当前位置:网站首页>Direct select sort and quick sort
Direct select sort and quick sort
2022-06-25 06:41:00 【Salted fish learning code】
Hello everyone ! In this article, we will talk about direct selection sorting and quick sorting .
List of articles
- 1 Direct selection sorting
- 2 Quick sort
- 2.1 hoare The basic idea
- 2.2 hoare Thought process
- 2.3 hoare Method specific implementation
- 2.4 The thought flow of pit digging method
- 2.5 The concrete implementation of the excavation method
- 2.6 Front and back pointer method thought flow
- 2.7 The front and back pointer method is concretely realized
- 2.8 Time complexity
- 2.9 How to optimize quick sort
1 Direct selection sorting
1.1 The basic idea
Each time, select the smallest from the data elements to be sorted ( Or maximum ) An element of , Store at the beginning of the sequence , Until all the data elements to be sorted are finished .
1.2 Thought process

Here we write a better solution : Is to find two numbers at a time ( maximal , The smallest ), Put it in the right place .
We put the smallest one on the far left , The largest one is on the far right .
And then start with the next one , By analogy .
1.3 Concrete realization
According to the idea above , We convert it into code :
We test , It can be found that there is a problem :
Why is that ? Let's debug it :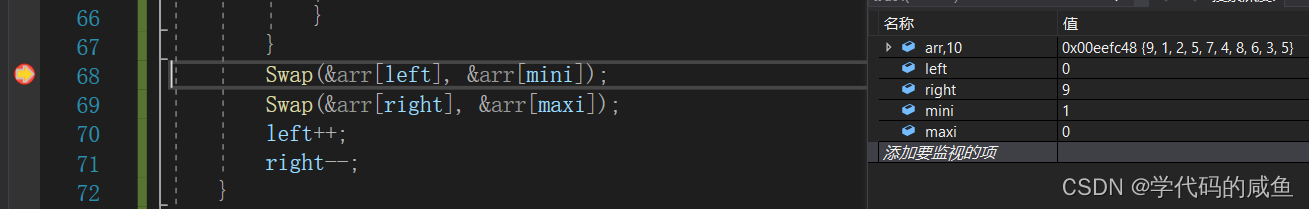
We can see that the smallest subscript at this time is 1, The largest subscript is 0, Then swap the first one , We'll see :
At this point, after the exchange ,maxi Point to or 0, But the maximum number at this time 9 Has reached the subscript 1 Location. . So errors will occur , We need to make some adjustments here .
1.4 Time complexity
here , What we write is the optimization method of direct selection sorting , For the first time N, And then there was N-2, And then there was N-4, And then there was N-6… So time complexity is O(N^2), And the bubble sort is N,N-1,N-2,N-3… So direct sorting is better than bubble sorting .
But in order : Direct selection sorting cannot determine whether it is orderly , Still have to choose layer by layer , And bubble sorting will be fast .
2 Quick sort
2.1 hoare The basic idea
Quick sort is Hoare On 1962 A binary tree structure of the exchange sort method , Its basic idea is :
Take any element in the element sequence to be sorted as the reference value , According to the sorting code, the set to be sorted is divided into two subsequences , All elements in the left subsequence are less than the base value , All elements in the right subsequence are greater than the base value , Then the leftmost and rightmost subsequences repeat the process , Until all the elements are aligned in their respective positions .
2.2 hoare Thought process
First , Let's take a look at the single trip , The single trip is also divided into three versions :
The first version :hoare edition
Choose one key, Usually the first number or the last number .
It is required that the values on the left are all greater than key Small , The values on the right are better than key Big , and key Equal anywhere .
Let's take a look at the dynamic diagram process :
From the graph we can see :R Find a comparison key Small ,L Find a comparison key Big , Exchange after finding , Go on . After meeting , Follow the value of the encounter position with key Value exchange of position .
ad locum , Some students may ask a question :
If the one on the left key The value is smaller than the value at the time of meeting , What should I do ?
This algorithm can avoid this problem as long as it satisfies one condition :
Going first on the right can guarantee .
It's divided into two situations :
Case one :R Stop first ,L Go over and meet R
After the two exchange ,R Go ahead ,R Find a comparison key Small , That is to say 3 stop 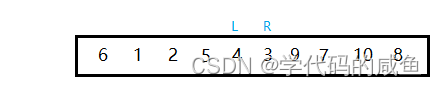
then L go , To find a comparison key Big , But one step is like R Equal .
Meeting 3 Than key Small .
The second case : Just exchanged ,R Go ahead ,R No better than key The small one directly follows L meet .
This situation , It's better than that key Small .
In the above example, we take the left as key, So we want to have on the right key What to do ?
Same thing , Let's go first on the left , The value ratio of the encounter position can be guaranteed key Big .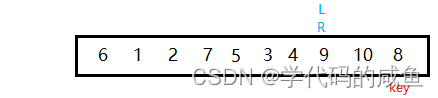
Let's take a look at its dynamic flow chart :
2.3 hoare Method specific implementation
First , We realize a single trip :
however , There are two problems in writing this way .
The first question is :
In the following set of data , It will have an endless cycle .
You can see key and right All are 5, It doesn't satisfy the cyclic condition , Don't go into the cycle .
then key and left All are 5, Nor does it satisfy the cycle condition , Don't go into the cycle .
In exchange for left and right Nothing has changed , So there's a dead cycle .
We can modify it like this :
The second question is :
There are still problems after the modification . Let's look at the following set of data :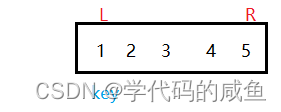
here key by 1,right Keep reducing , When right=1 when , Satisfy the cyclic condition , One more time , Just crossed the line .
therefore , We need to add one more condition :
After a single trip ,key It's in the right place .
If the left side is in order , Order on the right , Then we will be in order as a whole , So how are the left and right sides ordered ?
Divide and conquer solves sub problems .
The results of single pass sorting are as follows :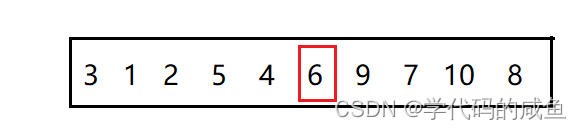
Now? 6 Already in the right place , Now we're going to let 6 The left and right sides of the are also orderly .
After a single sequence , You'll find that 3 And in the right place . Then we divide and conquer 3 On the left and right of .
The whole process is as follows :
The complete code is as follows :
2.4 The thought flow of pit digging method
First , Let's take a look at the motion picture :
then , Let me elaborate on the process of pit excavation :
First , Let's put the leftmost one on key in , In this way, a pit is formed on the far left . then ,R Let's go and find a better one key Small .
After finding it , We will 5 Put it in the pit . such 5 The location of the pit becomes a new pit .
then L Go and compare key Big , We find 7 after , take 7 Put it in the pit .
R I'm looking for a little girl , find 4 Put it in the pit .
L Find another big , find 9 Put it in the pit .
R I'm looking for a little girl , hold 3 Put it in the pit .
L Find another big , But and R Met , Just put key Put it in the pit , It's over .
such , The single trip process of pit excavation method is over .
Let's take a look at its dynamic flow chart :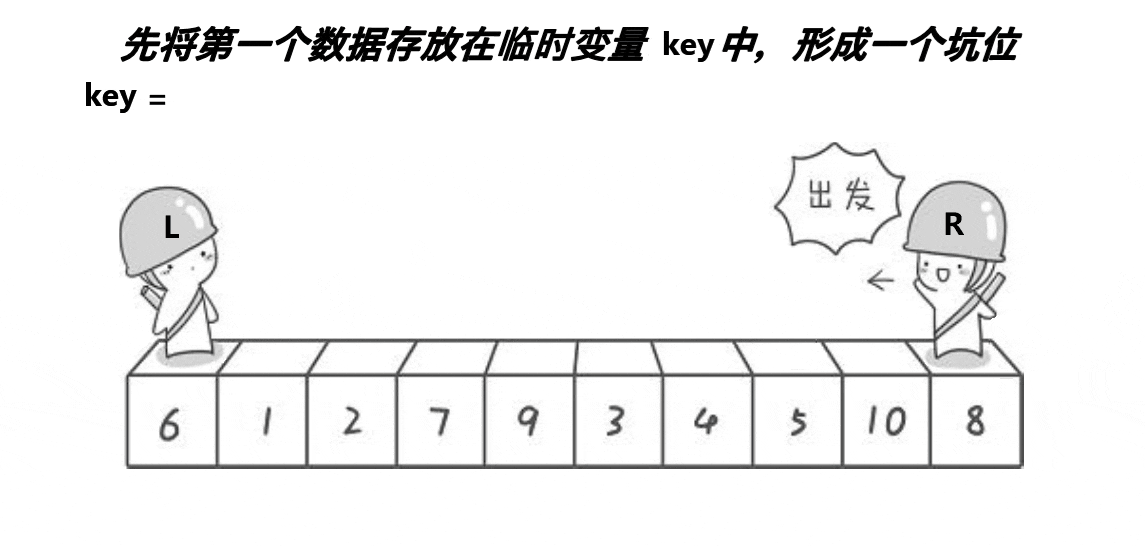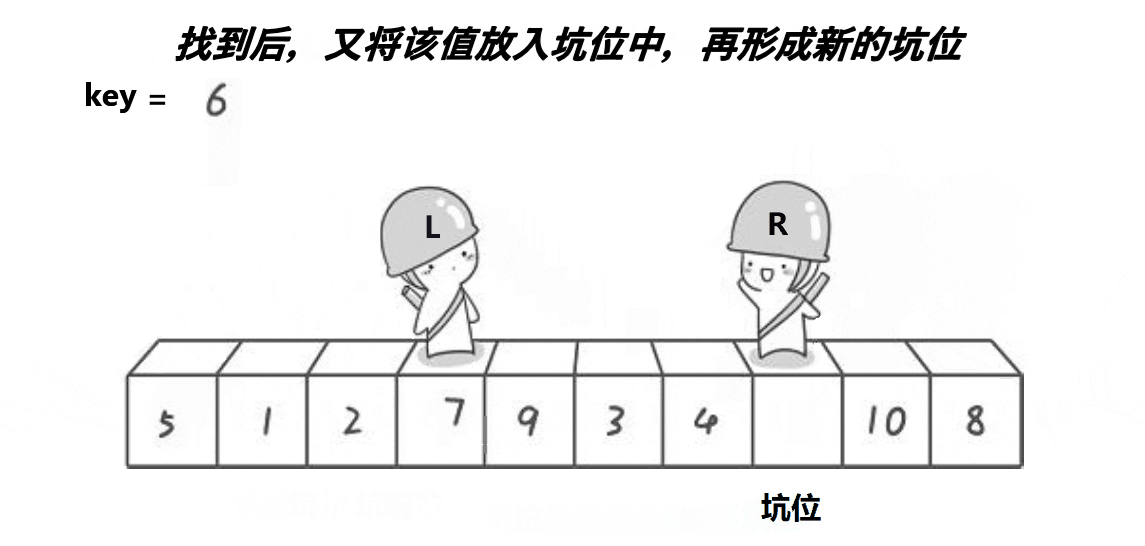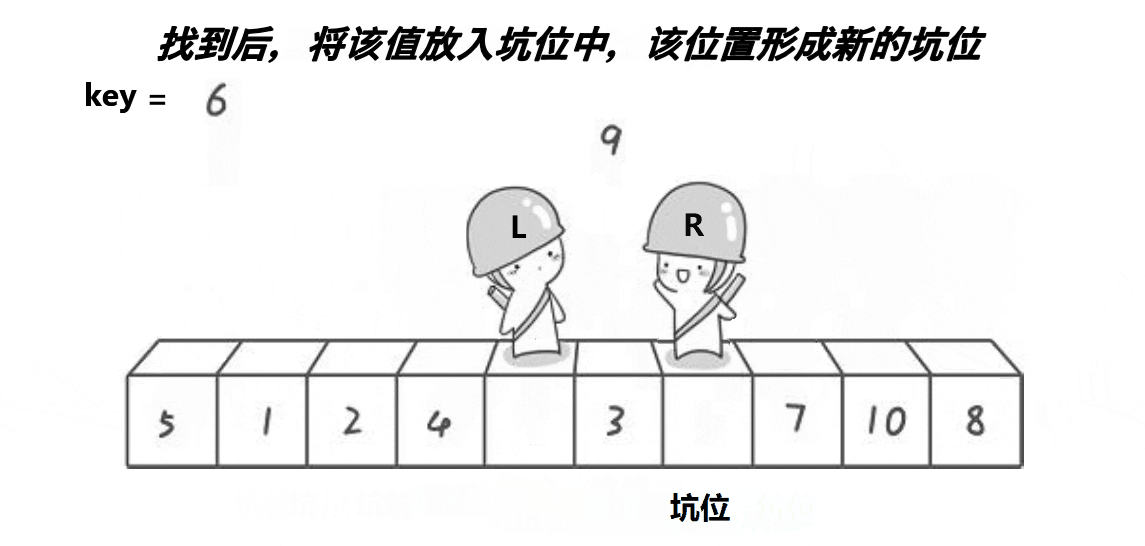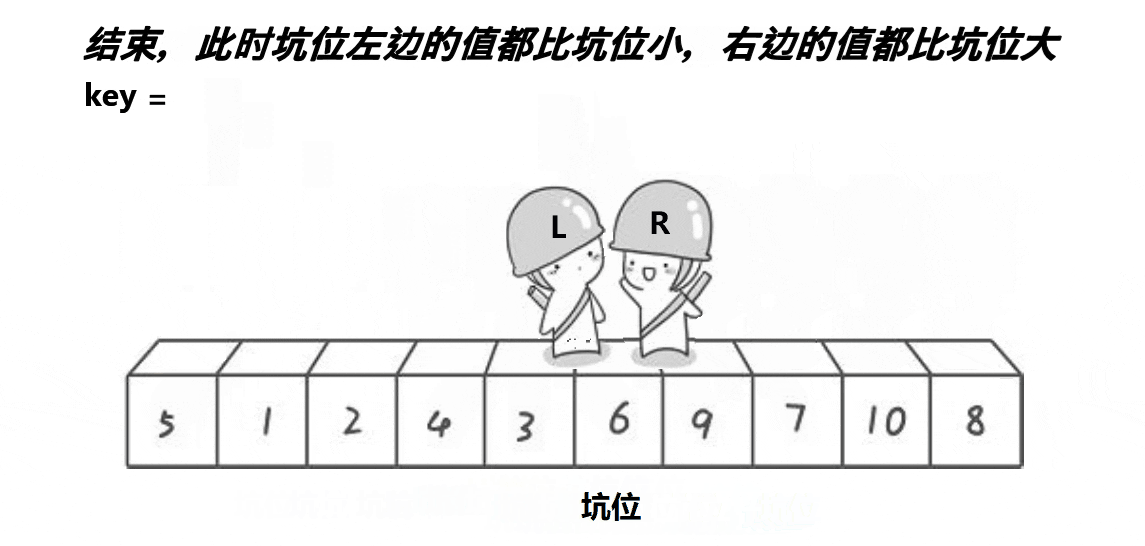
Well, the digging method and hoare What is the difference between law ?
There is no difference in essence . It's just that the digging method is better understood .
1. You don't need to understand why the final encounter is better than key Small .
2. You don't need to understand why the left side does key, Go first on the right .
Because at first we chose the left side as the pit , Then you will naturally think that ,R Go ahead and find Xiao , Fill the hole , When we finally meet, just fill up the hole .
2.5 The concrete implementation of the excavation method
Similar to the above idea :
2.6 Front and back pointer method thought flow
First , Let's take a look at the dynamic graph process :
then , Let me talk about the specific process :
In limine , Let's define a prev The pointer points to the beginning of the sequence , Define a cur Pointer to prev The last position of the pointer .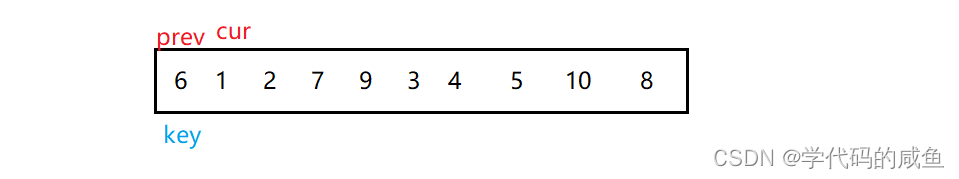
And then determine cur Whether the data pointed to by the pointer is less than key, If less than , be prev Move the pointer back one bit , And then cur Pointer to content exchange . then cur The pointer ++
From the previous set of data , We can see that 1,2, All are less than key Of , and prev Exchange doesn't change anything , When cur Go all the way to 3 The location of :
here ,prev The pointer should be moved back one bit , And then cur Pointer to content exchange , then cur The pointer ++
here ,cur Point to the 4 Less than 6 Of , Then fear prev Move back a bit , After exchanging content ,cur++
here cur It points to more than key Small ,prev++ after , In exchange for cur Content and prev The content of .
then cur++, here 10 Than key Big ,cur Again ++,8 Than key Big , Again ++
When cur Out of the sequence , In exchange for key and prev The content of .
So the single trip is over .
ad locum ,prev and cur The relationship is :
1.cur I haven't met anything better than key Large values ,prev Follow closely cur, One before and one after .
2.cur Meet the ratio key After a large value ,prev and cur There is a gap between key The interval of large values .
Let's take a look at its dynamic flow chart :
2.7 The front and back pointer method is concretely realized

Someone will ask. , If key I chose what to write on the far right ?
We need to prev and cur Dislocation :
We will cur to left,prev to left-1
The others are the same ,cur Looking for a small ,6 Than 8 Small ,++prev, here prev and cur Number of points 6 equal . therefore cur Again ++
And so on …
here ,cur Point to the 3 Than key Small ,++prev, In exchange for 
cur++ Go down in turn .
When cur Point to key when , ends .
But here , We can't exchange directly prev and cur, need prev++ And then exchange key
The code is as follows :
2.8 Time complexity
What is the time complexity of quick sorting ?
In the best case : Every election key All median
It means : After each single sequence ,key In the middle
It will form such :
On each floor key All need to go n Time , Altogether logN layer , So the time complexity will be :O(N*logN)
At worst : Every time you choose key Is the smallest or largest , That is, in an orderly order
That's it :
So it's an arithmetic sequence , Its time complexity is :O(N^N)
2.9 How to optimize quick sort
2.9.1 The middle of three numbers key

Choose not the biggest , Not the smallest one .
such , If there is order , We won't choose the biggest and smallest .
therefore , Let's start by writing a function in a triple :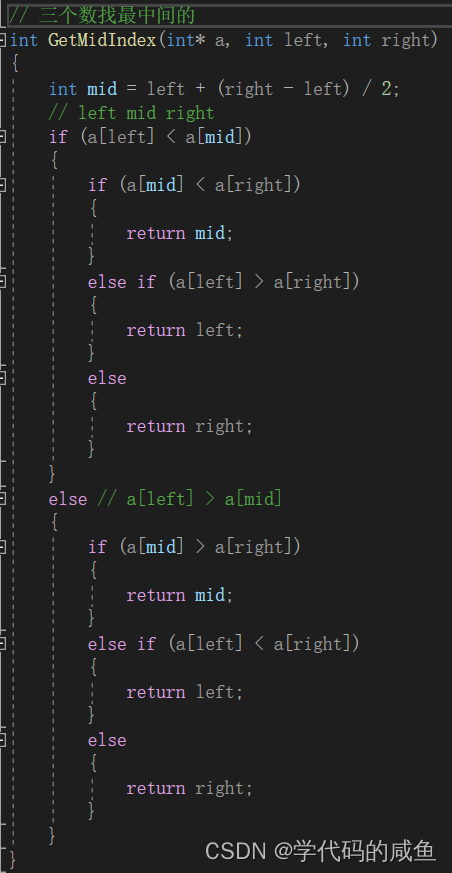
then , Swap the middle number with the leftmost or rightmost number , Other ideas remain the same .
2.9.2 Inter cell optimization
What is inter cell optimization ?
The interval is very small , Stop using the idea of recursive partition and make it orderly , Instead, insert sorting is directly used to sort cells , Reduce recursive calls .
What does that mean ? Let's take a look at the quick row recursive call expansion diagram :
hypothesis , We have 1000 Number , There is a 10 layer , The last layer is 1 Number , Also have 2^9 individual . The penultimate layer is 3 Number , Yes 2 ^8 individual . therefore , We can change the recursion of the following layers to direct insertion sorting :
void QuickSort(int* a, int begin, int end)
{
// Inter cell direct insertion sequencing control is in order
// When the number of intervals is less than or equal to 10 Number of hours , Just insert the sort directly
if (end - begin + 1 <= 10)
{
InsertSort(a + begin, end - begin + 1);
}
else
{
int keyi = PartSort3(a, begin, end);
// [begin, keyi-1]keyi[keyi+1, end]
QuickSort2(a, begin, keyi - 1);
QuickSort2(a, keyi + 1, end);
}
}
Because it's a closed interval , The number is subtracted from the two +1
The beginning of each insertion sort , We should be a+begin
边栏推荐
- 'how do I create an enumeration with constant values in rust?'- How can I create enums with constant values in Rust?
- Comparison test of mono 120W high power class D power amplifier chip cs8683-tpa3116
- Non-contact infrared temperature measurement system for human body based on single chip microcomputer
- Is the number of indexes in a table the more the better?
- [core content and derivation] the mystery of human memory system may be just like this
- JSON. toJSONString(object, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue); Second parameter action
- Laravel8+ wechat applet generates QR code
- cos(a+b)=cosa*cosb-sina*sinb的推导过程
- How do I turn off word wrap in iterm2- How to turn off word wrap in iTerm2?
- Ht513 I2S input 2.8W mono class D audio power amplifier IC
猜你喜欢

TCP BBR as rate based

Cloning and importing DOM nodes

Drosophila played VR and entered nature. It was found that there were attention mechanisms and working memory. The insect brain was no worse than that of mammals
JS to determine whether an element exists in the array (four methods)

Meta universe is over, Web 3.0 will be fooled again?

Ht7180 3.7V L 12v/2a built in MOS high current boost IC solution

Non-contact infrared temperature measurement system for human body based on single chip microcomputer

DataX tutorial (10) - hot plug principle of dataX plug-in

DataX tutorial (09) - how does dataX achieve speed limit?
Kubernetes cluster dashboard & kuboard installation demo
随机推荐
What is the IP address
From file system to distributed file system
アルマ / 炼金妹
Sophomores majoring in mechanics build a manipulator by hand -- full of compromise
ACWING/2004. 錯字
Period to string [repeat] - period to string [duplicate]
Meta universe is over, Web 3.0 will be fooled again?
joda.time获取日期总结
Sleep quality today 67 points
Introduction to sap ui5 tools
Acwing / 2004. Mauvaise écriture
直接选择排序和快速排序
ASP. Net core - encrypted configuration in asp NET Core
DataX tutorial (10) - hot plug principle of dataX plug-in
What is the real future of hardware engineers?
R & D thinking 07 - embedded intelligent product safety certification required
Are these old system codes written by pigs?
Understand what MSS is
[轻松学会shell编程]-5、计划任务
Go language library management restful API development practice