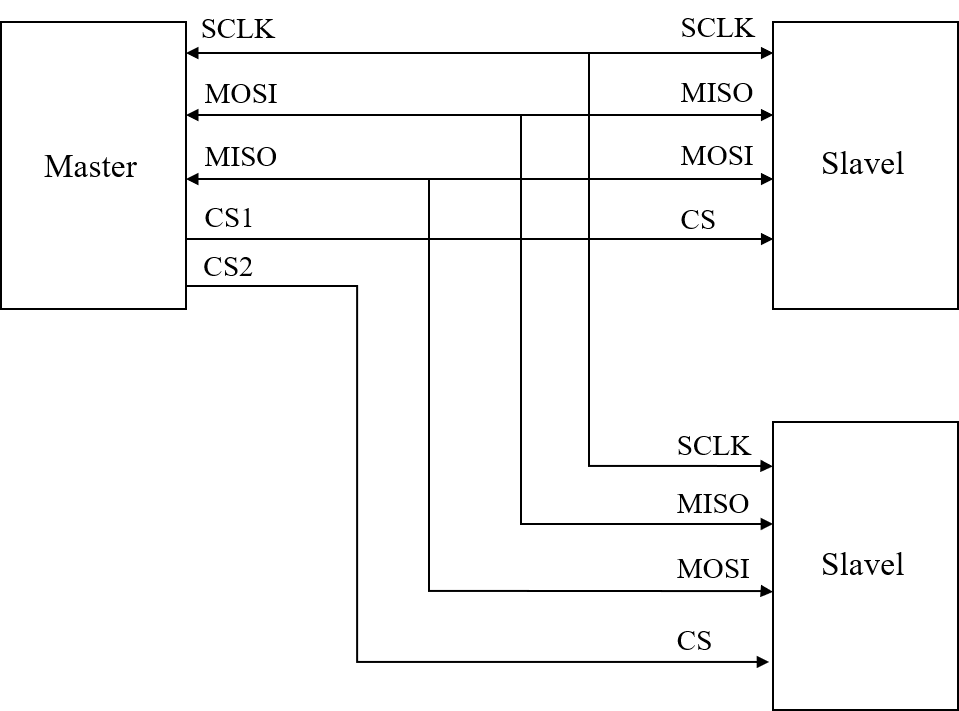 Communication process :
Communication process :
1、SPI Bus transfers data : Transmit the high order first , Then transmit the low order ; After a byte is transferred , No response required , You can start the transmission of the next byte
2、SPI The bus works synchronously , When the clock is on the rising or falling edge, the transmitter sends data to the data line , On the next falling or rising edge, the receiver reads data from the data line , So as to complete the transmission of one bit data ; Eight clock cycles can complete the transmission of one byte of data
Polarity and phase : ( Judge according to the chip manual )SPI The bus has four different working modes , Depending on Polarity (CPOL) and phase (CPHA)
CPOL Express SCLK The state of being idle :
When CPOL = 0,SCLK Low level indicates that the bus is idle
When CPOL = 1,SCLK A high level indicates that the bus is idle
CPHA Represents the sampling time :
When CPHA = 0, The first clock of each cycle is sampled along , The phase is 0, Rising edge data , Falling edge data
When CPHA = 1, The second clock of each cycle is sampled along , The phase is 1, Falling edge data , Rising edge closing data
I2C and SPI Similarities and differences
The same thing :
1、 Serial communication is adopted 、 How to synchronize
2、 All adopt TTL level , The transmission distance is similar to the application scenario ( Short range transmission , Onboard communication )
3、 Both work in master-slave mode
Difference :
1、I2C For half duplex communication ;SPI For full duplex communication
2、I2C There is a response mechanism ;SPI No response required
3、I2C Broadcast via bus Slave address To address ;SPI adopt ** Send the enable signal to the chip selection line ** To address
4、I2C The polarity and phase of the clock are fixed ;SPI The polarity and phase of the clock can be adjusted
边栏推荐
- Many to one, one to many processing
- 67 page overall planning and construction plan for a new smart city (download attached)
- Slf4j + logback logging framework
- redis21道经典面试题,极限拉扯面试官
- Understanding and application of least square method
- Is there a specific format for English papers?
- CMake基本使用
- MFC 获取当前时间
- Bigder: how to deal with the bugs found in the 32/100 test if they are not bugs
- maya渔屋建模
猜你喜欢
Chapter 3 of getting started with MySQL: database creation and operation

Is the multitasking loss in pytoch added up or backward separately?
MySQL 23道经典面试吊打面试官
CADD course learning (4) -- obtaining proteins without crystal structure (Swiss model)

Digital twin visualization solution digital twin visualization 3D platform

监控容器运行时工具Falco

详解用OpenCV的轮廓检测函数findContours()得到的轮廓拓扑结构(hiararchy)矩阵的意义、以及怎样用轮廓拓扑结构矩阵绘制轮廓拓扑结构图

How QT exports data to PDF files (qpdfwriter User Guide)

setInterval定时器在ie不生效原因之一:回调的是箭头函数
Cmake basic use
随机推荐
Thinkadmin V6 arbitrary file read vulnerability (cve-2020-25540)
论文的英文文献在哪找(除了知网)?
MySQL advanced learning notes (4)
直击产业落地!飞桨重磅推出业界首个模型选型工具
maya渔屋建模
What are the projects of metauniverse and what are the companies of metauniverse
经济学外文文献在哪查?
附加:token;(没写完,别看…)
Installing redis under Linux
Digital twin smart factory develops digital twin factory solutions
How to write the design scheme of the thesis?
Improvement of RTP receiving and sending PS stream tool (II)
程序分析与优化 - 9 附录 XLA的缓冲区指派
Happy Lantern Festival, how many of these technical lantern riddles can you guess correctly?
布隆过滤器
Architecture: database architecture design
在线预览Word文档
setInterval定时器在ie不生效原因之一:回调的是箭头函数
MATLAB signal processing [Q & a notes-1]
Digital twin visualization solution digital twin visualization 3D platform