当前位置:网站首页>Path Prefixes (倍增!树上の二分)
Path Prefixes (倍增!树上の二分)
2022-08-03 08:11:00 【lovesickman】
Path Prefixes (倍增!树上の二分)
题目描述
You are given a rooted tree. It contains $ n $ vertices, which are numbered from $ 1 $ to $ n $ . The root is the vertex $ 1 $ .
Each edge has two positive integer values. Thus, two positive integers $ a_j $ and $ b_j $ are given for each edge.
Output $ n-1 $ numbers $ r_2, r_3, \dots, r_n $ , where $ r_i $ is defined as follows.
Consider the path from the root (vertex $ 1 $ ) to $ i $ ( $ 2 \le i \le n $ ). Let the sum of the costs of $ a_j $ along this path be $ A_i $ . Then $ r_i $ is equal to the length of the maximum prefix of this path such that the sum of $ b_j $ along this prefix does not exceed $ A_i $ .
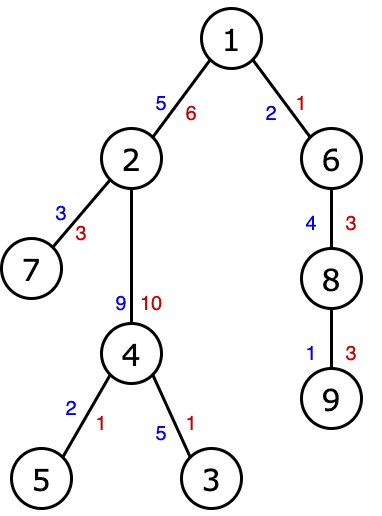 Example for $ n=9 $ . The blue color shows the costs of $ a_j $ , and the red color shows the costs of $ b_j $ .Consider an example. In this case:
Example for $ n=9 $ . The blue color shows the costs of $ a_j $ , and the red color shows the costs of $ b_j $ .Consider an example. In this case:
- $ r_2=0 $ , since the path to $ 2 $ has an amount of $ a_j $ equal to $ 5 $ , only the prefix of this path of length $ 0 $ has a smaller or equal amount of $ b_j $ ;
- $ r_3=3 $ , since the path to $ 3 $ has an amount of $ a_j $ equal to $ 5+9+5=19 $ , the prefix of length $ 3 $ of this path has a sum of $ b_j $ equal to $ 6+10+1=17 $ ( the number is $ 17 \le 19 $ );
- $ r_4=1 $ , since the path to $ 4 $ has an amount of $ a_j $ equal to $ 5+9=14 $ , the prefix of length $ 1 $ of this path has an amount of $ b_j $ equal to $ 6 $ (this is the longest suitable prefix, since the prefix of length $ 2 $ already has an amount of $ b_j $ equal to $ 6+10=16 $ , which is more than $ 14 $ );
- $ r_5=2 $ , since the path to $ 5 $ has an amount of $ a_j $ equal to $ 5+9+2=16 $ , the prefix of length $ 2 $ of this path has a sum of $ b_j $ equal to $ 6+10=16 $ (this is the longest suitable prefix, since the prefix of length $ 3 $ already has an amount of $ b_j $ equal to $ 6+10+1=17 $ , what is more than $ 16 $ );
- $ r_6=1 $ , since the path up to $ 6 $ has an amount of $ a_j $ equal to $ 2 $ , the prefix of length $ 1 $ of this path has an amount of $ b_j $ equal to $ 1 $ ;
- $ r_7=1 $ , since the path to $ 7 $ has an amount of $ a_j $ equal to $ 5+3=8 $ , the prefix of length $ 1 $ of this path has an amount of $ b_j $ equal to $ 6 $ (this is the longest suitable prefix, since the prefix of length $ 2 $ already has an amount of $ b_j $ equal to $ 6+3=9 $ , which is more than $ 8 $ );
- $ r_8=2 $ , since the path up to $ 8 $ has an amount of $ a_j $ equal to $ 2+4=6 $ , the prefix of length $ 2 $ of this path has an amount of $ b_j $ equal to $ 1+3=4 $ ;
- $ r_9=3 $ , since the path to $ 9 $ has an amount of $ a_j $ equal to $ 2+4+1=7 $ , the prefix of length $ 3 $ of this path has a sum of $ b_j $ equal to $ 1+3+3=7 $ .
输入格式
The first line contains an integer $ t $ ( $ 1 \le t \le 10^4 $ ) — the number of test cases in the test.
The descriptions of test cases follow.
Each description begins with a line that contains an integer $ n $ ( $ 2 \le n \le 2\cdot10^5 $ ) — the number of vertices in the tree.
This is followed by $ n-1 $ string, each of which contains three numbers $ p_j, a_j, b_j $ ( $ 1 \le p_j \le n $ ; $ 1 \le a_j,b_j \le 10^9 $ ) — the ancestor of the vertex $ j $ , the first and second values an edge that leads from $ p_j $ to $ j $ . The value of $ j $ runs through all values from $ 2 $ to $ n $ inclusive. It is guaranteed that each set of input data has a correct hanged tree with a root at the vertex $ 1 $ .
It is guaranteed that the sum of $ n $ over all input test cases does not exceed $ 2\cdot10^5 $ .
输出格式
For each test case, output $ n-1 $ integer in one line: $ r_2, r_3, \dots, r_n $ .
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
4
9
1 5 6
4 5 1
2 9 10
4 2 1
1 2 1
2 3 3
6 4 3
8 1 3
4
1 1 100
2 1 1
3 101 1
4
1 100 1
2 1 1
3 1 101
10
1 1 4
2 3 5
2 5 1
3 4 3
3 1 5
5 3 5
5 2 1
1 3 2
6 2 1
样例输出 #1
0 3 1 2 1 1 2 3
0 0 3
1 2 2
0 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 1
提示
The first example is parsed in the statement.
In the second example:
- $ r_2=0 $ , since the path to $ 2 $ has an amount of $ a_j $ equal to $ 1 $ , only the prefix of this path of length $ 0 $ has a smaller or equal amount of $ b_j $ ;
- $ r_3=0 $ , since the path to $ 3 $ has an amount of $ a_j $ equal to $ 1+1=2 $ , the prefix of length $ 1 $ of this path has an amount of $ b_j $ equal to $ 100 $ ( $ 100 > 2 $ );
- $ r_4=3 $ , since the path to $ 4 $ has an amount of $ a_j $ equal to $ 1+1+101=103 $ , the prefix of length $ 3 $ of this path has an amount of $ b_j $ equal to $ 102 $ , .
这是我的第一道树上倍增。还是dfs倍增好用
预处理 f a [ u ] [ i ] , g [ u ] [ i ] fa[u][i],g[u][i] fa[u][i],g[u][i] , g [ u ] [ i ] g[u][i] g[u][i] 表示从 u 节点开始向上跳跃 2 i 2^i 2i 层,从 u 到 f a [ u ] [ i ] fa[u][i] fa[u][i] 这条路径的 b b b 数组权值和。
深度随便开大点就行。
/* A: 10min B: 20min C: 30min D: 40min */
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#define pb push_back
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(f, x) memset(f,x,sizeof(f))
#define fo(i,a,n) for(int i=(a);i<=(n);++i)
#define fo_(i,a,n) for(int i=(a);i<(n);++i)
#define debug(x) cout<<#x<<":"<<x<<endl;
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
//#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,no-stack-protector,unroll-loops,fast-math,O3")
//#pragma GCC target("sse,sse2,sse3,ssse3,sse4,popcnt,abm,mmx,avx,tune=native")
template<typename T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,const vector<T>&v){
for(int i=0,j=0;i<v.size();i++,j++)if(j>=5){
j=0;puts("");}else os<<v[i]<<" ";return os;}
template<typename T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,const set<T>&v){
for(auto c:v)os<<c<<" ";return os;}
template<typename T1,typename T2>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,const map<T1,T2>&v){
for(auto c:v)os<<c.first<<" "<<c.second<<endl;return os;}
template<typename T>inline void rd(T &a) {
char c = getchar(); T x = 0, f = 1; while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-')f = -1; c = getchar();}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + c - '0'; c = getchar();} a = f * x;
}
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
typedef pair<long,long>PLL;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
const int N=2e5+10,M=1e9+7;
ll n,m,_;
int h[N],ne[N*2],e[N*2],idx;
ll w1[N],w2[N];
ll sa[N],sb[N];
ll dist[N],ans[N];
int dep[N];
int fa[N][30]; // f[u][i] 表示从u节点向上跳跃2^i层的祖先是谁
ll g[N][30]; // 表示从u节点出发向上跳跃2^i祖先 w2距离和是多少
void add(int a,int b){
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++;
}
void dfs(int u,int father){
// dfs打表lca
fa[u][0] = father;
g[u][0] = w2[u];
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++){
fa[u][i] = fa[fa[u][i-1]][i-1];
g[u][i] = g[fa[u][i-1]][i-1] + g[u][i-1];
}
for(int i=h[u];~i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(j==father)continue;
dep[j] = dep[u] + 1;
sa[j] = sa[u] + w1[j];
sb[j] = sb[u] + w2[j];
dfs(j,u);
}
}
void solve(){
cin>>n;
mem(h,-1);
fo(i,2,n){
ll u,a,b;cin>>u>>a>>b;
add(i,u),add(u,i);
w1[i]=a;w2[i]=b;
}
dfs(1,-1);
fo(i,2,n){
ll ans = dep[i];
int u = i;
if(sa[u]<sb[u]){
ll t = sb[u]-sa[u]; // 至少跳跃t
for(int j=20;j>=0;j--){
if(g[u][j]<=t){
t-=g[u][j];
u = fa[u][j];
ans -= (1<<j);
}
}
if(t>0)ans--;
}
cout<<ans<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main(){
cin>>_;
while(_--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
还可以树上二分,找小于等于 x 的最大值。
/* A: 10min B: 20min C: 30min D: 40min */
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#define pb push_back
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define mem(f, x) memset(f,x,sizeof(f))
#define fo(i,a,n) for(int i=(a);i<=(n);++i)
#define fo_(i,a,n) for(int i=(a);i<(n);++i)
#define debug(x) cout<<#x<<":"<<x<<endl;
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
//#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,no-stack-protector,unroll-loops,fast-math,O3")
//#pragma GCC target("sse,sse2,sse3,ssse3,sse4,popcnt,abm,mmx,avx,tune=native")
template<typename T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,const vector<T>&v){
for(int i=0,j=0;i<v.size();i++,j++)if(j>=5){
j=0;puts("");}else os<<v[i]<<" ";return os;}
template<typename T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,const set<T>&v){
for(auto c:v)os<<c<<" ";return os;}
template<typename T1,typename T2>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,const map<T1,T2>&v){
for(auto c:v)os<<c.first<<" "<<c.second<<endl;return os;}
template<typename T>inline void rd(T &a) {
char c = getchar(); T x = 0, f = 1; while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-')f = -1; c = getchar();}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + c - '0'; c = getchar();} a = f * x;
}
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
typedef pair<long,long>PLL;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
const int N=2e5+10,M=1e9+7;
ll n,m,_;
int h[N],ne[N*2],e[N*2],idx;
ll w1[N],w2[N];
ll S[N];
int ans[N];
void add(int a,int b){
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++;
}
void dfs(int u,int father,int dep,ll suma){
// dfs打表lca
suma += w1[u];
S[dep] = S[dep-1] + w2[u];
ans[u] = upper_bound(S+1,S+dep+1,suma)-S-1;
for(int i=h[u];~i;i=ne[i]){
int j=e[i];
if(j==father)continue;
dfs(j,u,dep+1,suma);
}
}
void solve(){
cin>>n;
mem(h,-1);
fo(i,2,n){
ll u,a,b;cin>>u>>a>>b;
add(i,u),add(u,i);
w1[i]=a;w2[i]=b;
}
dfs(1,-1,0,0);
fo(i,2,n){
cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main(){
cin>>_;
while(_--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- Poke the myth of Web3?Poke the iron plate.
- WPS EXCEL 筛选指定长度的文本 内容 字符串
- DeFi明斯基时刻:压力测试与启示
- 差分(前缀和的逆运算)
- ArcEngine(四)MapControl_OnMouseDown的使用
- HCIP实验(06)
- mysql5.7服务器The innodb_system data file 'ibdata1' must be writable导致无法启动服务器
- 数仓4.0(二)------ 业务数据采集平台
- ArcEngine (3) zoom in and zoom out through the MapControl control to achieve full-image roaming
- 【收获合辑】k-NN与检索任务的异同+jupyter转pdf
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Guava的Service
Unity关于编辑器扩展自定义标签,方便扩展Inspector
wordpress: 裁剪您的图片时发生错误
Dapr 与 NestJs ,实战编写一个 Pub & Sub 装饰器
Mysql的in和exists用法区别
redis stream 实现消息队列
用diskpart的offline命令弹出顽固硬盘
PowerShell:执行 Install-Module 时,不能从 URI 下载
HCIP练习(OSPF)
@Async注解的坑,小心
五、《图解HTTP》报文首部和HTTP缓存
002-字段不为null
跨域嵌套传递信息(iframe)
WPS EXCEL 筛选指定长度的文本 内容 字符串
thop 使用心得
Fortify白盒神器20.1.1下载及安装(非百度网盘)
mysqlbinlog: unknown variable 'default-character-set=utf8'
vim 折叠函数
ArcEngine (4) Use of MapControl_OnMouseDown
面渣逆袭:MySQL六十六问,两万字+五十图详解