当前位置:网站首页>Shell (10) array and bubble sort
Shell (10) array and bubble sort
2022-07-27 01:43:00 【A simple comparison】
List of articles
Shell(10) Array and bubble sort
Preface
An array is a collection of data of the same type , It opens up a continuous space in memory , Usually used together with recycling .
One 、 Array
1. The classification of arrays
Normal array : Direct definition without declaration , Subscript index can only be an integer .
Associative array : Need to use declare -A Otherwise, the system does not recognize it , The index can be a string .
2. Definition of array
Elements : Each value in the index group
Subscript indices : from 0 Start , It refers to the user-defined number corresponding to each element .
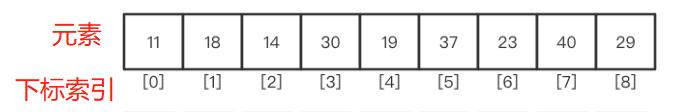
The first way to define : Directly enclose the elements to be added to the array in parentheses , Separate... With spaces in the middle
Array name = (value0 value1 value2)
arr=(1 2 3)
The second kind : Precisely define a value for each subscript index and add it to the array , Index numbers can be discontinuous
Array name =([0]=value [1] =value [2] =value...)
arr=([0]=1 [1]=2 [4]=3)
The third kind of : First assign all the elements to be added to the array to a variable , Then reference this variable and add it to the array
List name ="value0 value1 value2....”
Array name =($ List name )
list=“1 2 3 4”
arr=($list)
A fourth : Define according to the subscript
Array name [0]="value"
Array name [1]="value"
Array name [2]="value"
arr[0]="1"
arr[1]="2"
arr[2]="3"
3. Array command
The data types included in the array :1. value type 2. Character type : Use “ ” or ‘ ’ Definition .
arr=(1 2 3) # Create an array
echo ${#arr[*]} # Output array length
3
echo ${#arr} # Output the string length of the first element
1
echo ${arr[*]} # Output array contents
1 2 3
echo ${arr[2]} # Read the element corresponding to the specific subscript
3
echo ${arr[*]:1:2} # Element slice : Extract from index 1 At the beginning 2 Elements
2 3
echo ${arr[*]/2/4} # Element substitution : Put all the first characters in all elements 2 Replace with 4( Temporary output replacement , It does not replace the original contents of the array )
1 4 3
arr[2]=4
echo ${arr[*]} # According to the subscript , Permanently replace or add the corresponding element
1 2 4
echo ${arr[2-1]} #[] Middle representation operation , Output No 2-1=1 Elements corresponding to subscripts
2
unset arr # Delete array
unset arr[2] # Delete the subscript in the array as 2 The elements of
Arrays can be used as for In the loop list Pass on the reference :

Two 、 Bubble sort
It's like a bubble rising , Will move the data in the array from small to large or from large to small .
The basic idea of bubble sorting is to compare the values of two adjacent elements , Exchange element values if conditions are met , Move the smaller elements to the front of the array , Move large elements to the back of the array ( That is, to exchange the positions of two elements ), So the smaller elements rise from the bottom to the top like bubbles .
The first round of comparison :

To repeat , Compare the second round :

The third round only compares 1 and 2, There will be no transposition , Finally, the comparison is completed , After sorting, the array becomes 1,2,4,8. The index subscript of each number also becomes 0-1,1-2,2-4,3-8.
So to sum up ,shell Bubble sorting is after the number comparison , Assign a larger number to the index subscript of the next digit , Assign a small number to the index subscript of the previous digit . From this we can infer how to implement bubble sorting in scripts .
The algorithm idea is that the bubbling algorithm is realized by double-layer loops , The external loop is used to control the number of sorting rounds , Generally, the length of the array to be sorted minus 1 Time , Because there's only one array element left in the last loop , There's no need to compare , At the same time, the array has finished sorting . The inner loop is mainly used to compare the size of each adjacent element in the array , To determine whether to swap positions , The number of comparisons and exchanges decreases with the number of sorting rounds .

END
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Mqtt protocol ----- above
十三、命令小工具
![[question] what if Yum resources are occupied](/img/8d/50129fa1b1ef0aa0e968e6e6f20969.png)
[question] what if Yum resources are occupied

C language automatically generates code comments: korofileheader plug-in

Web Service (04) -- Introduction and construction of lamp +discuz Forum

DNS

Network foundation of software test interview questions

EXPECT免交互

VirtualBox VMS extended disk space
FTP服务
随机推荐
Understanding and learning of code blocks
Linux部署MYSQL
Regular expression gadget series
Shell(9)函数
4.1 It is super simple to install QT without using Sogou Chinese input method
Shell(13)三剑客
ESP8266 STA_ Server
6、 If statement
Understanding and learning of internal classes
Shell
Vector容器的底层实现
CDC only supports PostgreSQL database to version 12? Is there any plan to support version 14? Does anyone know?
39 installing LNMP
Problems and solutions of paddleocr packaging
9、 Bubble sort
32三剑客sed
七、循环语句
构造函数,拷贝函数和析构函数的区别
27shell conditional statement
DNS