当前位置:网站首页>GPS NMEA protocol, 0183 positioning data format dual mode positioning: gnxxx gps+bd full version
GPS NMEA protocol, 0183 positioning data format dual mode positioning: gnxxx gps+bd full version
2022-06-25 12:37:00 【haoming Hu】
author :haomingHu
email:[email protected]
background : I need to be in imx6ull Of Linux The board receives the information of the positioning module 0183 Format data and analyze it , And use QT Realization , Draw dynamic curves of various data of positioning information
GPS NMEA agreement ,0183 Positioning data format Dual mode positioning :GNXXX GPS+BD
If it is GN The first data is not distinguished , If it is GP perhaps BD The first data should be distinguished .
Data frame format :
$aaccc,ddd,ddd,…,ddd*hh
1、“$”—— Frame command start bit
2、aaccc—— Address field , The first two are identifiers , The last three digits are the name of the statement
3、ddd…ddd—— data
4、“*”—— Checksums prefix
5、hh—— The checksum (check sum),$ And * All characters between ASCII The check sum of the code ( XOR of each byte , Get verification
And after , Retransfer 16 In decimal format ASCII character .)
6、<CR><LF>——CR(Carriage Return) + LF(Line Feed) End of the frame , Carriage return and line change
Data types :
GNZDA:UTC Time and date
GNGGA:UTC Time information
GPGLL: Geolocation information
GPGSA: At present GPS Satellite information
BDGSA: The current Beidou Satellite Information
GPGSV:GPS Visible satellite information
BDGSV: Beidou visible satellite information
GNRMC: Recommended location information
GNVTG: Ground speed information
1. GNZDA: Time information :
UTC Time and date : there UTC Time is coordinated universal time , Equivalent to the prime meridian (0 Time in longitude ), Time difference with Beijing 8 Hours
The data sample : $GNZDA,092320.000,25,04,2021,00,00*40
The frame format :$GPZDA, <1>,<2>,<3>,<4>,<5>*hh
Data description :
- <1> :UTC Time ,dd:dd:dd.ddd —> Minutes and seconds
- <2>: Japan
- <3>: month
- <4>: year
- <5>: The difference between local time and world time
- <6>: Calibration position *hh
2. GNGGA: Satellite positioning information
The data sample :$GNGGA,092320.000,2519.0490,N,11024.8391,E,1,23,0.7,175.7,M,0.0,M,*7D
$GPGGA,<1>,<2>,<3>,<4>,<5>,<6>,<7>,<8>,<9>,M,<10>,M,<11>,<12>*hh
- <1> UTC Time ,hhmmss( Minutes and seconds ) Format and GNZDA Of UTC equally , Belongs to coordinated universal time
- <2> latitude ddmm.mmmm( Degrees ) Format ( Ahead 0 Will also be transmitted )
- <3> Latitude hemisphere N( Northern Hemisphere ) or S( southern hemisphere )
- <4> longitude dddmm.mmmm( Degrees ) Format ( Ahead 0 Will also be transmitted )
- <5> Longitude hemisphere E( East longitude ) or W( The west longitude )
- <6> GPS state :0= Not located ,1= Non differential positioning ,2= Differential positioning ,6= Estimating
- <7> The number of satellites using the solution position (00~12)( Ahead 0 Will also be transmitted )
- <8> HDOP Horizontal accuracy factor (0.5~99.9)
- <9> Altitude (‐9999.9~99999.9)
- <10> The height of the earth's ellipsoid relative to the geoid
- <11> Differential time ( The number of seconds since the last differential signal received , If not, differential positioning will be empty )
- <12> Differential station ID Number 0000~1023( Ahead 0 Will also be transmitted , If not, differential positioning will be empty )
a key :
Longitude latitude conversion method : For example, in the given data , The latitude we can get is 2519.0490 N, So the actual latitude =25+19.0490÷60, The longitude you get is 11024.8391, So the actual longitude is :110+24.8391÷60 It's because the standard metric format is used in the message , Because the ranges of longitude and latitude are 090、0180, So the cutting position is different
3. GPGLL: Geolocation information
Example data :$GNGLL,2519.0490,N,11024.8391,E,092320.000,A,A*4A
$GNGLL,<1>,<2>,<3>,<4>,<5>,<6>,<7> * hh
- <1> latitude ddmm.mmmmm ( Degrees )
- <2> Latitude hemisphere N ( Northern Hemisphere ) or S ( southern hemisphere )
- <3> longitude dddmm.mmmmm ( Degrees )
- <4> Longitude hemisphere E ( East longitude ) or W ( The west longitude )
- <5> UTC Time : hhmmss ( Minutes and seconds )
- <6> Positioning status , A= Effective positioning ,V= Invalid positioning
- <7> Mode indication (A= Self positioning ,D= Difference ,E= Estimate ,N= Invalid data )
4. GPGSA: At present GPS Satellite information
Example data :$GPGSA,A,3,09,17,33,02,34,06,14,36,19,35,04,28,1.2,0.7,1.0*3B
$GPGSA,<1>,<2>,<3>,<4>,<5>,<6>,<7>,<8>,<9>,<10>,<11>,<12>,<13>,<14>,<15>,<16>,<17>*hh
<1> Pattern 2:M = Manual , A = Automatically .
<2> Pattern 1: Positioning type 1 = Not located ,2 = Two dimensional positioning ,3 = Three dimensional positioning .
<3> The first 1 The satellite that the channel is using PRN Code number
<4> The first 2 The satellite that the channel is using PRN Code number
<5> The first 3 The satellite that the channel is using PRN Code number
<6> The first 4 The satellite that the channel is using PRN Code number
<7> The first 5 The satellite that the channel is using PRN Code number
<8> The first 6 The satellite that the channel is using PRN Code number
<9> The first 7 The satellite that the channel is using PRN Code number
<10> The first 8 The satellite that the channel is using PRN Code number
<11> The first 9 The satellite that the channel is using PRN Code number
<12> The first 10 The satellite that the channel is using PRN Code number
<13> The first 11 The satellite that the channel is using PRN Code number
<14> The first 12 The satellite that the channel is using PRN Code number
<15> PDOP Comprehensive position accuracy factor (0.5 ‐ 99.9)
<16> HDOP Horizontal accuracy factor (0.5 ‐ 99.9)
<17> VDOP Vertical precision factor (0.5 ‐ 99.9)
annotation :(Pseudo Random Noise, Pseudo random noise code ),01 to 32( If the number of leading digits is insufficient, it will be supplemented 0, Up to 12 Satellite information ) There must be twelve occupancy data , without , It will be empty , But it's also a occupancy data , The smaller the precision factor , The higher the accuracy ,
**5. BDGSA: The current Beidou Satellite Information **( Frame format and GPGSA Agreement )
Example data :$BDGSA,A,3,01,02,03,19,04,05,07,08,10,06,13,1.2,0.7,1.0*25
6. GPGSV:GPS Visible satellite information
Example data :
$GPGSV,4,1,15,02,34,276,40,03,15,039,04,07,080,38,06,57,317,4577
$GPGSV,4,2,15,09,15,112,43,12,08,323,14,42,164,45,17,53,053,477E
$GPGSV,4,3,15,19,55,009,44,24,05,279,28,56,168,45,33,41,115,4374
$GPGSV,4,4,15,34,32,164,43,35,57,065,46,36,55,145,404B
$GPGSV, <1>,<2>,<3>,<4>,<5>,<6>,<7>,…,<4>,<5>,<6>,<7>*<8>
(1) GSV The total number of sentences .
(2) This sentence GSV The number of .
(3) The total number of visible satellites (00-12, Ahead 0 Will also be transmitted ).
(4) Satellite number (01~32, Ahead 0 Will also be transmitted ).
(5) Satellite elevation (00-90 degree , Ahead 0 Will also be transmitted ).
(6) Satellite azimuth (000~359 degree , Ahead 0 Will also be transmitted )
(7) Carrier to noise ratio (00~99dB, Null when no satellite is tracked ).
notes : Every one of them GSV The statement includes information about up to four satellites , Information from other satellites will be in the next $GPGSV Output... In the statement
7. BDGSV: Beidou visible satellite information
Example data :
$BDGSV,3,1,12,01,42,122,46,02,48,229,39,03,62,180,45,04,29,109,406C
$BDGSV,3,2,12,05,26,251,35,06,05,164,35,07,59,159,45,08,65,340,4361
$BDGSV,3,3,12,10,80,228,44,13,61,283,44,19,41,074,48,20,05,038,*68
Frame format and GPGSV Agreement
8. GNRMC: Recommend minimal location information
Example data :$GNRMC,092320.000,A,2519.0490,N,11024.8391,E,0.00,0.00,250421,A7D
$GPRMC,<1>,<2>,<3>,<4>,<5>,<6>,<7>,<8>,<9>,<10>,<11>,<12><13>
<1> UTC(Coordinated Universal Time) Time ,hhmmss( Minutes and seconds ) Format
<2> Positioning status ,A= Effective positioning ,V= Invalid positioning
<3> Latitude, latitude ddmm.mmmm( Degrees ) Format ( If the number of leading digits is insufficient, it will be supplemented 0)
<4> Latitude hemisphere N( Northern Hemisphere ) or S( southern hemisphere )
<5> Longitude, longitude dddmm.mmmm( Degrees ) Format ( If the number of leading digits is insufficient, it will be supplemented 0)
<6> Longitude hemisphere E( East longitude ) or W( The west longitude )
<7> Ground speed (000.0~999.9 section ,Knot, If the number of leading digits is insufficient, it will be supplemented 0)
<8> Ground course (000.0~359.9 degree , With true north as the reference , If the number of leading digits is insufficient, it will be supplemented 0)
<9> UTC date ,ddmmyy( The year of the sun and the moon ) Format
<10> Magnetic Variation, Magnetic declination (000.0~180.0 degree , If the number of leading digits is insufficient, it will be supplemented 0)
<11> Declination, Magnetic declination direction ,E( In the east ) or W( In the west )
<12> Mode Indicator, Mode indication ( only NMEA0183 3.00 Version output ,A= Self positioning ,D= Difference ,E= Estimate ,N= Invalid data )
<13> The checksum
9. GNVTG: Ground speed information
Example data :$GNVTG,0.00,T,M,0.00,N,0.00,K,A*23
$GPVTG,<1>,T,<2>,M,<3>,N,<4>,K,<5>*hh
<1> Ground course with true north as reference (000~359 degree , Ahead 0 Will also be transmitted )
<2> Ground course with magnetic north as reference (000~359 degree , Ahead 0 Will also be transmitted )
<3> Ground speed (000.0~999.9 section , Ahead 0 Will also be transmitted )
<4> Ground speed (0000.0~1851.8 km / Hours , Ahead 0 Will also be transmitted )
<5> Mode indication ( only NMEA0183 3.00 Version output ,A= Self positioning ,D= Difference ,E= Estimate ,N= Invalid data )
annotation :
- The checksum : By calculation $ and * All characters between two symbols ASCLL The XOR operation of the code yields , Will get the result to ASCII Character representation
for example : For example, statement : $GNZDA05555.000,08,12,2015,00,00*4C, The checksum ( The red part is involved in the calculation ) The calculation method is as follows :
0X47 xor 0X4E xor 0X5A xor 0X44 xor 0X41 xor 0X2C xor 0X30 xor 0X39 xor 0X35 xor 0X35 xor 0X35 xor 0X35 xor 0X2E xor 0X30 xor 0X30 xor 0X30 xor 0X2C xor 0X30 xor 0X38 xor 0X2Cxop 0X31 xorl0X32 xor0X20 xor 0X32 xor 0X30 xor 0X31 xor 0X35 xor 0X2C xor 0X30 xor 0X30 xor 0X2C xor 0X30 xor 0X30
The result is 0X4C, use ASCII It means 4C.
This article is for reference only , If there is any wrong , Please leave a message in the comment area , Or send an email
边栏推荐
- Ramda rejects objects with null and empty object values in the data
- R language uses the scale function to scale the input data of neural network to the minimum and maximum, scale the data to between 0 and 1, and divide the data set into training set and test set
- Kotlin study notes
- Laravel excel export
- Repair the error that ECSHOP background orders prompt insufficient inventory when adding goods. Please reselect
- Initialize the project using the express framework
- A commonly used statistical modeling method -- difference analysis
- Dynamic proxy
- A set of automated paperless office system (oa+ approval process) source code: with data dictionary
- Qiantang Pingou source code -- Qiantang Pingou app system development source code sharing
猜你喜欢

Swagger document generated by node project API in vscode
High performance + million level Excel data import and export

Linear regression of common mathematical modeling models for College Students

How to use ARIMA model for prediction?

【数据中台】数据中台的OneID是个什么鬼,主数据它不香吗?

What is principal component analysis? Dimension reduction of classical case analysis variables
![[oceanbase] Introduction to oceanbase and its comparison with MySQL](/img/1c/bd2bcddb7af4647407d2bc351f5f5d.png)
[oceanbase] Introduction to oceanbase and its comparison with MySQL

SDN system method | 9 Access network
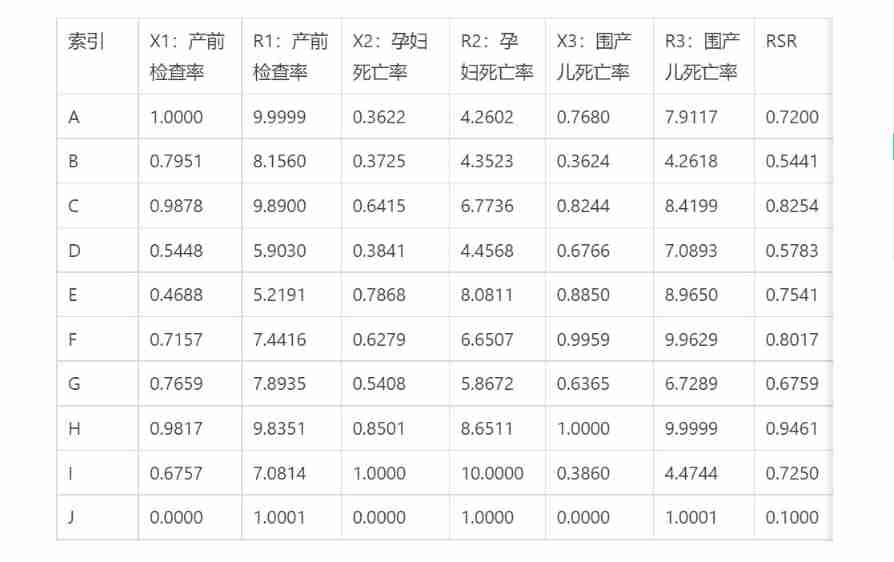
Rank sum ratio comprehensive evaluation method for common models in mathematical modeling

Zhangxiaobai's way of penetration (VIII) - detailed operation steps of SQL injection - Boolean blind injection of blind injection
随机推荐
R language uses GLM function to build Poisson logarithmic linear regression model, processes three-dimensional contingency table data to build saturation model, and poisgof function of epidisplay pack
Upgrade opsenssh to 8.8p1
Image tagging to obtain the coordinates of the image in the ImageView
The dist function of R language calculates the distance between two samples in dataframe data, returns the distance matrix between samples, and specifies the distance calculation method through the me
If you also want to be we media, you might as well listen to Da Zhou's advice
High performance + million level Excel data import and export
When MySQL queries fields in JSON format, it takes a property value of JSON data
ECSHOP quickly purchases goods, simplifies the shopping process, and improves the user experience through one-step shopping
Zhangxiaobai's way of penetration (VIII) - detailed operation steps of SQL injection - Boolean blind injection of blind injection
Spicy food advertising e-commerce system development function and spicy food advertising e-commerce app system development source code sharing
Heyangdao store management system -- share the development source code of heyangdao system
Zhangxiaobai's way of penetration (V) -- detailed explanation of upload vulnerability and parsing vulnerability
Online blind box system development function introduction and some source code sharing
Happy shopkeeper source code -- Introduction to happy shopkeeper system development mode
PHP takes the difference set of two arrays
Dynamic proxy
Service charge and time setting code sharing involved in crmeb withdrawal process
PHP replaces the key of a two-dimensional array with a specified element value
[on]learning dynamic and hierarchical traffic spatiotemporal features with transformer
一篇文章讲清楚MySQL的聚簇/联合/覆盖索引、回表、索引下推