当前位置:网站首页>Chapter 4 - network layer
Chapter 4 - network layer
2022-06-21 14:11:00 【I'm not smart】
4.1 The function of network layer
The network layer is OSI The third layer in the reference model , Between the transport layer and the data link layer , It provides the data frame transmission function between two adjacent endpoints in the data link layer , Further manage the data communication in the network , Try to transfer the data from the source to the destination through several intermediate nodes , Thus, the most basic end-to-end data transmission service is provided to the transport layer .
| OSI Reference model | Transmission units at all levels |
|---|---|
| application layer | message |
| Transport layer | Message segment |
| The network layer | IP The datagram , grouping ( If IP Datagrams that are too large are cut into packets ) |
| Data link layer | frame |
| The physical layer | The bit |
4.2 IP The datagram
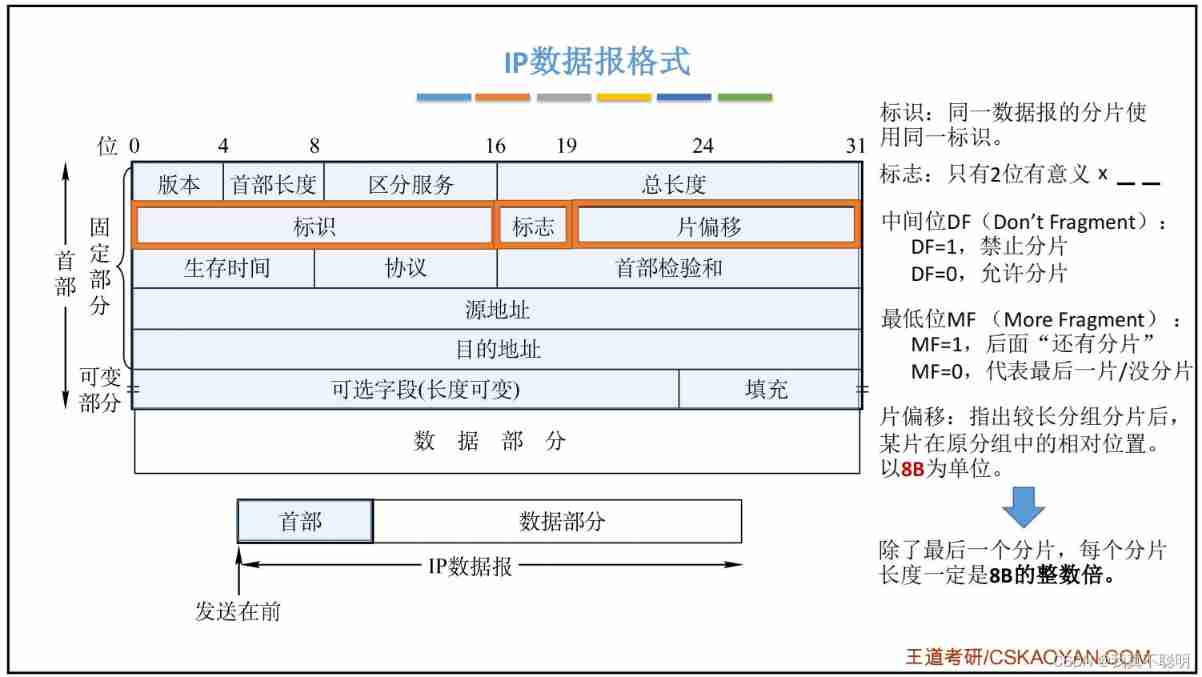
4.2.1 IP Datagram format

- edition (version)
Occupy 4 position , Express IP Version of protocol . Used by both parties IP The protocol version must be consistent . Currently widely used IP The agreement version number is 4, namely IPv4. - The length of the first ( Internet header length IHL)
Occupy 4 position , The maximum decimal value that can be represented is 15. The unit of the number represented by this field is 32 The word is long (1 individual 32 The bit length is 4 byte ). therefore , When IP The length of the head is 1111 when ( It's decimal 15), The length of the head reaches 60 byte . When IP The length of the head of the group is not 4 Integer times of bytes , It has to be filled with the last filled field .
The data part is always 4 The integer multiple of a byte starts , This is the realization of IP It's more convenient to make an agreement . The head length is limited to 60 The disadvantage of bytes is , Sometimes the length may not be enough , The reason for limiting the length is 60 byte , I want users to minimize overhead . The most common head length is 20 byte ( That is, the length of the head is 0101), No options are used at this time . - Distinguish between service (tos)
Also known as service type , Occupy 8 position , For better service . This field was called service type in the old standard , But it has never been used .1998 year IETF Change the name of this field to DiffServ (Differentiated Services,DS). Only when using differentiated services , This field works . - Total length (totlen)
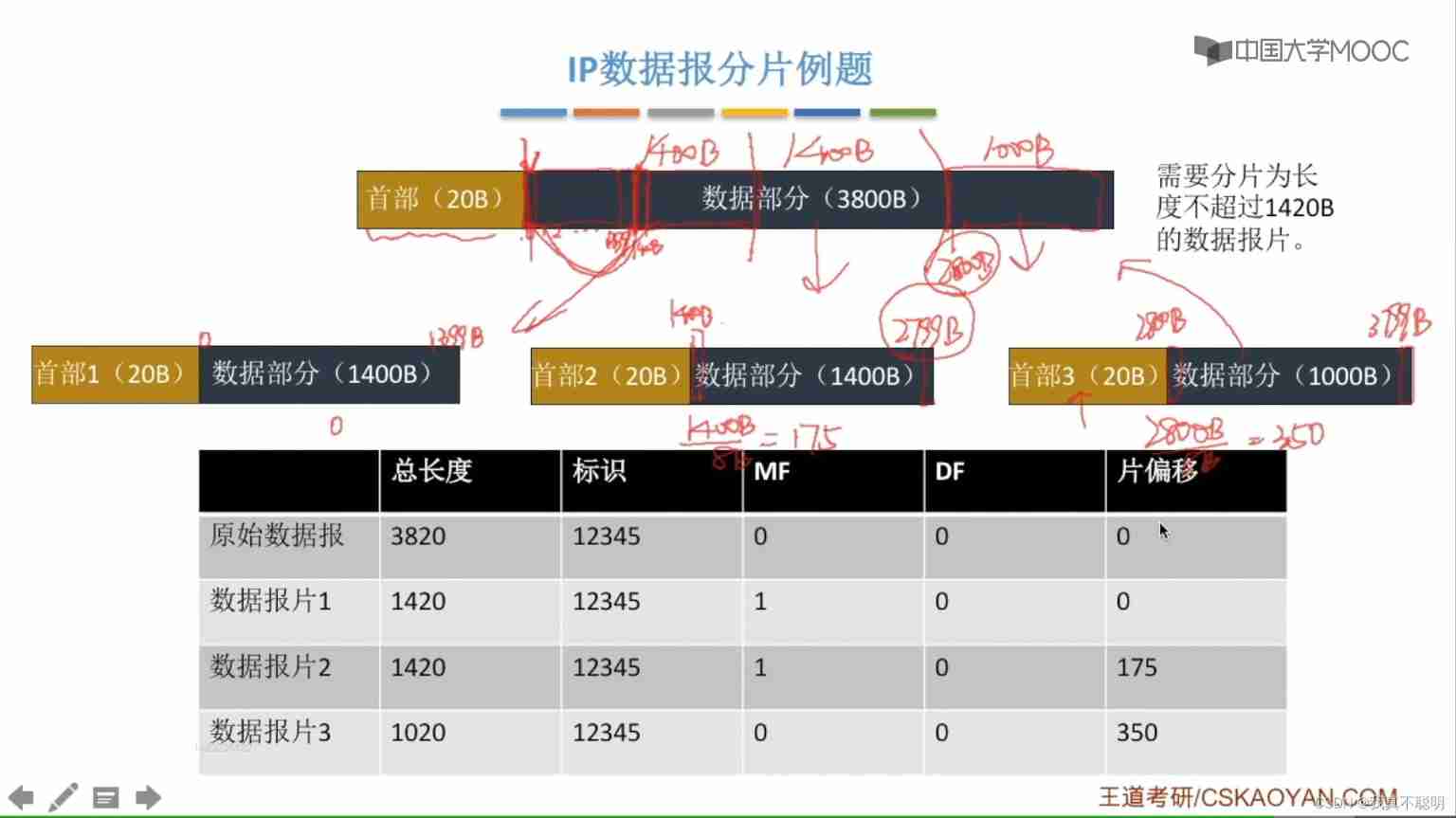
Sum of header and data , The unit is byte . The total length field is 16 position , So the maximum length of datagram is 2^16-1=65535B. - identification (identification)
Used to identify datagrams , Occupy 16 position .IP The protocol maintains a counter in memory . Every time a datagram is generated , The counter is added 1, And assign this value to the identification field . When the length of datagram exceeds that of network MTU, And when you have to segment , The value of the ID field is copied to the ID field of all datagrams . The segmented message with the same identification field value will be reconstituted into the original datagram . - sign (flag)
Occupy 3 position . The lowest bit of the flag field is MF,MF=1 It means that there are still pieces in the back ,MF=0 It means the last fragment ; The middle bit of the flag field is DF,DF=0 It's allowed to slice ,DF=1 No slicing . - Slice offset (offsetfrag)
Occupy 13 position . When the message is segmented , This field marks the relative position of the fragment in the original message . Film offset with 8 Bytes are offset units . therefore , Except for the last piece , The offset values of other tiles are 8 byte (64 position ) Integer multiple . - Time to live (TTL)
Indicates the lifetime of the datagram in the network , Occupy 8 position . This field is set by the source host issuing the datagram . Its purpose is to prevent undeliverable datagrams from being transmitted indefinitely in the network , Thus consuming network resources .
Before the router forwards the datagram , The first TTL Value reduction 1. if TTL Value reduced to 0, Then discard the datagram , No more forwarding . therefore ,TTL Indicates the maximum number of routers that datagrams can pass through in the network .TTL The maximum value of is 255. If the TTL The initial value of is set to 1, It means that this datagram can only be transmitted in the local LAN . - agreement
Indicates the protocol type used by the data carried in the data message , Occupy 8 position . This field is convenient for the destination host IP The layer knows what protocol to process the data part according to . Different protocols have different protocol numbers .
for example ,TCP The agreement number of 6,UDP The agreement number of 17,ICMP The agreement number of 1. - First inspection and (checksum)
Used to verify the header of a datagram , Occupy 16 position . Every time a datagram passes through a router , The fields in the header can change ( Such as TTL), So you need to recheck . The data part does not change , So you don't have to regenerate the check value . - source address
Represents the source of the datagram IP Address , Occupy 32 position . - Destination address
Indicates the purpose of the datagram IP Address , Occupy 32 position . This field is used to verify whether the transmission is correct . - Optional fields
This field is used for some optional header settings , Mainly used for testing 、 Purpose of commissioning and safety . These options include strict source routing ( Datagrams must go through the specified route )、 Internet timestamp ( Time stamp record when passing through each router ) And security restrictions . - fill
Because the length in the optional field is not fixed , Use several 0 Fill in the field , It can ensure that the length of the whole header is 32 Integer multiple of bits . - Data section
Represents the data of the transport layer , Such as preservation TCP、UDP、ICMP or IGMP The data of . The length of the data part is not fixed .
4.2.2 IP Segment data report
4.3 IPv4(Internet Protocol version 4,IPv4)
4.3.1 IPv4 Address
IPv4 It's a kind of There is no connection The agreement , It operates at the link layer using packet switching ( Ethernet ) On . This agreement will do its best to deliver the data package , This means that it does not guarantee that any packet will reach its destination , There is no guarantee that all packets will arrive in the correct order without repetition . These aspects are handled by the upper layer transport protocol .
Each host or router connected to the Internet is assigned a 32 The bit Globally unique identifier of the . namely IP Address ; Conventional IP Addresses are classified addresses , It is divided into A、B、C、D、E Five category .
No matter what kind IP Address , Both consist of network number and host number , namely IP Address ={< network number >,< Host number >}. network number Flag host ( Router ) The network you are connected to , A network number is unique throughout the Internet . Host number Mark the host ( Router ), A host number must be unique within the network range indicated by the network number in front of it .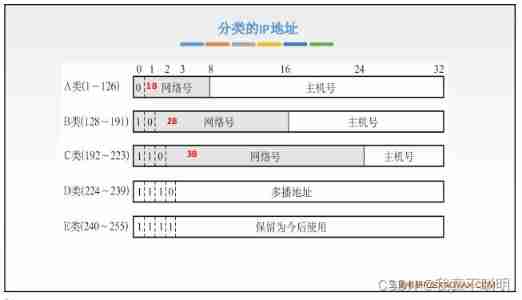
In all kinds of IP In the address , There are some IP Address has a special purpose , No need to be a host IP Address 

| Network category | Maximum number of available networks | The first available network number | The last available network number | The maximum number of hosts per network |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2^7-2 | 1 | 126 | 2^24-2 |
| B | 2^14-1 | 128.1 | 191.255 | 2^16-2 |
| C | 2^21-2 | 192.0.1 | 223.255.255 | 2^8-2 |
- A The reason why the maximum network number of class addresses is reduced by two : First of all , The network number fields are all 0 Of IP The address is reserved , namely
This network ; The second network number is 127 Of IP The address is loopback self test (Loopback Test) Address , This address represents any host itself . - B The number of available networks for class addresses is 2^14-1, reduce 1 The reason is that 128.0<10000000>( start IP) This network number is not assignable .
- C The number of available networks for class addresses is 2^21-1, reduce 1 The reason is that 192.0.0<11000000>( Reserved address ) Your network is not assignable .
4.4 Network address translation (Network Address Translation,NAT)
Network address translation (NAT) It refers to the private network address (INTERNET) Convert to public address ( Such as INTERNET), So as to hide the of internal management IP Address . It makes the whole private network only need one global IP The address can be connected to the Internet , Due to the private network IP Addresses can be reused , therefore NAT Great savings IP Address consumption . At the same time, it hides its internal structure , This reduces the risk of internal network attack .
The router is private to the destination address IP All datagrams of addresses are not forwarded . private IP The address is for LAN, Not used WAN Connect , So private IP The address cannot be used directly for Internet, Must be utilized through the gateway NAT It's private IP Address conversion to Internet Legal global IP Address can only be used for Internet. private IP The address can be LAN Repeated use .
In all routers on the Internet , Do not forward datagrams whose destination address is a private address . This is private IP The Internet of addresses is collectively referred to as the private Internet or the local Internet .
Use NAT It needs to be installed on the router connecting the private network to the Internet NAT Software ,NAT The router has at least one valid external global address . When a host using a local address communicates with the outside world ,NAT Router usage NAT The conversion table converts a local address to a global address , Or the global address translation cost is low .NAT The conversion table stores { Local IP Address : port } To { The global IP Address : port } The impression of . adopt {IP Address : port } Such a mapping , You can make multiple private IP Address mapping to the same global IP Address .
4.5 Subnet partition and subnet mask
Internet The organization defines five types of IP Address , Yes A、B、C Three types of address .A There are 126 individual , Every A Such networks may have 16777214 Console host , They are in the same broadcast domain . It is impossible to have so many nodes in the same broadcast domain , The network will be saturated by broadcast communication , Result in 16777214 Most of the addresses are not allocated . Based on each class IP The network is further divided into smaller networks , Each subnet is defined by the router and assigned a new subnet network address , The subnet address is created by borrowing the host part based on each type of network address . After dividing the subnet , By using a mask , Hide the subnet , Make the network unchanged from the outside , This is it. Subnet mask .
4.5.1 Subnet partition

- The division of subnets is purely a matter within a unit . The external performance of the unit is still a network without subnet division .
- Borrow several bits from the host number as the subnet number ;IP Address {< network number >< Subnet number >< Host number >}.
- All from other network send to this unit a host IP The datagram , Still more IP Destination network number of the datagram , First find the router connected to the company's Network . Then the router receives IP After the data report , Find the destination subnet by destination network number and subnet number . Finally, put IP Datagrams are delivered directly to the destination host .

4.5.2 Subnet mask
The subnet mask tells the router ,IP The first few digits of the address are the network address , The last number ( Residual bit ) It's the host address , Make the router correctly judge any IP Is the address of this network segment , So as to route correctly . The subnet mask is an associated with IP The address corresponds to 、 Long 32bit Binary string of , By a string of 1 With a string of 0 form ,1 The corresponding network is better than the subnet number ,0 Corresponding host number . Just put the computer IP Address and its corresponding subnet mask are bit by bit “ And ”(AND) operation , The corresponding subnet network address can be obtained 
Current Internet standards : All networks must use a subnet mask . If a network is not divided into subnets, the default subnet mask is used .A Class default subnet mask 255.0.0.0、B class 255.255.0.0、C class 255.255.255.255.0.
- A host is setting up IP Address information at the same time , You must set the subnet mask .
- All hosts belonging to the same subnet and corresponding ports of routers , The same subnet mask must be set .
- Router routing table , The main content of the information contained must have a destination network address 、 Subnet mask 、 Next hop address .
When using the subnet mask, the router's packet forwarding algorithm is as follows :
- Extract the destination from the header of the received packet IP Address , Write it down as D.
- First judge whether it is direct delivery . Check the network directly connected to the router one by one ; Use the subnet mask of each network and D Bit by bit facies , If it matches, the group will be delivered directly ; Otherwise, indirect delivery will proceed to the next step .
- If the destination address in the routing table is D Specific host routing for , Then the packet is transmitted to the next hop specified in the routing table ; Otherwise proceed to the next step .
- For each row in the routing table ( Destination network address 、 Subnet mask 、 Next hop address ) The subnet mask and D Bit by bit facies , The result is N. if N Matches the destination network address of the line , The packet is sent to the next hop router specified in the line .
- If there is a default route in the routing table , The packet is sent to the default router specified in the routing table ; otherwise , Report error .
4.5.3 Classless inter domain routing (Classless Inter-Domain Routing、CIDR)

Classless inter domain routing is an elimination method based on long subnet mask A、B、C Class network partition , And it can realize a kind of super network construction with the support of software IP Address division method .
- CIDR Although subnet is not used , But still use “ Mask ” The word" .CIDR No subnet Refer to CIDR Not in 32 The bit address indicates several bits as subnet fields . But assigned to a CIDR Organizations with fast addresses , Some subnets can still be divided within the organization according to needs .
- The network prefixes are all the same IP Address composition CIDR Address block . One CIDR Address blocks can represent many addresses , This aggregation of addresses is called Route aggregation or Constitute a supernetwork . Routing aggregation enables an item in the routing table to represent multiple routes with original traditional classified addresses .
longest-prefix matching

longest-prefix matching ( Best match ):
- Use CIDR when . Each entry in the routing table is represented by “ network prefix ” and “ Next hop address ” constitute . When looking up the routing table, you may get more than one match . In this case, the route with the longest network prefix should be selected from the matching results , Because the longer the network prefix , The smaller the address block , The more specific the route
4.6 ARP、DHCP、ICMP agreement
4.6.1 IP Address and hardware address (MAC Address )
IP Address is the address used by the network layer , It's hierarchical .MAC The address is the address used by the data link layer , It is flat . Through data encapsulation , hold IP Datagram packets are encapsulated as MAC After the frame , The data link layer cannot see the data in the datagram packet IP Address . Due to the isolation of the router ,IP You can't rely on... By broadcasting in the network MAC Address to complete cross network addressing , So in IP The network layer of the network only uses IP Address by address . When IP After the packet arrives at the target network through multiple routes , Change to target LAN Through the data link layer MAC Address is addressed by broadcast .
- stay IP Layer abstract on the Internet can only see IP The datagram .
- Although in IP There is a complete source in the header of the datagram IP Address and purpose IP Address , But the router only depends on the purpose IP Address network number for routing .
- At the data link layer , You can only see MAC frame . 2. Forwarding through the router IP In groups , this IP Packets are unpacked and repackaged by routers in each network . thus MAC The address keeps changing , This also determines that it cannot be used MAC Frame cross network communication .
- Although the hardware address systems of interconnected networks are different , but IP The layer of abstract internet shields the complex details of the lower layer . As long as we talk about it at the network level , Can use IP Address research questions .
4.6.2 Address resolution protocol (Address Resolution Protocol,ARP)
The address resolution protocol is based on IP Address gets a physical address TCP/IP agreement . When the host sends the information, it will include the target IP Address of the ARP Request broadcast to all hosts on the LAN , And receive the return message , To determine the physical address of the target ; After receiving the return message, it will be IP The address and physical address are stored in the machine ARP Cache and keep it for a certain time , The next time you ask for it, look it up directly ARP Cache to save resources . Each mainframe is equipped with a ARP Cache , It is used to store the information of hosts and routers on the local area network IP Address to MAC A map of addresses , be called ARP surface ; Use ARP To dynamically maintain ARP surface .
ARP Protocol workflow :
host A To a host on this lan B send out IP The data tell the time :
- First of all ARP Check whether there are hosts in the cache B Of IP Address . if there be , You can find out the corresponding hardware address , Writing this hardware address to MAC frame , And then through the local area network MAC Frames are sent to this hardware address . If the next step is not carried out .
- Through the purpose of use MAC The address is FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF To encapsulate and broadcast ARP The request packet , Use all hosts in the same LAN to receive ARP request . host B Received this ARP Post request to the host A Respond ARP grouping , Include hosts in group B Of IP And MAC Address mapping , host A Write this mapping to... When received ARP cache , Then send it according to the queried hardware address MAC frame .
Be careful :ARP Used to solve the same problem LAN On the host or router IP Address and hardware address mapping problem ; If not in the same LAN On , Then we have to go through ARP Find the hardware address of a router on this LAN , Then give the packet to the router , Forwarded by the router to the next network , The rest of the work is left to another network
4.6.3 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol,DHCP)
Dynamic host configuration protocol is used to dynamically allocate IP Address , It provides a plug and play networking mechanism , This mechanism allows a computer to join a new network and acquire IP Address without manual participation .DHCP Application layer protocol , It is based on UDP(User Datagram Protocol) User datagram protocol .
DHCP How it works :
- Using customer / Server mode . need IP When the host of the address is started, it will send DHCP Server broadcast discovery message , Then the host becomes DHCP Customer
- All hosts on the local network can receive this broadcast message , But then DHCP The server answers this message .
- DHCP The server first looks up the configuration information of the computer in its database . If you find , Then return the found information .
- If not found, from the server's IP Take an address from the address pool and assign it to the computer .
4.6.4 Internet control message protocol (Internet Control Message Protocol,ICMP)
ICMP Used in IP host 、 Routing control messages between routers . Control message means that the network is not accessible 、 Whether the host can reach 、 Whether the route is available and so on . Although these control messages do not transmit user data , But it plays an important role in the transmission of user data .



4.7 IPV6((Internet Protocol version 6,IPv6)
IPv6 It's the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Designed to replace IPv4 The next generation of IP agreement , The number of addresses is said to be able to make an address for every grain of sand in the world . because IPv4 The biggest problem is the lack of network address resources , Seriously restricted the application and development of the Internet .IPv6 Use , It can not only solve the problem of the number of network address resources , It also solves the barrier of connecting various access devices to the Internet .
4.7.1 IPV6 Datagram format

4.7.2 IPV6 And IPV4

4.7.3 IPV6 Address representation

IPV6 The destination address of a datagram can be one of the following three basic types :
- unicast : Unicast is the traditional point-to-point communication .
- multicast : Point to multipoint communication , Packets are delivered to each computer of a group of computers .
- Ren Bo : The destination of anycast is a set of computers , But the packets are delivered to only one of the computers , Usually the nearest one .
4.7.4 IPV6 towards IPV4 The strategy of transition

4.8 Routing algorithm and protocol
4.8.1 Classification of routing algorithms

4.8.2 Autonomous systems (Autonomous System,AS)
Autonomous systems : A group of routers managed by a single technology , These routers use a AS Internal routing protocols and common metrics are used to determine the packets in the network AS Routing within , It also uses a AS A routing protocol is used to determine the packet in AS The route between .
Internal gateway protocol (Interior Gateway Protocol,IGP)
The internal gateway protocol is the routing protocol used in an autonomous system , It has nothing to do with what routers other autonomous systems in the Internet choose .—RIP、OSPF
External gateway protocol (External Gateway Protocol,EGP)
The source and destination stations are in different autonomous systems , When a datagram reaches the boundary of an autonomous system ( Two AS Different... May be used IGP) You need to use EGP Transfer routing information to another autonomous system .
4.8.3 RIP agreement (Routing Information Protocol, Routing information protocol ) And distance vector algorithm
The routing information protocol is an internal gateway protocol (IGP) The first protocol used in .RIP It is a distributed routing protocol based on distance vector , Its biggest advantage is simplicity .
RIP Regulations
- Each router in the network maintains a distance record from itself to each other destination network ( So this is a set of distances , It's called the distance vector ).
- Distance is also called hop count (Hop Count) Specify the distance from a router to a directly connected network ( Hops ) by 1. Every time you go through a router , distance ( Hops ) Add 1.
- RIP It is considered that a good route is one that has fewer hops through the router , That is, the path with less hops is preferred .
- RIP Allow a path to contain at most 15 Router ( At most 15 jump ). When the distance is equal to 16 when , It means that the network is unreachable . thus it can be seen RIP Only for the small Internet . Loop may occur in distance vector routing , The purpose of specifying the maximum number of hops on the path is to prevent datagrams from circulating on the loop , Reduce the possibility of network congestion .
- RIP The default for each 30 Broadcast once a second RIP Route update information , In order to automatically establish and maintain the routing table .
- stay RIP Subnet mask is not supported in RIP radio broadcast , therefore RIP The subnet mask must be the same for each network in the .
RIP characteristic
- Only exchange information with neighboring routers .
- The information exchanged by the router is all the information known by the current router , That is, its own routing table .
- Exchange routing information at fixed time intervals .
Distance vector algorithm
Each routing table entry has three key data < Destination network N , distance d, Next hop router address X> For the data sent by each adjacent router RIP message , Perform the following steps :
The address is X From neighboring routers of RIP message , Modify all items in this message first — Change the addresses in the next field to X, And the values of all distance fields +1.
For the modified RIP Each item in the message performs the following steps
When there is no destination network in the original routing table N when , Add this item to the routing table .
When there is a destination network in the original routing table N, And the address of the next router is X when , Replace the items in the original routing table with the received items .
When there is a destination network in the original routing table N, And the address of the next router is not X yes , If the project distance is received d Less than the distance in the routing table , Then replace with the received ; Otherwise, do nothing


RIP Advantages and disadvantages
The advantage is to realize 、 Low overhead 、 Fast convergence process .
shortcoming :
- RIP Limited network size , Can use the maximum 15.
- The complete routing table in the router is exchanged between routers , Therefore, the larger the network size, the greater the overhead .
- When the network fails , There will be slow convergence , Make the update time longer .
RIP It's the application layer protocol , It USES UDP Transmit data ( port 520).RIP The chosen path is not necessarily the shortest , But it must be the path with the least routers .
4.8.4 OSPF agreement (Open Shortest Path First, Open shortest path first protocol )
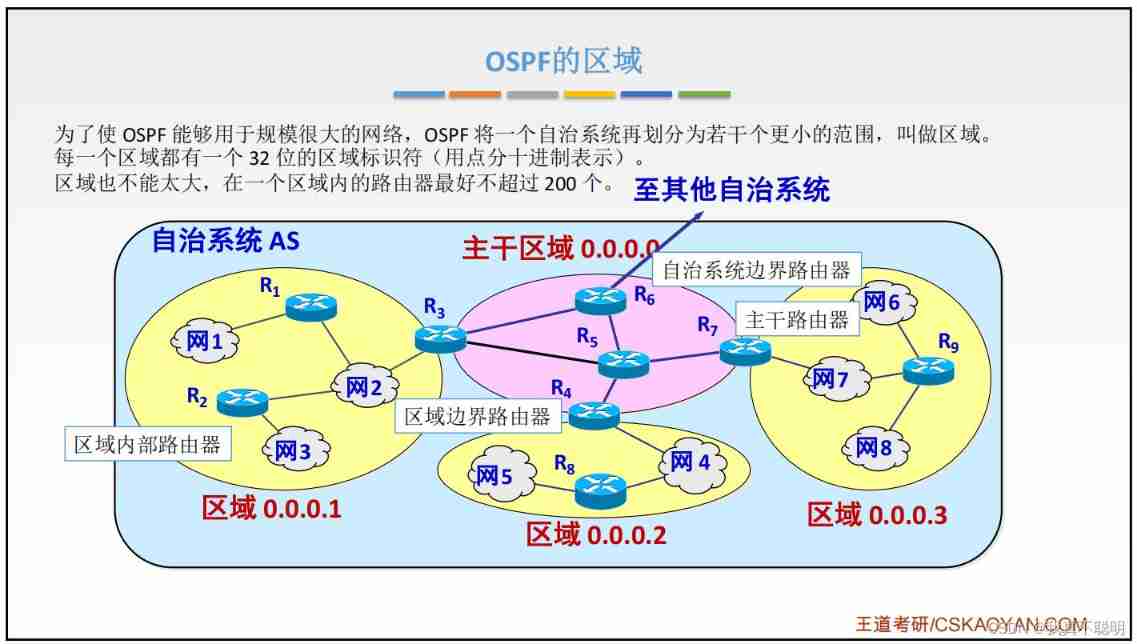
OSPF Routing protocol is a typical link state (Link-state) The routing protocol of , It is generally used in the same routing domain . ad locum , A routing domain is an autonomous system (Autonomous System), It refers to a group of networks that exchange routing information with each other through a unified routing protocol . In this AS in , be-all OSPF Routers all maintain the same description of this AS Structured database , The database stores the status information of the corresponding links in the routing domain ,OSPF It is through this database that the router calculates its OSPF Routing table .
Link state routing algorithm

OSPF Area
OSPF characteristic
1. every other 30min, To refresh the link state in the database once .
2. Because the link state of a router only involves the connection state with adjacent routers , So it has nothing to do with the size of the Internet as a whole . because
When the Internet is very large ,OSPF The protocol is better than the distance vector protocol RIP Much better .
3.OSPF There is no problem of slow transmission of bad news , It converges very fast .
4.8.5 BGP agreement (Border Gateway Protocol, Border gateway protocol )
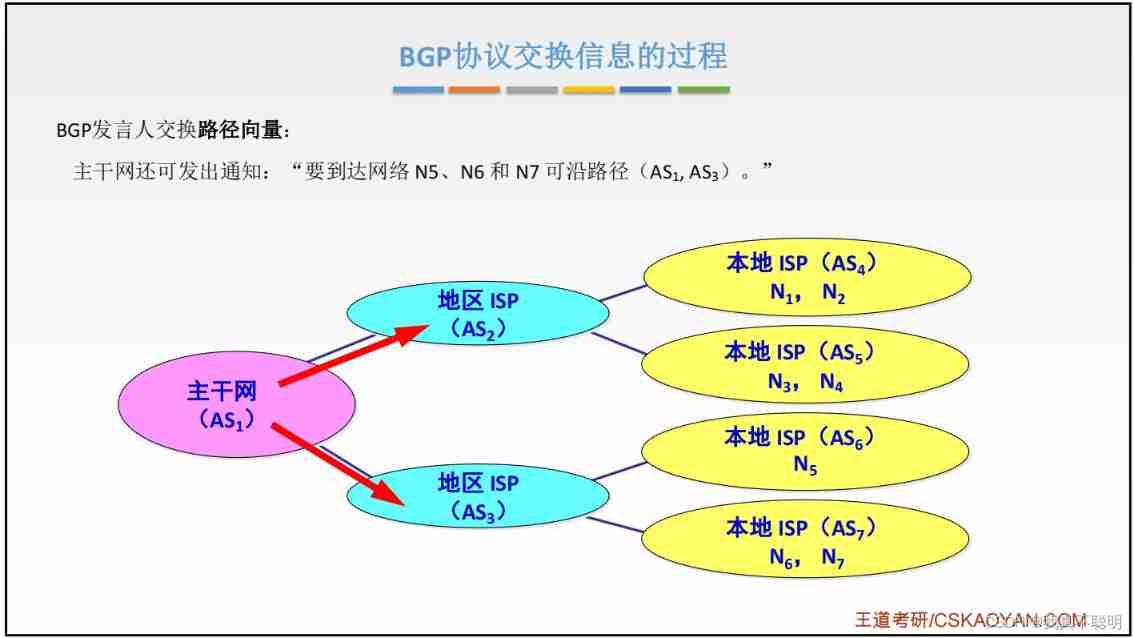
BGP It's a protocol to exchange routing information between routers of different autonomous systems , Is an external gateway protocol . The border gateway protocol is commonly used in the Internet gateway Between . The routing table contains a list of known routers , The address that the router can reach and the path and hops of each router .
BGP working principle
- Every AS The administrator of selected at least one router as the AS Of BGP Spokesman .
- One BGP Speakers and others BGP The speaker wants to exchange routing information .
- establish TCP Connect ,( so BGP The message is sent through TCP The transfer of , in other words BGP When the message TCP The data part of the message ) Then connect the switch again BGP The message is thus established BGP conversation , recycling BGP Session exchange routing information .
- When all BGP After speakers exchange network accessibility information with each other , various BGP The speaker can find a better route to each autonomous system .
Every BGP The speaker must run BGP Outside , You must also run the AS The internal gateway protocol used (OSPF、RIP)
BGP Workflow


BGP Message format

BGP characteristic
BGP Support CIDR, therefore BGP The destination network prefix should be included in the routing table 、 Next hop router , And each autonomous system sequence to reach the destination network . stay BGP Just running ,BGP The neighboring stations are exchanging the whole BGP Routing table . But in the future, you only need to update the changed part when it changes . such It is good for saving network bandwidth and reducing the processing cost of routers .
BGP-4 message
BGP-4 It provides a new mechanism to support classless inter domain routing . These mechanisms include broadcasting that supports network prefixes 、 Cancel BGP In the network “ class ” The concept of .BGP-4 A mechanism is also introduced to support route aggregation , Include AS Aggregation of paths . These changes provide support for the proposed hypernetwork scheme .
4.8.6 Comparison of three protocols

4.9 IP Multicast
IP Multicast (IP multicasting) It is an abstraction of hardware multicast , It's about standards IP Extension of network layer protocol . It works by using specific IP Multicast address , According to the principle of maximum delivery , take IP Packets are transmitted to a multicast group (multicast group) Set of hosts . Its basic method is : When a person sends data to a group of people , It doesn't have to send data to everyone , Just send the data to a specific reservation group address , All participants in this group can receive this data . So for the sender , Data can be sent to all recipients only once , It greatly reduces the load of the network and the burden of the sender .

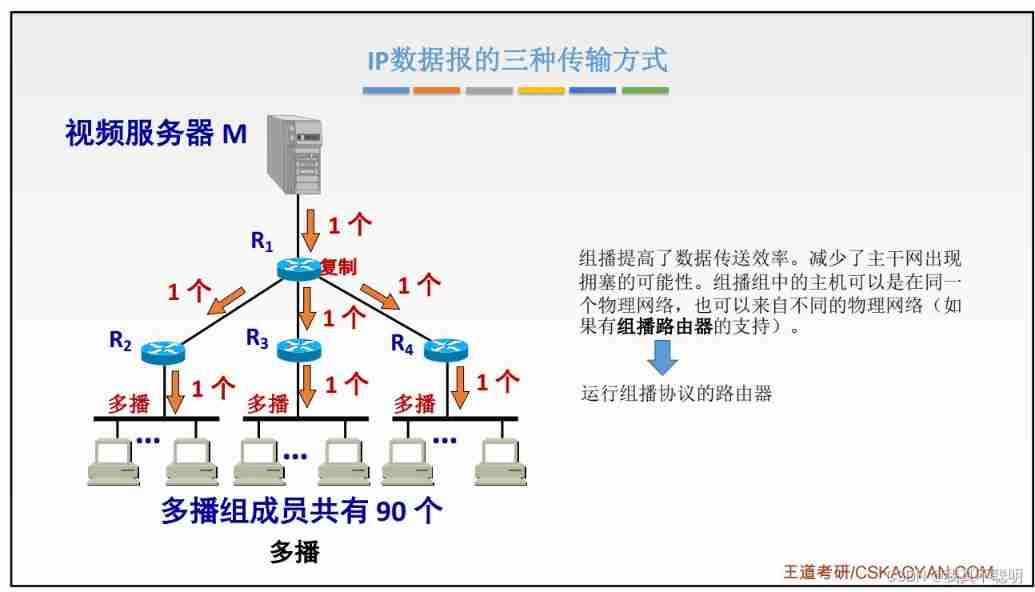

4.9.1 Hardware multicast
Hardware multicast (multicasting) It is a form of multi-point delivery , It uses hardware technology , Communicate by using a large number of multicast addresses . When a certain When the group machine needs to communicate , Select a multicast address , And configure the corresponding network interface hardware , Identify the multicast address , Thus, the multicast address is received A copy of the group on .
4.9.2 IGMP agreement (Internet Group Management Protocol, Internet Group Management Protocol )
If the router knows the information of multicast group members , Need to use IGMP agreement , The multicast router connected to the LAN must work with other multicast routers on the Internet , In order to transmit multicast datagrams to all group members at the least cost , This requires the use of multicast routing protocol .
IGMP It is not a protocol to manage all multicast group members in the Internet .IGMP I do not know! IP The number of members in the multicast group , I don't know which networks these members are distributed on .IGMP Let link to local LAN The multicast router on the LAN knows whether there are hosts participating in or launching a multicast group .
IGMP Workflow
IGMP Shall be deemed TCP/IP Part of , Its work can be divided into two stages .
4.9.3 Multicast routing algorithm
Multicast routing is actually to find the multicast forwarding tree with the source host as the root node , Each packet is transmitted only once on each link ( That is, the router on the multicast forwarding tree will not receive duplicate multicast datagrams ). Different multicast groups correspond to different multicast forwarding trees ; The same multicast group will have different multicast forwarding trees for different source points .

4.10 Move IP

4.10.1 Move IP Communication process of

4.11 Network layer devices
4.11.1 Composition and function of router
A router is one that has multiple inputs / Dedicated computer for output port , The task is to connect different networks and complete routing forwarding ( Forwarding packet ), In multiple logical networks ( That is, multiple broadcast domains ) A router must be used for interconnection
When the source host and the target host are on the same network , Then you don't need to deliver directly through the router .
When the source host and the target host are not on the same network , Then the router follows the forwarding table ( Routing table ) The indicated route forwards the packet to the next router , This is called indirect delivery .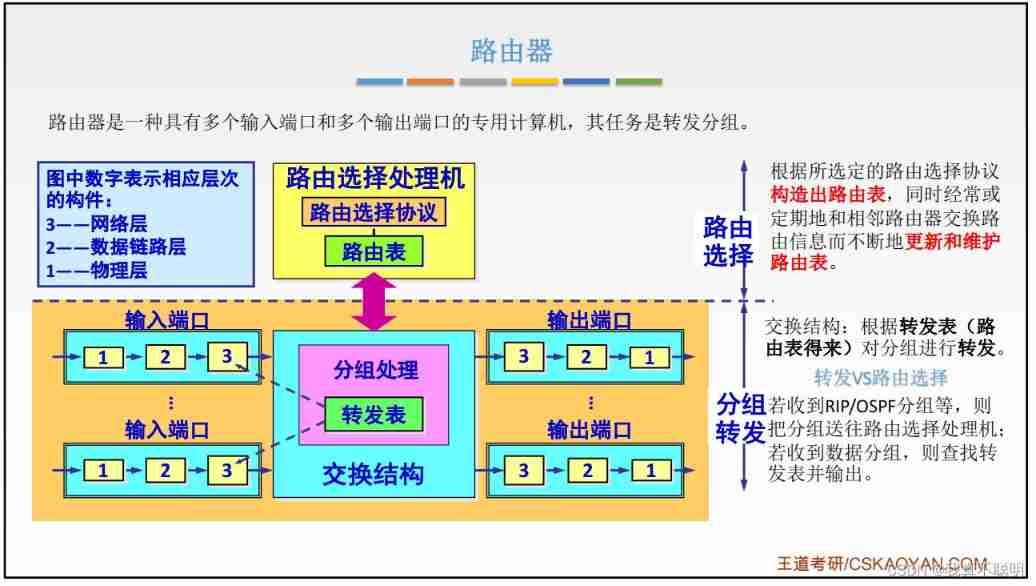
structurally , Router consists of routing and packet forwarding ; It implements the physical layer of the network model 、 Data link layer 、 Network layer so it is a network layer device .
4.11.2 Routing table and routing forwarding

边栏推荐
- Getting started with qt-1-ui
- Swift return button
- Redis学习(3)—— 持久化机制
- Prepare for the golden three silver four, are you ready? Summary of software test interview questions
- Design and implementation of object system in redis
- Unbounded territory won the title of innovative brand of digital culture industry in 2022
- 6. functions
- Add SSL security certificate to web site
- Implementation of queue
- Redis learning (1) -- overview and common commands
猜你喜欢

Async get and post request interface data (add, delete, modify and query pages)

Master the basic usage of SQLite3

Redisson distributed lock design from a bug

Write a compile time annotation

Automation operation and maintenance 1 - installation and deployment of ansible

Set up ZABBIX monitoring and email alarm

Summary of the latest remote deployment O & M tools

Use map set or list set to store list set

MySQL - built in functions

Mr. Ali taught you how to use JMeter for pressure test (detailed drawing)
随机推荐
Automatic operation and maintenance 4 - variables and encryption in ansible
Alibaba cloud log service is available in Net project
module ‘selenium. webdriver‘ has no attribute ‘PhantomJS‘
Swift return button
MySQL - user management
2. data type
CSDN's test teacher teaches JMeter to generate stress test reports
What is software testing?
The new plan for national treasures - the exclusive digital collection of the four museums is coming!
Imitation B station web, app, background
Understand the use of protobuf serialization protocol
Must the database primary key be self incremented? What scenarios do not suggest self augmentation?
MySQL - index
MySQL - built in functions
Installation of oracle19c under alicloud lightweight application server linux-centos7
Blazer page element authorization -- use of the authorizeview component
PostgreSQL query by date range
Write a code hot deployment
Oracle client11 and pl/sql12 installation
[googolu] takeout rebate system - business domain name of KFC configuration applet