当前位置:网站首页>Memcached (high performance memory object cache)
Memcached (high performance memory object cache)
2022-06-21 12:58:00 【51CTO】
Case study : High performance memory object cache
Memcached
Skill goal :
understand Memcached The core concept
Will be carried out in Memcached Related deployment operations
Will be carried out in Memcached Primary primary replication operation
Will be carried out in Memcached Service high availability configuration
2.1 case analysis
2.1.1 Case Overview
Memcached It is an open source high-performance distributed memory object caching system , It stores all the data inside
In storage , Because the memory will maintain a huge Hash surface , Therefore, any storage type of data is supported . Many networks
Station use Memcached Improve the speed of website visit , Especially large websites that need to access data frequently .
Memcached Is a typical C/S framework , So you need to build Memcached Server side and Memcached API customer
Home end .Memcached The server side uses C language-written , and Memcached API The client can write in any language
Write , Such as PHP、Python、Perl etc. , And pass Memcached Deal with the Memcached Server side communication .
Typical architectures are shown in the figure 2.1 Shown .
chart 2.1 Memcache Common architecture
When Web The client sends a request to Web Server application , The application will call Memcached API
Client library interface to connect Memcached Server query data . If Web The data requested by the client is in
Memcached The server has been cached , be Memcached The server will return the data to Web client ; otherwise , Will Web Client requests are sent to MySQL database , The database queries and returns the requested data to Memcached as well as Web client , meanwhile Memcached The server will also save the data , Convenient for the next user request .
2.1.2 Case pre knowledge points
1. Data storage method and data expiration method
Memcached It has unique data storage mode and data expiration mode .
1) Data storage mode :Slab Allocation
Slab Allocation That is, allocate memory by group , Assign one at a time Slab, Equivalent to a size of 1M
Page of . then , stay 1M The space is divided into the same size according to the data Chunk, Pictured 2.2 Shown . The method
It can effectively solve the problem of memory fragmentation , But it may also waste memory space .
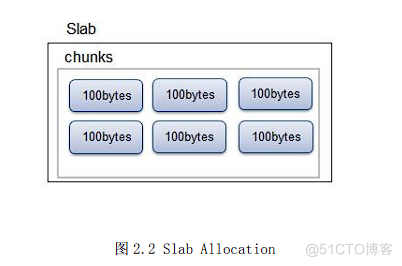
chart 2.2 Slab Allocation 2) Data expiration method :LRU、Laxzy Expiration
LRU and Laxzy Expiration There are two ways to expire data .
Ø LUR When the additional data space is insufficient , Will be based on LRU Eliminate the least recently used records .
Ø Laxzy Expiration That is, the inertia expires , Refers to the use of get View the record time when , So the inspection record is
No has expired .
2. Memcached Caching mechanisms
Cache is the data resident in memory , Can read quickly , and Memcached This is a very
Excellent caching software . When a program writes a cache data request ,Memcached Of API The interface will Key Input path
The algorithm module routes to a service in the cluster , After that by API Interface to communicate with the server , Complete one minute
Cloth cache write , Pictured 2.3 Shown .

chart 2.3 Memcached Caching mechanisms
3. Memcached Distributed
Memcached Distributed deployment mainly depends on Memcached Client side implementation of , Multiple Memcached
The server is independent . How distributed data is stored is determined by the routing algorithm .
When Count According to the To reach customer Household End cheng order library , customer Household End Of count Law Just In accordance with the According to the road from count Law Come on " set Protect save Of
Memcached The server . When reading data , The client selects and based on the same routing algorithm used to save data
When storing data, the same server reads the data , Pictured 2.4 Shown .

chart 2.4 Memcached Distributed
4. Memcached Routing algorithm
1) Mod hash Algorithm
Mod hash The algorithm starts with key do hash The operation results in an integer , Do it again hash Algorithm , according to
Remainder for routing , This algorithm is suitable for most data requirements . But it's not suitable for dynamic environment , Than
If a large number of machines are added or deleted , This will cause a large number of object storage locations to fail .
2) Uniformity hash Algorithm
Uniformity hash The algorithm is suitable for use in dynamic environment . The principle is based on hash The algorithm corresponds to
key Through certain hash After the algorithm is processed, the mapping forms a closed loop with head and tail connected , Then by using and
Like storage hash The algorithm also maps machines into rings , Clockwise calculation stores all objects in
In your nearest machine , Pictured 2.5 Shown .
chart 2.5 Uniformity hash Algorithm
2.1.3 Case environment
This case uses three CentOS 7.3 The system is complete , among : Two are Memcached The server , The other is Ji
On LAMP Architecture Memcached Extended Memcached API client , The specific structure needs to be adjusted according to the needs of the enterprise . The case environment is shown in the table 2-1 Shown .

2.2.1 install Memcached The server
1. install Libevent
Libevent Is a cross platform event processing interface encapsulation , Event access that is compatible with multiple operating systems .
Memcached Installation of depends on Libevent, Therefore, it needs to be completed first Libevent Installation .
[[email protected] ~]# tar -zxvf libevent-2.1.8-stable.tar.gz -C /usr/src/
[[email protected] libevent-2.1.8-stable]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/libevent
[[email protected] libevent-2.1.8-stable]# make && make install
Here we are Libevent Installation completed , Next you can install Memcached.
2. install Memcached
Use the source code Memcached Build and install , During installation, you need to specify Libevent Installation
route .
[[email protected] ~]# tar -zxvf memcached-1.5.1.tar.gz -C /usr/src/ [[email protected] ~]# cd
/usr/src/memcached-1.5.1/
[[email protected] memcached-1.5.1]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/memcached
--with-libevent=/usr/local/libevent
[[email protected] memcached-1.5.1]# make && make install
3. Set up Memcached Service script
Memcached After the server is installed , You can use the... Under the installation directory bin/memcached To start the service
service . however , For more convenient management Memcached, Write scripts to manage Memcached service .
[[email protected] ~]# vim /usr/local/memcached/memcached_service.sh
#!/bin/bash
CMD="/usr/local/memcached/bin/memcached"
start(){
$CMD -d -m 128 -u root
}
stop(){
killall memcached;
}
ACTION=$1
case $ACTION in
'start')
start;;
'stop')
stop;;
'restart')
stop
sleep 2
start;;
*)
echo 'Usage:{start|stop|restart}'
esac Which starts Memcached when ,-d Option to run as a daemon Memcached service ,
-m Is for Memcached Distribute 128M Of memory , It should be adjusted according to the needs of the enterprise ,-u Specify the user account to run .
Then set script permissions , start-up Memcached service .
[[email protected] ~]# chmod 755 /usr/local/memcached/memcached_service.sh
[[email protected] ~]# /usr/local/memcached/memcached_service.sh start
After the service starts , monitor 11211/tcp port .
[[email protected] ~]# netstat -antp |grep memcached
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:11211 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 10196/memcached
tcp6 0 0 :::11211 :::* LISTEN 10196/memcached
2.2.2 Memcached API client
So that the program can directly call Memcached Libraries and interfaces , have access to Memcached Extension components
take Memcache Added as PHP A module of . This extension uses Libmemcached Library provides the API And
Memcached The server interacts with each other .
The client needs to install apache And php To test memcache, about Apache And PHP Configuration process
It is omitted here .
1. Compilation and installation Libmemcached
Compiling Memcached When extending components , You need to specify the Libmemcached Location of the library , So install it first
Libmemcached library .
[[email protected] ~]# tar -xzvf libmemcached-1.0.18.tar.gz
[[email protected] ~]# cd libmemcached-1.0.18/
[[email protected] libmemcached-1.0.18]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/libmemcached
--with-memcached=/usr/local/memcached
[[email protected] libmemcached-1.0.18]# make && make install
2. Compilation and installation Memcached Expand
install Libmemcached Behind the library , You can do it PHP Of Memcached Extension component installation .
[[email protected] ~]# wget http://pecl.php.net/get/memcached-2.2.0.tgz
[[email protected] ~]# tar -xzvf memcached-2.2.0.tgz
[[email protected] ~]# cd memcached-2.2.0/
Be careful : To configure Memcached API when ,memcached-2.2.0.tgz By default, there is no... In the source package configure with
Set script , Need to use PHP Of phpize Script generation configuration script configure.
[[email protected] memcached-2.2.0]# /usr/local/php5/bin/phpize
Configuring for:
PHP Api Version: 20121113
Zend Module Api No: 20121212
Zend Extension Api No: 220121212
[[email protected] memcached-2.2.0]# cp -r /usr/local/php5/include/php/ext/ ./
[[email protected] memcached-2.2.0]# ./configure \
--enable-memcached --with-php-config=/usr/local/php5/bin/php-config \
--with-libmemcached-dir=/usr/local/libmemcached \
--disable-memcached-sasl
Be careful : When configuring, use --disable-memcached-sasl Options , close Memcached Of SASL Authentication function ,
Otherwise, an error will be reported .
[[email protected] memcached-2.2.0]# make
[[email protected] memcached-2.2.0]# make test
[[email protected] memcached-2.2.0]# make install
[[email protected] memcached-2.2.0]# make install
Installing shared extensions: /usr/local/php5/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-zts-20121212/
// Share the location of the build
3. To configure PHP add to Memcached Components
edit PHP The configuration file php.ini, add to Memcached Component support .
[[email protected] ~]# cd /usr/local/php5/
[[email protected] php5]# vim php.ini
Add the following
extension_dir = "/usr/local/php5/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-zts-20121212/"
extension=memcached.so Can pass phpinfo, Check to see if you have added Memcached Extension module .
[[email protected] ~]# vim /usr/local/httpd/htdocs/index.php
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
Use a browser to access , The result is shown in Fig. 2.6 Shown , Added successfully .
chart 2.6 phpinfo Information
4. test Memcached-API function
By writing simple PHP Test code calls Memcache Program interface to test whether it is connected with Memcached The server
Working together , The code is as follows :
[[email protected] ~]# vim /usr/local/httpd/htdocs/test.php
<?php
$memcache = new Memcached();
$memcache->addServer('192.168.9.200', 11211);
$memcache->set('key', 'Memcache test successful!', 0, 60);
$result = $memcache->get('key');
unset($memcache);
echo $result;
?>
The purpose of this code is to connect the client Memcached The server , Set the name to ‘key’ The value of the key of is
‘Memcache test successful!’, And read the display , Success indicates that the server and client work together normally , send
Access with a browser , The test results are shown in the figure 2.7 Shown .
chart 2.7 The test page
2.3 Memcached Database operation and management
Memcache The protocol is simple and can be used directly telnet Connect Memcached Of 11211 Port pair Memcached data
Library for operation and management .
[[email protected] ~]# telnet 127.0.0.1 11211
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to 127.0.0.1.
Escape character is '^]'.
// Enter the operation instructions
Operation command format :<command name> <key> <flags> <exptime> <bytes> <data block>
Here is Memcached Common operation instructions for databases .
1. Add a key value data
add username 0 0 7
example
STORED
among add username 0 0 7 Indicates that the key value is named username, The tag bit indicates that the custom information is 0, Be overdue
Time is 0( Never expire , The unit is in seconds ), The number of bytes is 7; example Key value , Note that the input length is 7 byte ,
Conform to the set value .
2. Query key data
get username
VALUE username 0 7
example
END
gets username
VALUE username 0 7 4
example
END
among get Followed by the key name , If checking for recent updates , have access to gets, The last one shows the update
factor , The number of update factors will be increased by one for each update .
3. Update a key data
set username 0 0 10
everything
STORED
get username
VALUE username 0 10
everything
END
among set Followed by the key name that needs to be updated 、 Marker bit 、 Expiration time 、 Number of bytes . If the key name does not exist ,set phase
When add add to . If you just want to simply update without adding functions , Use replace. The updated key name must be
There must be , If the key name does not exist, it will report NOT_STORED Error of .
replace username 0 0 7
lodging
STORED
gets username
VALUE username 0 7 6
lodging
END
replace username1 0 0 7
example
NOT_STORED
4. Clear a cache of data
delete username
DELETED
get username
END
Use delete Delete a key with a value of usernmame Cache data , Use get Check that no content exists .
5. Update after checking check and set
gets username
VALUE username 0 7 7
example
END
cas username 0 0 7 1
lodging
EXISTS
cas username 0 0 7 7
lodging
STORED
gets username
VALUE username 0 7 8
lodging
END
If cas The number of the last update factor of is the same as gets The number of update factors returned is equal , Update ; Otherwise return to
EXISTS.
6. Additional data
append username 0 0 7 // After adding 7 byte
example
STORED
get username
VALUE username 0 14
lodgingexample
END
In the key name username Add data after the original key value append.
prepend username 0 0 2 // Pre append 2 byte
un
STORED
get username
VALUE username 0 16
unlodgingexample
END
In the key name username Append data before the original key value prepend.
7. Clear all cached data
flush_all
OK
8. View server statistics
stats
stats items // Returns all key value pair Statistics
stats cachedump 1 0 // Returns the key value pair of the specified storage space
stats slabs // Display each slab Information about , Include chunk Size 、 number 、 Usage, etc
stats sizes // Output all item Size and number of
stats reset // Clear statistics
2.4 Memcached Ways to achieve primary replication and high availability
Memcached Primary primary replication refers to the replication of data on any computer Memcahed The modified data of the server will be synchronized to another server ,
however Memcahed API The client cannot determine which one to connect to Memcahed The server , So you need to set VIP
Address , Provide to Memcahed API Client connection . have access to keepalived produce VIP Address connection master Memcahed
The server , And provide high availability architecture .
2.4.1 Memcached Primary primary replication Architecture
Memcached The replication function of supports multiple Memcached Copy each other ( Two way replication , Both active and standby are readable
Written ), Can solve Memcached Disaster recovery of .
To use Memcached Replication Architecture , Before uninstalling memcache1 On the machine 1.5.1 Version of memcached,
Re download the... That supports replication Memcached Installation package .
[[email protected] ~]# yum -y install psmisc
[[email protected] ~]# /usr/local/memcached/memcached_service.sh stop
[[email protected] ~]# netstat -lnupt | grep memcached
The installation process is the same as that of the previous installation Memcached In the same way , Here is a brief introduction .
1. Install with replication Memcached
installation is complete libevent after , Will download memcached-1.2.8-repcached-2.2.tar.gz Into the
Line unzip , After that, complete the configuration, compilation and installation .
[[email protected] ~]# cd memcached-1.2.8-repcached-2.2/
[[email protected] memcached-1.2.8-repcached-2.2]# ./configure
--prefix=/usr/local/memcached_replication --enable-replication
--with-libevent=/usr/local/libevent
modify memcached.c The configuration file
[[email protected] memcached-1.2.8-repcached-2.2]# vim memcached.c
#ifndef IOV_MAX
#if defined(__FreeBSD__) || defined(__APPLE__)
# define IOV_MAX 1024
#endif
#endif
Change to :
/* FreeBSD 4.x doesn't have IOV_MAX exposed. */
#ifndef IOV_MAX
# define IOV_MAX 1024
#endif
Compilation and installation
[[email protected] memcached-1.2.8-repcached-2.2]# make && make install
2. start-up Memcached service
Copy the function of Memcached After installation , You need to compile and install libevent-2.1.so.6 model
Copy block to /usr/lib64 Under the table of contents , Otherwise, start the with replication function Memcached Service times are wrong .
[[email protected] ~]# ln -s /usr/local/libevent/lib/libevent-2.1.so.6 /usr/lib64/
When starting the service , Use -x Options point to the opposite end .
[[email protected] ~]# /usr/local/memcached_replication/bin/memcached -d -u root -m 128 -x
192.168.9.202
[[email protected] ~]# netstat -antp |grep memcached
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:11211 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
16863/memcached
tcp 0 0 192.168.9.200:42786 192.168.9.202:11212 ESTABLISHED
16863/memcached
tcp6 0 0 :::11211 :::* LISTEN
16863/memcached
Also start memcached2 The server , Pay attention to start Memcached Service points to the opposite end .
3. Use telnet Simply verify the replication function
1) stay Memcached1 Insert a characteristic key value on the
install telnet Tools
[[email protected] ~]#yum -y install telnet*
Connect memcached
[[email protected] Memcached1 lib]# 192.168.9.200 11211
192.168.9.200 11211
Trying 192.168.9.200...
Connected to 192.168.9.200.
Escape character is '^]'.
set username 0 0 8
20180523
STORED
get username
VALUE username 0 8
20180523
END
quit
Connection closed by foreign host. 2) stay Memcached2 To view the key value just inserted
[[email protected] ~]#  elnet 192.168.9.202 11211
elnet 192.168.9.202 11211
Trying 192.168.9.202...
Connected to 192.168.9.202.
Escape character is '^]'.
get username
VALUE username 0 8
20180523
END
get username2
END
Quit
Connection closed by foreign host. Same as The reason is , stay Memcached2 On insert Enter into Of Count According to the , stay Memcached1 also can With check see To . this Namely
Memcached Master copy of .
2.4.2 Memcached Master master copy + Keepalived High availability Architecture
because Memcached Master master replicates this architecture , When the program connects, it does not know which primary server it should connect to ,
the With need stay front End plus VIP The earth site , real present high You can use frame structure . this in use Keepalived real present , because and
Keepalived It's used to detect Memcached Whether the status of the server is normal , Pictured 2.8 Shown .

chart 2.8 Memcached High availability Architecture
keepalived through too No break check measuring Memcached Lord clothing service device Of 11211 End mouth , Such as fruit check measuring To
Memcached Service downtime or crash occurs , Will be VIP Move from master server to slave server , So as to realize
present Memcached High availability .
1. Installation configuration keepalived
[[email protected] ~]# yum install –y keepalived
1) Configuration master keepalived
[[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
notification_email {
}
notification_email_from [email protected]
smtp_server 192.168.200.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id LVS_DEVEL // Route identification , Keep the master and the slave in line
vrrp_skip_check_adv_addr
vrrp_strict
vrrp_garp_interval 0
vrrp_gna_interval 0
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER // Both active and standby status are MASTER
interface ens33
virtual_router_id 51 // Virtual routing ID, The master and the slave are the same
priority 100 // priority , The primary is superior to the standby
advert_int 1
nopreempt // Don't take the initiative to seize resources , Only in Master Or on a high priority server
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.1.100 // Definition VIP Address
}
}
virtual_server 192.168.1.100 11211 { //VIP Fault detection
delay_loop 6
lb_algo rr
lb_kind NAT
persistence_timeout 20
protocol TCP
sorry_server 192.168.9.202 11211 // Opposite end
real_server 192.168.9.200 11211 { // This machine
weight 3
notify_down /root/memcached.sh // When memcached Downtime , stop it keepalived service
TCP_CHECK {
connect_timeout 3
nb_get_retry 3
delay_before_retry 3
connect_port 11211
}
}
}
Set the execution script :
[[email protected] ~]# echo "/usr/bin/systemctl stop keepalived" > /root/memcached.sh
[[email protected] ~]# chmod +x memcached.sh
2) Configure the backup keepalived
Master-slave keepalived The content of the configuration file is similar , Copy directly to modify , Only the different ones are listed below
The place is sorted out .
[[email protected] ~]# scp /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf 192.168.9.202:/etc/keepalived/
// Omit
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER // The standby status is also MASTER
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 51 // Virtual routing ID, The master and the slave are the same
priority 99 // Low priority
advert_int 1
// Get rid of nopreempt
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
// Omit
virtual_server 192.168.1.100 11211 { //VIP Fault detection
delay_loop 6
lb_algo rr
lb_kind NAT
persistence_timeout 20
protocol TCP
sorry_server 192.168.9.200 11211 // Opposite end
real_server 192.168.9.202 11211 { // This machine
weight 3
notify_down /root/memcached.sh // When memcached Downtime , stop it keepalived service
// Omit
Also set the script :
[[email protected] ~]# echo "/usr/bin/systemctl stop keepalived" > /root/memcached.sh
[[email protected] ~]# chmod +x memcached.sh
2. Test verification
Start the master and slave respectively keepalived service .
[[email protected] ~]# systemctl start keepalived
[[email protected] ~]# systemctl start keepalived
1) Validation master keepalived obtain VIP Address
Use ip address show Command view VIP Address ( Use ifconfig Can't view ).
[[email protected] ~]# ip address
// Omit
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:f0:23:a6 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.9.200/24 brd 192.168.9.255 scope global dynamic eth0
valid_lft 7181sec preferred_lft 7181sec
inet 192.168.1.100/32 scope global eth0 // Have obtained VIP Address
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::dcdb:41a6:7a18:680b/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2) Verify high availability
close Memcached1 Server's Memcached service , stay Memcached2 Check the address letter on the server
Rest .( notes : Be sure to shut down both machines selinux)
[[email protected] ~]#setenforce 0
[[email protected] ~]#setenforce 0
[[email protected] ~]# killall memcached
[[email protected] ~]# ip addr
// Omit
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:ad:1e:2b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.9.202/24 brd 192.168.9.255 scope global eth0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 192.168.1.100/32 scope global eth0 // Obtained VIP Address
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::5054:ff:fead:1e2b/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3. The architecture features
Keepalived To be able to Memcached A... Is generated on the database VIP Address , The program connects to this fixed VIP
Address to main Memcached database , Even if the back-end database is switched from master to slave , There is no need to change the address . Because being the Lord
Memcached Database Memcached When the service stops ,keepalived From Memcached Server reacquires
The original VIP Address , So as to realize master-slave switching , This process is called VIP Address drift .
边栏推荐
- 南京大学 静态软件分析(static program analyzes)-- introduction 学习笔记
- 如何编写测试用例
- TOOD: Task-aligned One-stage Object Detection
- Educoder 表格标签—表格高级样式的设置
- Educoder Web练习题---对表单进行验证
- Educoder Web练习题---页面结点元素
- What do you mean by concurrency, concurrency, and high concurrency?
- uva11292
- TOOD: Task-aligned One-stage Object Detection
- Add a description to the form component
猜你喜欢

Educator web exercise - create a drop-down list

Educator web exercises - grouping elements

Practical application of ankerui BM100 series signal isolator

高效远程办公手册| 社区征文

Apache ShardingSphere 5.1.2 发布|全新驱动 API + 云原生部署,打造高性能数据网关

Six relationships of UML - system learning IV
【深入理解TcaplusDB技术】TcaplusDB业务数据备份
Isn't this another go bug?

不止于ZeRO:BMTrain技术原理浅析

小程序直播互动功能运行在App里?
随机推荐
cartographer_ ceres_ scan_ matcher_ 2d
Implementation principle and application practice of Flink CDC mongodb connector
《网络是怎么样连接的》读书笔记 - ADSL
uva11991
Educoder Web练习题---结构元素
百度交易中台之钱包系统架构浅析
UVA1203 Argus
uva11300
居家辦公初體驗之新得分享| 社區征文
应用配置管理,基础原理分析
Educoder web exercises - structural elements
安科瑞BM100系列信号隔离器的实际应用
Educoder Web练习题---对表单元素分组
Educoder Web练习题---交互元素
Qinglong panel, JD timed task library, script library
如何阅读AI顶会论文?
PostgreSQL 初步了解(一)
uva11292
漫谈公网网络延迟
Three structures of program - system learning I