当前位置:网站首页>Gan: generative advantageous nets -- paper analysis and the mathematical concepts behind it
Gan: generative advantageous nets -- paper analysis and the mathematical concepts behind it
2022-07-28 04:56:00 【gongyuandaye】
One 、 Purpose
Input : Random noise
Output : Sample the image of self training sample distribution
Two 、 Model
Generate models G: Capture data distribution , Expect to produce as real a picture as possible , Cheated D.
Discriminant model D: Evaluate a sample from a training set rather than G The possibility of , Expect to accurately distinguish true and false pictures .
3、 ... and 、 Training
Two person system minimax game :
Algorithm is as follows :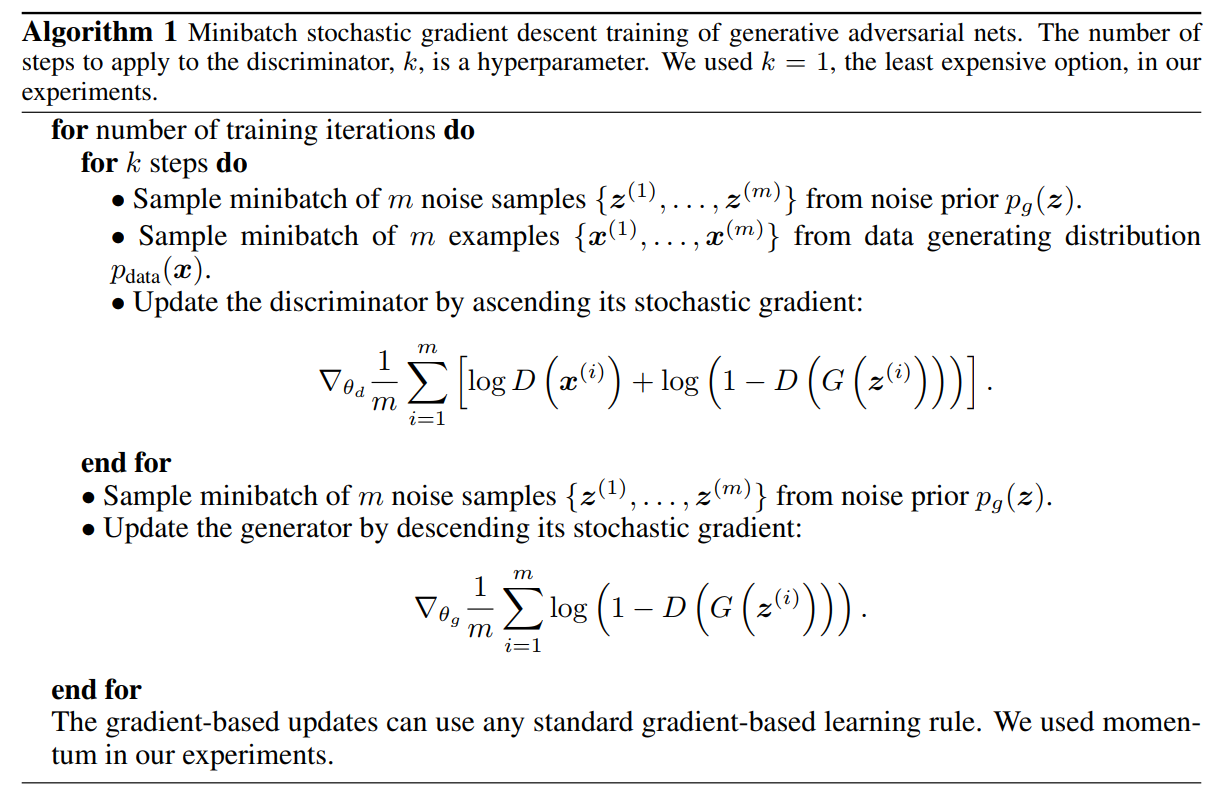
among :
1、 Complete in the inner loop D The optimization of is complex , And it will be fitted on a limited data set , So finish first k round D The optimization of the ( The gradient rises ), Finish another round G The optimization of the ( gradient descent , There are changes in actual use ). The result shows that as long as G Change is slow enough ,D It can be maintained near the optimal solution .
2、min The process ( gradient descent ) in , When the generated sample is very bad , The output value of the discriminator will be very small , The gradient of generator loss function here is very small , It makes the generator learn very slowly . contrary , When the generated sample is good , The output value of the discriminator will be large , The generator loss function has a large gradient here , Generator update is large .
So for min Make the following transformation :
3、 When the distribution of training samples and data does not coincide , It is impossible to update the gradient , So there is LSGAN、WGAN etc. .
Four 、 Mathematical concepts
4.1 Maximum likelihood estimation
P P P d a t a data data ( x ) (x) (x):G The data distribution of the image you want to find .
P P P G G G ( x ; θ ) (x;θ) (x;θ): from θ Determined distribution .
The goal is : determine θ Make the above two distributions similar , hypothesis P P P G G G ( x ; θ ) (x;θ) (x;θ) Gaussian mixture model ,θ The matrix and covariance matrix of Gaussian distribution .
step :
from P P P d a t a data data ( x ) (x) (x) Sample {𝑥1, 𝑥2, … , 𝑥𝑚}, Calculation P P P G G G ( x ; θ ) (x;θ) (x;θ) The likelihood of producing these samples :
By maximum likelihood estimation , We can find θ*:
( The subtraction of the penultimate step and θ irrelevant , from KL The last step of divergence definition is min)
Maximize likelihood = To minimize the KL The divergence ( A measure of the similarity between two probability distributions , Asymmetric )
4.2 Definition of generator
utilize neural network To build the generator G, The network output defines a density distribution 𝑃𝐺.
P P P d a t a data data Unknown , Only its sampling data can be obtained . Sample from a prior probability distribution z As input . To make the two distributions close, we need to calculate the divergence of the two distributions , Need a discriminator .
4.3 Definition of discriminator

because G Fixed , Therefore, the training should be maximized V(G, D) Of The optimal D*.
The training process has the following characteristics :
Maximize V(G, D) The formula of is derived as follows :
So equation (4) Can have :
Thus there are :
among :
1、 The sum of probability distributions is 1.
2、JSD Express JS The divergence ( symmetry ), It is KL A distortion of divergence , It also indicates the difference between the two distributions :
Go back to the original formula (1), Now come back to beg The optimal G, After the above derivation, there are :
JS by 0, Indicates that the two distributions are exactly the same , The upper bound is log2, That is, when the two distributions do not coincide , here GAN Obviously, I can't train .
4.4 The calculation process
To minimize JSD When , Think of it as a loss function L(G), Through gradient descent :
To maximize V(G, D) when , Using the gradient rise method .
So how to calculate in a given G In the case of V(G, D) To maximize the D* Well ?
Maximize the following formula :
namely :
The complete calculation process is as follows :
边栏推荐
- Clickhouse填坑记2:Join条件不支持大于、小于等非等式判断
- alter和confirm,prompt的区别
- 【CPU占用高】software_reporter_tool.exe
- HDU 3666 the matrix problemdifferential constraint + stack optimization SPFA negative ring
- 阿里巴巴面试题【杭州多测师】【杭州多测师_王sir】
- Redis configuration file explanation / parameter explanation and elimination strategy
- 基于MPLS构建虚拟专网的配置实验
- Automated test tool playwright (quick start)
- 解析智能扫地机器人中蕴含的情感元素
- Introduction to testcafe
猜你喜欢

could only be written to 0 of the 1 minReplication nodes. There are 0 datanode(s) running and 0 node

Flink mind map

RT_ Use of thread mailbox

如何在 FastReport VCL 中通过 Outlook 发送和接收报告?
Program life | how to switch to software testing? (software testing learning roadmap attached)

C语言ATM自动取款机系统项目的设计与开发
FreeRTOS learning (I)

Dynamic SQL and paging

动态sql和分页

全方位分析STEAM和创客教育的差异化
随机推荐
RT_ Use of thread mailbox
Histogram of pyplot module of Matplotlib (hist(): basic parameter, return value)
解析智能扫地机器人中蕴含的情感元素
[Hongke technology] Application of network Multimeter in data center
[Sylar] framework Chapter 6 collaborative scheduling module
HDU 1522 marriage is stable
HDU 1435 stable match
[Sylar] framework -chapter24- support business modularization
App test process and test points
Nat fundamentals and private IP
ADB environment configuration
[Sylar] practical part - redis based parameter query service
Jupyter notebook installation code prompt function
Comprehensively analyze the differences between steam and maker Education
Know etcd
驾驭EVM和XCM的强大功能,SubWallet如何赋能波卡和Moonbeam
Testcafe provides automatic waiting mechanism and live operation mode
The difference between alter and confirm, prompt
[Sylar] framework Chapter 8 timer module
低代码是开发的未来吗?浅谈低代码平台