当前位置:网站首页>Rethink healthy diet based on intestinal microbiome
Rethink healthy diet based on intestinal microbiome
2022-06-30 21:34:00 【Guhe Niubo】
Gu He health

Write it at the front
《 Think about your diet based on your gut flora 》
So-called “ disease enters by the mouth ”, Diet is the core of human health .
Have you found such a phenomenon ? Our daily diet is transitioning to a western style diet , meanwhile , All kinds of chronic diseases are eroding .
Recently 《CELL》 Several evidence-based scientific researches and reviews on intestinal flora, healthy diet and the occurrence of diseases have been successively published in the sub journal , Various intervention measures and medication have also been found in the long-term intestinal flora detection practice of Guhe All need to consider the nutritional part of the diet , Combined with the intervention of intestinal flora Will play a role More effective and long-term The effect of , For example, during the intervention treatment of patients with inflammatory bowel disease , It needs to be adjusted or supplemented in combination with Nutrition Reshaping intestinal flora and immune balance .
A series of rigorous prospective cohort studies and randomized controlled trials provide strong validation for the characteristics of healthy diet :
Vegetables and fruits 、 Whole grains bring benefits , Harmful effects of processed food .
However , There are still many controversies , You may be right “ Healthy diet ” This concept remains vague , There are still many puzzles, such as :
- What are the health promoting foods and eating patterns ?
- What is the relationship between chronic diseases and diet ?
- What role does intestinal flora play in it ?
- How to apply the intestinal flora in promoting nutrition strategies ?
- Different people have different responses to dietary intervention , How to use the intestinal flora for personalized nutrition strategy ?
- How does this scientific evidence translate into a diet guide that can really guide people's lives ?
- ...

In this article, we try to start from Microbiome science The angle of , Discuss Food based dietary guidelines And all aspects of healthy eating , Try to integrate the scientific knowledge we already know into it , Of course, the discussion is limited to Suggestions on health promotion and disease prevention for the general population , This is also the purpose of dietary recommendations based on intestinal flora and food nutrition .
01
“ do or think the same without prior consulation ” National dietary guidelines
Food based dietary guidelines provide information about food 、 Food components and dietary patterns The advice of , In order to realize the Reference intake of nutrients , Prevention of chronic diseases , And maintain the overall health of the general population .
The following table shows the past 10 A non exhaustive overview of the key information of the foreign food based diet guidelines updated in the middle of the year , These guidelines are divided into the most common and complementary food groups : Vegetables and fruits 、 Cereal products 、 dairy 、 Meat and meat substitutes and processed foods .
A non exhaustive list of national food based dietary guidelines And the recommended intake for the general adult food group



doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2022.04.016
2022 year 4 month 26 Japan ,《 Dietary guidelines for Chinese residents (2022)》 Release , Put forward eight principles of balanced diet :
- One 、 The food is varied , Reasonable collocation ;
- Two 、 Eating balance , Healthy weight ;
- 3、 ... and 、 Eat more fruits and vegetables 、 dairy 、 The whole valley 、 soybean ;
- Four 、 Eat fish in moderation 、 The birds 、 egg 、 Lean meat ;
- 5、 ... and 、 Less salt, less oil , Control sugar and alcohol ;
- 6、 ... and 、 Regular meals , Drink plenty of water ;
- 7、 ... and 、 Can cook and choose , Can read the label ;
- 8、 ... and 、 Eating with chopsticks , put an end to waste .
Guidelines for countries with different food cultures , Yes Strong consistency , All the guides are telling us :
Suggest Limit or avoid add to High sugar 、 High in salt and saturated fat The food , Some countries specifically mention avoiding processing 、 Super Machining and / Or packaged food .
More than half Your diet should include vegetables 、 Fruit and cereal products , Whole grain first For refined grains . These diets need to be supplemented A small amount of animal protein ( fish 、 Lean meat 、 poultry 、 Eggs and dairy products ) and / or Plant protein ( peas and beans 、 nuts ).
02
Recommended interactions between food and intestinal flora
below , We discuss dietary guidelines in the context of the microbiome , The focus is on human research , Despite its limitations ( for example , High dose administration and human transformation ), However, animal models have advantages in establishing molecular mechanisms and causal relationships .
Whole plant foods
In all dietary guidelines :
Suggest Edible vegetables 、 Fruits 、 Whole grains 、 Beans and nuts Whole plant foods
Should be Limit your intake Add sugar 、 Salt or saturated fat Processed food
Dietary fiber
Whole plant foods are Dietary fiber The only relevant natural source , Dietary fiber is a kind of It is difficult to digest Carbohydrate polymers , In chemical composition 、 There are great differences in physical and chemical properties and physiological effects .
Of particular relevance to the intestinal microbiota is Fermentable fiber , Also known as microbiota, carbohydrates are available (MAC), If they show established health benefits associated with selective effects on the microbiota , Then for Prebiotics .
fiber by Inhibiting mucosan metabolism Microorganisms provide growth substrate , prevent Intestinal mucus depletion 、 Bacteria invade the mucus layer 、 Downstream inflammation and infection .
The main of fiber fermentation The end product is short chain fatty acids (SCFA), Acetate 、 Propionate and butyrate , They cause a variety of physiological effects .
These effects include :
- Ecological impact on the microbiota ( for example , Antibacterial properties 、 Reduce the diffusion of oxygen into the intestinal cavity );
- Effect on intestinal barrier function ( for example , Induction of tight junction proteins 、 The production of mucus );
- Direct metabolic and immune effects on the host ( for example , Increase the production of hormones that control satiety , Increase lipolysis of adipose tissue , Improve insulin sensitivity )
A high fiber diet can Reduce heart attack 、 Stroke and cardiovascular disease The risk of .
In the near future , A vertical 、 Random 、 Cross design mainly studies two popular purified fibers , Arabinoxylans (AX) And long chain inulin (LCI), The results are published in 《CELL Host & Microbe》.
- Arabinoxylans are common in whole grains , Like rye 、 Wheat 、 oats 、 rice 、 barley 、 Corn, etc ;
- Long chain inulin is commonly found in onions 、 Chicory root 、 Garlic and artichokes .
This study shows a single purified fiber Impact on the microbiome , In depth understanding of the impact of fiber supplements and Fiber induced Lower cholesterol The mechanism behind it .

doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2022.03.036
It turns out that ↓↓↓
Arabinoxylans :
- During the intake of arabinoxylans , The participants' blood lipid status was improved , Low density lipoprotein in the body (“ bad ” Cholesterol )、 Levels of total cholesterol and other lipids have decreased .
- Further research shows that , The reduction of cholesterol by arabinoxylans is related to the increase of bile acid secretion or other changes in bile .
Long chain inulin :
- Low dose intake was associated with a slight decrease in inflammatory markers and an increase in Bifidobacterium abundance ;
- However , Excessive intake brings harmful effects . stay 30 g / Days of high-dose intake , Participants' levels of inflammation and alanine aminotransferase in the liver (ALT) The level will rise significantly (ALT It is a potential marker of liver injury ).
in general , Every fiber Can cause Individuation and Fiber specificity Biochemistry and Microbiota reaction , therefore , Dietary fiber is good for health The benefits vary from person to person , It may also depend on the specific Type of fiber ingested and Intake dose .
Phytochemicals
Another key ingredient in whole plant foods is Phytochemicals , They are Non nutritive and biologically active compounds , Usually combined with dietary fiber , Give the plant color 、 flavor 、 Smell and astringency .
majority (90%–95%) Phytochemicals Can't Absorbed by the small intestine , Therefore, it will interact with the intestinal microbiota Two way interaction .
Gut microbes are responsible for By demethylation 、 Ring opening and dehydroxylation For phytochemicals Conduct Biotransformation , thus increase Their Bioavailability 、 absorption as well as antioxidant and Immunity Regulation .
Effects of whole plant foods on intestinal microbiota And to host physiology 、 Immunity 、 Effects of metabolism and disease risk

doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2022.04.016
Processed food
Although whole plant foods have beneficial effects , But the consumption of whole plant food in industrialized countries has always been Below the recommended level , The packaged food is processed in different degrees .
according to NOVA Food classification tools , Degree of food processing Is the main factor of diet quality Drivers , The most highly processed foods are classified as “ Super processed food ”. Its harmful effects ( Increase energy intake and weight gain ) It has been experimentally verified in the study of strictly controlled feeding . However , There is little consistency in the definition of ultra processed foods or examples of such foods , The comprehensive recommendation to avoid all over processed foods without considering their individual nutritional properties is controversial .
How processed food can have adverse effects ?
The functional characteristics of processed foods are fundamentally different from those of whole plant foods . Processed foods usually have Higher energy density , also lack In plant cells Three dimensional structure . therefore , Nutrients are mainly acellular ( It is not contained in the cell ), More easily digested by the host , This increases the kinetics of nutrient absorption .
These easily fermentable nutrients may Promote bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine , as well as Harmful microorganisms Composition and metabolic status , Thus, immune and endocrine functions are affected negative effect , and junction Intestinal microbiota Can't get These nutrients .
for example , High fructose corn syrup It has been shown to cause Fatty liver disease and glucose Intolerant , The pattern is related to the changes of intestinal microbiota composition and function .
Processed food : Food additives affect the flora
Food additives in processed foods , Sure Further improve the taste and quality guarantee period , But will Affect the intestinal microbiota .
Synthetic emulsifier carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and Polysorbate -80 Damage the intestinal barrier function , Cause the microbiota to invade the epithelium , Promote the metabolic abnormality and Mild inflammation , And genetically susceptible mice colitis , There is a causal relationship between the mode and the intestinal microbiota .
In another emulsifier Glycerol monolaurate Similar results were also observed in mice . Short term human consumption CMC It will be Significant changes in microbiota composition , Reduce Fecal short chain fatty acid levels , And induce Bacteria invade the mucus layer .
In processed foods High salt The content may also change the microbiota . Salt intake Reduced lactic acid bacteria The abundance of , This is related to the helper effect in mouse intestinal lamina propria lymphocytes and human peripheral blood lymphocytes T cells 17 An increase in the number of and High blood pressure of .
Another study on mice reported similar results , The high salt diet reduced the abundance of lactic acid bacteria , increase 了 Proinflammatory genes The expression of , and exacerbate In two different disease models colitis .
therefore , The available evidence shows that , The effects of processed foods and whole plant foods on human health Contrast effect Partly by Intestinal microbiome mediated Of .
Effects of processed foods on gut microbiota And to host physiology 、 Immunity 、 Effects of metabolism and disease risk

doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2022.04.016
For more information on food additives and flora, see the previous article :
Your anxiety may be related to food additives , Beware of microbiota changes caused by food additives
Fruits and vegetables
According to the dietary guidelines , Healthy diet The biggest components should be vegetables and fruits . At present, the scientific evidence about the ability of vegetables and fruits to prevent a variety of chronic diseases is very strong .
▸ Vegetables and fruits are rich in dietary fiber
Fruits and vegetables can serve up to 8g Dietary fiber , And contains a variety of fibers , Including pectin 、 Inulin 、 cellulose 、 Xylan 、 Raffinose and stachyose . These fibers cause The microbiome is independent ( For example, delayed absorption of large amounts of nutrients ) and The microbiome depends on ( For example, short chain fatty acids mediate the decline of insulin resistance ) Physiological effects .
Findings of human controlled feeding experiment , Rich in Inulin Our vegetables are Increase the level of bifidobacteria , Promote satiety , And lose weight .
In mice fed a high-fat diet , Antibiotic Treatment Reduces the metabolic benefits of inulin , Such as reducing these benefits : Inducing the incretin hormone glucagon like peptide in the small intestine 1 And protection against metabolic syndrome , This indicates the causal role of the microbiota .
▸ Vegetables and fruits are also important sources of phytochemicals
Include Polyphenols 、 Glucosinolates 、 Terpenoids 、 Phytosterols and alkaloids .
Cranberry extract It is a rich source of polyphenols , In mice fed a high-fat, high sugar diet Induced metabolic improvement ( for example , Reduce visceral obesity and Improve insulin sensitivity ), This is related to Akkermansia muciniphila Related to the increase of .
notes :Akkermansia muciniphila Bacteria have shown beneficial physiological effects in both animals and humans . For more information about the bacterium, see the previous article :
Important intestinal bacteria ——Akkermansia Muciniphila, How it protects gut health
Nature | AKK bacteria —— The next generation of beneficial bacteria
From clinical and preclinical studies , There is also new evidence that the microbiome is broccoli Play a role in the physiological effects of . The latter laid the foundation for the biological activity of broccoli derived glucosinolates to be converted into chemopreventive isothiocyanates Genetic and biochemical basis of Bacteroides .
in general , Available evidence supports the role of gut microbiota in mediating the health effects of vegetables and fruits .
Food to the host - Effects of microbial interactions And how they are consistent with the recommendations in the dietary guidelines

doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2022.04.016
Extended reading : Common fruits are harmful to intestinal flora 、 Effects of intestinal peristalsis and constipation
Whole grain
Most dietary guidelines recommend Eat whole grains Not refined grains . The bran layer of whole grains is removed to produce refined grains , Contains phytochemicals ( Such as ferulic acid 、 Flavonoids ) And dietary fiber .
▸ Whole grains contain unique fibers , The anti-inflammatory effect is related to the flora
Whole grains contain Unique hemicellulose fiber , Such as xylan and β-(1→ 3,1 → 4)— Remove cellulose 、 Resistant starch and oligosaccharides , also glucan . Whole grains can Reduce the risk of chronic diseases The evidence base is convincing . Human intervention tests show that , Anti inflammatory effects of whole grains In parallel with changes in the intestinal microbiota .
In healthy adults , It shows the health Enrichment of beneficial microorganisms , Such as Bifidobacteria and Butyric acid producing bacteria ( Eubacterium rectale Eubacterium rectale、Roseburia faecis, Roseburia intestinalis), Short chain fatty acid producing bacteria Lachnospira An increase in , Faeces Acetate and total short chain fatty acids increased , Enterobacteriaceae decreased .
Although changes in the microbiome provide a potential explanation for anti-inflammatory effects , But these studies are not consistent ; Further research reports have no impact , No causal relationship has been established .
▸ Some of the metabolic benefits of whole grains are mediated by the intestinal flora
Studies combining human studies with mouse experiments have shown that , Microbiome has a causal effect on the health of whole grains .
eating Barley kernel bread Of people are divided into “ Responder ” and “ No responders ”,“ Responder ” Glucose metabolism Improved by intervention .
Responder Prevotella / Bacteroides ratio and Prevotella copri abundance elevated , as well as code Degradation of complex polysaccharides Of microbial genes in responders elevated .
About Prevotella copri See for details : Important cornerstone bacteria of the intestine —— Prevotella Prevotella
Sterile mice were gavaged with Prevotella or containing P.copri Of “ Respondent ” After the human microbiota , After feeding standard food , Glucose tolerance has improved , This is in mechanism It is related to the increase of liver glycogen storage .
Further research confirms , stay The baseline It contains high-level Prevotella , Meeting Cause overweight , And Eat whole grains The diet of an individual lose weight .
Plant protein food
Some dietary guidelines ( Canadian Food Guide 、 Dietary guidelines for the Brazilian population and for the UK Eatwell guide ) It is recommended that you always Eat vegetable protein food ( Such as beans 、 nuts ), Because they are good for human health .
peas and beans
Beans are rich in fiber , Especially cellulose 、 pectin 、 Mannan 、 Stachyose 、 Raffinose and resistant starch .
Legumes also contain Flavonol etc. Phytochemicals , Flavonol is a known antiinflammatory Flavonoid subclasses , Also contains Phenolic acid , Compared with phenolic acids in grains , Phenolic acids in beans Higher bioavailability .
Emerging evidence suggests that , The intestinal microbiota plays a role in the health effects of legumes .
for example , Mung bean supplements Reduce Mice fed a high-fat diet Weight gain and fat accumulation , But it did not reduce weight gain and fat accumulation in sterile mice fed the same diet .
nuts
Nuts are Unsaturated fatty acid 、 Fiber and phytochemicals The source of the , All these may affect the interaction between host and microorganism .
In a controlled feeding study , Add... Every day walnut can increase Faecalis (Faecalibacterium)、 Roche (Roseburia)、 Clostridium (Clostridium) And D (Dialister).
In a Almond Similar compositional changes were observed in the control feeding study , It shows that the genus Roche (Roseburia)、 Clostridium (Clostridium)、 D. monocytogenes (Dialister) And Spirillum (Lachnospira) The relative abundance of increase .
Nuts are right Abundance of the genus Roche The impact of is already in meta It is confirmed in the analysis .
The main Butyric acid producing bacteria Such as Roseburia intestinalis Can break down the indigestible glycans in nuts β- Mannan is metabolized to butyrate .
In nuts omega-3 Fatty acids It may also enhance the presence of Roche , Because in humans , A diet that supplements walnuts and a diet that does not contain walnuts and has the same fatty acid composition increase The relative abundance of the genus rhodobacteria .
In addition to the fiber and unsaturated fatty acids in nuts , Intestinal microbes also Plant chemicals Ellagic tannins and ellagic acid Metabolize to urolithin , Urolithin is a biological activity antiinflammatory compound .
All in all , Increasing nut intake seems to affect the functional components of the microbiota in part Good for host health .
Anti inflammatory see current research linking the benefits of plant protein foods to the microbiome , But the research in this field is still in the preliminary stage .
Plant protein Than animal protein More difficult to digest And thus provide a potential substrate for colonic microorganisms , This can lead to Produce beneficial bioactive metabolites , For example, tryptophan metabolism . However , Proteolytic microbial fermentation can also be harmful ( See discussion below —— Red meat and processed meat ). At present, it is not clear whether the metabolic results of microbial fermentation of plant proteins are different from those of animal proteins , Further research is needed .
fish
Dietary guidelines have always encouraged Fish as a good source of protein and Good fatty acids form .
Fatty fish
Fatty fish are long chains ω-3 Fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) And docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) The main One of the natural dietary sources .
Strong evidence from observational and intervention studies shows that , Fatty fish The increase in intake has Heart protection effect , Intestinal microbiota It may be these health effects Potential intermediaries .
Fish oil
Mouse experiments show that , With lard ( Rich in saturated fat ) comparison , Fish oil decreases 了 Toll Like receptor activation and white adipose tissue inflammation , This is related to Improve insulin sensitivity of .
In addition to the different effects of these two fats on the composition of the microbiota ( Lard increases Bilophila bacteria ) outside , Compared with mice fed with traditional lard , Feed fish oil After colonization of cecal microbiota in sterile mice and mice fed antibiotics , lose weight , White adipose tissue Inflammation is relieved .
This study provides evidence for the causal role of the gut microbiota in the inflammatory effects of saturated fat .
No causal inference has been made in humans , But found in fatty fish and other dietary sources omega-3 Fatty acids Has been proposed As a candidate prebiotic , Because they are used by specific gut microbes .
In a randomized controlled trial , Fish origin omega-3 supplements Added Coprococcus The abundance of , It is correlated with the level of triglyceride rich lipoprotein negative correlation .
therefore , Intestinal microbiome may be the mediator of the cardioprotective effect of polyunsaturated fatty acids .
All the above dietary recommendations are close to one dietary pattern , That's the Mediterranean diet , As one of the most popular dietary patterns ,
What is unique about the Mediterranean diet ?
What are the effects on the flora ?
Next, learn more about the Mediterranean diet .
03
Focus on eating patterns : Mediterranean diet
We are beginning to realize that , health Not just by individual foods Influence , It is Affected by their mutual connection and synergy . therefore , Recently updated several dietary guidelines , Such as 《 Chinese diet guide 2022》、《2020-2025 American dietary guidelines 》、《 Canadian Food Guide 》 When the focus on eating patterns has changed .
The interaction between foods is also related to their impact on the intestinal microbiota , People's understanding of dietary patterns , Especially those with established health benefits ( Like the Mediterranean diet ) How to affect host health through changes in microbiota composition and function .
▸ The Mediterranean diet combines many food groups that have beneficial effects on host microbial interactions
Mediterranean diet recommend vegetables 、 Fruits 、 Whole grains 、 peas and beans 、 Nuts and olive oil As a staple food , Moderate intake fish 、 poultry 、 Eggs and dairy products , and Limit your intake Red and processed meat and processed food .
In a randomized controlled trial of overweight individuals , Compared to the control diet , Sticking to a Mediterranean diet can Reduce plasma cholesterol concentration , and increase Butyric acid producing bacteria Clostridium praecox (F. prausnitzii) and Roche (Roseburia) The abundance of .F.prausnitzii and Roseburia It is also a taxon determined by random forest model , These models can best predict diet compliance scores .
▸ Mediterranean diet improves cognition in the elderly
In a large multicenter randomized controlled trial , The test involves continuity 12 Months eating Mediterranean diet The elderly . These taxa are related to Improvement of cognitive function There is a positive correlation , It is negatively correlated with inflammatory markers and weakness .
▸ The Mediterranean diet reduces the risk of myocardial infarction
In a prospective cohort study , Long term adherence to Mediterranean diet and F. prausnitzii, Eubacterium eligens, Bacteroides cellulosilyticus There is a positive correlation . This study further shows that , With those who carry P.copri Compared with ,P.copri Risk of myocardial infarction in people with low abundance and adherence to the Mediterranean diet The lower .
Microbiological studies of the Mediterranean diet emphasize its importance in dietary recommendations . Recently, the updated dietary guidelines of some countries recommend a dietary pattern similar to the Mediterranean diet , Such as diet to prevent hypertension (DASH) diet , The role of microbiome in regulating its health effects was also studied .
04
diet - microorganism - Knowledge of host interactions Can you provide a solution ?
Although dietary guidelines have evolved to reflect new available evidence , And generally agreed with its recommendations , But the controversy still exists .
ad locum , We talked about host - How microbial interactions provide insight to help resolve these controversies .
Red meat and processed meat
Red meat contain Essential micronutrients , It is an important source of high-quality protein . However , Most dietary guidelines recommend only moderate eating , Also suggest Avoid eating processed meat ( Salting 、 Cured and smoked meat )( surface 1).
▸ Red meat and processed meat are controversial ?
In cancer prevention , These assessments were conducted by the international agency for research on cancer (IARC) With the world cancer research foundation . Despite these unanimous suggestions , but 2019 A series of systematic reviews in concluded that , Adults should continue their current intake of red and processed meat , The reason is that there is insufficient evidence of their association with adverse health outcomes . This has caused controversy in the field of nutrition .
Intestinal flora provides another perspective on the debate
The effect of gut microbes on red meat and processed meat Proteolytic fermentation Can lead to Potentially harmful metabolites , For example, ammonia 、 P-cresol and hydrogen sulfide .
▸ Red meat and processed meat → Sulfide producing bacteria ferment → May cause cancer
hydrogen sulfide It is produced by sulfur-containing amino acids fermented by Vibrio desulfuricus and other bacteria , And as a mucus dissolving agent , Sure Increase intestinal permeability in mice .
This makes it possible for hemoglobin can Increase excessive proliferation and hyperplasia in the gut , Inhibition Tumor suppressor genes , and Activate Oncogene , All of these are cancer The underlying cause of .
Antibiotic administration Inhibition These effects in mice , indicate The causal role of the gut microbiota . In humans , The bacteria and ways of sulfide production are similar to Advanced colorectal cancer Is closely related to the .
▸ Red meat and processed meat →TMAO→ Cardiovascular disease
Intestinal microbes will be a large number of meat products L-carnitine and phosphatidylcholine To trimethylamine , Trimethylamine is oxidized by monooxygenase containing liver flavin (FMO) Oxidation to trimethylamine -N- oxide (TMAO).
TMAO It circulates in the plasma and is effectively excreted by the kidneys , And in Animal models in And Cardiovascular disease has cause and effect Relationship . Observational research reports TMAO There is a strong positive correlation between blood glucose levels and the risk of cardiovascular disease . However , Animal experiments are not consistent , and human beings Medium TMAO Levels are often confused and It may be caused by the decline of renal function cause .
Besides ,TMAO Paradigm and will be rich in TMAO Epidemiological findings linking fatty fish and their precursors to beneficial cardiac metabolic outcomes atypism .
Food other than meat ( Cruciferous vegetables ) Can inhibit FMO3 Activity of , send The results More complicated .
In order to clarify the TMAO The causal contribution of , Controlled feeding trials of sufficient duration are required in humans , To evaluate alternative markers of proven cardiovascular disease .
▸ Processed meat contains other compounds that are not present in lean red meat , These compounds may amplify the harmful effects mediated by microorganisms
Most processed meat Rich in saturated fat , can stimulate Liver in small intestine bile acid Secrete .
Some primary bile acids escape enterohepatic recirculation and enter the large intestine , There they are converted by microbes into secondary bile acids . among , Deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid Can cause oxidative stress and DNA Damage , And with Colon cancer Occurs in relation to .
A meta-analysis found that , stay colorectal cancer In patients , The functional characteristics of the intestinal microbiome are Increased production of secondary bile acids . A systematic review shows that Saturated fat will decrease The richness and diversity of microorganisms .
Besides , Curing agents used in processed meat Nitrates and nitrites Constitute microbial biotransformation into N- Substrate of nitroso compounds , They lead to DNA Alkylation damage , Therefore has cancer sex .
▸ “ Eat lean and red meat moderately and avoid processed meat ” The scientific basis of
In view of the above points , Gut microbes from red meat and processed meat Toxicity of metabolites And explain them The impact on health of .
Although there is evidence that red meat is a risk factor for colon cancer , but Metabolites produced by protein fermentation ( Such as hydrogen sulfide and ammonia ) Less toxic , at present Not yet classified It is a human carcinogen .
by comparison , Microbial metabolites from processed meat only (N- Nitroso compounds and secondary bile acids ) have Higher toxicity and carcinogenicity .
Considering the possible dose - reaction Relationship , Toxicological considerations justify IARC/ WHO Expert Group on red meat (2A Group , Possible carcinogens ) And processed meat (1 Group , Carcinogens ) Rationality of risk classification , And current dietary guidelines : Moderate consumption Lean meat, red meat and avoid Processed meat .
dairy
▸ A long-standing controversy : To what extent should dairy products be included in a healthy diet ?
- One side , They are calcium 、 Phosphorus and vitamins D The main dietary source of .
- On the other hand , People are concerned about the presence of saturated fats in dairy products .
Most dietary guidelines recommend using skim and low fat (0%-2%) dairy , and Avoid using high fat dairy (>25%, Such as some cheese 、 Cream products and butter ). However , For whole milk products, there are also There is no consensus (∼3.5%), Its harmful effects have been questioned , Some dietary guidelines ( surface 1) Not encouraged .
▸ Interaction between milk fat and intestinal microbiota
A groundbreaking study shows that , Milk derived saturated fat induces taurine binding to bile acids , Promote the production of hydrogen sulfide bacteria Bilophila wadsworthia The outbreak , So as to cause the genetic susceptibility of mice colitis .
Another study on mice confirmed these findings , It mainly comes from A high-fat diet with milk fat increase 了 B. wadsworthia Abundance and Cecal bile acid levels , Which leads to Intestinal barrier dysfunction and Metabolic syndrome .
These animal models emphasize the effect of milk derived saturated fat on the dynamic balance of the microbiota Potentially harmful effects , Support It is recommended to limit high-fat dairy products Diet guide .
As far as we know , There is a lack of human intervention trials to assess whether saturated fat levels in whole milk products affect good control of the microbiota , Such research is necessary , Can provide information for future dietary guidelines .
Low fat and low carbohydrate diet
“ Low fat ”、“ Low carbon ”, For dieters , Is very familiar with .
current Dietary guidelines do not cover Whether limiting fat or carbohydrate intake supports optimal health .
▸ How these diets affect microbiota metabolism and long-term health effects ?
Low fat diet Usually rich in vegetables 、 Fruits 、 Whole grains and plant proteins , So provide beneficial Dietary composition , Change microbial metabolism .
contrary , Low carbs diet Usually fat and / Or high protein content , therefore Low fiber content , This leads to a negative effect on colon health Harmful metabolites .
This was confirmed in a randomized controlled trial , In this experiment , A high protein, low carbohydrate diet increase 了 N- Concentration of nitroso compounds , Reduce The levels of butyrate and anti-inflammatory phenolic compounds were determined .
In another study , High fat 、 A low carbohydrate diet results in the gut microbiota of healthy young people 、 Stool metabonomics and plasma proinflammatory mediators Adverse changes occur .
These findings raise concerns about the long-term health consequences of a low carbohydrate diet , It is consistent with the meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies , The study shows that , eating Animal low carbohydrate diet Participants The mortality rate is the highest .
therefore , It is necessary to improve the low carbohydrate diet by targeting the microbiome .
05
Application of gut microbiota in advancing nutrition strategies
Contemporary national dietary guidelines Highly consistent , Talk to researchers about how diet affects health-related microbes - Host interacting Understanding is the same .
This consistency is remarkable Of , Observational and intervention studies to confirm dietary guidelines Microbiome is not considered . This suggests that the gut microbiota is a key mediator in the physiological effects of diet , In view of Mammalian Anatomy 、 physiology 、 The central aspects of immunity and metabolism have been driven by diet throughout evolution - microorganism - Formed by host interaction , This function may be evolutionarily ingrained .
Although the consistency between the disciplines of nutrition and microbiomics is to a large extent Validated current dietary guidelines , But the researchers think , More systematic The earth combination Nutrients affect the host - Molecular basis of microbial interactions , It is possible to strengthen and innovate human nutrition .
Here is an overview of the opportunities for microbiome perspectives to advance nutritional strategies , And then a Integrating the research framework of intestinal microbiomics , For experimental verification .
Consider evolutionary factors
The most convincing support for the hypothesis that humans and their gut microbiota are coevolutionary comes from Breast milk oligosaccharides (HMO) Explanation of functional characteristics . Breast milk makes up the diet 、 Examples of the importance of evolutionary relationships between the microbiome and human health .
Modern diet may not match human physiology in evolution , This may be Important drivers of chronic disease epidemics .
At present, it is suggested that women and men Take in... Every day 25 Gram and 38 Gram fiber . A series of systematic reviews and meta-analyses support Higher intake The argument of , Indicates daily intake exceed 25–29 Grams of fiber Will bring Additional benefits . Participants received vegetables every day 、 Eat in a fruit and nut diet 100 More than grams of fiber , Sure Significantly reduce serum cholesterol levels , Increase short chain fatty acids in feces .
In a human experiment , African Americans and rural South Africans ( Get used to eating separately Low fiber and High fiber diet ) Exchanged their diet , Leading to African American Mucosal proliferation rate and colitis ( Biomarkers of colon cancer risk ) falling , Rural South Africans experienced adverse changes in these experiments .
The effect of diet exchange is similar to Secondary bile acids Abundance and Short chain fatty acids are produced The opposite change of relevant . For dietary microbiota How interactions affect evolutionary considerations of human physiology , Can suggest for diet 、 Provide information on targeted nutrition strategies and food development to combat the risk of chronic diseases . Evolutionary considerations have also laid the foundation for the recovery strategy of the microbiome .
Bioremediation strategies
Industrialization has resulted in the increase of non communicable chronic diseases and the depletion of the microbiome , Its features It's microbial diversity Reduce , The ability of enzymes to utilize carbohydrates Reduce , Fermentation decreases , And the enrichment of mucus degrading organisms .
Although restoring the microbiota to its ancestral state may be Not reality Of , It could be Not an option Of , But people are right about Develop microbiota recovery strategies 、 There is a growing interest in reconstructing health-related functional features .
Whole plant food
This strategy is supported by the results of a human intervention study , The study tested Rich in whole plant foods ( Provide... Every day 45 Gram fiber ) The diet of , at present Improve short chain fatty acids The output of , and increase The relative abundance of carbohydrate degrading enzymes .
Microbial community restoration methods focusing only on dietary fiber It is unlikely to replace the lost microbial species . It has been put forward Reintroduce Suggestions for Flora lost due to industrialization . Although this is a promising method in the long run , But many The pathogenicity of extinct species Unknown , This makes it possible to translate them into nutritional strategies challenging .
Fermented food
The other way is Fermented food , It is defined as food produced by ideal microbial growth and enzymatic conversion of dietary ingredients , The result usually has Enhanced nutritional properties .
Examples of fermented foods are kefir 、 yogurt 、 Kombucha 、 Fermented soya bean 、 pickled cabbage etc. . Fermented foods rank high in current dietary trends , Popular all over the world . If the raw , Fermented foods usually contain A large number of living microorganisms , These microorganisms have a long history of safe eating .
▸ Research on the health benefits of fermented food
The benefits of fermented foods have been approved by a Overview of qualitative systems It is summarized , This review evaluates observational and experimental studies , According to the report yogurt 、 Kefir and other fermented milk and gastrointestinal health 、2 Type 2 diabetes is associated with cancer risk and good outcomes in weight management .
Besides , One aimed at 120000 Large observational studies with multiple participants have found , gain weight And Yogurt intake between Significant negative correlation Relationship . However , Evidence from randomized controlled trials is scarce , Fermented foods are just beginning to be recommended in dietary guidelines .
A randomized controlled trial on a daily basis included 6 Fermented food The diet was tested , Find out Increased microbiome diversity , and Reduced several proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines .
Additional well-designed randomized controlled trials are needed , And verify the alternative endpoint , With Justify the inclusion of fermented foods in the dietary recommendations . Such studies should consider To some fermented food ( Such as fermented sausage 、 Some cheese and sweetened yogurt ) Of Harmful nutrition aspect , Such as a lot of salt 、 saturated fat 、 Sugar and hardener , May outweigh the potential benefits of living microorganisms .
probiotics 、 synbiotics
Theoretically , You can also use probiotics and synbiotics in your diet ( A combination of probiotics and prebiotics ) To realize the restoration strategy of microbial community .
There are numerous studies exploring these strategies in many clinical settings , Different mechanisms are proposed , For example Immune regulation effect . If the human body is used Bacterial strains inherent in the gastrointestinal tract , Probiotics can Successful long-term colonization .
This strategy can diversify the microbiota , But it is understood that , This has not been systematically tested .
It has also been suggested to explore dietary recommendations for daily intake of live microorganisms , To promote health . To make this concept feasible , Epidemiological studies and randomized controlled trials are needed , To test the value of probiotics in the prevention of chronic diseases .
Reformulation of processed foods
In order to improve the food quality of the whole population , Reformulation recommended Instead of abolishing processed food .
Such an attempt will require Innovation in Food Engineering , This will benefit from diet - microorganism - Host interaction considerations . for example , It can be used Non digestible fermentable starch And other fiber parts replace White flour in food , thus Change the inherent characteristics of processed foods ( Such as fiber content 、 Glycemic index and nutrient digestibility ), With offset Effects on intestinal flora and host metabolism Harmful effects .
In a statistical model study , This approach has had a wide range of implications , The study predicts , If the UK 50% The market share of processed food is about 3 Gram fiber ,2 Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases The risk of illness will Reduce 70% above .
Similar methods can be applied to Reintroduce other bioactive compounds , Such as Phytochemicals , May be linked with dietary fiber .
Instead of relying on personal change Their eating habits improve their health , Why not use more reformulated foods To improve the quality of diet , Without significantly changing your eating habits .
Targeted microbiome regulation
determine “ Healthy microbiota ”
Although it is difficult to define what is “ health ” Microbiome , But the specific taxa and functional characteristics of the intestinal microbiota , especially Taxonomic groups and functional characteristics affected by diet ( for example , Health related SCFA And secondary bile acids ) And health outcomes of .
Once the health promoting taxa and microbiota characteristics have been identified , Can Target them with nutritional strategies .
for example , Metabolically harmful A low carb or high meat diet , It can be done by Add fermentable fiber , To transform microbial metabolism from protein to carbohydrate fermentation , Improve intestinal barrier integrity , And induce systemic metabolic benefits through short chain fatty acids . In view of dietary fiber and low carbohydrate diet Independent metabolic effects , Their combination May arise Synergy .
Extended reading : Healthy human microbiome
Use dietary fiber to enhance the assumed healthy flora
In this way, the flora and its metabolites are promoted . This method is basically In line with prebiotics The concept of , Prebiotics are defined as substrates selectively utilized by host microorganisms , Have health benefits .
Unfortunately , This definition does not constitute “ selectivity ” effect 、 How this effect is causally related to health benefits and how to distinguish prebiotics from dietary fiber provide clear guidance . These concerns led the European food safety agency to prescribe , Prebiotics cannot be marked as prebiotics , But it must be labeled as dietary fiber .
The dietary guidelines also do not mention prebiotics from food sources , This is unfortunate. , because Target microbiome regulation The general concept of There's a lot of hope .
▸ Use dietary fiber to obtain predictable changes in microbiota composition
The researchers proposed a conceptual framework , Using this framework , have access to Dietary fiber with discrete structure ( Defined as “ A unique chemical structure …… It is consistent with the gene cluster encoded in the bacterial genome ”), Come on Obtain predictable and desirable changes in microbiota composition .
The frame was tested in human experiment , In this experiment ,IV The subtle structural differences of type a resistant starch Export short chain fatty acids Lead propionate or butyrate , Propionate or butyrate have different metabolic and physiological functions .
Targeted nutritional microbiome regulation has great prospects for dietary guidelines and therapeutic foods , But there are still questions about which aspects of the microbiome should be targeted , Randomized controlled trials are required To prove whether these strategies can translate into improved health outcomes .
Precise nutrition
Even well controlled dietary interventions can be beneficial to Individuals have different influences . This is of great significance to those currently used in dietary guidelines “ One size fits all ” The method raises questions .
Precise nutrition ( Also known as “ Personalized nutrition ”) The emerging field of science aims to take advantage of human personality , First determine Which? specific features Sure forecast Response to dietary interventions , then Adjust nutrition accordingly , To achieve the same response from different people .
Considering the effect of gut microbiota on diet Highly personalized reaction , Microbiota testing is a key component of precise nutrition strategies for the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases , And other personal specific factors ( for example , genetics 、 Baseline metabolism and physical activity ).
▸ application : The same way to lose weight , What kind of people are more likely to achieve the effect ?—— Machine learning helps you predict
Machine learning methods It can be applied to large participant queues , To determine which characteristics can predict health outcomes . for example , Machine learning algorithms utilize participants' information about blood parameters 、 eating habits 、 Data on microbiome composition and other factors , Accurately predict the postprandial blood glucose response of standardized diet .
Such predictions can Benefit from the combination of microbiome and host genetic data , As a study shows , The baseline Prevotella/ Bacteroides The rate is high , Sure forecast Copy number of salivary amylase gene The lower Of the subjects , It is rich in dietary fiber 、 Whole grain 、 After eating fruits and vegetables Lose more weight .
▸ application : Microbiome combined with mobile phone for diet monitoring —— Machine learning provides you with high-dimensional data , Finally realize personalized suggestions
National dietary guidelines currently do not consider precise or personalized methods , Its implementation will be in Population size is challenging . However , The technology to do this already exists , And you can A combination of microbiome sequencing and smartphone applications for dietary monitoring , Finally, it provides high-dimensional data for machine learning algorithm , So as to feed back personalized nutrition suggestions to users .
▸ Precise nutrition and sustainable conditions
Multi center validation of prediction model Must be in different groups ( Including non western countries and developing countries ) In the middle of , To determine its wide applicability and encourage further improvement . Precise nutrition methods will Depends on continued collaboration between the nutrition and microbiology disciplines , Its population wide implementation will require regulatory agencies 、 Substantial additional input from professional associations and decision makers .
The way forward
Information about dietary microbiome host interactions is possible Further verify 、 Improve and innovate diet suggestions .
take The intestinal microbiome is included in dietary guidance , Need to have The evidence proves that The role of microbiome in the physiological effects of diet Mechanism and causality . To determine the role of gut microbiota in human disease susceptibility Causal relationship It's still a Challenge , This is more complicated in nutrition research , Because diet 、 The interaction between gut microbiota and human health is complex and multi-directional .
diet 、 Between gut microbiota and human health complex 、 Multidirectional causality

doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2022.04.016
Human studies to assess the role of the microbiome in nutrition are due to the Complex ecological characteristics ( Between individuals 、 Geographical and temporal variability ) and Limitations of nutrition research ( Even applicable to randomized controlled trials ) And become more complex ( for example , Difficult to assess dietary intake and adherence to the study protocol 、 Collinearity and confounding factors of dietary composition ).
When designing future nutrition research , These complexities must be considered , With clarify What factors ( Including the microbiome ) It mediates the effect of diet on health .
Researchers recommend excellent reviews outlining best practice guidelines for dietary microbiome research , And by using Three pillars Integrate the intestinal microbiome into nutrition research All stages of the experimental framework to extend these comments .
One 、 The discovery of the microbiota makes assumptions for a healthy diet
The gut microbiota can provide information for nutrition beyond the validation of established dietary strategies , And help determine Microbiota characteristics as future Nutrition goals .
It has been determined that Intestinal flora And human disease Between states relation . Multinomial techniques ( Such as metagenomics 、 Macroproteomics 、 Metabonomics ) And the use of advanced analytical methods , already The potential mechanism and causal basis supporting the biological pathway are established . High-quality 、 Large cohort studies have helped to provide an evidence base for dietary guidelines .
Recent research has extended this framework , and Combine microbiomics with nutritional epidemiology , To clarify the role of microbiomics in diet induced physiological effects . The microbiome can be found 、 The link between health and a particular diet or dietary composition .
The potential mechanism and biological rationality of these interactions and their value as nutritional targets and diagnostic markers can be confirmed in the experimental system .
Two 、 Integration of microbiome and human intervention tests
▸ Randomized controlled trials : Gold standard of nutrition
▸ Cross design : Allow the elimination of individual differences in individual specific factors
▸ Intervention test : Determine cause and effect , Tell the dietary guidelines directly
Randomized controlled trials Is to establish human causality Gold standard of nutrition , If they do well , At the level of evidence Structurally superior to observational tests . This hierarchical structure is also applicable to microbial research . Nutrition randomized controlled trials can Use of microbiome in Epidemiology Apply the same Multigroup approach Expand , With Integrate the intestinal microbiome and effectively test the interaction of specific dietary microbiome . Alternative markers that effectively predict disease risk can be linked to microbiome endpoints ( For example, the composition changes 、 Functions and metabolites ) Combined with molecular markers of biological processes , It is assumed that these biological processes link the metabolic activities of the intestinal microbiome with host immune metabolism ( Gut hormones 、 Cytokines 、TMAO And intestinal barrier integrity markers ), With Confirm the research results and provide hypothetical mechanism explanation .
Cross design about The end point is the microbiome A randomized controlled trial Have an advantage , Because the participants act as their own control , this Allow the elimination of individual differences in individual specific factors ( For example, microbiome 、 genetics 、 Metabolite profiles and baseline clinical measurements ). The study should be further Control for other confounding variables , Such as demography ( Age and gender ) And lifestyle factors ( Habitual diet and drug use ). under these circumstances , Stool consistency and alcohol consumption are accidental confounding factors . You should use Hierarchical randomization to balance Participants' allocation to the treatment group based on age and gender , And should Collect detailed information about confounding variables , In order to control it in statistical analysis . Through the participation of free living or settlement Adequate control Feeding studies , Provide all food , Including sufficient running in period , Sure Eliminate the substantial confounding factors of habitual diet . Such research is difficult and expensive , But it has been in the field of microbiome Successful application .
Intervention test Sure determine The influence of diet on health Causal relationship , thus Tell the dietary guidelines directly . If the microbiome is integrated , Randomized controlled trials It can also provide a hypothetical mechanism explanation for the role of the microbiome in dietary health effects , And provide biomarkers based on diagnostic microbiome for precise nutrition strategies . Regression and correlation analysis It can be used to determine the microbial components induced by diet / Association between functional changes and clinical and mechanical endpoints . Besides , Machine learning model It can be determined whether diet induced physiological changes can be predicted through the impact on the microbiome or host biological processes affected by the microbiome . However , Unless these tests and analyses are extended by specific experimental and statistical methods , Otherwise, they cannot determine the causal role of the gut microbiota in dietary effects .
3、 ... and 、 Mechanism insight and causal inference on the role of microbiome in dietary effects
▸ Collect longitudinal data , Using mathematical methods , Unravel cause and effect
▸ Identify potential mechanisms through animal model expansion
▸ The most commonly used and complex models for establishing causal relationships among flora
▸ Animal models have limitations , But it's valuable for perfecting assumptions
In a randomized controlled trial Collect longitudinal data , For causal inference , Because you must use methods such as mediation analysis , Precede the effect in time . Other mathematical methods , Such as structural equation modeling and Bayesian network , It's fine too Untie diet 、 Between microbiome and human health Causal relationship . so to speak , The most promising experimental design for causal reasoning directly in humans is “ Interventionist framework ”, When the intervention against the assumed cause has a beneficial effect , Can Infer causality . This method can It is suitable for diet intervention with good characteristic effect , To test for microbiome characteristics or to give microbial metabolites ( Suppose the cause ) Whether it can produce the desired effect .
Human research can Extend through animal models , To determine the causal role of the microbiome , Identify causal components in the microbiome , and Identify potential mechanisms . Specific microorganisms, either alone or as a community, can be tested in sterile animal disease models ( Gnostic animals ) Or microbial metabolites related to the physiological effects of human dietary intervention . primate Allow the removal or addition of specific microorganisms , To determine the pathogenic components in the microbial community , And it can be challenged with a feed that mimics the human diet .
Related to human microorganisms (HMA) Rodents are The most common and complex models for establishing microbiome causality , Transplanting human fecal microbiota into rodent disease models .HMA Animals can Compare... Very effectively Human microbiome with or without response to dietary interventions , Especially if it is assumed that the difference is caused by the presence or absence of specific microorganisms . However ,HMA Animals have... In making causal inferences about diet induced changes in the composition of the human microbiome Great limitations . Diets that do not provide live microorganisms are unlikely to add or remove microbial species from the microbiota , But it will only change the relative proportion in the community . This change is unlikely to replicate in recipient animals , Because the ecological and evolutionary forces that form the microbiota are different from those in the donor .
Despite its limitations , But animal models , Especially if its microbiota is well controlled and combined with a multiomic approach , Ability to supplement human research , Because of them Established the mechanism basis of dietary influence . By using animals that better mimic human physiology , Such as pigs and primates , These studies can be further improved . Although it is not necessary to gain insights from mechanism and causal studies , To determine and confirm the health effects of dietary components or the utility of microbiome based biomarkers , But this Very valuable for perfecting assumptions , Sure Innovatively develop targeted nutrition strategies , And provide additional evidence for dietary recommendations .
An experimental framework for integrating the intestinal microbiome into all stages of nutrition research , To promote the understanding of the role of microbiome in healthy diet :
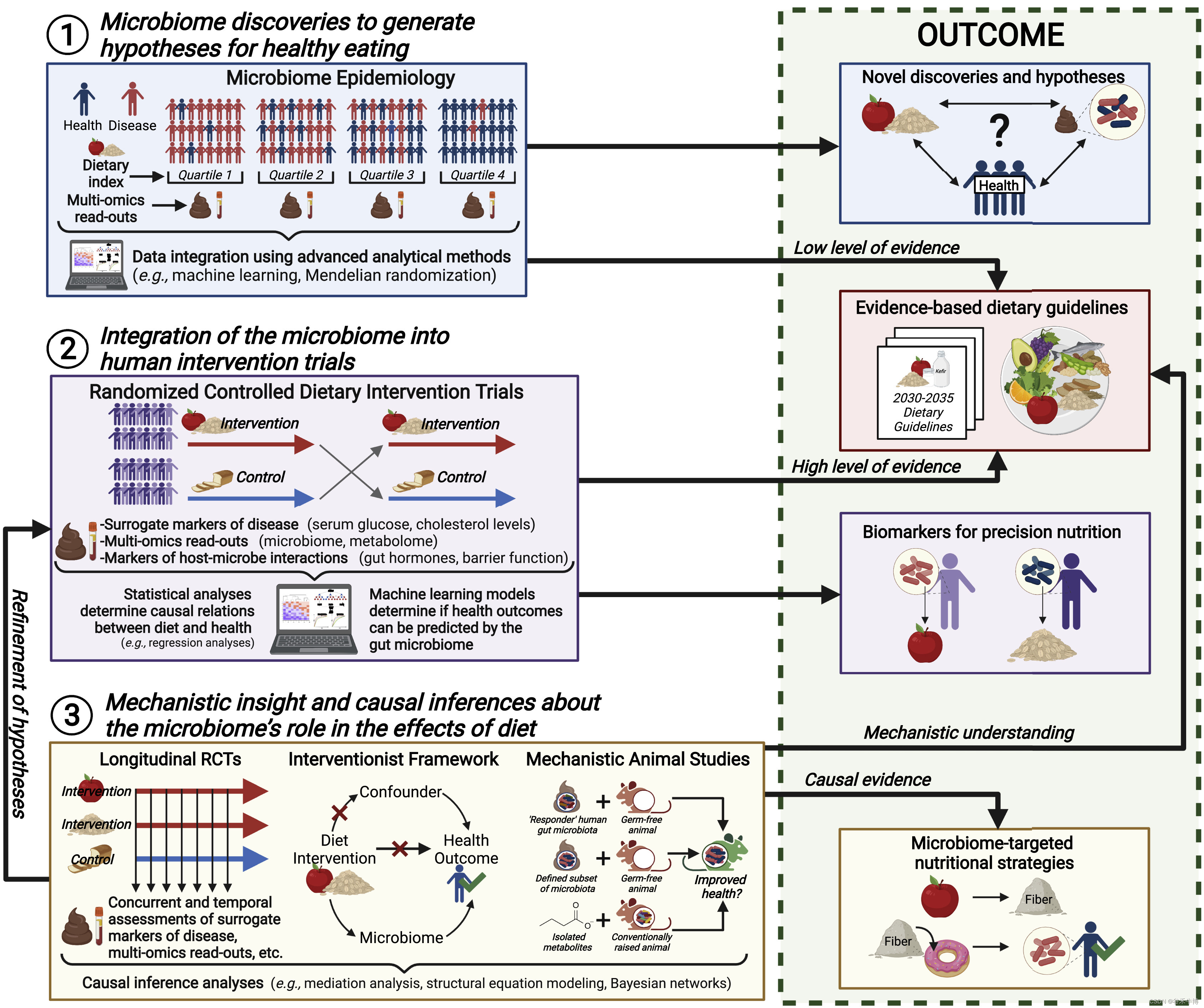
doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2022.04.016
06
junction language
Diet is closely related to disease , And disease is associated with the microbiota . The intestinal microbiota may be a component of nutritional research “ black box ”, diet — The interaction of microbiota may help to establish the mechanism basis of dietary physiological effects .
These two fields have strong biological and evolutionary reasons to expand the already active and ongoing cooperation , To deepen the understanding of how to optimize health through diet .
Microbiome centric endpoints should be integrated into all aspects of nutrition science , To strengthen the evidence base of dietary guidelines . Nutritional microbiology research has the potential to comprehensively understand all aspects of healthy diet , Thus, it is helpful to solve the prevention and management of diet related diseases .
Guhe will also continue to provide information on how the intestinal microbiota affects and mediates dietary compounds 、 Advances in research on the mechanism of physiological effects of specific foods and dietary patterns , Applied to intestinal flora health detection , Constantly update the existing framework , Provide the public with nutritional strategies for the microbiota .
Main references :
Armet AM, Deehan EC, O'Sullivan AF, Mota JF, Field CJ, Prado CM, Lucey AJ, Walter J. Rethinking healthy eating in light of the gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe. 2022 Jun 8;30(6):764-785. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2022.04.016. PMID: 35679823.
Lancaster SM, Lee-McMullen B, Abbott CW, Quijada JV, Hornburg D, Park H, Perelman D, Peterson DJ, Tang M, Robinson A, Ahadi S, Contrepois K, Hung CJ, Ashland M, McLaughlin T, Boonyanit A, Horning A, Sonnenburg JL, Snyder MP. Global, distinctive, and personal changes in molecular and microbial profiles by specific fibers in humans. Cell Host Microbe. 2022 Jun 8;30(6):848-862.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2022.03.036. Epub 2022 Apr 27. PMID: 35483363; PMCID: PMC9187607.
Deehan EC, Walter J. The Fiber Gap and the Disappearing Gut Microbiome: Implications for Human Nutrition. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2016 May;27(5):239-242. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Apr 11. PMID: 27079516.
Guthrie L, Spencer SP, Perelman D, Van Treuren W, Han S, Yu FB, Sonnenburg ED, Fischbach MA, Meyer TW, Sonnenburg JL. Impact of a 7-day homogeneous diet on interpersonal variation in human gut microbiomes and metabolomes. Cell Host Microbe. 2022 Jun 8;30(6):863-874.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2022.05.003. Epub 2022 May 27. PMID: 35643079.
边栏推荐
- Analysis and proposal on the "sour Fox" vulnerability attack weapon platform of the US National Security Agency
- 1-15 nodemon
- 介绍一款|用于多组学整合和网络可视化分析的在线平台
- Phoenix architecture: an architect's perspective
- twelve thousand three hundred and forty-five
- 数字货币:影响深远的创新
- ca i啊几次哦啊句iu家哦11111
- 布隆过滤器
- Testing media cache
- 【回溯】全排列 leetcode46
猜你喜欢

1-2 install and configure MySQL related software

《Dynamic Routing Between Capsules》论文学习总结

Arcmap|assign values to different categories of IDS with the field calculator

Clickhouse native monitoring item, system table description

Reading notes of Clickhouse principle analysis and Application Practice (2)
![[untitled]](/img/42/47a8c8faaed33a1d9e864cb2ef7b72.png)
[untitled]
笔记【JUC包以及Future介绍】

MySQL advanced 3

开源实习经验分享:openEuler软件包加固测试

Jupyterbook clear console output
随机推荐
Clickhouse native monitoring item, system table description
jenkins下载插件下载不了,解决办法
AKK菌——下一代有益菌
1-1 数据库的基本概念
What about degradation of text generation model? Simctg tells you the answer
sdfsdf
给苏丹国安德森苏丹的撒过 d s g
What happens when word encounters an error while trying to open a file?
jupyter notebook/lab 切换conda环境
兴奋神经递质——谷氨酸与大脑健康
Four Misunderstandings of Internet Marketing
Open source internship experience sharing: openeuler software package reinforcement test
ca i啊几次哦啊句iu家哦11111
1-17 express中间件
侧睡哈哈哈哈
网络营销之四大误解
“信任机器”为发展赋能
笔记【JUC包以及Future介绍】
Testing media cache
A group of K inverted linked lists
