当前位置:网站首页>Master the basic usage of SQLite3
Master the basic usage of SQLite3
2022-06-21 13:19:00 【m0_ fifty-four million eight hundred and fifty thousand four hu】
Catalog
??? 1. Commonly used instructions
??? 4.? Import / Export database ?
??? 13.? Delete the data in the record table
One 、 Basic grammar
1. Commonly used instructions
.open filename -- Open file
-- annotation
.show -- Show SQLite The default setting of the command prompt
.q -- sign out
.databases -- Display database ( notes : Show open databases )
.help -- help
.dump -- Import export database
.tables -- See the table
2. data type
Storage type
describe
NULL
Null value
int
plastic
text
A text string
blob
One blob data
integer
A signed integer , According to the size of the value stored in 1、2
、3、4、6 or 8 In bytes
real
Value is a floating point value , Stored as 8 Floating point number of bytes
…
…
3. Create database
.open test.db -- Create without
sqlite3 DatabaseName.db
The above command will create a file in the current directory testDB.db. The file will be deleted SQLite The engine acts as a database . If you have noticed sqlite3 Command after successfully creating the database file , A will be provided sqlite> Prompt .
.databases The command is used to check whether it is in the database list .
.open operation

4. Import / Export database
sqlite3 test.db .dump > filename -- export
sqlite3 test.db < filename -- Import
The above transformation flows through testDB.db The contents of the database to SQLite The statement of , And dump it to ASCII text file testDB.sql in . You can generate from the in a simple way testDB.sql recovery , As shown below I'll delete it testDB.db after :

5. Create table
-- Be careful , You can only operate when you open the database
CREATE TABLE database_name.table_name(
column1 datatype PRIMARY KEY(one or more columns),
column2 datatype,
column3 datatype,
.....
columnN datatype,
);
CREATE TABLE Is a keyword that tells the database system to create a new table .CREATE TABLE Statement followed by the unique name or ID of the table . You can also choose to specify with table_name Of database_name.

As shown in the figure above , We created COMPANY DEPARTMENT Two tables . among ID A primary key ,NOT NULL The constraint of indicates that these fields cannot be... When creating records in the table NULL.
6. See table details
.schema -- Be careful : Only when the database is opened

7. Delete table
DROP TABLE database_name.table_name;
 Above , Deleted the name DEPARTMENT Table of
Above , Deleted the name DEPARTMENT Table of
8. insert data
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME [(column1, column2, column3,...columnN)]
VALUES (value1, value2, value3,...valueN);
ad locum ,column1, column2,…columnN Is the name of the column in the table to insert data .
If you want to add values to all columns in the table , You may also not need to be in SQLite Specify the column name... In the query . But make sure that the values are in the same order as they are listed in the table .SQLite Of INSERT INTO The grammar is as follows :
INSERT INTO TABLE_NAME VALUES (value1,value2,value3,...valueN);
Now? , I have created COMPANY surface , as follows
CREATE TABLE COMPANY(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
NAME TEXT NOT NULL,
AGE INT NOT NULL,
ADDRESS CHAR(50),
SALARY REAL
);
Now? , The following statement will be in COMPANY Create six records in the table :
INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY)
VALUES (1, 'Paul', 32, 'California', 20000.00 );
INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY)
VALUES (2, 'Allen', 25, 'Texas', 15000.00 );
INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY)
VALUES (3, 'Teddy', 23, 'Norway', 20000.00 );
INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY)
VALUES (4, 'Mark', 25, 'Rich-Mond ', 65000.00 );
INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY)
VALUES (5, 'David', 27, 'Texas', 85000.00 );
INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY)
VALUES (6, 'Kim', 22, 'South-Hall', 45000.00 );
The output is as follows :

We can also use the second grammar in COMPANY Create a record in the table , As shown below :
INSERT INTO COMPANY VALUES (7, 'James', 24, 'Houston', 10000.00 );
The output is as follows :

9. Format output
.header on
.mode column
.timer on -- Turn on CPU Timer
SELECT * FROM table_name; -- Display table table_name
Unformatted output

Format output
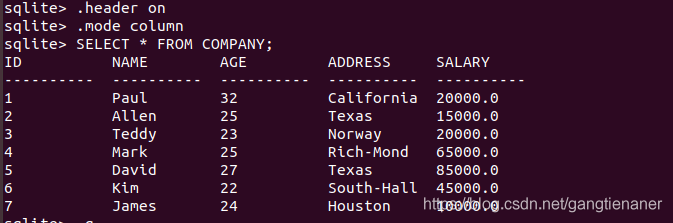
10. Output table
Full output
.header on
.mode column
SELECT * FROM COMPANY;

Output specified column
.header on
.mode column
SELECT ID, NAME, SALARY FROM COMPANY; -- Only the output ID, NAME and SALARY The three column

Set the width of the output column
.width num1,num1,num3....
SELECT * FROM COMPANY;
below .width The command sets the width of the first column to 10, The width of the second column is 20, The width of the third column is 10. The output is as follows :

11. Operator
sqlite The operator is mainly used for SQLite Of the statement WHERE Clause , Such as comparison and arithmetic operation .
Operator is used to specify SQLite The condition in the statement , And connect multiple conditions in the statement .
Arithmetic operator :
Operator
describe
example
Add - Add the values on both sides of the operator
a + b Will get 30
-
Subtraction - Subtract the right operand from the left operand
a - b Will get -10
*
Multiplication - Multiply the values on both sides of the operator
a * b Will get 200
/
division - Left operand divided by right operand
b / a Will get 2
%
modulus - The remainder of the left operand divided by the right operand
b % a will give 0
Comparison operator
Operator
describe
example
==
Check that the values of the two operands are equal , If they are equal then the condition is true .
(a == b) Not true .
=
Check that the values of the two operands are equal , If they are equal then the condition is true .
(a = b) Not true .
!=
Check that the values of the two operands are equal , If they are not equal then the condition is true .
(a != b) It's true .
<>
Check that the values of the two operands are equal , If they are not equal then the condition is true .
(a <> b) It's true .
>
Check whether the value of the left operand is greater than the value of the right operand , If so, the condition is true .
(a > b) Not true .
<
Check whether the value of the left operand is less than the value of the right operand , If so, the condition is true .
(a < b) It's true .
>=
Check whether the value of the left operand is greater than or equal to the value of the right operand , If so, the condition is true .
(a >= b) Not true .
<=
Check that the value of the left operand is less than or equal to the value of the right operand , If so, the condition is true .
(a <= b) It's true .
!<
Check whether the value of the left operand is not less than the value of the right operand , If so, the condition is true .
(a !< b) For false .
!>
Check that the value of the left operand is not greater than the value of the right operand , If so, the condition is true .
(a !> b) It's true .
Logical operators
Operator
describe
AND
AND Operator is allowed in a SQL Of the statement WHERE The existence of multiple conditions in the clause .
BETWEEN
BETWEEN Operator is used to search for a value in a series of values within a given range of minimum and maximum values .
EXISTS
EXISTS Operator is used to search for the existence of rows in the specified table that meet certain conditions .
IN
IN Operator is used to compare a value with a series of values in a specified list .
NOT IN
IN The opposite of operator , Used to compare a value with a value that is not in a series of specified lists .
LIKE
LIKE Operator is used to compare a value with a similar value using the wildcard operator .
GLOB
GLOB Operator is used to compare a value with a similar value using the wildcard operator .GLOB And LIKE The difference is , It's case sensitive .
NOT
NOT The operator is the opposite of the logical operator used . such as NOT EXISTS、NOT BETWEEN、NOT IN, wait . It is a negative operator .
OR
OR Operator is used to combine a SQL Of the statement WHERE Multiple conditions in clause .
IS NULL
NULL Operator is used to associate a value with NULL Value comparison .
IS
IS Operators and = be similar .
IS NOT
IS NOT Operators and != be similar .
||
Connect two different strings , Get a new string .
UNIQUE
UNIQUE Operator to search each row in the specified table , Make sure it's unique ( No repetition ).
An operator
p
q
p & q
p | q
0
0
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
The following is a direct example
I have a COMPANY The table is as follows :
ID NAME AGE ADDRESS SALARY
---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------
1 Paul 32 California 20000.0
2 Allen 25 Texas 15000.0
3 Teddy 23 Norway 20000.0
4 Mark 25 Rich-Mond 65000.0
5 David 27 Texas 85000.0
6 Kim 22 South-Hall 45000.0
7 James 24 Houston 10000.0
use SELECT List SALARY Greater than 50,000.00 All records :
SELECT * FROM COMPANY WHERE SALARY > 50000;
The output is as follows :

use SELECT List SALARY Equal to all records of :
SELECT * FROM COMPANY WHERE SALARY = 20000;
The output is as follows :

use SELECT List AGE Greater than or equal to 25 And SALARY Greater than or equal to 65000.00 All records :
SELECT * FROM COMPANY WHERE AGE >= 25 AND SALARY >= 65000;
The output is as follows :

12.where Clause
SQLite Of WHERE Clause is used to specify the conditions for getting data from one or more tables . If a given condition is satisfied , It's true (true) when , Returns a specific value from the table . You can use WHERE Clause to filter records , Just get the records you need .WHERE Clause can be used not only in SELECT In the sentence , It can also be used in UPDATE、DELETE In the sentence , wait . Use case reference operators .
13. Delete the data in the record table
SQLite in , Delete record table data as DELETE sentence , We can use it with WHERE Clause DELETE.
The grammar is as follows :
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE [condition];
We have the following record sheet :

Delete ID by 7 The column of :
DELETE FROM COMPANY WHERE ID = 7;
Output the result again :

14.update sentence
SQLite Of UPDATE Queries are used to modify existing records in a table . You can use the WHERE Clause UPDATE Query to update the selected row , Otherwise, all the lines will be updated .
grammar :
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2...., columnN = valueN
WHERE [condition];
notes : These three lines are actually the same line .
Now I have the following data table :

hold COMPANY In the table ID by 6 The customer address of is changed to Texas:
UPDATE COMPANY SET ADDRESS = 'Texas' WHERE ID = 6;
Modify the result :

If you want to modify COMPANY In the table ADDRESS and SALARY All values for column , You don't need to use it WHERE Clause ,UPDATE Enquiries are as follows :
UPDATE COMPANY SET ADDRESS = 'Texas', SALARY = 20000.00;
Modify the result :

Two 、C/C++ operation
1. Interface API
The following interfaces can meet our basic needs , Need to learn more about operation , We can refer to the official documents .
Serial number
API & describe
1
sqlite3_open(const char *filename, sqlite3 **ppDb)
This routine opens a pointer to SQLite Connection to database files , Returns a for other SQLite The database connection object of the program .
If filename Parameter is NULL or ‘:memory:’, that sqlite3_open() Will be in RAM Create an in memory database , This will only happen session For the duration of .
If the filename filename Not for NULL, that sqlite3_open() This parameter value will be used to try to open the database file . If the file with that name does not exist ,sqlite3_open() A new database file with that name will be created and opened .
2
sqlite3_exec(sqlite3*, const char *sql, sqlite_callback, void *data, char **errmsg)
This routine provides an execution SQL Shortcut to command ,SQL The order was given by sql Parameters are provided , There can be more than one SQL Command composition .
ad locum , The first parameter sqlite3 Is an open database object ,sqlite_callback It's a callback ,data As its first parameter ,errmsg Will be returned to get any errors generated by the program .
sqlite3_exec() The program is parsed and executed by sql Every command given by the parameter , Until the end of the string or an error is encountered .
3
sqlite3_close(sqlite3*)
This routine calls... Before closing sqlite3_open() Open database connection . All connection related statements should be completed before the connection is closed .
If there are still queries that have not been completed ,sqlite3_close() Will return SQLITE_BUSY Disable closing error message .
2. Connect to database
Below C The code snippet shows how to connect to an existing database . If the database doesn't exist , Then it will be created , Finally, a database object will be returned .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sqlite3.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
sqlite3 *db;
char *zErrMsg = 0;
int rc;
rc = sqlite3_open("test.db", &db);
if( rc ){
fprintf(stderr, "Can't open database: %s
", sqlite3_errmsg(db));
exit(0);
}else{
fprintf(stderr, "Opened database successfully
");
}
sqlite3_close(db);
}
Compile command
gcc lianjie.c -l sqlite3
Running results

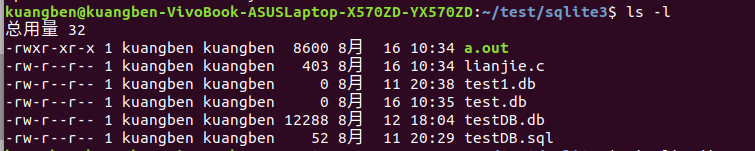
The input terminal ls -l Command found more than one test.db file , Pictured :
3. Create table
C Creating a language table is similar to creating a terminal , Only the command is given by sqlite3_exec() Functional sql Parameters of the incoming . The format is as follows :
sql = "CREATE TABLE COMPANY("
"ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,"
"NAME TEXT NOT NULL,"
"AGE INT NOT NULL,"
"ADDRESS CHAR(50),"
"SALARY REAL );";
Sample code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sqlite3.h>
static int callback(void *NotUsed, int argc, char **argv, char **azColName){
int i;
for(i=0; i<argc; i++){
printf("%s = %s
", azColName[i], argv[i] ? argv[i] : "NULL");
}
printf("
");
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
sqlite3 *db;
char *zErrMsg = 0;
int rc;
char *sql;
/* Open database */
rc = sqlite3_open("test.db", &db);
if( rc ){
fprintf(stderr, "Can't open database: %s
", sqlite3_errmsg(db));
exit(0);
}else{
fprintf(stdout, "Opened database successfully
");
}
/* Create SQL statement */
sql = "CREATE TABLE COMPANY("
"ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,"
"NAME TEXT NOT NULL,"
"AGE INT NOT NULL,"
"ADDRESS CHAR(50),"
"SALARY REAL );";
/* Execute SQL statement */
rc = sqlite3_exec(db, sql, callback, 0, &zErrMsg);
if( rc != SQLITE_OK ){
fprintf(stderr, "SQL error: %s
", zErrMsg);
sqlite3_free(zErrMsg);
}else{
fprintf(stdout, "Table created successfully
");
}
sqlite3_close(db);
return 0;
}
Output results :

Again ls -l:

We can see ,test.db The file size is significantly larger .
4. insert data
Similar to creating a table ,sql The parameter is set to :
sql = "INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY) "
"VALUES (1, 'Paul', 32, 'California', 20000.00 ); "
"INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY) "
"VALUES (2, 'Allen', 25, 'Texas', 15000.00 ); "
"INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY)"
"VALUES (3, 'Teddy', 23, 'Norway', 20000.00 );"
"INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY)"
"VALUES (4, 'Mark', 25, 'Rich-Mond ', 65000.00 );";
Sample code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sqlite3.h>
static int callback(void *NotUsed, int argc, char **argv, char **azColName){
int i;
for(i=0; i<argc; i++){
printf("%s = %s
", azColName[i], argv[i] ? argv[i] : "NULL");
}
printf("
");
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
sqlite3 *db;
char *zErrMsg = 0;
int rc;
char *sql;
/* Open database */
rc = sqlite3_open("test.db", &db);
if( rc ){
fprintf(stderr, "Can't open database: %s
", sqlite3_errmsg(db));
exit(0);
}else{
fprintf(stderr, "Opened database successfully
");
}
/* Create SQL statement */
sql = "INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY) "
"VALUES (1, 'Paul', 32, 'California', 20000.00 ); "
"INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY) "
"VALUES (2, 'Allen', 25, 'Texas', 15000.00 ); "
"INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY)"
"VALUES (3, 'Teddy', 23, 'Norway', 20000.00 );"
"INSERT INTO COMPANY (ID,NAME,AGE,ADDRESS,SALARY)"
"VALUES (4, 'Mark', 25, 'Rich-Mond ', 65000.00 );";
/* Execute SQL statement */
rc = sqlite3_exec(db, sql, callback, 0, &zErrMsg);
if( rc != SQLITE_OK ){
fprintf(stderr, "SQL error: %s
", zErrMsg);
sqlite3_free(zErrMsg);
}else{
fprintf(stdout, "Records created successfully
");
}
sqlite3_close(db);
return 0;
}
Output results :

5. Look up the table
sqlite3_exec() Provides us with a callback function , The statement is as follows :
typedef int (*sqlite3_callback)(
void*, /* Data provided in the 4th argument of sqlite3_exec() */
int, /* The number of columns in row */
char**, /* An array of strings representing fields in the row */
char** /* An array of strings representing column names */
);
The first parameter : That is, the data passed in by the fourth parameter
The second parameter : The number of columns in a row
The third parameter : An array of strings representing fields in a row , That is, the data in each row
Fourth parameter : An array of strings representing column names , Set when creating the linked list
Execute the process : Look up the table , Whether there is any qualified data . Yes , perform sqlite3_callback() function ; No, , sign out
That's it , Let's take an example :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sqlite3.h>
static int callback(void *data, int argc, char **argv, char **azColName){
int i;
fprintf(stderr, "%s: ", (const char*)data);
for(i=0; i<argc; i++){
printf("%s = %s
", azColName[i], argv[i] ? argv[i] : "NULL");
}
printf("
");
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
sqlite3 *db;
char *zErrMsg = 0;
int rc;
char *sql;
const char* data = "Callback function called";
/* Open database */
rc = sqlite3_open("test.db", &db);
if( rc ){
fprintf(stderr, "Can't open database: %s
", sqlite3_errmsg(db));
exit(0);
}else{
fprintf(stderr, "Opened database successfully
");
}
/* Create SQL statement */
sql = "SELECT * from COMPANY";
/* Execute SQL statement */
rc = sqlite3_exec(db, sql, callback, (void*)data, &zErrMsg);
if( rc != SQLITE_OK ){
fprintf(stderr, "SQL error: %s
", zErrMsg);
sqlite3_free(zErrMsg);
}else{
fprintf(stdout, "Operation done successfully
");
}
sqlite3_close(db);
return 0;
}
The above program shows how to create from the previous COMPANY Get and display records in the table , The output is as follows :

I do not specify the query conditions here , Means to query all .
6. Data deletion
sql Parameter setting :
sql = "DELETE from COMPANY where ID=2; " \ Delete ID be equal to 2 The line of
"SELECT * from COMPANY"; \ Display table
The difference between this and the above is that there is one more command , The surface of the sql Parameters can consist of multiple commands .
Sample code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sqlite3.h>
static int callback(void *data, int argc, char **argv, char **azColName){
int i;
fprintf(stderr, "%s: ", (const char*)data);
for(i=0; i<argc; i++){
printf("%s = %s
", azColName[i], argv[i] ? argv[i] : "NULL");
}
printf("
");
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
sqlite3 *db;
char *zErrMsg = 0;
int rc;
char *sql;
const char* data = "Callback function called";
/* Open database */
rc = sqlite3_open("test.db", &db);
if( rc ){
fprintf(stderr, "Can't open database: %s
", sqlite3_errmsg(db));
exit(0);
}else{
fprintf(stderr, "Opened database successfully
");
}
/* Create merged SQL statement */
sql = "DELETE from COMPANY where ID=2; "
"SELECT * from COMPANY";
/* Execute SQL statement */
rc = sqlite3_exec(db, sql, callback, (void*)data, &zErrMsg);
if( rc != SQLITE_OK ){
fprintf(stderr, "SQL error: %s
", zErrMsg);
sqlite3_free(zErrMsg);
}else{
fprintf(stdout, "Operation done successfully
");
}
sqlite3_close(db);
return 0;
}
Output :

7.UPDATE operation
The operation sample :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sqlite3.h>
static int callback(void *data, int argc, char **argv, char **azColName){
int i;
fprintf(stderr, "%s: ", (const char*)data);
for(i=0; i<argc; i++){
printf("%s = %s
", azColName[i], argv[i] ? argv[i] : "NULL");
}
printf("
");
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
sqlite3 *db;
char *zErrMsg = 0;
int rc;
char *sql;
const char* data = "Callback function called";
/* Open database */
rc = sqlite3_open("test.db", &db);
if( rc ){
fprintf(stderr, "Can't open database: %s
", sqlite3_errmsg(db));
exit(0);
}else{
fprintf(stderr, "Opened database successfully
");
}
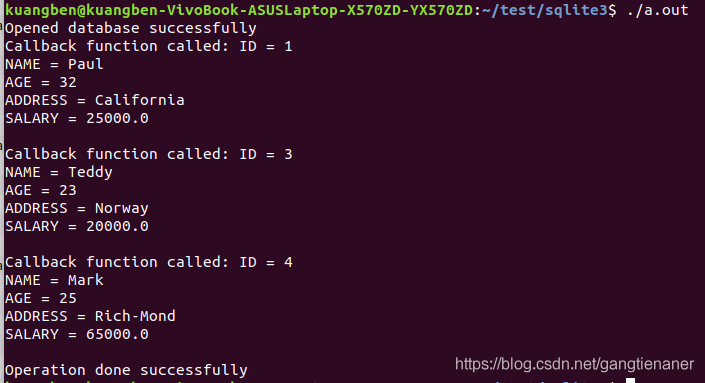
/* Create merged SQL statement */
sql = "UPDATE COMPANY set SALARY = 25000.00 where ID=1; "
"SELECT * from COMPANY";
/* Execute SQL statement */
rc = sqlite3_exec(db, sql, callback, (void*)data, &zErrMsg);
if( rc != SQLITE_OK ){
fprintf(stderr, "SQL error: %s
", zErrMsg);
sqlite3_free(zErrMsg);
}else{
fprintf(stdout, "Operation done successfully
");
}
sqlite3_close(db);
return 0;
}
Output results :
3、 ... and : Conclusion
Now? , About sqlite3 I have finished the basic usage of , If there is something wrong, please point out .
边栏推荐
- Kubernetes' fast practice and core principle analysis
- 百问百答第43期:应用性能探针监测原理-PHP探针
- 不止于ZeRO:BMTrain技术原理浅析
- What do you mean by concurrency, concurrency, and high concurrency?
- Summary of the latest remote deployment O & M tools
- 实践 DevOps 时,可能面临的六大挑战
- 小程序直播互动功能运行在App里?
- 用时间戳优化 TCP 实践
- 咨询:微证券是什么证券公司,开户安全吗?
- Heat mapping using Seaborn
猜你喜欢

Reading notes on how to connect the Internet ADSL
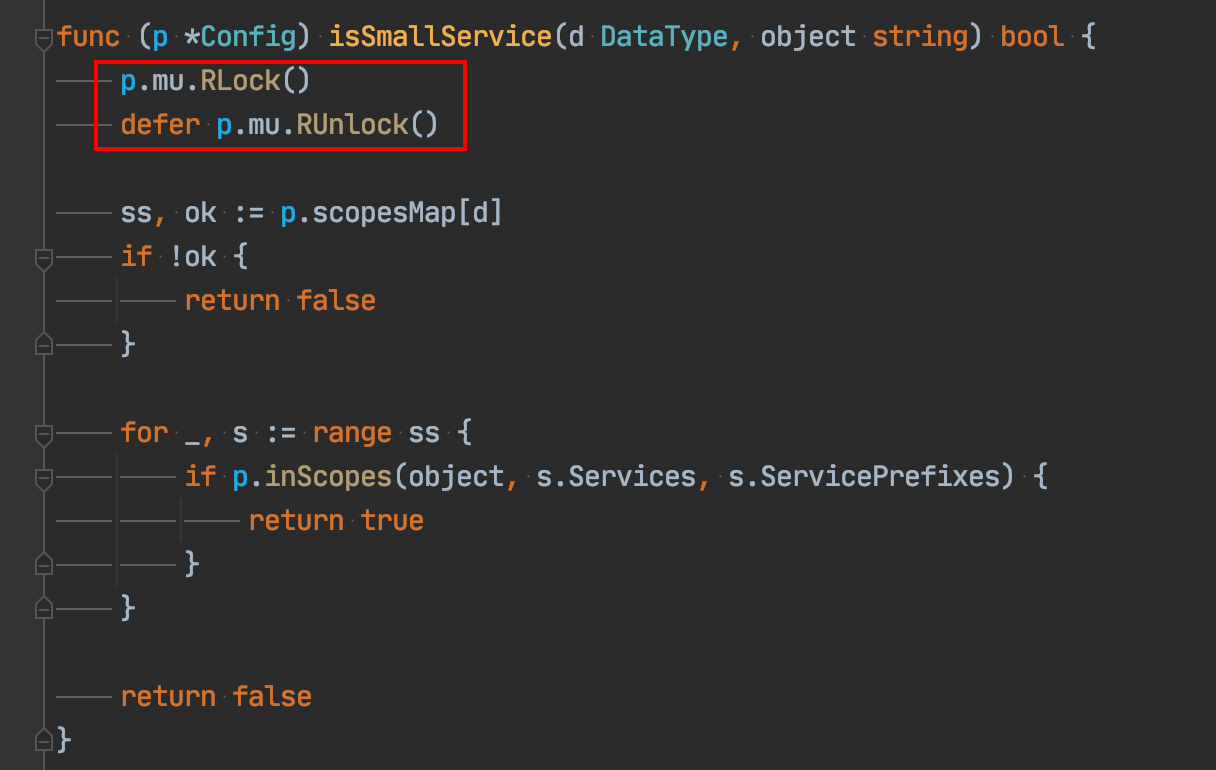
Isn't this another go bug?

塔米狗项目解读:济宁华源项目管理有限公司34%股权转让

Summary of the latest remote deployment O & M tools

如何编写测试用例

Cvpr2022 | the action sequence verification task was first proposed by X xiaohongshu of Shanghai University of science and technology, which can be applied to multiple scenarios such as scoring of spo

南京大学 静态软件分析(static program analyzes)-- introduction 学习笔记

Huawei cloud releases desktop ide codearts
![[in depth understanding of tcapulusdb technology] tcapulusdb business data backup](/img/74/dcb7cfefd258fa17573c96a6e78323.png)
[in depth understanding of tcapulusdb technology] tcapulusdb business data backup
Analysis on the wallet system architecture of Baidu trading platform
随机推荐
What do you mean by concurrency, concurrency, and high concurrency?
Pingcap was selected as the "voice of customers" of Gartner cloud database in 2022, and won the highest score of "outstanding performer"
Nanjing University static program analyses -- Introduction learning notes
微证券开户正规安全吗,怎么操作开户?
应用配置管理,基础原理分析
Questions and answers No. 43: application performance probe monitoring principle PHP probe
The xdd-plus login prompt on the Qinglong panel is "the current login environment is abnormal. To ensure the security of your account, you cannot log in temporarily. It is recommended to connect the t
分布式事务处理方案大 PK
UVA1203 Argus
处理接口幂等性的两种常见方案
PHP uses grafika to synthesize pictures and generate poster images
Qinglong panel, JD timed task library, script library
[Anxin cup 2019]easy_ web-1
分布式事务,原理简单,写起来全是坑
Distributed transaction processing scheme big PK
[deeply understand tcapulusdb technology] tmonitor system upgrade
Summary of the latest remote deployment O & M tools
Memcached (high performance memory object cache)
SCCM基于已安装的 APP创建客户端集合并定期推送应用更新
不止于ZeRO:BMTrain技术原理浅析

