当前位置:网站首页>One article deals with the microstructure and instructions of class
One article deals with the microstructure and instructions of class
2022-07-05 22:48:00 【Thousands of miles in all directions】
Catalog
1.1. Class Bytecode file structure
1.7. Class index 、 Parent index 、 Interface index
1.7.1. this_class( Class index )
1.7.2. super_class( Parent index )
Previous parts , We all introduce it from a macro perspective JVM The role and function of each part of , At the beginning of this chapter, we start from a micro perspective , From the perspective of bytecode JVM How exactly is it carried out . The content of this chapter is to further deepen and expand the previous chapters , Specifically, it includes the following important parts :
1.class What is in the bytecode file , What's the result .
2. How these bytecodes are executed step by step , That is, how the execution of instructions works .
3. We analyze the loading process in detail from the perspective of bytecode , And how to realize its important characteristics .
I believe that after learning this chapter , You will be right. JVM Further understanding .
1. Class File structure
In official documents 《The Java Virtual Machine Specification-JavaSE8》 It's detailed in class The structure of bytecode , Especially the starting position of the file , The meaning of each byte has a clear meaning .
1.1. Class Bytecode file structure
| type | name | explain | length | Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| magic number | u4 | magic | magic number , distinguish Class File format ,CAFEBABE | 4 Bytes | 1 |
| Version number | u2 | minor_version | Sub version number ( Small version ) | 2 Bytes | 1 |
| u2 | major_version | The major version number ( The big version ) | 2 Bytes | 1 | |
| Constant pool set | u2 | constant_pool_count | Constant pool counter | 2 Bytes | 1 |
| cp_info | constant_pool | Constant pool table | n Bytes | constant_pool_count - 1 | |
| Access signs | u2 | access_flags | Access signs | 2 Bytes | 1 |
| Index set | u2 | this_class | Class index | 2 Bytes | 1 |
| u2 | super_class | Parent index | 2 Bytes | 1 | |
| u2 | interfaces_count | Interface counter | 2 Bytes | 1 | |
| u2 | interfaces | Interface index set | 2 Bytes | interfaces_count | |
| Field table set | u2 | fields_count | Field counter | 2 Bytes | 1 |
| field_info | fields | Field table | n Bytes | fields_count | |
| Method table set | u2 | methods_count | Method counter | 2 Bytes | 1 |
| method_info | methods | Method table | n Bytes | methods_count | |
| Property sheet set | u2 | attributes_count | Property counter | 2 Bytes | 1 |
| attribute_info | attributes | Property sheet | n Bytes | attributes_count |
1.2. Class File data type
| data type | Definition | explain |
|---|---|---|
| An unsigned number | Unsigned numbers can be used to describe numbers 、 Index reference 、 Quantity value or according to utf-8 The string value formed by encoding . | Among them, the unsigned number belongs to the basic data type . With u1、u2、u4、u8 To represent respectively 1 Bytes 、2 Bytes 、4 Bytes and 8 Bytes |
| surface | A table is a composite data structure composed of multiple unsigned numbers or other tables . | All watches use “_info” ending . Since the table has no fixed length , So we usually add a number description before it . |
1.3. magic number
Magic Number( magic number )
Every Class At the beginning of the document 4 An unsigned integer of four bytes is called a magic number (Magic Number)
Its only function is to determine whether the file is a valid and legal one that can be accepted by the virtual machine Class file . namely : Magic number is Class The identifier of the file .
Magic number fixed to 0xCAFEBABE. Will not change .
If one Class The document does not contain 0xCAFEBABE start , The virtual machine will directly throw the following error when checking the file :
Error: A JNI error has occurred, please check your installation and try again Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassFormatError: Incompatible magic value 1885430635 in class file StringTestUsing magic numbers instead of extensions for identification is mainly based on security considerations , Because the file extension can be changed at will .
1.4. Document version number
Next to the magic count 4 One byte stores Class Version number of the document . also 4 Bytes . The first 5 And the first 6 A byte represents the minor version number of the compilation minor_version, And the first 7 And the first 8 A byte is the major version number of the compilation major_version.
Together they form class File format version number . For example, some Class The main version number of the document is M, The sub version number is m, So this Class The format version number of the file is determined as M.m.
Version number and Java The corresponding relations of compilers are shown in the following table :
Class Correspondence of file version number
| Main version ( Decimal system ) | Sub version ( Decimal system ) | Compiler Version |
|---|---|---|
| 45 | 3 | 1.1 |
| 46 | 0 | 1.2 |
| 47 | 0 | 1.3 |
| 48 | 0 | 1.4 |
| 49 | 0 | 1.5 |
| 50 | 0 | 1.6 |
| 51 | 0 | 1.7 |
| 52 | 0 | 1.8 |
| 53 | 0 | 1.9 |
| 54 | 0 | 1.10 |
| 55 | 0 | 1.11 |
Java The version number of is from 45 At the beginning ,JDK1.1 Every one after JDK The major version number is added upward 1. Different versions Java Compiler compiled Class The version of the file is different . at present , The high version of the Java A virtual machine can execute Class file , But the lower version Java The virtual machine cannot execute Class file . otherwise JVM Will throw out java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError abnormal .( Backwards compatible ).
in application , Because of the difference between development environment and production environment , It could lead to the problem . therefore , We need to develop , Pay special attention to developing and compiling JDK Version and production environment JDK Version consistency . virtual machine JDK Version is 1.k(k>=2) when , Corresponding class The range of file format version number is 45.0 - 44+k.0( Including both ends ).
1.5. Constant pool set
The constant pool is Class One of the areas with the most content in the file , Constant pool for Class File fields and methods also play a crucial role in parsing . The function of constant pool is similar to that of a small warehouse , Stored a lot of class information , so to speak , The constant pool is the whole Class The cornerstone of the document .
After the version number , Next comes the number of constant pools , And several constant pool table entries .
The number of constants in a constant pool is not fixed , So you need to put an entry at the entrance of the constant pool u2 The unsigned number of type , Represents the constant pool capacity meter value (constant_pool_count). And Java Chinese language habits are different Yes. , This capacity count is from 1 instead of 0 At the beginning .
| type | name | Number |
|---|---|---|
| u2( An unsigned number ) | constant_pool_count | 1 |
| cp_info( surface ) | constant_pool | constant_pool_count - 1 |
As can be seen from the above table ,Class The file uses a front-end capacity counter (constant_pool_count) Add several consecutive data items (constant_pool) To describe the content of a constant pool . We call this series of continuous constant pool data a constant pool collection .
In constant pool table entries , It is used to store all kinds of literal and symbol references generated during compilation , This part will be stored in the runtime constant pool of the method area after the class is loaded
1.5.1. Constant pool counter
constant_pool_count( Constant pool counter )
Because the number of constant pools is not fixed , For a short time , So you need to put two bytes to represent the constant pool capacity count value .
Constant pool capacity meter value (u2 type ): from 1 Start , Represents how many constants there are in the constant pool . namely constant_pool_count=1 Indicates that there is... In the constant pool 0 Constant items .
Demo The value of is :
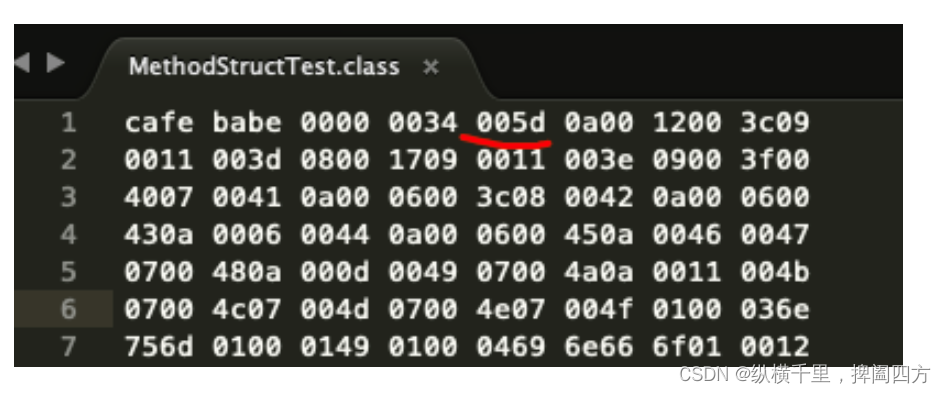
Its value is 0x005d, Namely 93. It should be noted that , It's actually just 93-1=92 Item constant . The index for the range is 1-92. Why , Because we usually write code from 0 At the beginning , But the constant pool here comes from 1 Start , Because it puts the first 0 The item constant is empty . This is to satisfy the requirement that some data pointing to the index value of constant pool need to be expressed under specific circumstances “ Don't reference any constant pool project ” The meaning of , In this case, the index value can be used 0 To express .
We use the following command , It can be seen that only 92 term :
javap -v MethodStructTest.class
1.5.2. Constant pool table
constant_pool It's a table structure , With 1 ~ constant_pool_count - 1 Index , Indicates how many constant items are following . Then there is the constant pool table , It mainly stores two kinds of constants : Literal (Literal) And symbol reference (Symbolic References). The so-called literal is the text string or declared as final Constant value of . The so-called symbolic reference is “ Fully qualified names of classes and interfaces ”、“ Name and descriptor of the field ”、“ The name and descriptor of the method ”.
All in all , It contains class All string constants referenced in the file structure and its substructures 、 Class or interface name 、 Field names and other constants . Every item in the constant pool has the same characteristics . The first 1 Bytes as type tags , Used to determine the format of the item , This byte is called tag byte( Tag bytes 、 Tag bytes ).
This information enters the runtime constant pool of the method area after the bytecode is loaded , This is it. The relationship between constant pool of bytecode and runtime constant pool .
| type | sign ( Or identification ) | describe |
|---|---|---|
| CONSTANT_Utf8_info | 1 | UTF-8 Encoded string |
| CONSTANT_Integer_info | 3 | Integer literal |
| CONSTANT_Float_info | 4 | Floating point literal |
| CONSTANT_Long_info | 5 | A long typeface |
| CONSTANT_Double_info | 6 | Double precision floating point literal |
| CONSTANT_Class_info | 7 | A symbolic reference to a class or interface |
| CONSTANT_String_info | 8 | String type literal |
| CONSTANT_Fieldref_info | 9 | Symbol reference for field |
| CONSTANT_Methodref_info | 10 | Symbolic references to methods in class |
| CONSTANT_InterfaceMethodref_info | 11 | Symbolic references to methods in interfaces |
| CONSTANT_NameAndType_info | 12 | Symbolic references to fields or methods |
| CONSTANT_MethodHandle_info | 15 | Represents a method handle |
| CONSTANT_MethodType_info | 16 | Type of marking method |
| CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic_info | 18 | Represents a dynamic method call point |
Before reading these constants , We need to figure out a few concepts .
All names are limited com/test/test/Demo This is the fully qualified name of the class , Just the name of the package “.“ Replace with ”/”, In order to avoid confusion among consecutive fully qualified names , At the end of use, a “;” Indicates the end of the full name limit .
Simple name A simple name is a method or field name that has no type or parameter modifiers , For example, the add() Methods and num The simple names of the fields are add and num.
The descriptor Descriptors are used to describe the data types of fields 、 Method ( Include quantity 、 Type and order ) And return values . According to the descriptor rule , Basic data type (byte、char、double、float、int、long、short、boolean) And represents no return value void All types are represented by an uppercase character , The object type uses the characters L Add the fully qualified name of the object to indicate , For details, see table below. :
| identifier | meaning |
|---|---|
| B | Basic data type byte |
| C | Basic data type char |
| D | Basic data type double |
| F | Basic data type float |
| I | Basic data type int |
| J | Basic data type long |
| S | Basic data type short |
| Z | Basic data type boolean |
| V | representative void type |
| L | object type , such as :Ljava/lang/Object; |
| [ | An array type , Represents a one-dimensional array . such as :`double[] is [D |
When using descriptors to describe methods , According to the first parameter list , Description of the sequence of the returned values , The parameter list is placed in a set of parentheses in strict order of the parameters “()” within . Such as the method java.lang.String tostring() The descriptor of is ()Ljava/lang/String; , Method int abc(int[]x, int y) The descriptor of is ([II)I.
Additional explanation :
The virtual machine is loading Class Dynamic link will only be performed when the file is loaded , in other words ,Class The final memory layout information of each method and field is not saved in the file . therefore , The symbolic references of these fields and methods cannot be directly used by virtual machines without conversion . When the virtual machine is running , You need to get the corresponding symbol reference from the constant pool , Then in the parsing phase of the class loading process, replace it with a direct reference , And translate it into the specific memory address .
Here is the difference and correlation between symbolic reference and direct reference :
Symbol reference : A symbolic reference describes the referenced target with a set of symbols , A symbol can be any form of literal quantity , As long as it can be used to locate the target unambiguously . Symbol references are independent of the memory layout of the virtual machine implementation , The target of the reference is not necessarily loaded into memory .
Direct reference : A direct reference can be a pointer directly to the target 、 Relative offset or a handle that can be indirectly located to the target . Direct reference is related to the memory layout of the virtual machine , The direct references translated from the same symbol reference on different virtual machine instances are generally not the same . If there is a direct quote , That means that the target of the reference must already exist in memory .
Ⅱ. Constant types and structures
Every constant in the constant pool is a table ,J0K1.7 After that, we have 14 There are two different table structure data . As shown in the table below :

According to the description of each type in the figure above, we can also know what each type is used to describe in the constant pool ( It's mainly literal 、 Symbol reference ) Of . such as : CONSTANT_Integer_info It is used to describe literal information in constant pool , And it's just integer literal information .
Mark is 15、16、18 The constant item type of is used to support dynamic language calls (jdk1.7 When I joined you ).
Details :
CONSTANT_Class_info Structs are used to represent classes or interfaces
CONSTAT_Fieldref_info、CONSTAHT_Methodref_infoF and lCONSTANIT_InterfaceMethodref_info Structure represents the field 、 Fang Huihe's a little bit of a mouth
CONSTANT_String_info Structure is used to show String Constant object of type
CONSTANT_Integer_info and CONSTANT_Float_info Express 4 byte (int and float) The numerical constant of
CONSTANT_Long_info and CONSTAT_Double_info Structural representation 8 Word writing (long and double) The numerical constant of
stay class The most common pool table of files , What we did a Bytes are always borrowed in two table members ( term ) My empty question . If one CONSTAHT_Long_info and CNSTAHT_Double_info Structure in the constant pool n, Then an available index bit in the constant pool n+2, In this case, the index in the constant pool length is n+1 The item for is still valid but must be considered unavailable .
CONSTANT_NameAndType_info Structures are used to represent fields or methods , But it's the same as before 3 It's a different structure ,CONSTANT_NameAndType_info Structure does not specify the class or interface to which the field or method belongs .
CONSTANT_Utf8_info The value used to represent a character constant
CONSTANT_MethodHandle_info Structure is used to represent a method handle
CONSTANT_MethodType_info Structure representation method type
CONSTANT_InvokeDynamic_info Structural representation invokedynamic The boot method used by the command (bootstrap method)、 The name of the dynamic call used to boot the method (dynamic invocation name)、 Parameters and return types , And you can pass in a series of static parameters to the boot method (static argument) The constant .
analytic method :
Parsing one byte at a time
Use javap Command parsing :javap-verbose Demo.class or jclasslib Tools will be more convenient .
summary 1:
this 14 Kind of watch ( Or constant term structure ) What we have in common is : The first one at the beginning of the table is a u1 Flags of type (tag), Represents the table structure used by the current constant item , Which constant type .
In the list of constant pools ,CONSTANT_Utf8_info Constant term is an improved way to use UTF-8 Encoding format to store such as text strings 、 The fully qualified name of a class or interface 、 Simple name of field or method and constant string information such as descriptor .
this 14 Another feature of constant term structure is , among 13 Constant items occupy fixed bytes , Only CONSTANT_Utf8_info Occupied bytes are not fixed , Its size is determined by length decision . Why? ? Because it can be seen from the contents of constant pool , It stores literal and symbolic references , In the end, all of this will be a string , The size of these strings is determined when writing a program , For example, you define a class , Class names can be long or short , So before compiling , Size is not fixed , After compiling , adopt utf-8 code , We can know its length .
summary 2:
Constant pool : It can be understood as Class The repository of resources in the file , It is Class The most data types associated with other projects in the file structure ( Many of the following data types will point here ), It's also occupation Class One of the largest data projects in file space .
Why do constant pools contain these contents ?Java The code is in progress Javac When compiling , Don't like C and C++ There is “ Connect ” This step , It's loading on the virtual machine C1ass Dynamic link when the file is loaded . in other words , stay Class Methods are not saved in the file 、 Field's final memory layout information , So these fields 、 Method can't get the real memory entry address without running time conversion , It can't be used directly by virtual machine . When the virtual machine is running , You need to get the corresponding symbol reference from the constant pool , It is then parsed at class creation or runtime 、 Translate to specific memory address . About the creation of classes and dynamic links , In the virtual machine class loading process will be explained in detail
1.6. Access signs
Access signs (access_flag、 Access signs 、 Access tags )
After the constant pool , Following the access sign . The tag uses two bytes to represent , Used to identify some class or interface level access information , Include : This Class Class or interface ; Is it defined as public type ; Is it defined as abstract type ; If it's a class , Is it declared as final etc. . The various access tags are as follows :
| Logo name | Flag value | meaning |
|---|---|---|
| ACC_PUBLIC | 0x0001 | Mark is public type |
| ACC_FINAL | 0x0010 | The logo is declared to be final, Only classes can set |
| ACC_SUPER | 0x0020 | The logo allows the use of invokespecial New meaning of bytecode instruction ,JDK1.0.2 The flag of the compiled class is true by default .( Using enhanced methods to call parent methods ) |
| ACC_INTERFACE | 0x0200 | Mark this is an interface |
| ACC_ABSTRACT | 0x0400 | Is it abstract type , For interfaces or abstract classes , Secondary flag value is true , Other types are false |
| ACC_SYNTHETIC | 0x1000 | The flag class is not generated by user code ( namely : Class generated by compiler , There is no source code correspondence ) |
| ACC_ANNOTATION | 0x2000 | Mark this is an annotation |
| ACC_ENUM | 0x4000 | Flag this is an enumeration |
The access rights of the class are usually ACC_ The starting constant .
Each type of representation is made by setting access tags 32 A specific bit in a bit . such as , if public final Class , Then the mark is ACC_PUBLIC | ACC_FINAL.
Use ACC_SUPER Methods that allow a class to be more accurately positioned to its parent class super.method(), Modern compilers set and use this flag .
Additional explanation :
with ACC_INTERFACE logo class Files represent interfaces, not classes , Instead, it represents a class, not an interface .
If one class The file is set ACC_INTERFACE sign , Then it has to be set at the same time ACC_ABSTRACT sign . At the same time, it can no longer be set ACC_FINAL、ACC_SUPER or ACC_ENUM sign .
If not set ACC_INTERFACE sign , So this class The file can have all the characters except ACC_ANNOTATION All the other signs except . Of course ,ACC_FINAL and ACC_ABSTRACT Except for such mutually exclusive flags . These two signs cannot be set at the same time .
ACC_SUPER The flag is used to identify... In a class or interface invokespecial What kind of execution semantics does the instruction use . in the light of Java The compiler of virtual machine instruction set should set this flag . about Java SE 8 And later versions , No matter what class What is the actual value of this flag in the file , No matter class What is the version number of the file ,Java Virtual machines think that every class The files are all set with ACC_SUPER sign .
ACC_SUPER Logo is for backward compatibility from old Java Designed for code compiled by a compiler . current ACC_SUPER The logo is created by JDK1.0.2 Generated by previous compilers access_flags There is no definite meaning in , If the sign is set , that 0racle Of Java Virtual machine implementations ignore it .
ACC_SYNTHETIC Flag means that the class or interface is generated by the compiler , Instead of being generated from source code .
Annotation type must be set ACC_ANNOTATION sign . If set ACC_ANNOTATION sign , Then you have to set ACC_INTERFACE sign .
ACC_ENUM Flag indicates that the class or its parent class is an enumeration type .
1.7. Class index 、 Parent index 、 Interface index
After accessing the tag , The category of this class... Will be specified 、 Parent class category and implemented interface , The format is as follows :
| length | meaning |
|---|---|
| u2 | this_class |
| u2 | super_class |
| u2 | interfaces_count |
| u2 | interfaces[interfaces_count] |
These three data are used to determine the inheritance relationship of this class :
The class index is used to determine the fully qualified name of this class
The parent index is used to determine the fully qualified name of the parent of this class . because Java Language does not allow multiple inheritance , So there's only one parent index , except java.1ang.Object outside , be-all Java Class has a parent class , So in addition to java.lang.Object Outside , all Java The parent index of the class is not e.
The interface index set is used to describe which interfaces this class implements , These implemented interfaces will press implements sentence ( If the class itself is an interface , It should be extends sentence ) The subsequent interfaces are arranged from left to right in the interface index set .
1.7.1. this_class( Class index )
2 Byte unsigned integer , Index to constant pool . It provides the fully qualified name of the class , Such as com/test/java1/Demo.this_class The value of must be a valid index value for an item in the constant pool table . Constant pool members at this index must be CONSTANT_Class_info Type structure , The structure represents this class The class or interface defined by the file .
1.7.2. super_class( Parent index )
2 Byte unsigned integer , Index to constant pool . It provides the fully qualified name of the parent class of the current class . If we don't inherit any classes , Its default inheritance is java/lang/object class . meanwhile , because Java Multiple inheritance is not supported , So there's only one parent .
super_class The parent class pointed to cannot be final.
1.7.3. interfaces
Points to the constant pool index collection , It provides a symbolic reference to all implemented interfaces
Because a class can implement multiple interfaces , Therefore, it is necessary to save the index of multiple interfaces in the form of array , Each index representing the interface is also a constant pool CONSTANT_Class( Of course, this has to be the interface , Rather than class ).
Ⅰ. interfaces_count( Interface counter )
interfaces_count The value of the item represents the number of direct hyperinterfaces of the current class or interface .
Ⅱ. interfaces[]( Interface index set )
interfaces[] The value of each member in must be a valid index value to an item in the constant pool table , Its length is interfaces_count. Every member interfaces[i] It has to be for CONSTANT_Class_info structure , among 0 <= i < interfaces_count. stay interfaces[] in , The interface sequence represented by each member and the interface sequence given in the corresponding source code ( From left to right ) equally , namely interfaces[0] Corresponding to the leftmost interface in the source code .
1.8. Field table set
fields
Used to describe variables declared in an interface or class . Field (field) Including class level variables and instance level variables , But not inside the method 、 Local variables declared inside the code block .
What's the name of the field 、 Field is defined why data type , These are not fixed , Only constants in the constant pool can be referenced to describe .
It points to the constant pool index collection , It describes the complete information for each field . For example, the identifier of a field 、 Access modifier (public、private or protected)、 Class variable or instance variable (static Modifier )、 Is it a constant (final Modifier ) etc. .
matters needing attention :
Fields inherited from parent classes or implemented interfaces are not listed in the field table collection , But it's possible to list the original Java Fields that do not exist in the code . For example, in order to maintain the accessibility of external classes in internal classes , Fields that point to external class instances are automatically added .
stay Java Fields in a language cannot be overloaded , The data types of the two fields 、 The modifier is the same or not , Must use a different name , But for bytecode , If the descriptors of the two fields are inconsistent , The duplicate name of that field is legal .
1.8.1. Field counter
fields_count( Field counter )
fields_count The value of represents the current class file fields Number of members of the table . Use two bytes to represent .
fields Each member in the table is a field_info structure , Used to represent all class fields or instance fields declared by the class or interface , Variables declared inside methods are not included , Fields inherited from the parent class or interface are not included .
| Logo name | Flag value | meaning | Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| u2 | access_flags | Access signs | 1 |
| u2 | name_index | Field name index | 1 |
| u2 | descriptor_index | Descriptor index | 1 |
| u2 | attributes_count | Property counter | 1 |
| attribute_info | attributes | Attribute set | attributes_count |
1.8.2. Field table
Ⅰ. Field table access identifier
We know , A field can be modified by various keywords , such as : Scope modifier (public、private、protected)、static Modifier 、final Modifier 、volatile Modifiers, etc . therefore , It can be like the access flag of a class , Use some flags to mark fields . Field access flags are as follows :
| Logo name | Flag value | meaning |
|---|---|---|
| ACC_PUBLIC | 0x0001 | Is the field public |
| ACC_PRIVATE | 0x0002 | Is the field private |
| ACC_PROTECTED | 0x0004 | Is the field protected |
| ACC_STATIC | 0x0008 | Is the field static |
| ACC_FINAL | 0x0010 | Is the field final |
| ACC_VOLATILE | 0x0040 | Is the field volatile |
| ACC_TRANSTENT | 0x0080 | Is the field transient |
| ACC_SYNCHETIC | 0x1000 | Is the field generated automatically by the compiler |
| ACC_ENUM | 0x4000 | Is the field enum |
Ⅱ. Descriptor index
Descriptors are used to describe the data types of fields 、 Method ( Include quantity 、 Type and order ) And return values . According to the descriptor rule , Basic data type (byte,char,double,float,int,long,short,boolean) And represents... With no return value void All types are represented by an uppercase character , And objects use characters L Add the fully qualified name of the object to indicate , As shown below :
| identifier | meaning |
|---|---|
| B | Basic data type byte |
| C | Basic data type char |
| D | Basic data type double |
| F | Basic data type float |
| I | Basic data type int |
| J | Basic data type long |
| S | Basic data type short |
| Z | Basic data type boolean |
| V | representative void type |
| L | object type , such as :Ljava/lang/Object; |
| [ | An array type , Represents a one-dimensional array . such as :`double[] is [[[D |
Ⅲ. Property sheet set
A field may also have some properties , For storing more extra information . Like initialization values 、 Some annotation information, etc . The number of attributes is stored in attribute_count in , The specific contents of attributes are stored in attributes Array .
// Take the constant property as an example , The structure is :
ConstantValue_attribute{
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
u2 constantvalue_index;
}explain : For constant properties ,attribute_length Constant value 2.
1.9. Method table set
methods: Points to the constant pool index collection , It completely describes the signature of each method .
In bytecode files , every last method_info Items correspond to method information in a class or interface . For example, access modifiers for methods (public、private or protected), The return value type of the method and the parameter information of the method .
If the method is not abstract or native Of , So it's reflected in bytecode .
One side ,methods The table only describes the methods declared in the current class or interface , Does not include methods inherited from a parent class or interface . On the other hand ,methods It is possible for the table to have methods added automatically by the compiler , The most typical is the method information generated by the compiler ( such as : class ( Interface ) Initialization method clinit() And instance initialization method init()).
Precautions for use :
stay Java In language , To reload (Overload) One way , In addition to having the same simple name as the original method , It is also required to have a signature different from the original method , Signature is a set of field symbol references of each parameter in the constant pool in a method , That is because the return value is not included in the signature , therefore Java Language can't just rely on different return values to overload an existing method . But in Class In file format , Signature signature has a wider range , As long as the descriptors are not exactly the same two methods can coexist . in other words , If the two methods have the same name and signature characteristics , But the return value is different , Then it can coexist legally in the same class In file .
in other words , Even though Java The syntax specification does not allow multiple methods to be declared in a class or interface with the same signature , But and Java Grammatical norms are the opposite , In the bytecode file, however, multiple methods with the same signature are allowed to be stored , The only condition is that the return values between these methods cannot be the same .
1.9.1. Method counter
methods_count( Method counter )
methods_count The value of represents the current class file methods Number of members of the table . Use two bytes to represent .
methods Each member in the table is a method_info structure .
1.9.2. Method table
methods[]( Method table )
methods Each member in the table must be a method_info structure , A complete description of a method in the current class or interface . If a method_info Structural access_flags Item is not set ACC_NATIVE The logo is not set either ACC_ABSTRACT sign , Then the structure should also include the Java Virtual machine instructions .
method_info Structs can represent all the methods defined in classes and interfaces , Including example methods 、 Class method 、 Instance initialization methods and class or interface initialization methods
The structure of the method table is actually the same as that of the field table , The structure of the method table is as follows :
| Logo name | Flag value | meaning | Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| u2 | access_flags | Access signs | 1 |
| u2 | name_index | Method name index | 1 |
| u2 | descriptor_index | Descriptor index | 1 |
| u2 | attributes_count | Property counter | 1 |
| attribute_info | attributes | Attribute set | attributes_count |
Method table access flag
Just like the field table , The method table also has access flags , And part of their logo is the same , Part of it is different , The specific access flag of the method table is as follows :
| Logo name | Flag value | meaning |
|---|---|---|
| ACC_PUBLIC | 0x0001 | public, Methods can be accessed from outside the package |
| ACC_PRIVATE | 0x0002 | private, Method can only be accessed by this class |
| ACC_PROTECTED | 0x0004 | protected, Methods are accessible in themselves and subclasses |
| ACC_STATIC | 0x0008 | static, Static methods |
1.10. Property sheet set
The property table collection after the method table collection , refer to class The auxiliary information carried by the file , Let's say class The name of the source file of the file . And anything with RetentionPolicy.CLASS perhaps RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME Annotations . This kind of information is usually used to Java Verification and running of virtual machine , as well as Java Program debugging , Generally, there is no need to know more about .
Besides , Field table 、 Method tables can have their own property tables . Used to describe specific information about certain scenarios .
The restriction of property sheet collection is not so strict , There is no longer a strict order for individual property sheets , And as long as it does not duplicate the existing property name , Any compiler implemented by anyone can write their own defined attribute information to the attribute table , but Java When the virtual machine runs, it ignores the properties it doesn't know .
1.10.1. Property counter
attributes_count( Property counter )
attributes_count The value of represents the current class The number of members of the file property sheet . Every item in the property sheet is a attribute_info structure .
1.10.2. Property sheet
attributes[]( Property sheet )
The value of each item in the property sheet must be attribute_info structure . The structure of attribute table is flexible , The various properties are as long as they satisfy the following structure .
The general format of attributes
| type | name | Number | meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| u2 | attribute_name_index | 1 | Property name index |
| u4 | attribute_length | 1 | Attribute length |
| u1 | info | attribute_length | Property sheet |
Attribute types
Property sheets can actually have many types , What you see above Code Attributes are just one of them ,Java8 It's defined in it 23 Species attribute . Here are the predefined properties in the virtual machine :
| The attribute name | Use location | meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Code | Method table | Java Bytecode instructions compiled by code |
| ConstantValue | Field table | final Constant pool defined by keyword |
| Deprecated | class , Method , Field table | Be declared deprecated Methods and fields |
| Exceptions | Method table | The exception thrown by the method |
| EnclosingMethod | Class file | Only if a class is a local class or an anonymous class can have this property , This property is used to identify the peripheral methods of this class |
| InnerClass | Class file | Inner class list |
| LineNumberTable | Code attribute | Java Source line number and bytecode instructions corresponding relationship |
| LocalVariableTable | Code attribute | Method's local variable description |
| StackMapTable | Code attribute | JDK1.6 New properties in , For new types to check whether the verifier and the class needed to handle the local variables and operands of the target method match |
| Signature | class , Method table , Field table | Used to support method signature in the case of generics |
| SourceFile | Class file | Record source file name |
| SourceDebugExtension | Class file | For storing additional debugging information |
| Synthetic | class , Method table , Field table | Flag methods or fields are generated automatically by the compiler |
| LocalVariableTypeTable | class | Yeah, it's hard to replace descriptor with signature , It is added to describe generic parameterized types after the introduction of generic syntax |
| RuntimeVisibleAnnotations | class , Method table , Field table | Support for dynamic annotation |
| RuntimeInvisibleAnnotations | class , Method table , Field table | Used to indicate which annotations are not visible at run time |
| RuntimeVisibleParameterAnnotation | Method table | The functions and RuntimeVisibleAnnotations Properties are similar to , It's just the object or method of action |
| RuntimeInvisibleParameterAnnotation | Method table | The functions and RuntimeInvisibleAnnotations Properties are similar to , It's just the object or method of action |
| AnnotationDefault | Method table | Used to record the default values of annotation class elements |
| BootstrapMethods | Class file | Used to hold invokeddynamic Boot method qualifier for instruction reference |
perhaps ( Check the website )

Some of the attributes are explained in detail
① ConstantValue attribute
ConstantValue Property represents the value of a constant field . be located field_info Structure in the property sheet .
ConstantValue_attribute{
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
u2 constantvalue_index;// Index of field value in constant pool , The constant pool entry at the index gives the constant value represented by the property .( for example , The value is 1ong Type , In the constant pool is CONSTANT_Long)
}② Deprecated attribute
Deprecated Property is in JDK1.1 To support keywords in annotations @deprecated And the introduction of .
Deprecated_attribute{
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
}
③ Code attribute
Code Property is the code in the method body . however , Not all method tables have Code attribute . Like interfaces or abstract methods , They don't have specific methods , So there won't be Code The attribute is .Code Structure of property sheet , Here's the picture :
| type | name | Number | meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| u2 | attribute_name_index | 1 | Property name index |
| u4 | attribute_length | 1 | Attribute length |
| u2 | max_stack | 1 | Maximum operand stack depth |
| u2 | max_locals | 1 | The persistence space required by the local variable table |
| u4 | code_length | 1 | The length of the bytecode instruction |
| u1 | code | code_lenth | Store bytecode instructions |
| u2 | exception_table_length | 1 | Exception table length |
| exception_info | exception_table | exception_length | Anomaly table |
| u2 | attributes_count | 1 | Property set counter |
| attribute_info | attributes | attributes_count | Attribute set |
You can see :Code The first two items of the property sheet are consistent with the property sheet , namely Code The property sheet follows the structure of the property sheet , The latter are his custom structures .
④ InnerClasses attribute
For the convenience of illustration, a class or interface is defined Class The format is C. If C The constant pool of contains a CONSTANT_Class_info member , And the class or interface represented by this member does not belong to any package , that C Of ClassFile The attribute table of the structure must contain the corresponding InnerClasses attribute .InnerClasses Property is in JDK1.1 To support internal classes and interfaces , be located ClassFile Structure's property sheet .
⑤ LineNumberTable attribute
LineNumberTable Attributes are optional variable length attributes , be located Code Structure's property sheet .
LineNumberTable Property is used to describe Java The correspondence between source line number and bytecode line number . This property can be used to locate the number of lines of code executed during debugging .
start_pc, Bytecode line number ;1ine_number, namely Java Source code line number .
stay Code In the property sheet of the property ,LineNumberTable Attributes can appear in any order , Besides , Multiple LineNumberTable Attributes can collectively represent what a line number represents in the source file , namely LineNumberTable Attributes do not need to correspond to the lines of the source file one by one .
// LineNumberTable Property sheet structure :
LineNumberTable_attribute{
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
u2 line_number_table_length;
{
u2 start_pc;
u2 line_number;
} line_number_table[line_number_table_length];
}
⑥ LocalVariableTable attribute
LocalVariableTable Is an optional variable length attribute , be located Code In the property sheet of the property . It is used by the debugger to determine the local variable information of the method during execution . stay Code In the property sheet of the property ,LocalVariableTable Attributes can appear in any order .Code Each local variable in a property can have at most one LocalVariableTable attribute .
start pc + length Represents the offset of the beginning and end of the life cycle of this variable in bytecode (this The life cycle starts from scratch e To the end 10)
index This is the slot of this variable in the local variable table ( The slots are reusable )
name It's the variable name
Descriptor Represents the local variable type description
// LocalVariableTable Property sheet structure :
LocalVariableTable_attribute{
u2 attribute_name_index;
u4 attribute_length;
u2 local_variable_table_length;
{
u2 start_pc;
u2 length;
u2 name_index;
u2 descriptor_index;
u2 index;
} local_variable_table[local_variable_table_length];
}⑦ Signature attribute
Signature Attributes are optional fixed length attributes , be located ClassFile,field_info or method_info Structure in the property sheet . stay Java In language , Any class 、 Interface 、 Initializes the generic signature of a method or member if it contains a type variable (Type Variables) Or parameterized type (Parameterized Types), be Signature Property records generic signature information for it .
⑧ SourceFile attribute
SourceFile Attribute structure
| type | name | Number | meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| u2 | attribute_name_index | 1 | Property name index |
| u4 | attribute_length | 1 | Attribute length |
| u2 | sourcefile index | 1 | Source code file prime citation |
You can see , Its length is always fixed 8 Bytes .
⑨ Other attributes
Java The predefined properties in a virtual machine are 20 Multiple , I won't introduce them here , Through the introduction of the above attributes , Just grasp the essence , The interpretation of other attributes is also very easy .
边栏推荐
- Some tutorials install the database on ubantu so as not to occupy computer memory?
- Spectrum analysis of ADC sampling sequence based on stm32
- 一文搞定垃圾回收器
- Practice: fabric user certificate revocation operation process
- Global and Chinese market of diesel fire pump 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Global and Chinese market of water treatment technology 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- [error record] groovy function parameter dynamic type error (guess: groovy.lang.missingmethodexception: no signature of method)
- Qtquick3d real time reflection
- Analysis of the problem that the cookie value in PHP contains a plus sign (+) and becomes a space
- VIM tail head intercept file import
猜你喜欢

Golang writes the opening chapter of selenium framework

Navigation day answer applet: preliminary competition of navigation knowledge competition
I closed the open source project alinesno cloud service

我把开源项目alinesno-cloud-service关闭了
d3dx9_ How to repair 31.dll_ d3dx9_ 31. Solution to missing DLL

航海日答题小程序之航海知识竞赛初赛
ESP32 hosted
鏈錶之雙指針(快慢指針,先後指針,首尾指針)
一文搞定JVM常见工具和优化策略
Ultrasonic sensor flash | LEGO eV3 Teaching
随机推荐
Starting from 1.5, build a micro Service Framework -- log tracking traceid
Activate function and its gradient
IIC bus realizes client device
Qtquick3d real time reflection
[error record] groovy function parameter dynamic type error (guess: groovy.lang.missingmethodexception: no signature of method)
Binary tree (II) -- code implementation of heap
Shelved in TortoiseSVN- Shelve in TortoiseSVN?
The countdown to the launch of metaverse ape is hot
Practice: fabric user certificate revocation operation process
Global and Chinese markets for reciprocating seal compressors 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
[groovy] mop meta object protocol and meta programming (Introduction to groovyobject interface | introduction to metaclass | implementation of class methods using groovyobject invokemethod)
傅里叶分析概述
Metasploit (MSF) uses MS17_ 010 (eternal blue) encoding:: undefined conversionerror problem
一文搞定class的微观结构和指令
I closed the open source project alinesno cloud service
Global and Chinese market of water treatment technology 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
thinkphp5.1跨域问题解决
如何快速体验OneOS
audiopolicy
Error when LabVIEW opens Ni instance finder