当前位置:网站首页>[flask advanced] deeply understand the endpoint of flask routing from the source code
[flask advanced] deeply understand the endpoint of flask routing from the source code
2022-07-23 17:24:00 【Hall owner a Niu】
Personal profile
- Author's brief introduction : Hello everyone , I'm Daniel , New star creator of the whole stack .
- Blogger's personal website : A Niu's blog house
- Stand by me : give the thumbs-up + Collection ️+ Leaving a message.
- Series column :flask Framework quick start
- Maxim : To be light , Because there are people who are afraid of the dark !

Catalog
Preface
A lot of people flask There is a wrong understanding of the routing mechanism , In this section, I will analyze the source code , Take you to know more about flask The routing mechanism of .
flask Route analysis
There are many people to our flask Have a wrong understanding , Think our url Directly corresponding to the view function , There really seems to be no problem on the surface , But you just ignored our endpoint!
Logically speaking , We know url after , There is no problem directly corresponding to our view function , This is positive , Then we reverse the view function to our url It's not very convenient , therefore , our endpoint Can play a reverse construction url The role of .

url_for And endpoint Reverse build url
Let me say something about endpoint How to reverse build URL Of , Actually this endpoint and url_for Is closely linked ,url_for Just reverse construction URL Of .
as follows :
from flask import Flask,url_for
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/', endpoint='my_index')
def index():
return 'index page'
@app.route('/hello')
def hello():
return url_for('.my_index', _external=True)
app.run(debug=True)

notes :
1. stay url_for In reverse , Accept one endpoint Or the function name is parameter ( If it is endpoint,endpoint You need to add a dot in front ), Return the corresponding url Address ( See the source code ).
2. If you use url_for When , Also need to add some , Such as :{ { url_for(‘.my_index’) }}.
3._external=True If set to True, Then generate an absolute path URL, Pictured above .
Reverse construction is mentioned here by the way , Now let's get back to the point , Look at the following two pieces of code :
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
# @app.route('/user')
# Our decorators also have endpoint Parameters , Under normal circumstances, we omit , If omitted, the default value is function name
@app.route("/user",endpoint="user")
def user():
return "a niu"
app.run(debug=True)
Our decorators also have endpoint Parameters , Under normal circumstances, we omit , If omitted, the default value is function name .
Let's look at the following code :
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
# @app.route("/user",endpoint="user")
def user():
return "a niu"
app.add_url_rule(rule="/user",endpoint="user",view_func=user)
app.run(debug=True)

Still no problem , thus it can be seen @app.route() and app.add_url_rule() It is equivalent. , In fact, this is what happened at the bottom of the decorator .
add_url_rule() This method has four parameters :
1.rule: This parameter is very simple , Is the matching routing address
2.endpoint: This parameter is what I want to focus on today ,endpoint.
3.view_func: This parameter is the view function we wrote
4.**options: Variable number of parameters
app.add_url_rule(rule="/user",endpoint="user",view_func=user,methods=['GET'])
Then let's Start with the decorator Go and have a look at the source code , There is a better way to look at the source code is breakpoint debugging , You can try , We can enter flask Inside , Line by line !

Break the decorator , Right click to start debugging , Then move the mouse to route Click on , then ctrl + B Enter our source code

We can see that the bottom layer of the decorator is indeed add_url_rule, there self We can see from the following variables , It's ours app object .

Then click the above image several times to enter , We will see the part in the above figure that I have framed in red , We can see that this part of the code is right endpoint Judge whether it is empty , If it's empty endpoint Is the view function name .
We continue to step into 
We can see that our rule Added to the url_map in .

And then you can see , Save our view function in views_functions In the dictionary , Each key happens to be endpoint, It just forms a mapping .
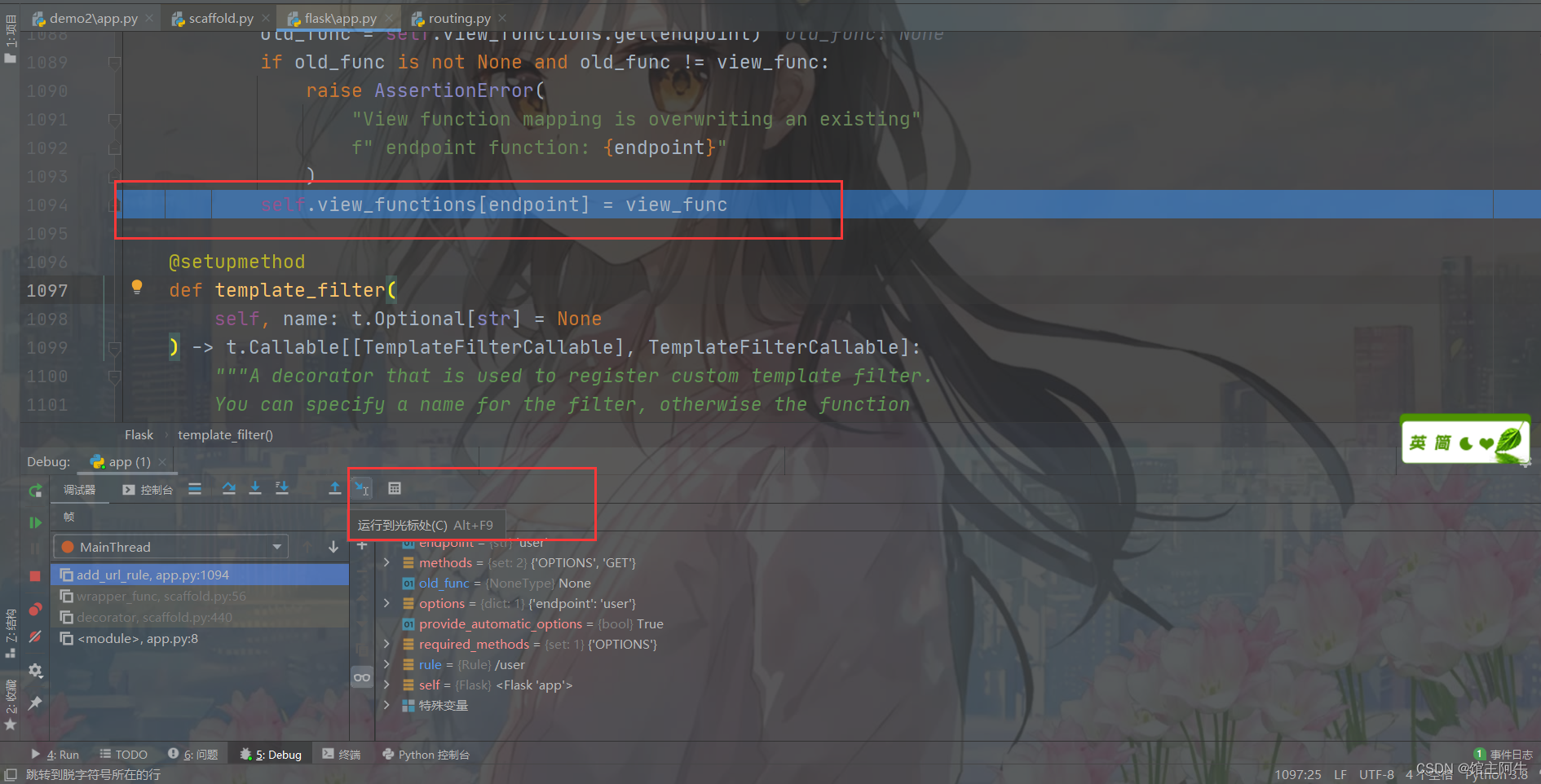
Then we point the cursor to this line , Click Run below to the cursor , At this point, the operation we want to study is over .
Then click on it self, find url_map, Look at the end url_map What's in it ?

You can see url_map It's a list , Deposit is rule-endpoint mapping , And above we also analyzed endpoint and view_func mapping , It's a dictionary .
Here we can print our url_map and view_functions Come and have a clear look :
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
# @app.route('/user')
# Our decorators also have endpoint Parameters , Under normal circumstances, we omit , If omitted, the default value is function name
@app.route("/user",endpoint="user")
def user():
return "a niu"
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(app.url_map)
print(app.view_functions)
app.run()
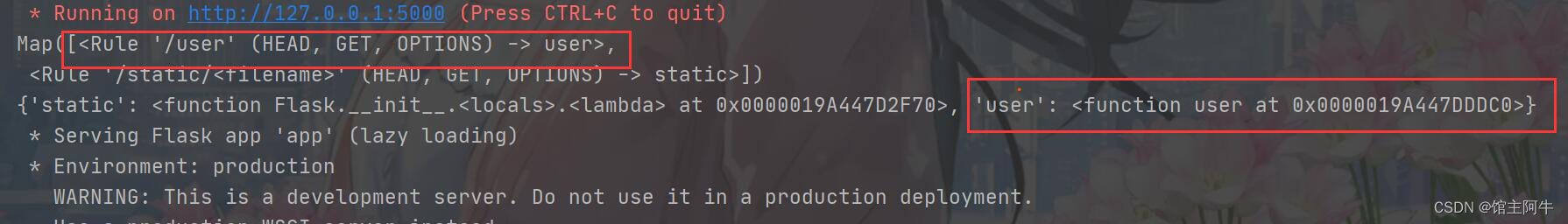
It's the same as looking at the source code analysis !
summary
Every application app There is one. view_functions, This is a dictionary , Storage endpoint-view_func Key value pair .add_url_rule The first function of is to view_functions To add a key-value pair ( This is in the application run It was done before )
Every application app There is one. url_map, It's a Map class ( The concrete realization is werkzeug/routing.py in ), It contains a list , The list element is Rule Example , namely url To endpoint Mapping (werkzeug/routing.py in ).add_url_rule The second function of is to url_map Add Rule Example ( It is also in the application run It was done before )
Conclusion
If you think the blogger's writing is good , You can pay attention to the current column , Bloggers will finish this series ! You are also welcome to subscribe to other good columns of bloggers .
Series column
Soft grinding css
Hard bubble javascript
The front end is practical and small demo
边栏推荐
- PMP practice once a day | don't get lost in the exam -7.23
- 阿里二面:什么是CAS?
- [31. Maze walking (BFS)]
- Thoughts on software quality system
- Pinduoduo app product details interface to obtain activity_ ID value (pinduoduo activity_id interface)
- Opencv finding the intersection of two regions
- 食品安全|火腿肠午餐肉,真有说的那么不堪?
- July training (day 23) - dictionary tree
- keras——accuracy_ Score formula
- C语言·结构体(线性表入门)
猜你喜欢
IDEA中给项目添加依赖的jar包

Function secondary development / plug-in development of JMeter (detailed version)

场景小小记

keras——accuracy_score公式
合宙ESP32C3基于VSCode PIO Arduino开发框架初探教程
SQL bool盲注和时间盲注详解

unity之制作二维码扫描

Pymoo学习 (4): 多标准决策

Shrimp noodles: what do you know about the JVM memory layout?

Preliminary tutorial of Hezhou esp32c3 PIO Arduino development framework based on vscode
随机推荐
Pymoo学习 (4): 多标准决策
Eureka笔记
Kubernetes kubelet 硬核知识 架构
ROS2自学笔记:RQT可视化工具
Compressed storage of arrays and special matrices
软件测试计划包括哪些内容,测试计划如何编写。分享测试计划模板
Add dependent jar packages to the project in the idea
Pymoo学习 (2):带约束的双目标优化问题
程序环境和预处理
项目中遇到的问题及解决
Lake Shore - empx-h2 low temperature probe station
Scene notes
树
How many common SQL misuses are there in MySQL?
数组和特殊矩阵的压缩存储
腾讯撕开中国NFT的“遮羞布”
Opencv open camera, edge detection
【redis入门系列】redis的数据类型及相关命令
Pymoo learning (4): multi criteria decision making
CSR、SSR 与 SSG