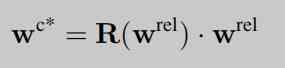1. The above summary
「 Make up a missed lesson 」 In progress : Design pattern series
2. Command mode
Command mode is a highly cohesive mode , The definition for :
Encapsulate a request as anobject,thereby letting you parameterize clients with differentrequests,queue or log requests,and support undoable operations.( Encapsulate a request as an object , So you can parameterize the client with different requests , Queue or log requests , Can provide command undo and restore function .)
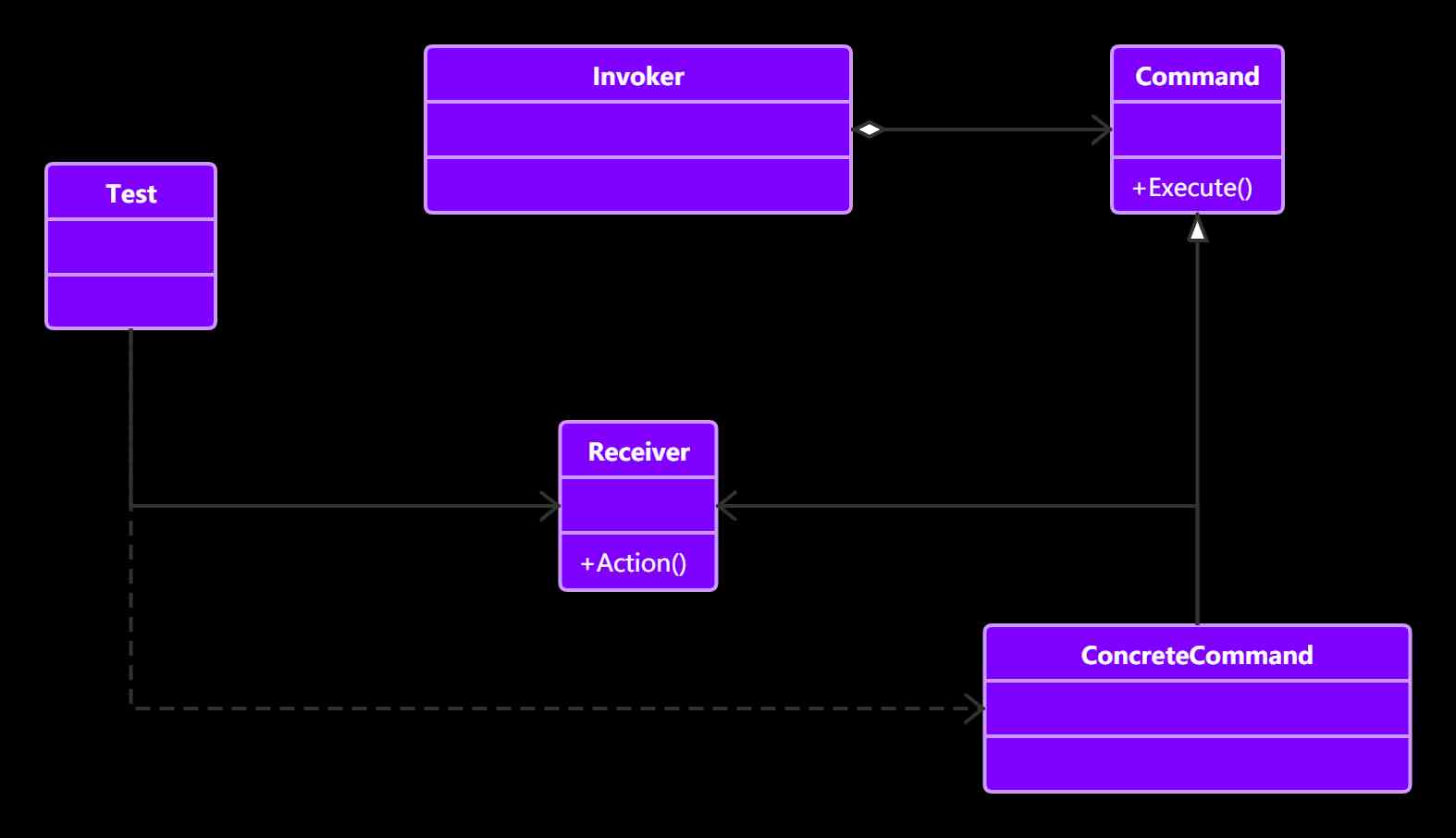
- Receive: Receiver role , This role is the role of work , Commands are passed here to be executed .
- Command: Command character , All commands that need to be executed are declared here .
- Invoker: The role of the caller , Received an order , And execute the command .
2.1 Universal Receiver class
public abstract class Receiver {
public abstract void doSomething();
}
The reason for using abstract classes here is that recipients can have multiple , If there are more than one, you need to define an abstract set of all features —— The abstract receiver .
2.2 Concrete Receiver class
public class ConcreteReceiver1 extends Receiver {
@Override
public void doSomething() {
}
}
public class ConcreteReceiver2 extends Receiver {
@Override
public void doSomething() {
}
}
Each receiver must define certain business logic .
2.3 In the abstract Command class
public abstract class Command {
public abstract void execute();
}
2.4 Concrete Command class
public class ConcreteCommand1 extends Command {
private Receiver receiver;
public ConcreteCommand1(Receiver receiver) {
this.receiver = receiver;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
this.receiver.doSomething();
}
}
public class ConcreteCommand2 extends Command {
private Receiver receiver;
public ConcreteCommand2(Receiver receiver) {
this.receiver = receiver;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
this.receiver.doSomething();
}
}
Two specific Command Implementation class , Every concrete command class here , According to the constructor, it defines which receiver is issued , At the same time, it defines the subject of command receiving .
2.5 caller Invoker
public class Invoker {
private Command command;
public void setCommand(Command command) {
this.command = command;
}
public void action() {
this.command.execute();
}
}
The caller is where the final method call is made , All commands are called by the caller .
2.6 Test class
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Invoker invoker = new Invoker();
// Define the recipient
Receiver receiver = new ConcreteReceiver1();
// Define a command to send to the receiver
Command command = new ConcreteCommand1(receiver);
// Leave the command to the caller to execute
invoker.setCommand(command);
invoker.action();
}
}
2.7 advantage :
- Decoupling between classes : There is no dependency between the caller role and the receiver role , The caller only needs to call Command The abstract class execute The method will do , There's no need to know which receiver is executing .
- Extensibility : Command Subclasses of can be easily extended , And the caller Invoker And high level modules Client No serious code coupling .
2.8 shortcoming :
Command mode also has disadvantages , Please pay attention to Command Subclasses of : If there is N An order , The problem arises , Command The subclasses of are not a few , It is N individual , This class is very inflated , So be careful when using command mode .