当前位置:网站首页>Chorus translation
Chorus translation
2022-06-11 17:36:00 【Foolish fox Fairy】
Chorus
Abstract
The traditional recommendation system is mainly inherent to users 、 Modeling long-term preferences , Dynamic user requirements are also very important . Usually , Historical consumption will affect users' demand for their relationship items . for example , Users often buy complementary products at the same time (iPhone and Airpods), Instead of buying alternative products (Powerbeats and Airpods), Although alternatives can still meet user preferences . In order to better simulate the influence of historical sequence , Previous studies have introduced the semantics of item relationships to capture users' recommendation needs . However , We think , The time evolution of the effects caused by different relationships can not be ignored . In the example above , When a user needs a new headset , Users' demand for earphones can be increased after a long time . In order to establish the dynamic meaning model of the project in different sequence environments ,Chorus In this paper, a new method considering project relationship and corresponding time dynamics is proposed . The goal of chorus is to deduce the embedding of target items through a way of knowledge perception and time perception , Each item will get its basic representation and related representation . then , According to whether there are relation items in the historical sequence and the running time , Design Temporal kernel function To dynamically combine these representations . Enhanced target item embedding can flexibly calculate ranking scores and generate recommendations with various algorithms . Based on extensive experiments on three real data sets , Compared with the most advanced baseline method , The chorus has been significantly improved . Besides , The time-dependent parameters are highly interpretable , Can enhance the interpretability of recommendations .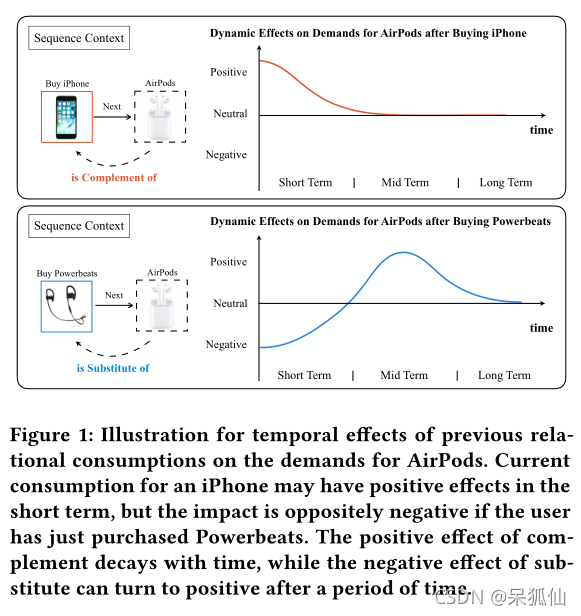
chart 1: The previous relationship consumption is right AirPods Description of the time impact of requirements :iPhone Current consumption may have a positive impact in the short term , But if the user just bought Powerbeats, The effect is the opposite . The positive effect of complement decays with time , The negative effect of substitutes will turn into positive effect after a period of time .
1. Introduce
With the overload of information on the Internet , Recommendation system is playing a more and more important role in our daily life . It not only provides information that caters to users' tastes , It is also helpful to discover the internal preferences of users . Traditional recommendation methods mainly focus on user preference modeling [11,13,19,33]. for example , Potential factor model [21] Embed users and items into a potential space , The user's embeddedness represents various preferences , It doesn't change at different recommended times .
However , Although user preferences are static most of the time , But the consumer demand of users is actually dynamic 、 Variable . In different environments , The same items have different meanings for the same user . actually , Sequential consumption behavior can be seen as a process to meet the needs of users in different aspects . The consumption of one item may have an impact on other related items , And the impact of this different relationship is also different . Take complementarity and substitution as examples , chart 1 Explains how the effect of purchasing items with different relationships changes over time . Add : Assume that the user currently purchases iPhone, He / She may buy... In the short term AirPods( namely iPhone A supplement to ). But after a while , The positive effect will be reduced ( Users may already have headphones , The recommender system should not continue to provide AirPods). For alternatives : If he / What she has just consumed is AirPods substitute , Such as Powerbeats, The short-term impact is expected to be mainly negative , Because the user doesn't need another headset immediately . Although the negative impact may turn into positive in the medium term , Because the user may need to buy a new headset , And the newly released AirPods May be attractive . This positive effect will gradually weaken , Users may lose interest in the headset , Or buy another earphone in other ways .
From the example above , We can see that the current consumption of different relationship items has different effects on the target items . what's more , Each relationship has a different time trend . There are also studies that introduce project relationships into recommendation systems [16,40,44,45], But the time dynamics of different relationships are not considered . Although some studies involve long-term and short-term preferences [16], But project relationships are only used to model the transformation of short-term projects , Lack of modeling of the continuous evolution of different relationship effects . Another recent study investigated repeated consumption [41] Time dynamics of . However , Consumption will not only affect the same commodity itself , It will also affect related goods . therefore , The project relationship and the corresponding time dynamics are the key to obtain the dynamic meaning of the project in different contexts .
This paper presents a method of embedding target items based on knowledge and time perception —— Chorus . As far as we know , We are the first to explicitly model the evolution of the effects of different relationships over time , This helps to better capture the meaning of each item in the context of different sequences . Specially ,Chorus The translation based graph embedding method assigns a basic representation and various relational representations to each item . then , These representations are dynamically combined through temporary kernel functions , It depends on how much time has been spent since the relationship was consumed , This is why it was named Chorus Why . The proposed temporal kernel function enables the relational representation to contribute to the final term embedding in different ways . therefore ,Chorus Can dynamically acquire knowledge and time aware project embedding , This can easily be used by various recommended algorithms . Besides , The highly interpretable time-dependent parameters make it possible to interpret the recommendation results in different time periods . The main contributions of this work are summarized as follows :
∙ \bullet ∙ We suggest to consider both the project relationship and the corresponding time dynamics . As far as we know , We are the first to explicitly simulate the duration evolution of the effects of different relationships .
∙ \bullet ∙ We designed a novel and flexible method Chorus, When the target item plays different roles in the sequence , Enhance the modeling of target objects by dynamically combining different representations . The final project embedding can easily work with various recommended algorithms .
∙ \bullet ∙ Comparative experiments on three real datasets show that Chorus The effectiveness of the , And the high interpretability parameters further help to improve the interpretability of the model .
2. Related work
2.1 Timing recommendations
Different from the traditional recommendation method , Sequence recommendation is based on Markov chains , Use sequence data to predict users' next consumption , Markov chain assumes that the next action depends on the previous action sequence [34,37].Rendleet al.[34] Combined with matrix decomposition [21] And Markov decomposition chain , Give the next basket of recommendations for the previous basket . lately , There is a lot of work using recurrent neural networks (RNN)[36] Encode interaction history into hidden vectors [6,12,23,27,32,38].Hidasi wait forsomeone [12] First of all, will RNN Introduced into the sequence recommendation , And achieved impressive performance gains .Loyolaet al.[27] and Peiet al.[32] Will pay attention to the mechanism [39] be applied to RNN, To get more effective recommendations . Besides , Many follow-up studies have focused on extending the RNN The ability of the model .
Although based on RNN The sequential recommendation method has strong expression ability , But due to the lack of external knowledge , They are still not good at simulating complex user requirements , And there are serious interpretability problems [26]. The difference is , Our approach clearly addresses project relationships and the corresponding temporal dynamics , To better capture user needs .
2.2 Project relationship modeling
In a real application , Items with specific semantics usually have multiple relationships . Some recent studies have focused on how to introduce project relationships into recommendation systems [16,28,30,40,44,45], Most of them use knowledge maps (KG)[42] To represent the project relationship .CFKG[45] The user and product relationship diagram is introduced as an entity , Think of buying as another relationship , And then use TransE[3] Represent heterogeneous information networks and make recommendations .Xin wait forsomeone [44] A general recommendation task is proposed , This task contains multiple relationships between projects , And integrate relational data into collaborative filtering (CF)[35] in .Ma wait forsomeone [28] A joint learning framework is proposed , It integrates the induction of interpretable rules from the knowledge graph .
However , All these methods assume that the impact of relational item consumption is static , And it has nothing to do with time information , under these circumstances , Even if the user does not need a complement , It may also continue to recommend complements after a long period of time .
2.3 Time dynamics modeling
Considering the time information , There are two main types of work . One side , Some work aims to use temporal information as a contextual feature .TimeSVD++[20] Divide time into slots , And design parameters related to time .TransMF utilize FM Use timestamp as an additional context feature [31]. Tensor decomposition is also a major method [2,17], Where time is regarded as the user - The third dimension of the object interaction cube . On the other hand , Some work focuses on simulating the time decay effect of historical interactions . In this line ,Hawkes Process (HP)[8] It is always used to model the mutual excitation characteristics of user consumption sequence [7,22,24,41].Du wait forsomeone [7] First of all, will Hawkes The process should be used for time sensitive recommendations .SLRC[41] Combined with the Hawkes Process and collaborative filtering to simulate the time dynamics of repeated consumption .
However , These methods do not take into account the temporal dynamics of different relationships . therefore , To better model dynamic user requirements , We creatively considered the project relationship and the corresponding time evolution .
3 Preprocessing
3.1 Task definition
Definition 3.1( Problem definition ): Whereas the user u ∈ U u \in U u∈U And interaction history S u = ( i 1 , t 1 ) , ( i 2 , t 2 ) . . . ( i N u , t N u ) ∈ S S_u={(i_1,t_1),(i_2,t_2)...(i_{N_u},t_{N_u})}\in S Su=(i1,t1),(i2,t2)...(iNu,tNu)∈S, In time t n < t n ′ t_n< t_{n′} tn<tn′ For arbitrary n < n ′ < N u n < n′< N_u n<n′<Nu Of N u N_u Nu Secondary interaction , The recommended tasks are : Consider the target time t( Write it down as S u t S^t_u Sut) Previous interaction sequence , Generate a sequence table , This includes the user in t May be interested in k A project .
Besides , set up R A collection of all item relationships , Each item relationship r ∈ R r\in R r∈R There's a matrix I r ∈ N M × M I_r\in N^{M\times M} Ir∈NM×M, among M Is the total number of items , If the relationship r Pair item i and j If it is established, then I r ( i , j ) I_r(i,j) Ir(i,j) = 1, Otherwise 0. Relationship r Can be complementary , And so on .
3.2 Knowledge graph embedding
Information about project relationships can be viewed as a knowledge map , Its components are a set of triples (i,r,j), among i and j Represent different items ,r Represents the relationship type . for example ,(AirPods, is_complementary _o f,iPhone) Express AirPods yes iPhone A supplement to . It should be noted that , Sometimes the opposite of a triple may not hold ( for example iPhone No AirPods A supplement to ), So the graph is directional .
In order to introduce the structure information of the diagram into the recommendation system , It is very important to obtain the embedding with the semantic meaning of project relationship . Among various embedding methods , Translation based model [3,25,43] With its efficiency and effectiveness . Its internal idea is to embed projects and relationships into the same potential space , And find a translation function to minimize the scoring function :
among D(·) Is a measure function of distance ( Usually l 2 − n o r m l_2-norm l2−norm).Trans(i,r) Is an arbitrary translation function , It can be a simple pan operation , It can also be a specially designed neural network . A lot of work has focused on the ability expansion of translation functions , Such as TransE [3], TransH [43], TransR[25] etc. . about TransE[3], The translation function is Trans(i,r) = i +r, For any triple (i,r,j) application l 2 − n o r m l_2-norm l2−norm The scoring function is f ( h , r , t ) = ∣ ∣ h + r − t ∣ ∣ 2 f (h,r,t) = ||h +r−t||_2 f(h,r,t)=∣∣h+r−t∣∣2.
To learn project and relationship embedding from diagrams , Will be based on marginal losses [45] To minimize the , As shown below :
For each triplet , The tail term is a random sampling term j ′ j ' j′ Replace , In order to ensure that ( i , r , j ′ ) (i,r,j ') (i,r,j′) Not observed in the knowledge map . Similarly , The title item is i ′ i ' i′ Replace , also ( i ′ , r , j ) (i ',r,j) (i′,r,j) Don't set up . The purpose of the above objective function is to distinguish between observed triples and corrupted triples , And force embeddedness to maintain relationships between projects .
3.3 Recommend basic methods
The project modeling method proposed in this paper can be flexibly used with various recommended algorithms . Because Bayesian personalized sorting (Bayesian Personalized Ranking, BPR)[33] It is a widely used matrix factorization method , And generalized matrix factorization (Generalized matrix factorization, GMF)[11] It is one of the most advanced methods based on neural network , We chose them as the basic recommendation model to verify the effectiveness of our method .
This paper briefly reviews the two collaborative filtering methods .CF The method assumes that similar users like similar items . stay BPR Under the circumstances , There is one for each user and item k Dimensional potential factor , The ranking score is calculated as follows :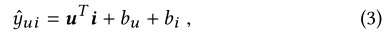
among b u b_u bu and b i b_i bi The preferences of each user and project .
stay GMF Under the circumstances , The ranking score is obtained by multilayer neural network , It can be expressed as :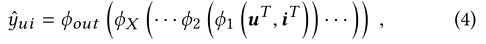
among ϕ o u t \phi_{out} ϕout and ϕ x \phi_{x} ϕx Represents the output layer and the... Respectively X Mapping function of a neural co filtering layer , share X Nerves CF layer . then , According to the predicted score y ^ u i \hat y_{ui} y^ui Rank the candidate projects .
In order to learn the parameters in the recommendation model , You can sort the losses in pairs [33] To optimize :
among , σ \sigma σ by s Type of function , A negative term j ∉ S u j \notin S_u j∈/Su Is a random sample of each training instance .
4 Chorus model
4.1 Model overview
Chorus is a two-stage model , It integrates the project relationship and its specific time effect . chart 2 The whole model structure is demonstrated . In the first phase ( Relationship modeling ), Using graph embedding, the structural information of project relationship is encoded into embedding . Here you can flexibly use the 3.2 The various translation based methods described in section . The results of graph embedding will be used to derive the basic and relational representations in our chorus model .
In the second phase (Dynamic Item Representation) in , There are two key modules :(1) Dynamic integration ,(2) Design of temporal kernel function . First , In addition to the basic relationship representation based on the translation function , Each entry will get ∣ R ∣ |R| ∣R∣ Relationship means , The translation function represents the representation of the target item when it plays different roles in the context . then , According to whether there is corresponding relationship consumption and running time in the historical sequence , Dynamically integrate these representations . To combine the temporal dynamics of each relationship , We propose a time kernel function with a specific relationship to control the polarity and intensity of the effect . therefore , Relational representations have different contributions to final item embedding in different contexts , Thus, the dynamic items of knowledge perception are embedded . Last , Many algorithms can use enhanced item embedding to calculate ranking scores and make recommendations . In the rest of this section , We will elaborate on the key modules of chorus in the second stage .
4.2 Dynamic integration
First , According to the results embedded in the diagram , Define the basic representation of each item ( Write it down as i b i_b ib) And relationship means ( Write it down as i r i_r ir Represents the relationship r ∈ R r\in R r∈R). The basic representation encodes the inherent characteristics of the item , Use the item embedding learned in the first stage to initialize i b i_b ib, Then we use the translation function to get the relation representation :
among e r e_r er yes r ∈ R r\in R r∈R The relationship is embedded in , such , Relational representation integrates the semantic information corresponding to each relationship .
After obtaining the basic and relational item representations , Here we focus on how to dynamically combine them according to different contexts , This is ours Chorus The core idea of the model . Be careful , Relational representation is knowledge aware , But it is still static . Our goal is to derive a context aware coefficient for each relational representation f r f_r fr, To reflect the actual level of influence in the current context . Finally, context and knowledge aware items are embedded i C h o r u s i_{Chorus} iChorus Put forward the following expression :
It consists of two parts : Basic item representation and scaled relational item representation , Where context ( Historical sequence S t u S^u_t Stu, Time t And target projects i) As a coefficient f r f_r fr The input of . Next, we focus on how to get reasonable from a given context f r f_r fr.
Intuitively speaking , Some relationships indicate that in some cases there may be no impact , Even negative effects . chart 3 Some examples are given , Explain how these representations contribute to the final embedding in different contexts . The three corners of the triangle represent different representations of the target item . When there is no relation to consumption ( Context A) when , The final embedding is just the basic item representation , The other two relationships have no effect . When Powerbeats or iPhone When I first bought ( Context B and C), The corresponding relationship indicates that there should be negative and positive effects respectively . And if the substitute was purchased a long time ago ( Context D), The characterization of alternatives may have a positive impact on the final embedding . Besides , When there are many different relational terms in the sequence , All three representations will work in varying degrees .
To integrate the temporal dynamics of different relationships , We creatively designed a time kernel function for each relationship , It is a continuous function of the lag time between consumption . The purpose of temporal kernel function is to control the influence degree of consumption of each previous relationship . The polarity of the function value indicates the polarity of the effect . Suppose we have obtained the time kernel function κ r i ( ∆ t ) κ^i_r(∆t) κri(∆t), In terms of i And relationship r Index ( The specific design and related discussion are left in the next section ), We suggest defining the relationship coefficient f r f_r fr as follows :
among I r I_r Ir Is a relational matrix . Every previous consumption and target project i i i The relationship between r r r The coefficient will be f r f_r fr There is a superposition effect , By kernel function k r i ( ⋅ ) k^i_r(·) kri(⋅) control . such , Different from the previous research on static project embedding , The correlation coefficient makes different representations have different contributions to the final embedding . Because of the existence of time kernel function , Relational representations may be too long apart to work , In some cases, it may even have a negative impact . therefore , Choral embedding can better capture the meaning of items in different contexts , So as to better simulate the change of user requirements over time .
Besides , For simplicity and efficiency , We can only consider the latest relational terms in the historical sequence , under these circumstances ,Equ.(7) It can be expressed directly as :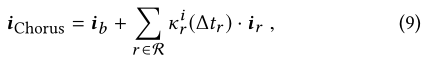
In style , ∆ t r ∆t_r ∆tr Indicates the elapsed time since the last consumption , With the current item r r r relevant . If there is no relation item in the history sequence of a relation , We assume that there is a relation term with a positive infinite time interval ( ∆ t r = + ∞ ∆t_r= +\infty ∆tr=+∞). Suppose that the temporal kernel function approaches zero with time , Then the corresponding relationship embedding is not affected .
4.3 Design of temporal kernel function
Next , We focused on how to design temporal kernels for each relationship . actually , The concrete form of time kernel function can be regarded as a kind of artificial intervention to the model . One side , We can design functions according to the characteristics of each relationship . for example , Pictured 1 Shown , Complementary relationships have a positive impact in a short time , This effect decays over time . On the other hand , It can be designed according to the subjective requirements of the system . If we want substitutes to appear on the recommended list in the short term , The time-domain kernel function can be designed with a positive initial value , Decay faster . In this paper , We mainly study two kinds of relations : Complementarity and substitution . As an instance , According to the general cognition and characteristics of these two relations, we design the corresponding time kernel function .
For supplements , In addition to the overall downward trend , The positive effect usually lasts for a period of time , Then it begins to decay in daily life . therefore , We choose the normal distribution with zero mean as its time kernel function , Instead of an intuitive exponential distribution that decays too fast :
In style N ( ∆ t ∣ μ , σ ) N(∆t|\mu,\sigma) N(∆t∣μ,σ) yes ∆t along with μ \mu μ Mean and σ \sigma σ Normal distribution of standard deviation . Note the parameters here σ c z ( i ) \sigma^{z(i)}_c σcz(i) And z ( i ) z(i) z(i) of , z ( i ) z(i) z(i) Represents a project i Categories . We do not estimate project specific parameters , Because category is usually a more appropriate level , To simulate the characteristics of a group of projects . Term specific parameters can also be plagued by data sparsity .
For alternatives , We expect that the impact will change from negative to positive , Because we don't need another thing with similar effect in the short term , But hopefully at the end of its life [41] Replace new items when necessary . therefore , We use two opposite normal distributions to simulate such characteristics :
This is a (1) Short term inhibition ( negative ) and (2) Lifelong promotion ( just ) The superposition . The negative normal distribution is designed as zero mean , Because the effect of retraining is usually the strongest after alternative consumption . In positive numbers , Parameters μ s z ( i ) \mu^{z(i)}_s μsz(i) To some extent, it represents the life cycle of this class , That is, the impact will peak at this time .
chart 2 Shows these two temporary kernel functions . Other forms of temporary kernel functions can also be designed to meet different needs . Besides , Chorus is not limited to these two relationships . Many relationships can be merged , Such as the same brand 、 Same manufacturer, etc ,
The only thing to do is to design a corresponding temporal kernel function on the basis of prior knowledge .
ad locum , We get the final knowledge aware dynamic project embedding . Then use various algorithms to recommend , Using our algorithm instead of embedding the original target term . Different from the previous model ,Chorus It also integrates sequence information 、 Project relationship modeling and corresponding time dynamics . Recently proposed CFKG and SLRC Or just focus on commodity relations , Or just focus on the time dynamics in the consumption order . surface 1 The related methods and our Chorus The difference between models . More details on these baselines will be found in section 5.1.3 Section describes .
4.4 Parameter learning
In order to obtain better robust performance , We use a two-stage training process to learn the model parameters : First , Optimize L r e l L_{rel} Lrel Get the project and relationship embedding with structural information , In the second stage, the basic item representation and relationship embedding are initialized ; Then minimize L r e c L_{rec} Lrec To learn all the parameters of the model . In the second phase , We will not freeze what we have learned before . Experiments show that , use L r e c L_{rec} Lrec Better results can be obtained by optimization . On the other hand , It may also destroy meaningful embeddedness at the beginning of training . therefore , In the second phase , We reduce the learning rate of embedding basic item representation and relationship 0.1. because Adam[18] It has been successful in many recommendation models , So use it as a learning algorithm at every stage .
5. experiment
5.1 Experimental setup
5.1.1 Data sets The experiment was conducted in a public interview Amazon Data sets [9] on . Except for user interaction sequences with time stamps , It also has project metadata , Include also_view,also_buy and category information A list of . Following previous studies [28,29] after , We will also_view As an alternative relationship ,also_buy As a complementary relationship . The difference is , In our work , Relationship means being complementary and replaced . therefore , The original also_view,also_buy The direction of the relationship should be reversed .
We use three representative sub datasets :Grocery and Gourmet Food (Grocery), phones and Accessories (Cellphones), and Home and Kitchen (Home). surface 2 The statistics of three data sets are summarized . Be careful , stay Home Data set , The proportion of test cases related to historical items is very low , And the relational data is relatively sparse .


5.1.2 Evaluation protocol We use the leave one method to evaluate , This method has been widely used in the literature [4,10,15]. For each consumption sequence S u ∈ S S_u\in S Su∈S, We use each user's recent interaction to test , Verify with the second most recent entry , Use the remaining items to train . Considering that when the data set is large , Some methods of sorting all items are time-consuming , We randomly selected 99 Projects that the target user has not interacted with , take ground-truth Projects with these negative Items are sorted together . This method is also widely used [11,41,44].
In order to evaluate the recommended quality , We use hit rate (HR) And normalized discounted cumulative gain (NDCG)[14] As an evaluation indicator [email protected] It's evaluation “ground-truth” Whether it is in the top of the recommended rankings k Bit of website ,[email protected] It's evaluation “ground-truth” Whether it is in the top of the recommended rankings k Bit of website . We repeated each experiment with different random seeds 5 Time , And report the average score .
5.1.3 Baseline approach We will Chorus Model and 7 The two baseline methods are compared in different aspects , Including traditional collaborative filtering 、 Sequential recommendations and methods that include project relationships or temporal dynamics :
•BPR[33]: This method proposes a matrix decomposition model with pairwise ordering loss optimization .
•GMF[11]: This is an advanced collaborative filtering method , Using multilayer neural network .
•Tensor[17]: This method divides time into multiple containers , And decompose a three-dimensional tensor ( user - project - Time ).
•GRU4Rec[12]: This is a sequential recommendation model , application GRU[5] Get the ranking score .
•NARM[27]: The model uses GRU And attention mechanism to improve the performance of sequential recommendation , This is a session based approach .
•CFKG[45]: This method considers various commodity relationships , And regard purchase as another relationship between users and commodities . then , utilize TransE Learn graph embedding and make suggestions .
•SLRC Of [41]:SLRC combination Hawkes and CF To simulate the time dynamics of repeated consumption . Considering that the Amazon data set has removed repeated consumption , We extend this setting to the impact of relational items , Name it SLRC '. But it still lacks semantic modeling of project relationships .
5.1.4 Implementation details We are PyTorch All models are implemented in . The implementation code has been released . For comparison , The embedded dimensions of all models are set to 64. All the super parameters are tuned to get the best results in the validation data set . about CFKG, We have considered also_view and also_buy The relationship is consistent with ours . about SLRC ' and Chorus, We find that there are few interactions between two or more relational terms in the historical sequence . therefore , For simplicity and efficiency , We do this without sacrificing versatility and performance , Consider the latest relational interactions in the sequence . Besides , It is also used in chorus TransE As a translation function . For numerical stability , All time related parameters are initialized to 1, Other parameters are usually initialized to 0 Mean and 0.01 Standard deviation .
5.2 Overall performance
surface 3 Shows all baselines and our Chorus The model is used in BPR and GMF Performance when calculating ranking scores , Expressed as C h o r u s B P R , C h o r u s G M F Chorus_{BPR},Chorus_{GMF} ChorusBPR,ChorusGMF.
First , Different types of baselines show significant performance gaps . For collaborative filtering methods ( for example BPR and GMF), They serve as benchmarks , Because the only information they have is the user - Project interaction . The tensor method is superior to the basic method by considering the time dynamics CF Method . Sequential recommendation method ( Such as GRU4Rec and NARM) Further better performance , This illustrates the importance of the dynamic user needs for the delivery of recently consumed items .CFKG Got a fair result , It has become the best baseline on some indicators , This shows that the project relationship does help recommend . about SLRC’, Because of its explicit modeling of the mutual incentive characteristics of the consumption sequence , Generally, the best results are obtained in the baseline .
secondly , our Chorus The model performed better than other baselines in all data sets , This benefits from dealing with project relationships and their temporal dynamics . This shows that the proposed model can better capture the dynamic needs of users and the meaning of items in different contexts . And CFKG comparison , Chorus not only considers the relationship between objects , It also integrates time dynamics between items . And SLRC comparison , Chorus can simulate the semantic and category specific temporal effects of each relationship . stay SLRC in ,Hawkes The basic form of may be more concerned with the impact of relationship projects , therefore , In the absence of a prior relationship , It usually affects performance consumption ( See chapter for more discussion 5.4). The difference is ,Chorus Integrating project relationships into knowledge aware dynamic project representation , This is more effective and flexible .
On the other hand , Please note that , stay Home Data set , The improvement is relatively small . The possible reason is that the relationship information is too sparse and not so reliable . We use CFKG Similar relation graph embedding method , But the performance of this method on this data set is also very poor . Even though TransE Works well in other datasets , however Home Relationships in data sets can be so complex , So much so that TransE Not enough to model accurately . More evidence in 5.3 Section provides .
5.3 Ablation Experiment
To verify the effect of relationship modeling and time dynamic processing in our model , We compared the chorus with two variants :
• Chorus \ R. The model assigns a separate project embed for each relationship , And through optimization Lr ec Estimate all parameters . The results of graph embedding are not used to initialize the basic representation and derive the relational representation .
• Chorus \ T. The model does not consider the time dynamic relationship , Suppose that all time kernels ( namely :∆t) All are constants , The value is 1.
chart 4 Shows c h o r u s B P R chorus_BPR chorusBPR Of [email protected]0 And its variants , as well as SLRC’. We can conclude that , Relationship modeling and time dynamics are very important . The lack of chorus module leads to the loss of performance . Besides , We have the following views :
First , Project relationships are really helpful . stay Grocery and phones Data set ,Chorus\R The biggest performance loss , This shows the importance of relational structure information modeling , And our translation based approach , Derive relational representations through graph embedding .
secondly , It is very important to build time dynamic models of different relationships . Without time information , Chorus \T Moderate loss of performance in the first two datasets . This does not mean that the temporal dynamics dealt with in our model are unimportant . Literally , The relationship between commodities has a greater impact on users' consumption decisions . therefore , It is reasonable to model project relationships to bring greater improvements than modeling time dynamics . On the other hand , And Chorus\T comparison , The chorus has made consistent improvements , Especially in Home in , This shows the usefulness of moving forward , Take into account the temporal dynamics of the project relationship .
Third , The diagram is embedded in Home Poor performance in data set , among Chorus\T The biggest loss of performance , and Chorus\R Less performance loss . This is another proof that the relational model is inadequate . although TransE Is the natural choice of translation function , And it usually works well on the other two datasets , But we found it in Home Data set scenarios may not be enough , stay Home Data set CFKG Use TransE As its graph embedding method, it also performs badly . chart 4 Show , No relationship modeling , Performance won't degrade much (Chorus\R). But if there is relational modeling and there is no temporal kernel function (Chorus\T), Improper embedding of items and relationships will affect performance . It also shows that , The temporal dynamics handled in our model can help to adaptively avoid the possible bad effects of chaotic relationships , This shows the usefulness and necessity of considering time dynamics .
5.4 Different scene performance
In addition to the improvement of overall performance , We also want to figure out where these improvements come from . Here we study the performance of the model in different scenarios . say concretely , We construct three subsets of the test data set according to whether there is corresponding relationship consumption in the historical sequence . Normal means that there were no related items before . Complement means that the target item is the complement of some items in the historical sequence . Similarly , A substitute is a situation in which previous consumption is used as a substitute . When there were two kinds of relation items before , Test cases may be in both complement and substitution groups . chart 5 It shows different models in the three subsets of the mobile phone data set ( That's ok ) Of [email protected] And the number of cases ( strip ). We can see , Although there are fewer cases in the complement and substitution groups , But models tend to perform better in these situations . They may prove some patterns in essence , In this way, all models can achieve better performance than normal , Even if the project relationship is not explicitly considered BPR So it is with .
Besides , Chorus can combine the advantages of various methods , So as to achieve the best average score . Be careful , about SLRC and CFKG, They all have their own advantages and disadvantages . Even though SLRC Good performance in relationship cases , Especially in Substitute In the group , But it's even better than BPR Worse . This shows that SLRC ' It is easy to over fit the relationship , This, in turn, can damage normal performance . On the other hand , Even though CFKG It performed well in the normal group , But in the relational case , It's not as good as SLRC ' Powerful , because SLRC ' The temporal characteristics of each relationship are explicitly simulated . As for chorus , It captures the temporal dynamics of project relationships and their category specific . It is worth noting that , Under normal circumstances ,Chorus And CFKG similar ; In the supplementary case , Chorus ratio SLRC A little bit better. , Both of these are the best baselines in each scenario . Although singing in alternative groups is not as good as SLRC’ strong , But with CFKG It is obviously improved . result ,Chorus Significantly better average results were obtained , This shows the importance of integrating project relationships and fine-grained temporal dynamics .
5.5 Parameter interpretability
ad locum , We hope to verify whether the time-dependent parameters have interpretable meaning when designing the time kernel function . Be careful , These parameters are indexed by item category , This shows how the impact of previous relationship consumption on this category changes over time . Although the overall trend of a particular relationship tends to converge because of its functional form , But their concrete forms reveal the characteristics of category . chart 6 It shows the temporal kernel functions of some representative categories learned in the mobile phone data set .
The figure on the left corresponds to the complementary relationship between headphones and replacement parts . As shown in the figure , The effect on the earphone decays much faster than the replacement part . One side , After buying a mobile phone , It is reasonable to recommend earphones to users as a supplement . But if the user doesn't use the recommended headphones , He / She may already have a headset or buy one from somewhere else . therefore , The positive effect of complement is expected to fade soon , Otherwise, continuous recommendation of earphones may cause trouble to users . On the other hand , For replacement parts such as backup batteries , The positive effect of supplementary consumption will last for some time . Because users usually buy backup batteries after the original equipment battery runs out for a period of time .
Although the general form consists of two opposite normal distributions , But the time kernel function in the basic case is very different from the other two cases , The component of inhibition effect is almost flat . This shows that when users buy mobile phone cases , Will not have a strong negative impact , Because we often change the case for various reasons , For example, the edge is broken , Or just want to try new styles . For international chargers and mobile phones , Their time-domain kernel functions show obvious negative effects and positive peaks . It's reasonable , Because if we just bought a charger or cell phone , There is usually no need for another charger or mobile phone . Interestingly , The time intervals corresponding to the peaks of the two items are similar , This reflects that changes in mobile phones often lead to changes in matching chargers . Besides , Compared with charger , The curve of the mobile phone is smoother . The reason might be , We can change mobile phones for various reasons , But if the charger works , It is seldom replaced . therefore , New phones can be used after a long time interval .
in summary , our Chorus The time-dependent parameters in the model are highly interpretable , It well reflects the characteristics of different types of projects . These parameters can help the recommendation system to interpret the recommendation results . for example , The user has purchased iPhone, This happens to be the peak value of the time kernel function of the mobile phone , Recommending a new mobile phone can be explained as “ Your mobile phone has been used for a long time , Take a look at some new products ?”
6 Conclusion and future work
In this work , We propose a new approach to choral knowledge and time aware project modeling . As far as we know , We are the first to explicitly model the impact of different relationships over time , And embed this information into the project . We use graph embedding to learn structural information from the project diagram , Then derive different relational representations for each item . Using a specific time kernel function to control the time dynamics of the relationship , And according to the time interval between the target item and the relation item in the historical sequence, the dynamic combination relation is expressed , Get the dynamic term representation of knowledge perception . in addition , The design of temporal kernel function can be regarded as a kind of human intervention to the model , It can be used to meet different requirements for recommended results . because Chorus The flexibility of the , It can easily use a variety of embedding based algorithms to calculate ranking scores and make recommendations . A large number of experimental results show that , Chorus is superior to the most advanced baseline , This shows that project relationships and their time evolution effects are very important . Besides , The time-dependent parameters in chorus are highly interpretable , Help to improve the interpretability of recommendations .
The model still has some limitations , Such as predefined time function and two-stage learning process . Besides , Although the method based on translation works well on the whole , But in some cases , We found its shortcomings , Further research is needed . future , We will study how to adaptively estimate the time evolution effects of different relationships , And try to design a more suitable method , Closely combine project relationship modeling and recommendation .
边栏推荐
- 7-1 均是素数
- Dynamic: capturing network dynamics using dynamic graph representation learning
- 简单理解事件
- Sohu tout le personnel a été escroqué, quels problèmes ont été exposés?
- 使用exe4j 将.jar文件打包为.exe文件
- 从制造到“智造”,探索制造企业破局之道
- Tidb lightning configuration data restore route
- 论文阅读 dyngraph2vec: Capturing Network Dynamics using Dynamic Graph Representation Learning
- Service学习笔记04- 其他服务实现方式与替代方式
- Leetcode force deduction question
猜你喜欢
自动化测试-Selenium

搜狐全员遭诈骗,暴露哪些问题?
What subclasses inherit, polymorphism, and upward transformation

ADB command learning notes

Format eslint automatique lorsque vscode enregistre le Code

05_ Feature Engineering - dimension reduction

Test basis: black box test

有效的括号---2022/02/23

The use of histogram function in MATLAB

合并两个有序链表---2022/02/24
随机推荐
Bentley uses authing to quickly integrate application system and identity
Tidb GC related problems
Vscode configures eslint to automatically format with an error "the setting is deprecated. use editor.codeactionsonsave instead with a source“
Chapter II relational database
Authing CEO 谢扬入选福布斯 2021 年 30 Under 30 亚洲榜单
Merge K ascending linked lists ---2022/02/26
聚类方法汇总
sql server中移除key lookup书签查找
Hands on deep learning - multiple input and output channels in the convolution layer
Leetcode力扣刷题
From manufacturing to "intelligent manufacturing", explore the way for manufacturing enterprises to break the situation
6-3 读文章(*)
mysql 大表的拆分方式
Remove key lookup bookmark from SQL Server
vscode保存代码时自动eslint格式化
Classification and method of feature fusion
Service learning notes 04 other service implementation methods and alternative methods
tidb-数据误删恢复的几种方式
定制 or 订阅?未来中国 SaaS 行业发展趋势是什么?
R language mice package error in terms Formula (TMP, simplify = true): the model formula in extractvars is incorrect