当前位置:网站首页>1- enter the database
1- enter the database
2022-06-09 05:03:00 【7777 high】
1.1.1 Basic concepts
- Information
- data
- database
- Database management system
- Database system
Information (Information)
- Definition :
Information is the reflection of people on the attributes and motion state of objective things . What information reflects is about... In an objective system , The mode of existence of something or the state of motion at a certain time .
- features :
- The content of information is knowledge about objective things or thoughts ;
- Information is useful ;
- Information can be transmitted in space and time ;
- Information needs some form to express .
data (Data)
- Definition
Data is a record that reflects the existence mode and motion state of objective things , Is the carrier of information .
From a computer perspective , Data generally refers to those symbols that can be accepted and processed by the computer , Is the basic object stored in the database .
The symbolic record that describes things is called data
- features
- The data are “ type ” and “ value ” Points ;
- Data usage is constrained by data type and value range ;
- Data can take many forms ;
- Data has clear semantics .
The meaning of data is called data semantics , Data and its semantics are inseparable .

database (DataBase,DB)
- Definition
database (DataBase, abbreviation DB), It is to organize relevant data together in a certain way , Keep it in a computer for a long time , Can be shared by multiple users , Independent of the application , Data collection under unified management .
Database is the core of database system , It is the management object of data system .
- features
- Data is organized according to a certain data model , Description and storage ;
- Long term storage ;
- It can be shared by multiple users ;
- Data independence is high ;
- Unified management .
Databases are stored in computers for a long time 、 organized 、 A collection of large amounts of data that can be shared . The data in the database is organized according to a certain data model 、 Describe and store , With less redundancy (redundancy)、 High data independence (data independency) And scalability (scalability), And can be shared for a variety of users .
Database management system (Data Base Management System,DBMS)
- Definition
Database management system (DataBase Management System, abbreviation DBMS) Is located between the user and the operating system , With data definition 、 Management and A collection of software that manipulates functions .
- function
- Data definition ;
- Data organization 、 Storage and management ;
- Data manipulation ;
- Database management and operation management ;
- Database establishment and maintenance ;
- Other features .
- DBMS Data sublanguage
- Data definition language ( abbreviation DDL);
- Data manipulation language ( abbreviation DML) ;
- Data control language ( abbreviation DCL) .

Database system (DataBase System,DBS)
- Definition :
Database system (DataBase System, abbreviation DBS) Support database A basic system that works , The whole computer system .
Database system is to realize organized 、 Dynamically store a large number of related structures Standardized data 、 Computer software that facilitates all kinds of users to access the database / Of hardware resources aggregate .
- characteristic :
- Data structure
The database system realizes the structure of the whole data , This is one of the main features of the database , It is also the essential difference between database system and file system .
So-called “ whole ” Structured means that the data in the database is no longer only for a certain application , But for the whole organization or enterprise ; Not only is the data internally structured , And the whole is structured , There is a connection between data .
2. High data sharing 、 Low redundancy and easy expansion
Data sharing can greatly reduce data redundancy , Save storage space . Data sharing can also avoid incompatibility and inconsistency between data . This makes the database system elastic , Easy to expand .
3. High data independence
1. Data independence : Manage data with the help of database .
1. Physical independence : The user's application and the physical storage of data in the database are independent of each other .
1. Logical independence : The logical structure of the user's application and database is independent of each other .
4. Data is managed and controlled by database management system
1. Data security (security) Protect
It refers to protecting data to prevent data leakage and damage caused by illegal use
2. Data integrity (integrity) Protect
The correctness of data 、 Effectiveness and compatibility .
3. Concurrent (concurrency) control
When concurrent processes of multiple users access 、 When modifying the database 、 It may interfere with each other to get wrong results or destroy the integrity of the database , Therefore, it is necessary to control and coordinate the concurrent operations of multiple users .
4. Database recovery (recovery)
The database is organized and stored in the computer for a long time 、 A lot of 、 Shared data collection . It can be shared by various users , It has minimum redundancy and high data independence . The database management system is established in the database 、 The database shall be under unified control during operation and maintenance , To ensure data integrity and security , And use the database for concurrency control in multiple users at the same time , Recover the database after failure .
1.1.2 Database system
Database system is supported by operating system and database management software , The database can Operation system , It is a necessary environment for data processing .
Database system is to realize organized 、 Dynamically store large amounts of data 、 Computer software that facilitates all kinds of users to access the database / A collection of hardware resources .
One 、 Data processing
1. Data processing definition
Data processing (Data Processing) It's the collection of data 、 Arrangement 、 Storage 、 classification 、 Sort 、 retrieval 、 maintain 、 machining 、 A series of operations of statistics and transmission . in short , Data processing is the process of converting data into information .
2. Data processing development 
Two 、 Database system architecture
The database system has an external level in the overall architecture 、 Concept level 、 Characteristics of internal three-level structure , This three-level structure is also known as “ Three level mode structure ” , or “ Three levels of data abstraction ” . The three-level schema structure of database system consists of external schema 、 Patterns and inner patterns form . <br />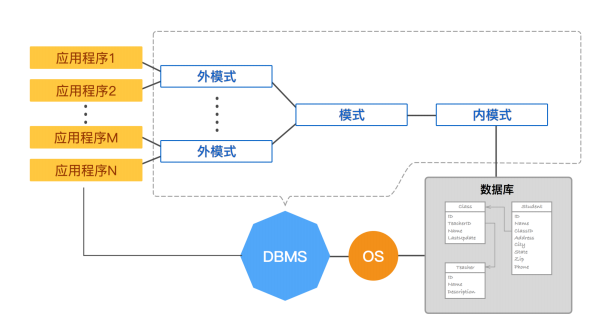
3、 ... and 、 Composition of database system
Database system is composed of hardware environment supporting database 、 Database software support ring habitat 、 database 、 Development 、 The personnel who use and manage the database application system .
1. Hardware environment
Hardware environment is the physical support of database system .
The database system should work with the support of the computer operating system , And it contains Database management routines 、 Applications, etc , Therefore, it is required to have enough memory to open pin . meanwhile , Due to the user's database 、 System software and application software shall be kept outside On the memory , Therefore, the requirement of external memory capacity is also very high , It should also have good communication Track performance .
2. Software environment
Systems software : It mainly includes operating system software 、 Database management system software 、 Develop the high-level language of the application system and its compilation system 、 Application system development tool software Pieces, etc .
Application software : It refers to the development of a database management system based on actual needs Application sent .
3. database
Database is the core of database system , Is the main body of the database system , yes The management object of the database system , It is an information source that provides data for users .
The database consists of two parts , Physical database and data dictionary .
4. personnel
The person who manages the database system refers to 、 Develop and use all aspects of the database system personnel , There are database administrators 、 Systems Analyst 、 Database designers 、 Applications Programmers and users .
1.2.1 Data model
The objective things in the real world are interrelated . Of objective things This universal connection , It determines the data and number as the object attribute record symbol There is also a certain connection between them , The database is organized in this way An abstraction of the relationship between data .
One 、 Data description
Data description : In order to “ data ” Form of symbol , From meeting the needs of users Please start , A description of the attributes and motion state of objective things .
Three data categories : Real world 、 Information world and computer world 
The information world : Use conceptual models to represent the abstraction and Simulation of the real world .
Computer world : use DBMS Supported data model performance .
Two 、 conceptual model
Conceptual model is a data model independent of computer system , It is only used to describe Draw a picture of a particular environment , In a particular system , The objective existence concerned by a specific demand object Information structure in .
Conceptual models usually use E-R Model 、 Extended E-R Model to represent .
1. Overview of model related terms
| Entity (Entity) : | Things that exist objectively and can be distinguished from each other . |
|---|---|
| attribute (attribute): | Attributes refer to the characteristics and properties of an entity . |
| code (Key) : | The attribute or attribute set that uniquely identifies the entity is called the code . |
| Domain (Domain): | The value range of an attribute is called the field of the attribute . |
| Entity set (Entity Set): | A collection of entities of the same type is called an entity set . |
| Solid type (Entity Type): | Use the entity name and its attribute name collection to abstract And depict the same kind The entity of is called the real body . |
| contact (Relationship): | Reflect the connections within the entity , Or connections between entities . |
(1) Entity (Entity)
Things that exist objectively and can be distinguished from each other . An entity can be a person 、 A thing or an abstract concept . 
(2) attribute (attribute)
Attributes refer to the characteristics and properties of an entity . An entity can be characterized by several attributes . (E-R Shown in the figure :“ ellipse ” The symbol of ) 
(3) code (Key)
An attribute or set of attributes that identifies a unique entity is called a code . 
(4) Domain (Domain)
The value range of an attribute is called the field of the attribute . 
(5) Entity set (Entity Set)
A collection of entities of the same type is called an entity set . 
(6) Solid type (Entity Type)
Set with entity name and its attribute name . (E-R Shown in the figure : “ rectangular ” The symbol of ) 
(7) contact (Relationship)
Reflect the connections within the entity , Or entity Connection between . (E-R Shown in the figure :“ The diamond ” The symbol of ) 




3、 ... and 、 relational model
relational model (Relational Model): It is to organize data in the form of two-dimensional table , It is convenient to use the relationship between various objective entities and attributes for storage and transformation , No layering There is no pointer , It is a very effective method to establish the relationship between spatial data and attribute data Data organization method .
1. data structure
Relational model related terms <br /> Relationship (Relation): A two-dimensional table is called relation .<br /> Tuples (Tuple): Rows in a table are called tuples . <br /> attribute (Attribute): The columns in the table are called attributes .<br /> code (Key): An attribute or attribute group in a table , Uniquely identifying a tuple is called a code . <br /> Domain (Domain): The value range of an attribute is called a field . <br /> component (Componet): An attribute value in a tuple is called a component .<br /> Relationship model ( Relation Schema): The description of a relationship is called a relationship pattern . <br />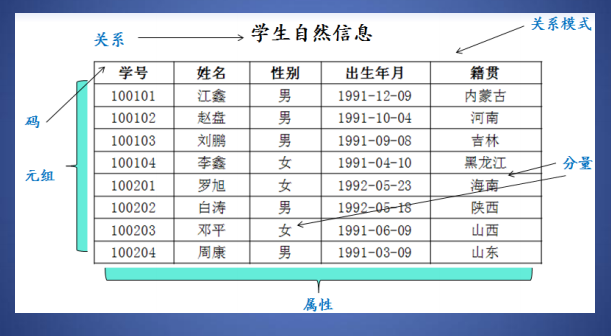
2. Data manipulation
The data operation of relational model is of the nature of set operation , That is, the object of data operation And operation results are all tuples , Or attribute set , Even some relationships operation .
The data operations of relational model mainly include query 、 Insert 、 Delete and modify .
3. Relationship integrity constraints
Relationship integrity constraints :
- Entity integrity :( Entity Integrity );
- Referential integrity :(Reference Integrity );
- User-defined integrity :(User-Defined Integrity).



1.2.2 Relational algebra I : and 、 hand over 、 Bad 、 The cartesian product
Relational algebra is the algebraic operation of a set of sets based on relations , Every time An operation takes one or more relations as the operation object , Its operation result Fruit is still a relationship .
In relational operations , Data manipulation language based on relational algebra said (Data Manipulation Language,DML) Control relationship operations .
Relational algebra includes traditional set operations and special relational operations .
Set operations
Traditional set operations include and 、 Bad 、 hand over 、 The cartesian product .
This kind of operation will “ Relationship ” As a set of tuples , Its operation is from Horizontal direction of the relationship ( The rows in the table ) To carry out .
Operators of set operations :
∪( and )、- ( Bad )、∩( hand over )、×( The cartesian product )
One 、 Union operation
Two known relationships R and S And will produce a containing R、S All are not New relations with tuples . Write it down as : 
The result is n Eye relations , Belong to R Or of S Tuple composition of .
The relationship between the operations of union must be compatible . 


Two 、 Difference operation
Two known relationships R and S Difference , All belong to R But that does not belong to S Yuan New relationships formed by groups . Write it down as : 
result : by n Eye relations , Belong to R It doesn't belong to S All tuples of are made up of .
The relations used in the difference operation must also be compatible .
The difference operation is ordered ,R-S It's not equal to S-R. 



3、 ... and 、 Cross operation
Two known relationships R and S Of , It belongs to R And also belong to S tuples A new relationship . Write it down as : 
result : by n Eye relations , Belong to both R It belongs to S Tuple composition of . 


Four 、 Cartesian product operations
Two known relationships R and S Cartesian product of , yes R Each tuple in the and S in Each tuple is connected to form a new relationship . Write it down as : 



1.2.3 Relational Algebra II : Projection 、 choice 、 Connect 、 except
Specialized relational operations include projection 、 choice 、 Join and divide . this Class operations will “ Relationship ” As a set of tuples , Its operation involves not only the relation The horizontal direction of the system ( The rows in the table ), It also involves the vertical direction of the relationship ( Column in table ).
Relational operator : 
One 、 Projection operation
Projection is a selection relation R A number of attributes in form a new relationship , And get rid of it. Repeated tuples , It is used to filter the attributes of the relationship . Write it down as : 
among :
A For the relationship R List of properties , The attributes are separated by commas , Property name It can also be replaced by its serial number .
Projection operation is a unary relation operation , The results tend to be more Less sex , Or change the attribute order of the original relationship , Or change the original relationship Sexual names, etc . The result of projection operation not only cancels some columns in the original relation , and It is also possible to cancel some tuples ( Avoid repeating lines ). 


Two 、 Select operation
Selection is to select a relationship according to a given condition R A number of tuples in A new relationship , Is to filter the tuples of the relationship . Write it down as : 
among :
F Is the selection condition , It consists of logical operators (∧、∨、 ¬) Sum ratio Comparison operator (>,≥,≤,<,= or ≠ ) A logical expression composed of . 


3、 ... and 、 Join operation
The connection is based on a given condition , From two known relationships R and S My Descartes In your plot , Select the one that meets the connection conditions ( Between attributes ) A number of tuples of A new relationship . Write it down as : 
among :
A、B: Respectively R and S A set of attributes with equal and comparable degrees .
θ: Comparison operator .
The difference between connection and Cartesian product is : Cartesian product is relation R and S all Combination of tuples , The connection only contains the following information: “ Choose the conditions ” Combination of tuples , If the connection is not “ Choose the conditions ” , Then the join operation becomes a Cartesian product operation .
Join operation conditional join 、 Equivalent connection 、 Natural join 、 External connection etc. .
(1) Conditional connection
From the Cartesian product of the two relations, select the properties that satisfy certain conditions Tuples .
(2) Equivalent connection
From the relationship R And S Select the tuple satisfying the equivalence condition from the Cartesian product of .
(3) Natural join
From the Cartesian product of two relations , Select the public attribute to satisfy the equivalence bar Tuples of pieces , But the new relationship does not contain duplicate attributes .
(4) External connection
Add a symbol on one side of the connection condition “*” , Its connection result Is to add an all by for the edge of the symbol “ Null value ” The line of composition .
The left outer join : The symbol in the join condition is to the left of the condition expression , It first R All tuples in are kept in the new relationship , Including public attributes Tuples that do not satisfy the equivalence condition , In a new relationship with S Corresponding non-public attributes All values of are empty .
Right connection : The symbol in the join condition is to the right of the condition expression , It first S All tuples in are kept in the new relationship , Including public properties does not Tuples satisfying equivalence conditions , In a new relationship with R Corresponding non-public attributes All values of are empty . 




1.2.4 Relationship normalization
In the theory of relational database design, relational normalization is very important theory .
The relationship is normalized to a specific problem , How to construct a number suitable for it According to the pattern , That is, several relational patterns should be constructed , What are the attributes of each relationship Composition, etc , Provide methods .
The content of relationship normalization theory
- Data dependency : Study the links between data .
- normal form : The standard for relational patterns .
- Pattern decomposition : The method of pattern design .

Relationship “ Student ” The problem is
- data redundancy
- Update exception : Due to data redundancy , Data generated when data needs to be modified According to the inconsistency .
- Insertion exception : The data to be inserted cannot be inserted .
- Delete exception : Data that should not be deleted is deleted abnormally .
Conclusion : Relationship “ Student ” Not a good relationship model .
resolvent : By decomposing the relational schema, the inappropriate numbers are eliminated According to dependence .
Two 、 Function dependency
Data dependency is reflected by the equality of values between attributes in a relationship The relationship between the data , A description of the interrelationship of data between attributes Statement .
What are functional dependencies ?
To put it simply : When one property set determines another property set , Call another An attribute set depends on the attribute set .
Functional dependency is a description of data dependency .
Definition 1
set up R(U) It's a property set U The pattern of relationships on ,X and Y yes U The son of Set , If for R(U) Any possible relationship of r,r There can be no two Tuples in X Property values on are equal , And in the Y The attribute values on are not equal , said “X The function determines Y” or “Y Function depends on X”, Write it down as X→Y.
namely : If the property X The value of can determine the attribute Y Value , Property Y Functions depend on attributes X.
example
There's a relationship model : Student ( Student number , full name , Gender , date of birth , Department number )
There is a unique identification number in the student relationship “ Student number ” , Each student has and There is only one department , Then the student number determines the value of the department number , therefore : Student number → system Number . 
Definition 2

Definition 3

3、 ... and 、 Standardization principle
The theory of relationship normalization is to study how to make an unreasonable relationship The theory that the model is transformed into an optimal data relation model , It's about paradigms And establish .
Depending on the conditions that meet the specifications , There are six paradigm levels : First model type ( abbreviation 1NF), Second normal form (2NF), Third normal form (3NF),BC normal form (BCNF), Fourth normal form (4NF) And the fifth paradigm (5NF).
1. First normal form (1NF)
If a relational pattern R(U) All properties of are non separable bases This data item , said R(U) For the first paradigm , namely R(U)∈1NF.
The first paradigm is the minimum requirement for the relationship model . Not satisfied with the first A normal form database schema cannot be called a relational database .
example
Students with known relationship patterns ( Student number , full name , Gender , date of birth , Class arrangement Number , Department number , Department name , Course number , Course name , achievement )
Let the relationship pattern satisfy the following functional dependencies :
F={ Student number → full name , Student number → Age , Student number → Gender , Student number → class Number , Class number → Department number , Department number → Department name , Course number → Course name ,( Student number , Course number )→ achievement }
Because the domain corresponding to each attribute of the relational schema is a simple domain , Namely its Field values cannot be subdivided , Conform to the definition of the first normal form , So the student relationship model is First normal form . 

2. Second normal form (2NF)
if R(U)∈1NF, And each non primary attribute is completely functionally dependent on a certain Candidate keys , call R(U) For the second paradigm , namely R(U)∈2NF.
example
It is known that : Student ( Student number , full name , Gender , date of birth , Class number , Department editor Number , Department name , Course number , Course name , achievement )
set up : Attribute group ( Student number , Course number ) For the relationship “ Student ” Code of . The name is not a primary attribute , Yes :( Student number , Course number )→ full name
The set of functional dependencies is known according to the student relationship pattern , Yes : 
How to improve
The relationship “ Student ” Attributes and partial functions that are completely dependent on the code in The attributes of Lai are decomposed into the following 4 A relationship model :
Student ( Student number , full name , Gender , date of birth , Class number , system Number )
departments ( Department number , Department name )
Course ( Course number , Course name )
achievement ( Student number , Course number , achievement )
In each relational schema after decomposition , The non primary attribute pair code is complete Function dependency , So the above 4 All the relationship patterns are 2NF.
3. Third normal form (3NF)
Set the relational pattern R(U)∈2NF, And each non primary attribute has no part The function depends on the code , Nor does the transfer function depend on the code , said R(U) For the third normal form , namely R(U)∈3NF.
example
If you have any :
Student ( Student number , full name , Gender , date of birth , Class number , Department number )
The relational schema has the following functional dependencies :
Student number → Class number , Class number → Student number , Student number → Department number
Although the relationship pattern satisfies 2NF, But there is a difference between the relationship model and the student attributes In passing dependencies , It is not 3NF.
A solution to eliminate delivery dependencies
To eliminate the above problems , Schema decomposition is required , Eliminate transfer function dependency .
Break the students down into the following patterns :
Student ( Student number , full name , Gender , date of birth , Class number )
class ( Class number , Department number )
After the decomposition of the relational model, students no longer have transitive dependency , So it's full foot 3NF.
The result of relationship normalization
Relationship model students ( Student number , full name , Gender , date of birth , Class number , system Number , Department name , Course number , Course name , achievement )
After the above decomposition for many times , Decompose into the following relational patterns :
Student ( Student number , full name , Age , Gender , date of birth , Class number )
class ( Class number , Department number )
departments ( Department number , Department name )
Course ( Course number , Course name )
achievement ( Student number , Course number , achievement )
Four 、 Pattern decomposition
The decomposition of the relational schema should conform to “ Lossless connection ” and “ Stay dependent on ” Principles , So that the decomposed relationship can not destroy the original functional dependency .
Keep the right amount of redundancy , To exchange space for time Purpose , It is also a pattern Important principles of decomposition .
1. Lossless connection
When it comes to relational patterns R When decomposing ,R Tuples will be placed in the corresponding attribute Sets are projected to produce new relationships . If the new relationship is naturally connected The set of tuples obtained is completely consistent with the original relation , It is called lossless connection .
2. Stay dependent on
When it comes to relationships R When decomposing ,R The functional dependency set of will also be set according to the corresponding Schema decomposition , If the total function dependency set after decomposition is consistent with the original function The lie set remains unchanged , Is called preserving functional dependencies .
In the actual database design , It is not that the higher the level of relationship normalization The better , Specific problems need to be analyzed . In short, the goal is to design a personality Good database mode .
边栏推荐
- TypeScript学习【5】 类类型
- ETF operation practice record: March 2, 2022
- application. Properties mysql. cj. jdbc. Driver red
- Faster RCNN
- Penetration test path dictionary, blasting dictionary
- 模式识别大作业——PCA&Fisher&KNN&Kmeans
- 2022 safety officer-c certificate examination practice questions simulated examination platform operation
- Lighting - brightness attenuation of light
- Applets have become a must for super apps, competing for private domain "reserve"
- Soft keyboard appears search
猜你喜欢

Cmdbuilding搭建简易流程及问题处理

Camtasia studio2022 free key serial number installation trial detailed graphic tutorial
![[004] [esp32 Development Notes] audio development framework ADF environment construction - based on esp-idf](/img/55/9eb286bc56ec991837fc014b42fc20.png)
[004] [esp32 Development Notes] audio development framework ADF environment construction - based on esp-idf

June 2022 Tsinghua Management Tsinghua University Ning Xiangdong

application. Properties mysql. cj. jdbc. Driver red

Recommend this UI automation testing framework and write use cases as colloquially as possible

Question bank and answers of G3 boiler water treatment examination in 2022

How to change the color of WPS ppt background picture

Openstack Learning Series 1: openstack introduction, installation and deployment of basic environment
![[series of troubles caused by inaccurate positioning] Part 2: what's wrong with the weak satellite signal](/img/fa/7ceac4a1ac181636de01de46cd272b.jpg)
[series of troubles caused by inaccurate positioning] Part 2: what's wrong with the weak satellite signal
随机推荐
Smart curly bracket escape
Penetration test path dictionary, blasting dictionary
2022 welder (elementary) special operation certificate examination question bank and simulation examination
ASP. Net core build scheduling service - use generic host with quartz Net
2022年安全员-A证考试试题及在线模拟考试
SQL summary statistics: use cube and rollup in SQL to realize multidimensional data summary
聊聊保证线程安全的10个小技巧
Transformer裏面的緩存機制
Faster RCNN
"Diwen Cup" electronic design competition of Hunan University of Arts and Sciences was successfully concluded
[sword finger offer II 001. integer division] the same as leedcode 29 Divide two numbers
2022 tea artist (intermediate) examination question simulation examination question bank and simulation examination
How to build fastdfs, vsftpd and miniio file servers in marathon environment
[006] [ESP32开发笔记] 使用Flash下载工具烧录固件步骤
Win10 registry failed to save changes to permissions access denied
Marathon环境下fastdfs和vsftpd和miniIo文件服务器搭建的方式
SWFUpload
Win10注册表无法保存对权限所作的更改拒绝访问
R language multivariable generalized orthogonal GARCH (go-garch) model for fitting and forecasting high-dimensional volatility time series of stock market
崔健没变,北汽极狐该做出改变了