当前位置:网站首页>MySQL VI Database lock
MySQL VI Database lock
2022-06-12 10:00:00 【A god given dream never wakes up】
MySQL 6、 ... and . lock
One of the difficulties with databases is : On the one hand, the maximum possible concurrency , On the other hand, the consistency of data read by users is also required ; So , The database is designed with a lock (locking) Mechanism ; As a developer , It is best to understand these mechanisms , Help us better realize our business processing ;
6.1 What is a lock
One of the biggest differences between a database and a file system is the locking mechanism ; The locking mechanism is used to handle shared resources and access them .InnoDB Support row level locks , But it's not just the row data of the database , In the cache pool LRU The addition, deletion, modification and query of the list all involve locks ;
Be careful : Different databases , Different storage engines have different lock implementations ;
6.2 lock and latch
lock and latch Can be called a lock , But the two have different meanings ; This chapter is mainly about lock
latch: latch , A lightweight lock , The time required for locking is very short , stay InnoDB In the storage engine latch It is divided into mutex and rwlock ; Ensure the accuracy of concurrent threads operating critical resources , There is generally no mechanism to check for deadlocks ;
lock: lock It's about business , It's used to lock objects in the database , As shown in the table , page , That's ok . And these are lock The object of is usually in the transaction commit Or is it rollback When releasing . There will also be deadlocks ;

My understanding is that latch It is the code lock implemented inside the database , Is a familiar database object , like Java The current thread in the object header ,lock Is the lock of the database object , Can represent a transaction
## sql see latch state (debug edition )
show engine Innodb mutex ; -- The output fields are as follows

### lock View of ;
SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS
select * from information_schema.INNODB_TRX/INNODB_LOCKS/INNODB_LOCK_WAITS
6.3 InnoDB Lock in storage engine
6.3.1 The type of lock
InnoDB The following two standard row level locks are implemented in
- Shared lock S LOCK Allow transactions to read a row of data
- Exclusive lock X LOCK Allow transactions to modify or delete a row of data ;
Business T1 obtain R Yes S lock , Business T2 You can also get it right away R Yes S lock ; But if T3 Want to get R Yes X lock In this case, you need to wait T1,T2 Release the lock
Compatibility is as follows
| S | X | |
|---|---|---|
| S | compatible | Are not compatible |
| X | Are not compatible | Are not compatible |
InnoDB Supports multi granularity locks , This kind of locking supports the existence of table level or row level locks ; Its concrete implementation is intention lock , Intent locks support multiple granularity Lock in

Now if you want to set the table 1 A record above r the previous X lock , that , You need to set your watch , page Last intent lock IX , Finally, on the record X lock ,; The grain size becomes finer layer by layer . In the process of locking , One of them is blocked , Subsequent locking operations need to wait until the previous locking is completed before further fine-grained locks can be added ;
InnoDB Support for multi granularity locking , Allow row locks and table locks to coexist , Intention lock is Table lock , Indicates that the transaction is later ( Shared locks are fully compatible ) What type of lock do you need to use for rows in the table ( Shared lock or exclusive lock ). There are two types of intent locks
- Of Intent to share locks (
IS) Indicates that a transaction intends to set a shared lock on several rows of data in the table . - Of Intent exclusive lock (
IX) Indicates that a transaction intends to set exclusive locks on several rows of data in the table .
Compatibility is as follows
| IS | IX | S | X | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS | compatible | compatible | compatible | Are not compatible |
| IX | compatible | compatible | Are not compatible | Are not compatible |
| S | compatible | Are not compatible | compatible | Are not compatible |
| X | Are not compatible | Are not compatible | Are not compatible | Are not compatible |
If the requested transaction is compatible with an existing lock , Then a lock is granted to the requesting transaction , But if it conflicts with the existing lock , Will not be . The transaction waits until the conflicting existing lock is released . If a lock request conflicts with an existing lock and is due to a Deadlock And cannot grant , An error will occur ;
stay InnoDB Lock information , The following three tables You can simply view and analyze possible lock problems
select * from information_schema.INNODB_TRX;
select * from information_schema.INNODB_LOCKS;
select * from information_schema.INNODB_LOCK_WAITS;
INNODB_TRX

This is the field of the old version , In the latest version, more detailed record data has been added
INNODB_LOCKS

INNODB_LOCK_WAITS
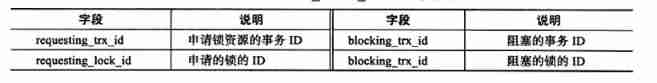
You can see which transaction is blocking another transaction
6.3.2 Consistent non-locked reads
Consistent non-locked reads consistent nonlocking read Refer to InnoDB The storage engine reads the data in the current time database through multi version control , If the data is executing update /delete The operation of , The read operation does not need to wait for the release of the lock , Instead, go back and read the historical snapshot of this part of data ;

Read through undo Segment implementation ; undo It is used to rollback transactions
stay InnoDB By default , This is the default read method , Reading data will not occupy the lock on the table , It can greatly improve the concurrency of the database ;
But at different transaction isolation levels , Different reading methods , Not every isolation level uses non locked consistent reads ; But even if it is a consistent unlocked read , Data snapshots are also defined differently ;
As you can see in the picture above , A data may have multiple historical versions , It is generally called multi version technology , The resulting version control , It's called multi version control MVCC
The isolation level of transactions is READ COMMITED and REPEATABLE READ (InnoDB The default isolation level of ),InnoDB Non locking consistent read is adopted . But the definition of snapshot is different .
READ COMMITEDUnder isolation level , Is the latest snapshot to read the locked row .REPEATABLE READUnder transaction isolation level Read the database version at the beginning of the transaction ;
Test it These features First create a table
create table demo
(
id int auto_increment
primary key,
name varchar(255) null
)
charset = utf8;
Raw data

READ COMMITED
| The order | result 1 | conversation 1 | conversation 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | begin ; | ||
| 2 | A | select * from demo where id = 120 ; | |
| 3 | begin ; | ||
| 4 | update demo set name = ‘B’ where id = 120; | ||
| 5 | A | select * from demo where id = 120 ; | |
| 6 | commit ; | ||
| 7 | B | select * from demo where id = 120 ; | |
| 8 | commit ; |
REPEATABLE READ
| The order | result 1 | conversation 1 | conversation 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ```sq | begin ; | |
| 2 | A | select * from demo where id = 120 ; | |
| 3 | begin ; | ||
| 4 | update demo set name = ‘B’ where id = 120; | ||
| 5 | A | select * from demo where id = 120 ; | |
| 6 | commit ; | ||
| 7 | A | select * from demo where id = 120 ; | |
| 8 | commit ; | ||
| B | select * from demo where id = 120 ; |
You can see in the REPEATABLE READ Under the isolation level of , The data read in a transaction is consistent ,( notes : But in case of update, I will still find the latest data ) READ COMMITED The data read is the latest version data , From the perspective of database theory , It violates the ACID The transaction I isolation Isolation,
6.3.3 Consistency lock read
InnoDB The default isolation level for transactions is REPEATABLE READ,select The operation of is a consistent nonlocked read , But in some cases , The user needs to lock the database read operation to ensure the consistency of data logic . This requires that the database should support locking statements , about select Statement such a read-only operation ,InnoDB Supports two types of consistent locked reads (locaking read):
- select … from update add to X lock Other transactions cannot be locked
- select … lock in share mode add to S lock Other business can add S lock But we can't add X lock
update
| The order | result 1 | conversation 1 | conversation 2 | result 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | begin ; | |||
| 2 | A | select * from demo where id = 120 for update ; | ||
| 3 | begin | |||
| 4 | select * from demo where id = 120 for update ; | wait for Hang up | ||
| 5 | select * from demo where id = 120( Inconsistent read ) | A | ||
| 6 | commit; | |||
| 7 | step 4 Pending status cancel Can read data | |||
| 8 | commit; |
share mode
| The order | result 1 | conversation 1 | conversation 2 | result 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | begin ; | |||
| 2 | A | select * from demo where id = 120 lock in share mode ; | ||
| 3 | begin | |||
| 4 | select * from demo where id = 120 lock in share mode | A | ||
| 5 | select * from demo where id = 120( Inconsistent read ) | A | ||
| 6 | select * from demo where id = 120 for update; | wait for Hang up | ||
| 7 | commit; | |||
| 8 | step 4 Pending status cancel Can read data | |||
| commit; |
6.3.4 Self growth and lock
Generally, when we create tables, we are used to using self - growing id. stay InnoDB In the memory structure of the storage engine , There is a self - increasing counter for every value table with self - increasing auto-increment counter. Every time there is data insertion , The counter will be initialized Execute the following statement to get the value of the counter
select max(auto_inc_col) from t from update;
The insert operation will be based on the self increasing counter value +1 To the self growing column where the row is to be inserted ; This way is called AUTI-INC Locking. This lock is a Special table locking mechanism . This table lock is released when the self growth value is obtained , Instead of waiting for the insert transaction to be released ;
This locking mechanism improves the performance of concurrent inserts to some extent ( Reduced lock time ), But there are still some problems ( Because the insert has a lock ); A transaction that inserts data must wait for the previous insert ( Not a transaction ) Completion . Second, if an insert is INSERT ....SELECT This kind of massive data insertion , Then the insertion in another transaction will be Blocking live ;
MySQL 5.1.22 After the new implementation mechanism : Self growth mechanism of lightweight mutex , Greatly improve the self growth insertion performance . And add parameters innodb_autinc_lock_mode To control the pattern of self growth . The default parameter is 1 ; Self growing insertions are also classified , The implementation of self - growth is also related to insert classification ;
| Insert category | explain |
|---|---|
| insert-like | All insert statements , Such as insert ,replace,insert…select ,replace…select, load data etc. |
| simple inserts | Know the number of inserted rows before inserting insert ,replace |
| bulk inserts | Not sure how many rows to insert before inserting insert…select ,replace…select, load data |
| mix-mode inserts | Part of it is self increasing One part is the definite insertion |
innodb_autinc_lock_mode | explain |
|---|---|
| 0 | AUTI-INC Locking The old implementation |
| 1 | simple inserts Use mutexes (mutex) To achieve .bulk insert ; Or the original AUTI-INC Locking Realization way If rollback is not considered , The self growth of each insertion is continuous , relication Can also work well |
| 2 | All are mutexes (mutex) To achieve , Each insertion is , There may be discontinuous self growing Columns relication Master slave architecture stay statment-Base There will be problems with the way ,ow-Base To ensure the consistency between the master and the slave |
In addition, we need to pay attention to :InnoDB and MyISAM Different MyISAM It's a watch lock design , There is no need to consider the problem of concurrent insertion Be careful : stay master Use InnoDB and slave Upper use MyISAM Of relication Under the master-slave replication architecture Questions to consider
Be careful : A self growing column must be an index , And as a composite index, it can't be put behind , Can only be placed in the first column
create table t3(
a int auto_increment,
b int,
key (b,a)
)engine = innodb;
[42000][1075] Incorrect table definition; there can be only one auto column and it must be defined as a key
6.3.5 Foreign keys and locks
I said before , Mainly for data integrity constraints , However, this constraint is not recommended in the database , Instead, do constraint checking at the application layer ; It is not recommended to use ;
If you update the table , Will query the associated foreign key table , The foreign key table has X lock ;
If it is a non lock consistent read , There may be data inconsistency
If you are using LOCK IN SHARE MODE Words , Foreign key table queries against associated tables will block , Know about the external inspection form X Release the lock
6.4 Lock algorithm
6.4.1 Three algorithms of row lock
InnoDB There are three algorithms for row locking
Record Lock: Lock on single line record ; Lock index records , Without an index , Just lock the primary keyGap Lock: Clearance lock , Lock a range , But not the record itself ;Next-Key Lock:Record Lock+Gap LockLock a range , Include the record itself ,
Next-Key Lock : This algorithm is only used for row queries , Such as the index 10,11,13,20 The four values By Next-Key Locking The lock interval is
(-∞,10],(10,11],(11,13],(13,20],(20,+∞),
This design is to solve phantom problem ( Virtual reading )
And the same thing previous locking technology The locked zone is (-∞,10),[10,11),[11,13),[13,20),[20,+∞),
Example : If Business T1 Next-Key Locking Lock the (10,11], (11,13] When data 12 Insert yes The scope of locking is (10,11], (11,12] (12,13]
When inquired The index is unique When , Lock meeting Downgrade by Record Lock ( Only a single query with a unique index is degraded , If the unique index is multiple columns , The query criteria only have one of multiple columns , In fact, the query has also become range Inquire about , instead of point Inquire about Not downgraded !!! )
Test data : demo
| id | name |
|---|---|
| 120 | A |
| 121 | B |
| 122 | D |
| The order | result 1 | conversation 1 | conversation 2 | result 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | begin ; | |||
| 2 | A | select * from demo where id = 120 lock in share mode ; | ||
| 3 | begin | |||
| 4 | INSERT INTO test.demo (id, name) VALUES (123, 'C'); | |||
| 5 | commit; | |||
| 6 | commit; |
2 There's only one record in It's not the scope unique index , The lock will be degraded to Record Lock ==> conversation 2 Insert in and execute immediately ==> Improve concurrency
Test data :demo2
| id( primary key ) | age ( Secondary index ) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 5 | 3 |
| 7 | 6 |
| 10 | 8 |
Secondary index Interval is (-∞,1],(1,3],(3,6],(6,8],(8,+∞),
Secondary index lock Next-Key Locking The locking range is
1 It's locked (1,3] ,
2 And will use gap lock Lock the next key value (3,6]
| The order | result 1 | conversation 1 | conversation 2 | result 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | begin ; | |||
| 2 | A | select * from demo2 where age = 3 for update; | ||
| 3 | begin | |||
| 4.1 | select * from demo2 where age = 5 lock in share mode ; | Hang up reason 1 | ||
| 4.2 | insert into test.demo2 (id, age) values (4, 2); | Hang up reason 2 | ||
| 4.3 | insert into test.demo2 (id, age) values (6, 5); | Hang up reason 2 | ||
| 4.4 | insert into test.demo2 (id, age) values (10, 10); | Direct execution | ||
| 5 | commit ; | |||
| 6 | commit; |
Be careful : The test sequence is 1,2,3,4.1 5 6 ; 1,2,3,4.2 5 6 ; …
Gap Lock To prevent multiple transactions from inserting records into the same scope , And this will lead to Phantom Problem (( Virtual reading )) Problem generation . For example, in the above example, the condition age > 3 lock Insert a age = 100 , There is no gap lock to lock all [3 ,+∞) The range of will cause the data read twice to be inconsistent ;
Can be displayed off Gap Lock
1. Set the isolation level to READ COMMITED
2. The parameter Innodb_locks_unsafe_for_binlog Set to 1
6.4.2 solve Phantom Problem
Phantom Problem: Under the same business , Perform the same... Twice in a row SQL Statements can lead to different results , The second time SQL Statement may return lines that did not exist before ;
At the default transaction isolation level REPEATABLE READ Next ,InnoDB The storage engine uses Next-Key Locking Mechanism to avoid Phantom Problem( It says that ), This is different from other databases , You may need to SERIALIZABLE Can achieve
6.5 The lock problem
The lock mechanism can realize the isolation requirements of transactions , Yes, transactions can work concurrently . Contrary , Locks can also cause potential problems
6.5.1 Dirty reading
Dirty reading (Dirty Read) , First, understand dirty data , Different from the dirty pages mentioned before ( The modified data pages in the cache pool , I haven't had time to refresh to disk yet , It is caused by the asynchrony between memory and disk ); Dirty data refers to data read by one transaction but not committed by another transaction ;
Not common in production environments , Because the isolation level is generally set at READ_UNCOMMITED above ;MySQL yes REPEATABLE READ ,SQLSERVER/ORACLE All are READ_COMMITED
6.5.2 It can't be read repeatedly
The data read twice in a transaction is different , This situation is called unrepeatable reading ;
The difference between unrepeatable and dirty reading is that : Dirty reading is reading uncommitted data , What can't be read repeatedly is the submitted data , But it violates the requirements of database transaction consistency
Generally speaking , The problem of unrepeatable reading is acceptable , Because it reads the submitted data , It's not a big problem in itself ; Therefore, some manufacturers set it as READ COMMITTED
InnoDB The default transaction isolation level for the storage engine is READ REPEATABLE, use Next-Key Lock Algorithm , Avoid the phenomenon of non repeatable reading
6.5.3 Lost update
The update operation of one transaction will be overwritten by the update operation of another transaction , This leads to data inconsistency ;
Business T1modify Record r byv1, Not yet submittedBusiness T2modify Record r byv2, Not yet submittedBusiness T1SubmitBusiness T2Submit
But at any isolation level of the current database ,DML operation You need to add a certain amount of lock T2 It will block , until T1 Submit ; But it will turn into another problem ; The result of program execution is
T1 The update result of the query is v1, After getting the program, it will be displayed on the page , When T1 At the time of submission The database is already v2 了 ,
For example, transfer business account ; user_id= 1 , money = 100
If sql All are
update account set money = money - xxx where user_id= 1
That's no problem , However, it is often the first to query in the business balance have a look Can I transfer money Then get the data after the transfer in set sql It is commonly
update account set money = 8000( A specific number ) where user_id= 1
Once you use the above method Is the loss of updated data
How to handle lost updates
| The order | result 1 | conversation 1 | conversation 2 | result 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | begin ; | |||
| 2 | select @money from account where user_id= 1 for update; | |||
| 3 | begin | |||
| 4 | select @money from account where user_id= 1 for update; | Hang up | ||
| 5 | It makes the business … @money Handle | ` | Hang up reason 2 | |
| 6 | update account set money [email protected] 8000 where user_id= 1 | Hang up reason 2 | ||
| 7 | commit ; | Direct execution | ||
| 8 | 4 Pending cancel Execute the query | |||
| 9 | update account set money [email protected] 6000 where user_id= 1 | |||
| 10 | commit; |
6.6 Blocking
Compatibility between locks , When two locks are incompatible , The lock in one transaction needs to wait for the lock in another transaction to release the occupied resources ;
show variables like '%innodb_lock_wait_timeout%'
| Variable_name | Value |
|---|---|
innodb_lock_wait_timeout | 50 |
The waiting time for the lock is 50s It can be modified dynamically ; The timeout error is
[40001][1205] Lock wait timeout exceeded; try restarting transaction
One more parameter Whether the transaction set to timeout is rolled back Default OFF Don't roll back
show variables like '%innodb_rollback_on_timeout%'
| Variable_name | Value |
|---|---|
innodb_rollback_on_timeout | OFF |
Be careful : InnoDB In most cases, exceptions are not rolled back ; Developers should make their own statements rollback perhaps commit
6.7 Deadlock
6.7.1 Deadlock concept
Deadlock : Two or more transactions are in the process of execution , A phenomenon of waiting for each other due to contention for lock resources ; Without intervention , Will be consumed consistently ;
The simplest solution is to set a timeout , That's what it says innodb_rollback_on_timeout When a timeout occurs, the lock resource will be released ; In addition to the timeout, the deadlock problem is solved , There's another way : At present, most databases adopt wait-for graph To detect deadlocks , A more active way to detect deadlocks InnoDB Page in this way , This requires the database to store the following two types of information ;
- A list of lock information
- Transaction waiting list
Through this information You can construct a graph , If there is a circuit in the diagram , It means that there is a deadlock , The arrow indicates the current waiting state , No shear head means that the lock already exists

stay Transaction waiting list Transaction Wait Lists Yes 4 One transaction t1t2t3t4 In waiting
Business t1 need row1 S lock Waiting ==> Business t2 hold row1 X lock ==> need Business t2 Release row1 X lock t1->t2
Business t2 need row2 X lock Waiting ==> Business t1 Business t4 hold row2 S lock ==> need Business t1 Business t4 Release row2 S lock t2->t1t2->t4
Business t3 need row2 X lock Waiting ==> Business t1 Business t4 hold row2 S lock ==> need Business t1 Business t4 Release row2 S lock t3->t1t3->t4
In order There will be t3->t2 ( although t2 Not yet X lock )
According to the above relation There will be the following figure , There is a loop (t1,t2), There are deadlocks

wait-for graph The depth first algorithm is used to realize ,InnoDB1.2 It was implemented recursively Poor performance compared to non recursive ,1.2 Then non recursive form ;
6.7.2 Deadlock probability ( Did not understand )
Wait at least twice before a deadlock is formed Pure mathematical analysis
threads: n+1 ==> transaction : n+1 A business :r+1 operation Each operation is R in 1 Data and hold the lock hypothesis nr<<R( Operation data is small )
Each thread needs to hold r+1 A lock On average ; Get the lock in one of them L Under the circumstances
Threads 1: Have obtained 1 A lock ; contrast obtain L The probability of locking is 1/(r+1), Threads 2: Have obtained 2 A lock ; contrast obtain L The probability of locking is 2/(r+1) ,
The number of locks acquired : (1+2+…r)/(r+1) About equal to r/2
Every thread : Each row of data is 1/R The waiting probability is nr/2R ;
If the lock length is 2 be Deadlock probability (n2*r4)/(4R2)
6.7.3 An example of a deadlock
| The order | result 1 | conversation 1 | conversation 2 | result 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | begin ; | |||
| 2 | select * from demo2 where id = 3 for update ; | |||
| 3 | begin | |||
| 4 | select * from demo2 where id= 5 for update ; | |||
| 5 | Hang up | select * from demo2 where id= 5 for update ; | ||
| 6 | |select * from demo2 where id = 3 for update ;|Deadlock found when trying to get lock; try restarting transaction Deadlock detection ` | |||
| 7 | commit ; |
6.8 Lock escalation
Lock escalation (Lock Escalation) It means to reduce the granularity of the current lock . Tabular 1000 Upgrade a row lock to a page lock , Or page locks can be upgraded to table locks . In the design of database, lock is considered as a rare resource , Locks consume a lot of memory space , And want to avoid lock overhead , You can upgrade the lock , To some extent, it improves the efficiency ;
InnoDB The storage engine does not have a lock escalation process ;, A lock is not created from records , It is locked according to the data pages accessed by each transaction , Whether a transaction locks one record or multiple records , The overhead is generally consistent
For example, a table has 300W page data , Every data page 100 Record , That is to say 3 Billion data , If it is the update of full table scan , All records need to be added X lock , If it is based on each row of data ,10byte/row ==> 3GB Memory ,
and InnoDB Use bitmaps (bitmap), All lock information recorded on a page exists bitmap above Each page lock requires 30 byte* 300W ==> 90MB
边栏推荐
- markdown_ Picture side by side scheme
- The white paper "protecting our digital heritage: DNA data storage" was released
- Combat tactics based on CEPH object storage
- Quickly build oncyber io
- 7-13 underground maze exploration (adjacency table)
- 2021-02-21
- Explication du principe d'appariement le plus à gauche de MySQL
- C# break continue return 三者区别
- MYSQL的最左匹配原则的原理讲解
- Example interview -- dongyuhang: harvest love in the club
猜你喜欢

Explication du principe d'appariement le plus à gauche de MySQL

基于SSM实现水果商城批发平台

What are the functions of resistance? (super full)
![[preview of the open class of Jishu] arm's strongest MCU core cortex-m85 processor helps the innovation of the Internet of things in an all-round way (there is a lottery)](/img/25/c3af3f51c04865820e3bbe2f010098.png)
[preview of the open class of Jishu] arm's strongest MCU core cortex-m85 processor helps the innovation of the Internet of things in an all-round way (there is a lottery)

Strange error -- frame detected by contour detection, expansion corrosion, and reversal of opening and closing operation effect

Auto.js调试:使用雷电模拟器的网络模式进行调试

【云原生 | Kubernetes篇】Kubernetes 网络策略(NetworkPolicy)

基于 Ceph 对象存储的实战兵法

Combat tactics based on CEPH object storage

在线电路仿真以及开源电子硬件设计介绍
随机推荐
string类对象的访问及遍历操作
Yarn scheduling
7-13 地下迷宫探索(邻接表)
Jetpack架构组件学习(3)——Activity Results API使用
Why is cross-border e-commerce so popular? Papaya mobile takes you to find out
Reading notes of the fifth cultivation
2022 pole technology communication - anmou technology ushers in new opportunities for development
Theoretical explanation of hash table
What are the functions of resistance? (super full)
markdown_ Picture side by side scheme
spark_ sql
Auto.js学习笔记10:实例化自定义对象,在子线程使用JSON.stringify()方法导致报错(已解决)
004:AWS数据湖解决方案
Mysql5.7 partition table
How to do industry analysis
《第五项修炼》读书笔记
Autojs learning notes 6:text (txt) Findone() will report an error when switching apps. Finally, solve the implementation effect and switch any app until the script finds the control with the specified
2021-01-13
2026年中国软件定义存储市场容量将接近45.1亿美元
In 2026, the capacity of China's software defined storage market will be close to US $4.51 billion