当前位置:网站首页>User and group management, file permissions
User and group management, file permissions
2022-07-23 13:01:00 【.98℃】
1. Users and groups
- linux Type of user in
- The super user —— The user is called root, It has all permissions , Only system maintenance ( for example : Establish users, etc ) Or other necessary circumstances to log in with super user , To avoid security problems in the system .
- System users ( Dummy user )—— yes Linux Users necessary for the normal operation of the system ; It is mainly established to meet the requirements of the corresponding system process for the file owner . for example :bin、daemon、adm、lp Waiting for users . System users cannot log in .
- Ordinary users —— To enable users to use Linux System resources , Most of our users fall into this category .
- linux Type of user group in
- Basic group ( Private group ): When establishing an account , If the group to which the account belongs is not specified , The system will create a group with the same user name , This group is the basic group .
- Additional group ( Public group ): Can accommodate multiple users , All users in the group have the rights owned by the group .
- linux Which file stores user information in ? And what do the fields mean ?
- file :/etc/passwd ----- User account file
- passwd It's a text file , Used to define the user account of the system , Because all users are right passwd Have the right to read , Therefore, only user accounts are defined in this file , Without saving the password .
- [[email protected] ~]# head -1 /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
| Field | meaning |
|---|---|
| 1 | user name |
| 2 | The user's password was originally stored directly in the second field , But for safety , Finally, there is a special /etc/shadow file , Now the default is x replace |
| 3 | User uid, In general root by 0,1-499 The default is the system account , Some are bigger to 1000,500-65535 Is the user's login account , Some systems start from 1000 Start . |
| 4 | User gid,linux Every user will have two ID, One is the user uid, One is the user group id, When we log in , Enter your username and password , In fact, we will arrive first /etc/passwd Check whether there is the account or user name you entered , If yes, match the account number with the corresponding UID and GID( stay /etc/group in ) Read it out . Then read the home folder and shell Set up , Then check whether the password is correct , If correct, log in normally . |
| 5 | User's account description |
| 6 | User's home directory folder |
| 7 | User used shell, If replaced /sbin/nologin/ There is no login environment by default . |
- User password file ——/etc/shadow
- [[email protected] ~]# head -1 /etc/shadow
root:$6$5Y4k7cG6IudYR.ju$OOjV5Sf7c2BtyPUhFFHv7ECguICMUfHggl3VmU2AwWv5wWqks7DKGwAFmItXjIRK6.yfkMwL/nP9j2tt9b9/60::0:99999:7:::
| Field | meaning |
|---|---|
| 1 | User login |
| 2 | encrypted password : User's password encryption field |
| 3 | Last modification time : Date the password has been used ( from 1970-01-01 Start , yes unix1969 Released in prototype , Based on the consideration of the system at that time , That's all. ) |
| 4 | Minimum time interval : At least how many days after the password can be changed ( The default value is 0, Means unrestricted ) |
| 5 | Maximum time interval : How many days after the password must be changed ( The default value is 99999, It means that there is no restriction ) |
| 6 | Warning time : Remind me to change the password a few days before ( The default value is 7 God ,0 Indicates that no warning is provided ) |
| 7 | Inactive time : If there is no modification, extend it for a few days ( In the example, extend 3 God ) |
| 8 | Failure time : In any case, it will expire at this time ( The default is empty. , Indicates permanently available ) |
| 9 | sign : Keep field , No meaning at present |
- linux What is the file in which the group information is stored ? And what do the fields mean ?
- User group account file ------ /etc/group
- [[email protected] ~]# head -1 /etc/group
root:x:0:
| Field | explain |
| Groupname | Group name |
| Passwd | Encryption password for the group |
| GID | It is the system that distinguishes different groups ID, stay /etc/passwd In domain GID Field is used to specify the basic group of users |
| Userlist | Yes, it is “,” Separate user names , The members listed take this group as an additional group |
2). Create the following users 、 Groups and group membership :
- 1. Create a sysmgrs Group
[[email protected] ~]# groupadd sysmgrs

- 2. Create user natasha At the same time specified sysmgrs As natasha Additional groups of
[[email protected] ~]# useradd natasha -G sysmgrs
![]()
- 3. Create user harry At the same time specified sysmgrs As harry Additional groups of
[[email protected] ~]# useradd harry -G sysmgrs

- 4. Create user sarah Appoint shell The type is /sbin/false( You do not have access to interactive on the system shell) It's not sysmgrs Members of
[[email protected] ~]# useradd -s /bin/false sarah
![]()
- 5. Set up natasha 、 harry and sarah All of your passwords are 123
[[email protected] ~]# echo 123 | passwd --stdin harry
[[email protected] ~]# echo 123 | passwd --stdin natasha
[[email protected] ~]# echo 123 | passwd --stdin sarah

- 6. Create user lockuser, And specify home directory as /home/lock, Then lock the user
[[email protected] ~]# passwd -l lockuser
![]()
- 7. Create user limituser, gid by 1555,userid by 1666, Let its password in 10 Expires in days
[[email protected] home]# groupadd -g 1666 grtxt
[[email protected] home]# useradd limituser -u1555 -g1666 -p 123
[[email protected] home]# chage -M 10 limituser
- 8. Unlock lockuser, And set that the password must be changed the next time you log in
[[email protected] home]# usermod -U lockuser && chage -d 0 lockuser

- 9. Give Way natasha With modification harry Password permissions (sudo)
vi sudo
Host_Alias RHCSA=lwz
User_Alias USER11=natasha
Cmnd_Alias CHPASS=/usr/bin/passwd harry
USER RCHSA=(root) CHPASS
- 10. Create user testuser And set the password , Change the user name to normaluser
[[email protected] home]# useradd testuser -p 123
[[email protected] home]# usermod testuser -l normaluser


- 11. Delete lockuser
[[email protected] home]# userdel lockuser

2. File system permissions
- 1. create a file , And give authority 611( Two ways , A kind of guoa, A kind of nnn)
[[email protected] power]# chmod a=rw file1
[[email protected] power]# chmod 666 file2


- 2. Create directory , And give authority 755( Two ways , A kind of guoa, A kind of nnn)
[[email protected] power]# chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=rx file1
[[email protected] power]# chmod 755 file2

- 3. create a file , And modify the owner and group of the file to other users
[[email protected] power]# chown rhcsa:rhcsa file1

- 4. Set up suid, Set for file suid( Two ways u+s and nnnn) The way
[[email protected] power]# chmod u+s file1
[[email protected] power]# chmod 4755 file2

- 5. Set up sgid, Set for file sgid( Two ways g+s and nnnn) The way
[[email protected] power]# chmod g+s file1
[[email protected] power]# chmod 2755 file2

- 6. Set up sbit, Set for directory sbit( Two ways o+t and nnnn) The way
[[email protected] power]# chmod o+t file1
[[email protected] power]# chmod 1755 file2

- 7. create a file , Query file acl

- 8. Set for file acl The user is testuser1 Permission is rwx
[[email protected] power]# setfacl -m u:testuser1:rwx file1
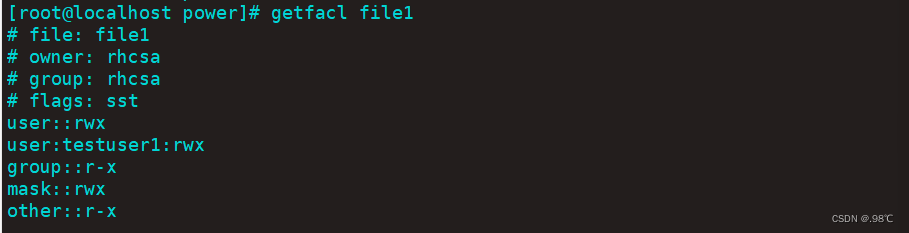
- 9. Set for file acl Of mask: Permission is r-x
[[email protected] power]# setfacl -m m:r-x file1

边栏推荐
- ACL 配置实例学习记录
- C # enter a letter and judge its case
- nfs服务部署笔记
- Integer times integer overflow
- Do a Cisco experiment!
- jenkins部署
- Rhcsa - - parcourir le contenu du fichier, couper, uniq, trier, utiliser les commandes.tr
- Solution rapide: xshell ne peut pas glisser dans un dossier ou un paquet
- 快速解决:Xshell拖不進去文件夾或者軟件包的問題
- Hcip --- condition matching and OSPF Protocol
猜你喜欢

Learning diary - (routing and switching technology) DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)

Routing extension configuration of OSPF and rip
![Build FRPC client in NAS [super brainless]](/img/02/bc150ab6cec73b9142d0e3c3532417.png)
Build FRPC client in NAS [super brainless]
DHCP configuration instance learning record
zabbix监控详细安装到部署

OSPF实验

融e学答案脚本制作(2020最新)

Super easy to use packet capturing tool tcpdump

OSPF single area configuration instance learning record

Hcip --- HCIA knowledge review (I)
随机推荐
Hcip --- mGRE comprehensive experiment
Super easy to use packet capturing tool tcpdump
静态路由原理与配置
Rk3588 compilation problem set
Delete node in binary sort tree
jenkins用到的插件
PPP configuration instance learning record
Do a Cisco experiment!
C#随机生成一个分数,判断其成绩等级(优、良、中、差、不及格)
zabbix监控详细安装到部署
Array leetcode977. Square of ordered array
psutil监控的简单使用
Unity mouse controls camera drag, rotation and zoom (simulation editor camera function)
Hcip --- condition matching and OSPF Protocol
在GPU上运行MATLAB程序
DHCP principle and configuration
OSPF 多区域配置实例学习记录
FTP 配置实例学习记录
ACL——net
在二叉排序树中删除节点