当前位置:网站首页>【数字IC验证快速入门】9、Verilog RTL设计必会的有限状态机(FSM)
【数字IC验证快速入门】9、Verilog RTL设计必会的有限状态机(FSM)
2022-07-05 20:06:00 【luoganttcc】
导读:作者有幸在中国电子信息领域的排头兵院校“电子科技大学”攻读研究生期间,接触到前沿的数字IC验证知识,旁听到诸如华为海思、清华紫光、联发科技等业界顶尖集成电路相关企业面授课程,对数字IC验证有了一些知识积累和学习心得。为帮助想入门前端IC验证的朋友,思忱一二后,特开此专栏,以期花最短的时间,走最少的弯路,学最多的IC验证技术知识。
文章目录
一、基础理论
状态机简写为 FSM( Finite State Machine),也称为同步有限状态机,我们一般简称为状态机,之所以说“同步”是因为状态机中所有的状态跳转都是在时钟的作用下进行的,而“有限”则是说状态的个数是有限的。状态机根据影响输出的原因分为两大类,即Moore 型状态机和 Mealy 型状态机,其共同点是:状态的跳转都只和输入有关。区别主要是在输出的时候:若最后的输出只和当前状态有关而与输入无关则称为 Moore 型状态机;若最后的输出不仅和当前状态有关还和输入有关则称为 Mealy 型状态机。状态机是时序逻辑电路中非常重要的一个应用,常在大型复杂的系统中使用较多。
二、自动售饮料机
2.1、问题描述
设计一个自动售饮料机,设饮料售价2.5元,可使用5角和1元硬币,具有找零功能。
注:同一时刻只能投1元或者5角,不能两个同时投。
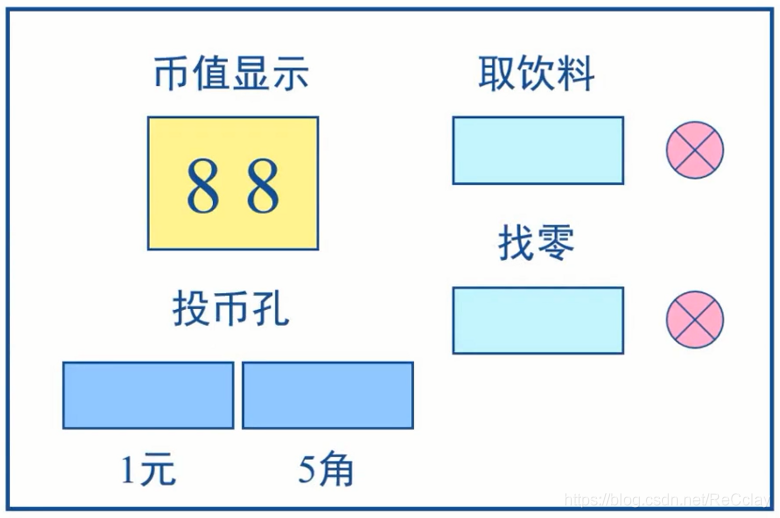
2.2、功能框图和接口定义
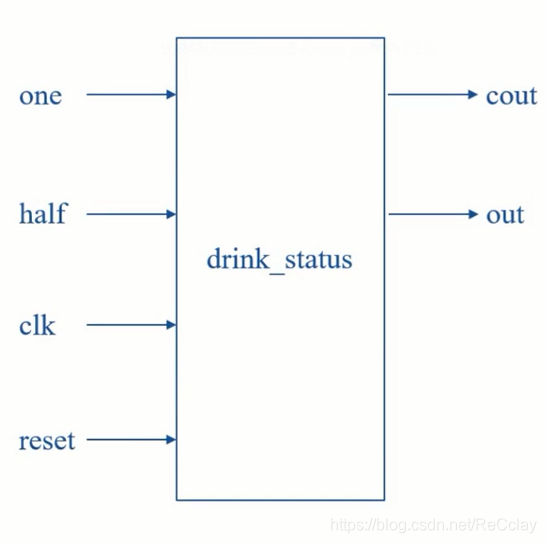
接口信号定义
- clk:时钟输入
- reset:系统复位信号
- half:投入5角硬币
- one:投入1元硬币
- cout:找零信号
- out:机器售出饮料
2.3、状态转换图 - moore FSM
注:Moore FSM 特点:输出只与当前的状态有关系,与输入没有关系!
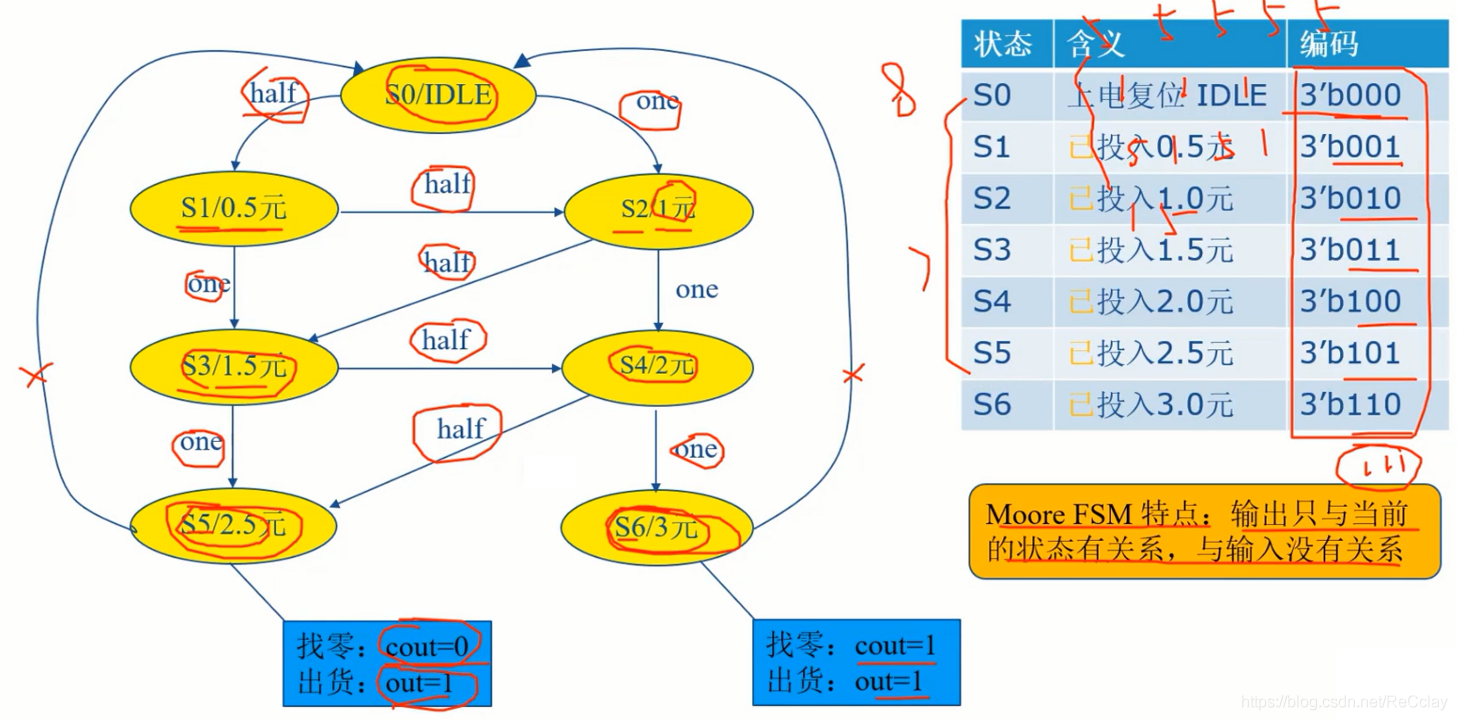
Moore FSM 的 RTL代码
module drink_status_moore(
input wire clk,
input wire reset,
input wire half,
input wire one,
output wire out,
output wire cout
);
parameter [2:0] S0 = 3'b000,
S1 = 3'b001,
S2 = 3'b010,
S3 = 3'b011,
S4 = 3'b100,
S5 = 3'b101,
S6 = 3'b110;
reg [2:0] curr_state;
reg [2:0] next_state;
//first segment:state transfer
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge reset)
if(!reset)
curr_state <= S0;
else
curr_state <= next_state;
//second segment:transfer condition
[email protected](*)
case(curr_state)
S0 : if(half == 1'b1) next_state = S1;
else if(one == 1'b1) next_state = S2;
else next_state = S0;
S1 : if(half == 1'b1) next_state = S2;
else if(one == 1'b1) next_state = S3;
else next_state = S1;
S2 : if(half == 1'b1) next_state = S3;
else if(one == 1'b1) next_state = S4;
else next_state = S2;
S3 : if(half == 1'b1) next_state = S4;
else if(one == 1'b1) next_state = S5;
else next_state = S3;
S4 : if(half == 1'b1) next_state = S5;
else if(one == 1'b1) next_state = S6;
else next_state = S4;
S5 : next_state = S0;
S6 : next_state = S0;
default : next_state = S0;
endcase
//third segment:state output
//moore type FSM
assign out = ((curr_state == S5) || (curr_state == S6) ) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
assign cout = (curr_state == S6) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
endmodule
FSM 三段式写法:
- 良好的编码风格
- 逻辑综合
- 可阅读星
2.4、状态转换图 - Mealy FSM
注:Mealy FSM 特点:输出不仅与当前的状态有关系,与输入也有关系!
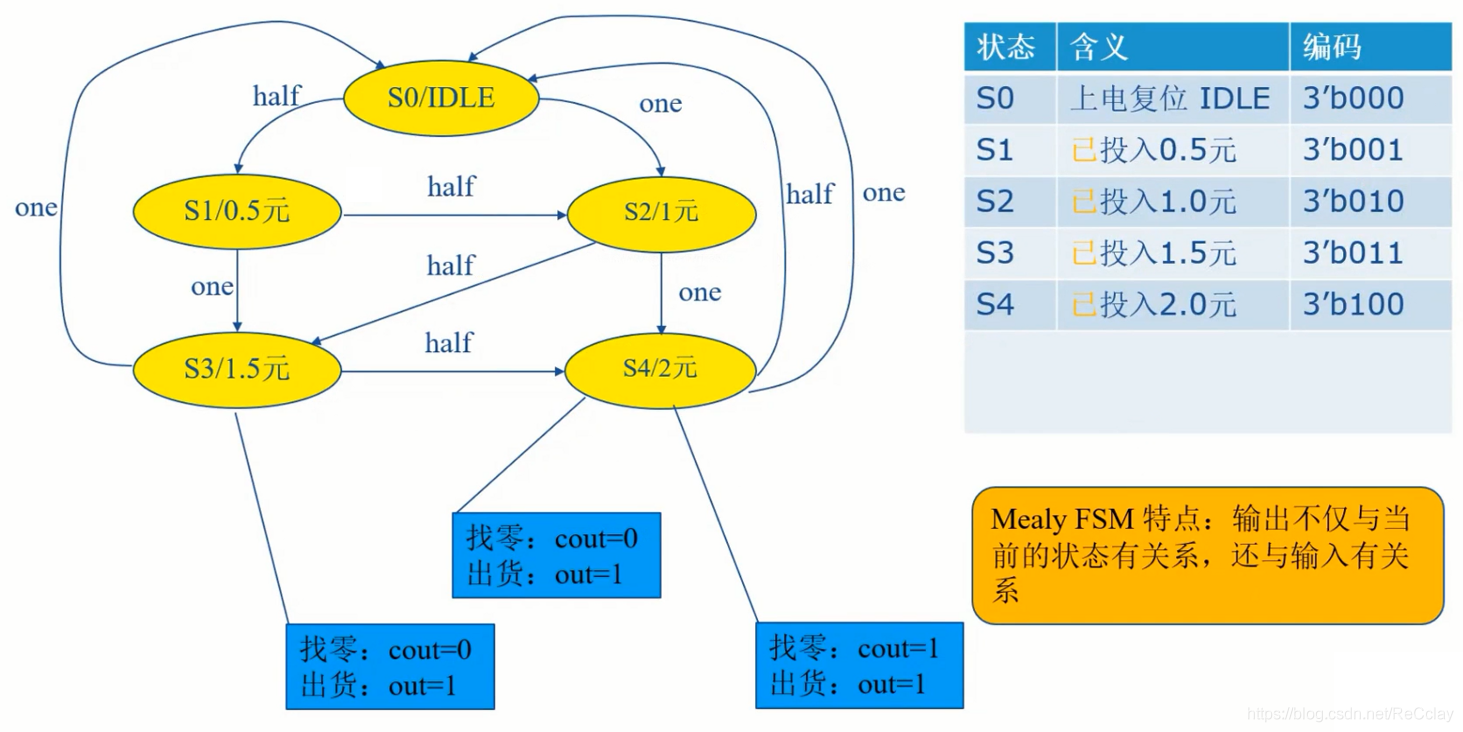
- Mealy 只用了5种状态,但是输出控制会变复杂!
Mealy FSM 的 RTL代码
module drink_status_mealy(
input wire clk,
input wire reset,
input wire half,
input wire one,
output wire out,
output wire cout
);
parameter [2:0] S0 = 3'b000,
S1 = 3'b001,
S2 = 3'b010,
S3 = 3'b011,
S4 = 3'b100,
S5 = 3'b101,
S6 = 3'b110;
reg [2:0] curr_state;
reg [2:0] next_state;
//first segment:state transfer
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge reset)
if(!reset)
curr_state <= S0;
else
curr_state <= next_state;
//second segment:transfer condition
[email protected](*)
case(curr_state)
S0 : if(half == 1'b1) next_state = S1;
else if(one == 1'b1) next_state = S2;
else next_state = S0;
S1 : if(half == 1'b1) next_state = S2;
else if(one == 1'b1) next_state = S3;
else next_state = S1;
S2 : if(half == 1'b1) next_state = S3;
else if(one == 1'b1) next_state = S4;
else next_state = S2;
S3 : if(half == 1'b1) next_state = S4;
else if(one == 1'b1) next_state = S0;
else next_state = S3;
S4 : if(half == 1'b1) next_state = S0;
else if(one == 1'b1) next_state = S0;
else next_state = S4;
default : next_state = S0;
endcase
//third segment:state output
//mealy type FSM
assign out = ((curr_state == S3 && one == 1'b1) || (curr_state == S4 && (half==1'b1 || one==1'b1)) ) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
assign cout = (curr_state == S4 && one == 1'b1) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
endmodule
2.5、有限状态机电路逻辑图
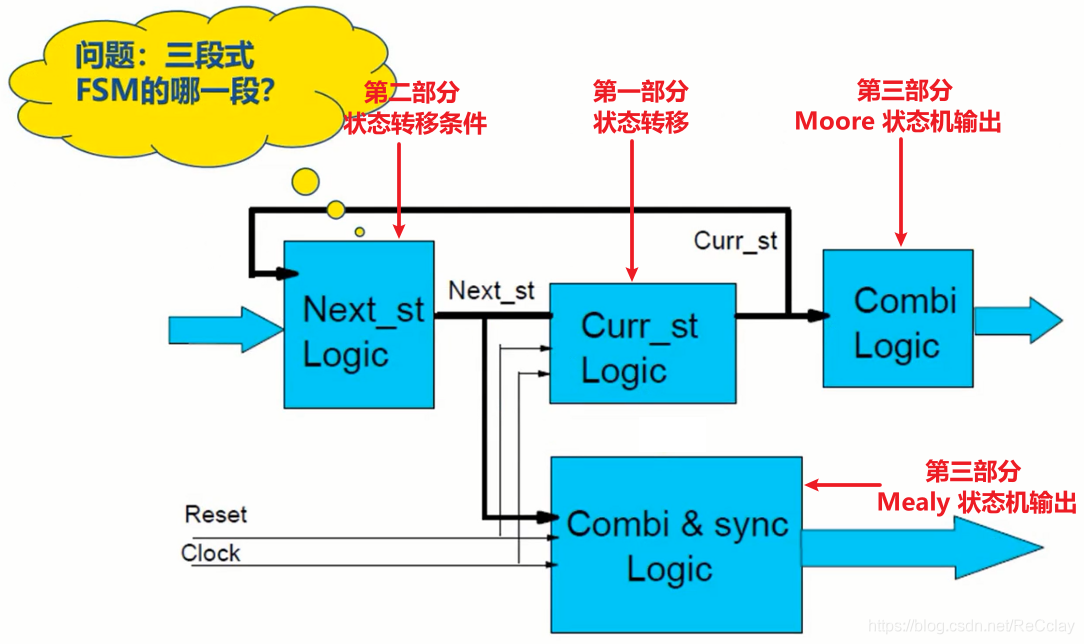
2.6、有限状态机小结
- FSM有限状态机的设计步骤
- 接口定义
- 状态定义和编码
- 状态的转换图
- 按照三段式编码风格实现RTL代码
- 编写TestBench代码
- 使用Questasim进行编译和仿真
- 通过波形工具查看输入激励、状态信号和输出信号
常见面试题:有限状态机分类?
- 答:Moore 型状态机:状态机的输出只与当前的状态有关
- Mealy 型状态机:状态机的输出不仅与当前的状态有关,还与当前的输入有关
常见面试题:两种状态机区别?
- 答:1、Moore状态机:在时钟脉冲的有限个门延时后,输出达到稳定。输出会在一个完整的时钟周期内保持稳定值,即使在该时钟内输入信号变化了,输出信号也不会变化。输入对输出的影响要到下一个时钟周期才能反映出来。把输入和输出分开,是Moore状态机的重要特征。
- 2、Melay状态机:由于输出直接受到输入影响,而输入可以在时钟周期的任意时刻变化,这就使得输出状态比Moore状态的输出状态提前一个周期到达。输入信号的噪声可能会出现在输出信号上。
- 3、对同一个电路,使用Moore状态机设计可能要比使用Mealy状态机多出一些状态。
状态机写法关键,分成三部分来写:
- 1、第一部分负责:状态跳转
- 2、第二部分负责:跳转条件
- 3、第三部分负责:输出信号
2.7、需要注意的问题:full case
- 定义完全状态,即使有的状态在电路中可能不会出现
- 目的是避免逻辑综合时出现组合逻辑环
- 组合逻辑环会导致STA没办法分析,DFT没办法覆盖
- 异步时序(timing 路径没办法约束,也就没办法分析)的问题
三、实战测试:序列检测器
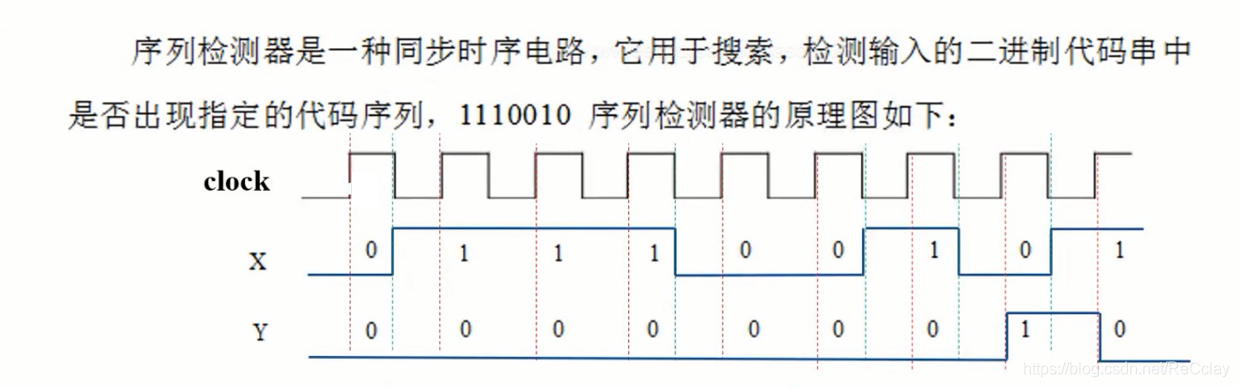
3.1、序列检测器的功能要求
- 设计要求
- 用状态机设计序列检测器(1110010)
- 设计功能
- 设计一个序列检测器,检测的序列为“1110010”
- 当输入信号X依次为“1110010”时,输出信号Y输出一个高电平
- 否则输出信号Y为低电平
注:工程中序列检测器用的还是比较多的,用于检测序列头!
3.2、时序检测器的时序图
3.3、时序检测器的状态转换图
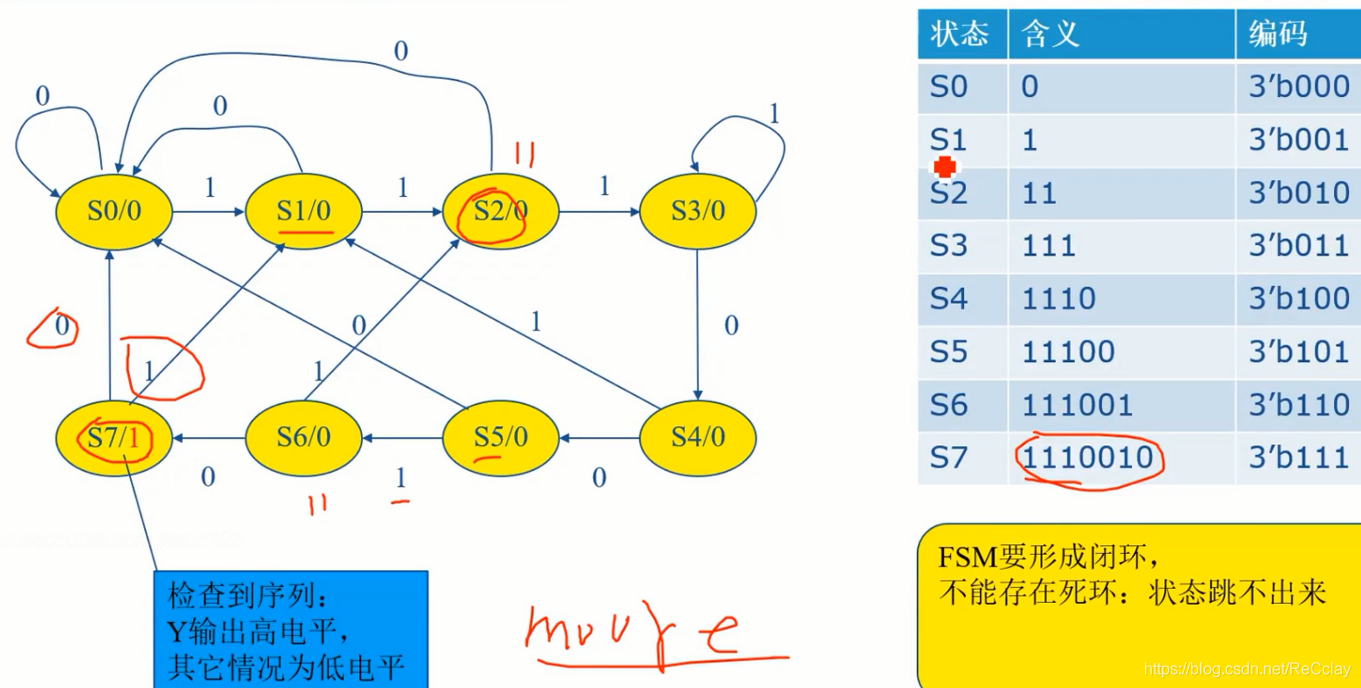
注意看,输出与输入无关,这是个Moore状态机!
3.4、序列检测器的参考代码
RTL 参考代码
// 1110010
module seq(
input wire in,
input wire clk,
input wire reset,
output wire out
);
parameter [2:0] S0 = 3'b000,
S1 = 3'b001,
S2 = 3'b010,
S3 = 3'b011,
S4 = 3'b100,
S5 = 3'b101,
S6 = 3'b110,
S7 = 3'b111;
reg [2:0] cur_state;
reg [2:0] next_state;
//first step: state transfer
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge reset)
if(~reset)
cur_state <= S0;
else
cur_state <= next_state;
//second: transfer condition
[email protected](*)
case(cur_state)
S0:begin
if(in == 1) next_state = S1;
else next_state = S0;
end
S1:begin
if(in == 1) next_state = S2;
else next_state = S0;
end
S2:begin
if(in == 1) next_state = S3;
else next_state = S0;
end
S3:begin
if(in == 0) next_state = S4;
else next_state = S3;
end
S4:begin
if(in == 0) next_state = S5;
else next_state = S1;
end
S5:begin
if(in == 1) next_state = S6;
else next_state = S0;
end
S6:begin
if(in == 0) next_state = S7;
else next_state = S2;
end
S7:begin
if(in == 0) next_state = S0;
else next_state = S1;
end
default: next_state = S0;
endcase
//third: output
assign out = (cur_state == S7) ? 1'b1 : 1'b0;
endmodule
TestBench 参考代码
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module tb_led();
//reg define
reg clk;
reg rst_n;
reg C;
//wire define
wire Y;
// //初始化系统时钟、全局复位
initial begin
clk = 1'b1;
rst_n <= 1'b0;
#10
rst_n <= 1'b1;
end
always #5 clk = ~clk;
[email protected](posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(rst_n == 1'b0)
C <= 1'b0;
else
C <= {$random} % 2;
seq seq_inst(
.clk (clk ),
.reset (rst_n ),
.in (C ),
.out (Y )
);
endmodule
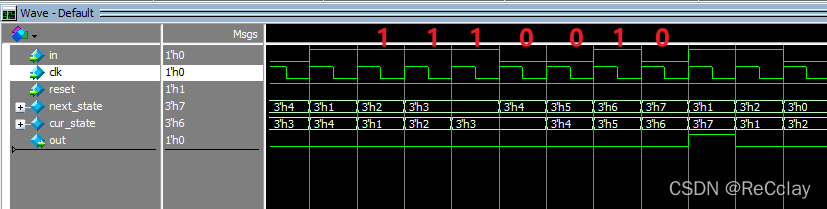
节选仿真结果如下:
参考
边栏推荐
- Is it safe for Galaxy Securities to open an account online?
- Based on vs2017 and cmake GUI configuration, zxing and opencv are used in win10 x64 environment, and simple detection of data matrix code is realized
- 国信证券在网上开户安全吗?
- ffplay文档[通俗易懂]
- 解决php无法将string转换为json的办法
- Leetcode brush questions: binary tree 18 (largest binary tree)
- C language OJ gets PE, OJ of ACM introduction~
- - Oui. Net Distributed Transaction and Landing Solution
- Flume series: interceptor filtering data
- Process file and directory names
猜你喜欢
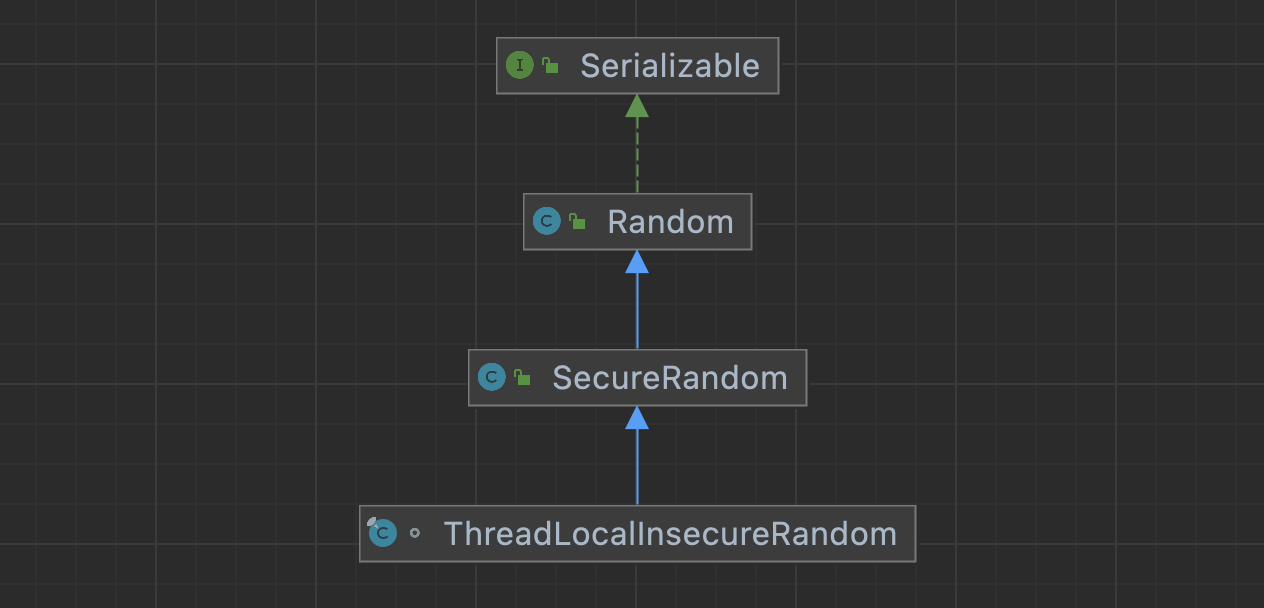
Let's talk about threadlocalinsecurerandom
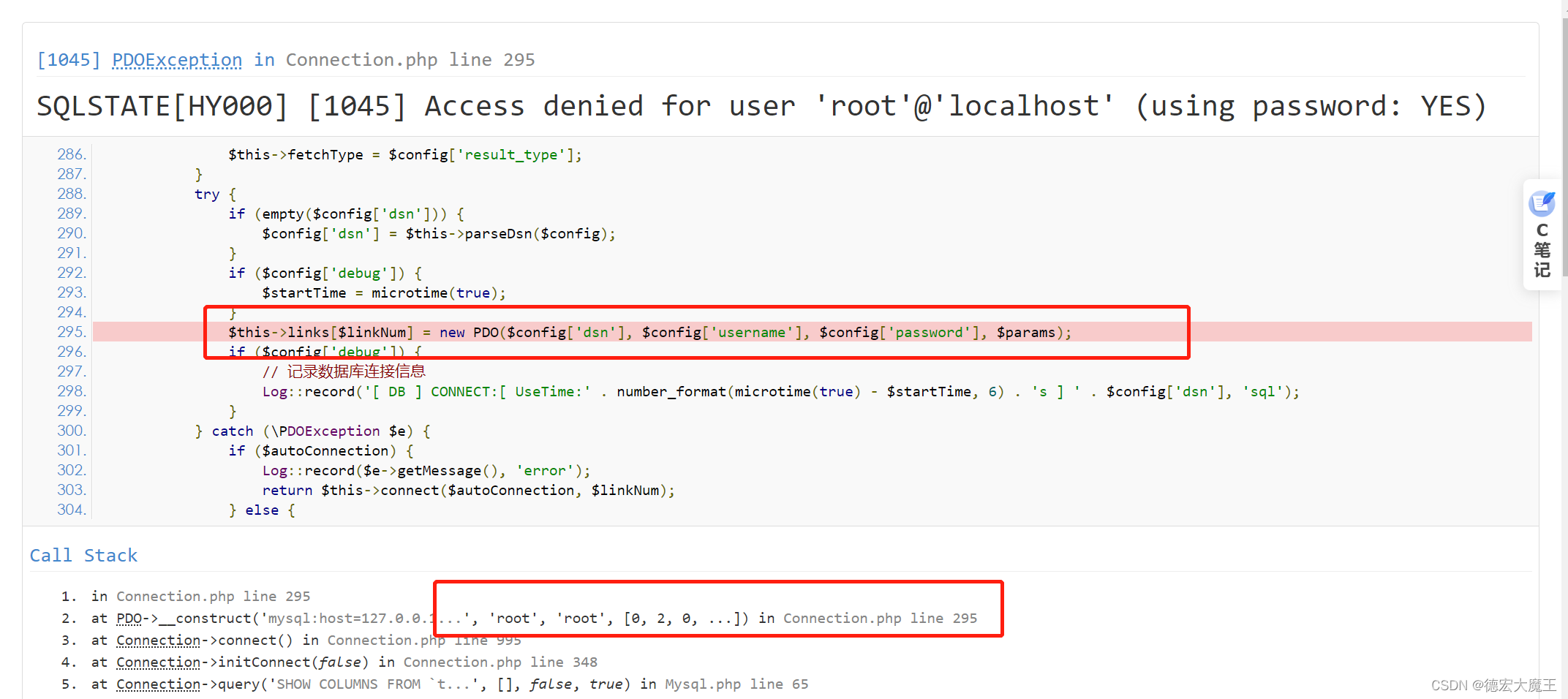
解决Thinkphp框架应用目录下数据库配置信息修改后依然按默认方式连接

Zhongang Mining: analysis of the current market supply situation of the global fluorite industry in 2022
Force buckle 1200 Minimum absolute difference
Force buckle 729 My schedule I
微信小程序正则表达式提取链接
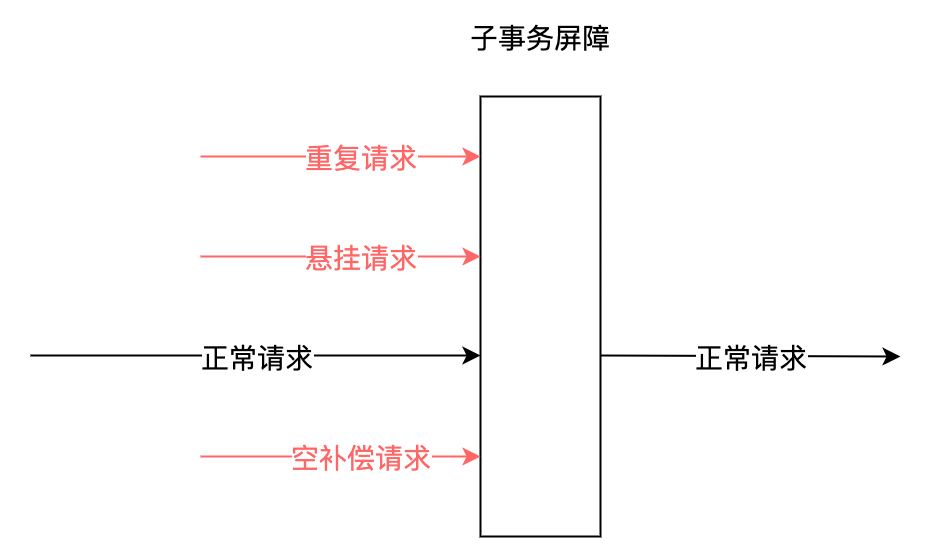
.Net分布式事務及落地解决方案
![[untitled]](/img/51/c89d35c855e299b02137d676790eb6.png)
[untitled]
Jvmrandom cannot set seeds | problem tracing | source code tracing

The city chain technology Digital Innovation Strategy Summit was successfully held
随机推荐
Debezium series: PostgreSQL loads the correct last submission LSN from the offset
Where is the operation of new bonds? Is it safer and more reliable to open an account
深度學習 卷積神經網絡(CNN)基礎
Float.floatToRawIntBits的返回值具体意思,将float转为byte数组
c语言oj得pe,ACM入门之OJ~
[untitled]
Force buckle 729 My schedule I
挖财钱堂教育靠谱安全吗?
How to retrieve the root password of MySQL if you forget it
Webuploader file upload drag upload progress monitoring type control upload result monitoring control
Zero cloud new UI design
Successful entry into Baidu, 35K monthly salary, 2022 Android development interview answer
Relationship between floating elements and parent and brother boxes
leetcode刷题:二叉树12(二叉树的所有路径)
期货如何网上开户?安不安全?
Go language learning tutorial (XV)
-v parameter of GST launch
淺淺的談一下ThreadLocalInsecureRandom
手机股票开户安全吗?靠不靠谱啊?
浅浅的谈一下ThreadLocalInsecureRandom