当前位置:网站首页>Shared memory synchronous encapsulation
Shared memory synchronous encapsulation
2022-06-25 15:07:00 【Knowledge first】
1 explain
Software development , Process communication is often required , Shared memory is a good choice when the amount of data is large . However, shared memory generally requires semaphores to achieve shared memory synchronization .
Again qt in , Shared memory is encapsulated as QSharedMemory class , The semaphore is encapsulated as QSystemSemaphore class , The source code of the underlying implementation calls the standard library interface .
And this article is in QSharedMemory And QSystemSemaphore Continue to perform a packaging on the basis of , So as to realize the function of shared memory and its synchronization .
gitee Project code hosting address :https://gitee.com/jiangtao008/shareMemory.git
Shared memory articles :https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42887343/article/details/118416994
2 Read write mode
There are generally read and write sides of shared memory , I have classified read and write , Reading and writing are divided into two modes , as follows :
- Direct write mode
- Contract write mode
- Conditional read mode
- Contract read mode
It will be analyzed in this summary .
2.1 Symbol description
Semaphore spin wait
When a process tries to get a semaphore that has been locked , This thread will not be busy waiting in spin like a spin lock , Instead, it will add itself to a waiting queue to sleep , Until another process or thread releases the semaphore , The process in the waiting queue will be awakened .
Semaphore release
Release semaphore , Used to wake up other processes or threads .
2.2 Direct write mode
Direct write means direct write … That is, when you write data to the shared memory, you can write it directly , There is no need to consider that there are processes reading shared memory ( Shared memory lock , No semaphore ).
After the shared memory is written , The semaphore needs to be released , Let other processes read .
2.3 Contract write mode
Writing by agreement means that both parties should agree to write to the read . Before writing on the write side , The reader cannot read , In turn, , Cannot write before reading .
So you need to spin the semaphore and wait before writing to memory , Wait for the reading process to release the semaphore after reading the memory .
You also need to release another semaphore after writing to memory ( And the above semaphore spin wait is not a semaphore ).
2.4 Conditional read mode
The most basic is the conditional read mode , You need to wait for the write semaphore to be released before reading .
If read directly , One is that the process does not know whether the memory is written , Repeated reads back waste cpu resources , The second is that the timing reading cannot achieve the real-time performance of memory synchronization ( After writing to memory , You may have to wait n The data is read after milliseconds ), So the best way is to wait for the semaphore to be released and read it immediately .
2.5 Contract read mode
Contract read is a pattern designed to work with contract write , The writing end is in the use of the contract writing mode , The reading end must release the corresponding semaphore after reading the memory , Otherwise, the writer will wait while writing data .
Read / write pattern matching
Write unconditionally + Conditional read

Write unconditionally + Contract read

The Convention writes + Contract read

The shared memory synchronization class implements
Ideas
en en en en en en
Code
The header file
#ifndef SYNSHAREMEM_H
#define SYNSHAREMEM_H
#include <QObject>
#include <QThread>
#include <QDebug>
#include <QSharedMemory>
#include <QSystemSemaphore>
class SynShareMem : public QThread
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
enum Type
{
eWrite_1_sema = 1, // Write unconditionally
eWrite_2_sema = 2, // The Convention writes ( Wait for other processes to read before writing )
eRead_1_sema = 3, // Conditional read
eRead_2_sema = 4 // Contract read ( Conditions for releasing writes after reading , And eWrite_2_sema Pattern matching )
};
public:
explicit SynShareMem(Type type,QString memKey, unsigned int size, QString semaKey, QObject *parent = nullptr);
~SynShareMem();
// In the agreed mode , Writing without receiving will fail , So we need to wait readFinished The signal
// Writing... Is not allowed in read mode , Write return 0( Failure )
bool writeMem (char *data, int size); // Write to shared memory - Fixed length
//void writeMem(QByteArray data); // Non fixed length
int readMem(char *data,int size);
// At present, all modes can be cleared
void cleanMem(char data = 0x00);
void stop();
protected:
void run();
signals:
void haveRead(char *data,int size); // Shared memory is read and sent once , Only valid in read mode
//void haveRead(QByteArray data); // Non fixed length
void readFinished(); // Only valid in double lock write mode , Identify that the other process has read the shared memory data , Call at this time writeMem Functions are not blocked
private:
bool quitFlag;
Type mType; // type
QSharedMemory *shareMem;
QSystemSemaphore *mSema_W2R;
QSystemSemaphore *mSema_R2W; // Semaphore - Read flags
char *mShareData; // Cache data segments
int mShareSize; // Shared memory size
QSharedMemory *creatShareMemory(QString key, int size, bool isWrite = 1);
void relaseShareMemory(QSharedMemory *mem);
bool writeShareMemory(QSharedMemory *mem, char *data, int size);
void readShareMemory(QSharedMemory *mem, char *data, uint size);
};
#endif // SYNSHAREMEM_H
cpp file
#include "synsharemem.h"
SynShareMem::SynShareMem(Type type,QString memKey, unsigned int size,QString readKey,QObject *parent)
: QThread(parent)
, quitFlag(0)
, mType(type)
, shareMem(nullptr)
, mSema_W2R(nullptr)
, mSema_R2W(nullptr)
, mShareData(nullptr)
, mShareSize(size)
{
// Shared data cache space , Only required for read mode
if(mType == eRead_1_sema || mType == eRead_2_sema)
mShareData = new char[mShareSize]; // Different thread heap spaces can be shared
// Semaphore
mSema_W2R = new QSystemSemaphore(QString("%1_Write->Read").arg(readKey), 1);
if(type == eWrite_2_sema || type == eRead_2_sema)
mSema_R2W = new QSystemSemaphore(QString("%1_Read->Write").arg(readKey), 1);
// Shared memory , Basis type 、key、 Size creates a shared memory block
bool isWrite = 0;
if(mType == eWrite_1_sema || mType == eWrite_2_sema)
isWrite = 1;
shareMem = creatShareMemory(memKey,size,isWrite);
if(!shareMem)
qDebug()<<"share memery creact ERROR!";
}
SynShareMem::~SynShareMem()
{
quitFlag = 1;
shareMem->detach();
if(mSema_W2R != nullptr)
delete mSema_W2R;
if(mSema_R2W != nullptr)
delete mSema_R2W;
if(mShareData != nullptr)
delete []mShareData;
}
void SynShareMem::stop()
{
// The following code is used to ensure that the child thread exits run function
quitFlag = 1;
if(mSema_W2R != nullptr)
mSema_W2R->release();
if(mSema_R2W != nullptr)
mSema_R2W->release();
}
bool SynShareMem::writeMem(char *data, int size)
{
writeShareMemory(shareMem,data,size);
mSema_W2R->release();
return 1;
}
int SynShareMem::readMem(char *data, int size)
{
int minSize = qMin(size,mShareSize);
readShareMemory(shareMem,data,minSize);
return minSize;
}
void SynShareMem::cleanMem(char data)
{
QByteArray textData(mShareSize,data);
char *source = textData.data();
writeMem(source,textData.size());
}
void SynShareMem::run()
{
if(quitFlag || mType == eWrite_1_sema )
return ;
if(mType == eWrite_2_sema)
{
qDebug()<<Q_FUNC_INFO<<"run to Write_2 model while(1)......";
while(1)
{
mSema_R2W->acquire(); // Wait for other processes to finish reading
if(quitFlag)
return ;
emit readFinished();
}
}
// The thread loop is only responsible for reading patterns
qDebug()<<Q_FUNC_INFO<<"run to Read model while(1)......";
while(1)
{
// White dot operation . Semaphore , Prevent the thread from looping and causing the software to jam when there is no write
mSema_W2R->acquire();
if(quitFlag)
return ;
qDebug()<<Q_FUNC_INFO<<"find write and start to read...";
// Memory operations
readShareMemory(shareMem,mShareData,mShareSize);
// Black dot operation
if(mType == eRead_2_sema)
mSema_R2W->release();
emit haveRead(mShareData,mShareSize);
}
}
QSharedMemory* SynShareMem::creatShareMemory(QString key,int size,bool isWrite) // Create a memory segment by default
{
bool haveError = 0;
QSharedMemory *mem = new QSharedMemory(key,this);
if(!mem->attach()) // Bind memory block
{
// The shared memory block does not exist , You need to create a build ( Because I'm not sure which side runs first , There is no distinction between write and read )
// Here we need to pay attention to , Whether to add mutex between processes
mem->lock();
haveError = !mem->create(size);
mem->unlock();
}
if(haveError)
{
qDebug() << Q_FUNC_INFO<<mem->errorString();
delete mem;
mem = NULL;
}
qDebug()<<Q_FUNC_INFO<<QString("create shareMemory end! isWrite:%1 error:%2")
.arg(isWrite)
.arg(mem->errorString());
return mem;
}
void SynShareMem::relaseShareMemory(QSharedMemory* mem)
{
if(mem == NULL) return ;
mem->detach(); // All processes are detach after , Will automatically free the memory block
delete mem;
mem = NULL;
qDebug()<<Q_FUNC_INFO<<"Relase shareMemory end!";
}
bool SynShareMem::writeShareMemory(QSharedMemory* mem,char *data,int size)
{
if(mem == NULL) return 0;
mem->lock();
char *dest = reinterpret_cast<char *>(mem->data());
int minSize = qMin(size,mem->size());
memcpy(dest, data, minSize);
mem->unlock();
qDebug()<<Q_FUNC_INFO<<"Write shareMemory end!";
return 1;
}
void SynShareMem::readShareMemory(QSharedMemory* mem,char *data,uint size)
{
if(mem == NULL) return ;
mem->lock();
char *source = (char*)mem->constData();
memcpy(data, source, size);
mem->unlock();
qDebug()<<Q_FUNC_INFO<<"Read shareMemory end!";
}
Class — Demonstration code
Interface design

Software implementation code
View the code hosting address :https://gitee.com/jiangtao008/shareMemory.git
Usage method
1、 Software double opening , A select write mode , A select read mode , The pattern is selected according to the matching method mentioned above .
2、 Fill in the same shared memory key and size, And semaphores key( If you can't set it, you can leave it alone ).
3、 Click Settings , Wait for the success and failure prompt boxes , If the prompt is successful, it indicates that the shared memory is successfully created or associated .
4、 Finally, read and write memory operations .
Examples of use
1、 Software A Set the contract write mode 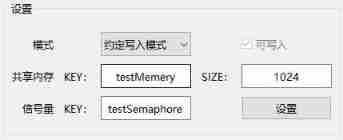
2、 Software B Set the contract read mode 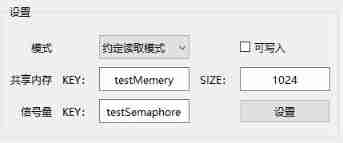
3、 Software A Write data 
4、 Software B Automatically read data and display ( Shared memory synchronization )
5、 Software B Is read mode , Check to write , You can also write to the shared memory 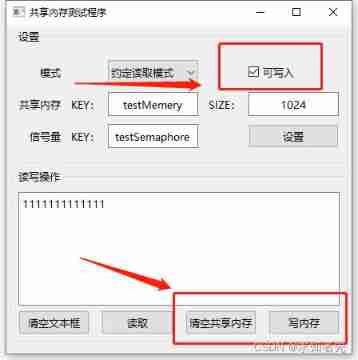
6、 If you need to change the mode 、 Shared memory or semaphore key、size Etc , Click settings after editing directly , See the source code for the specific implementation .
边栏推荐
- Learning notes on February 8, 2022 (C language)
- Bessie's weight problem [01 backpack]
- Common operations in VIM
- 2022年广东高考分数线出炉,一个几家欢喜几家愁
- Installing QT plug-in in Visual Studio
- QT file reading -qfile
- Ubuntu 20.04 installing mysql8.0 and modifying the MySQL password
- One code per day - day one
- 搭建极简GB28181 网守和网关服务器,建立AI推理和3d服务场景,然后开源代码(一)
- Customization and encapsulation of go language zap library logger
猜你喜欢

Master XSS completely from 0 to 1

basic_ String mind map

Source code analysis of zeromq lockless queue

开餐馆
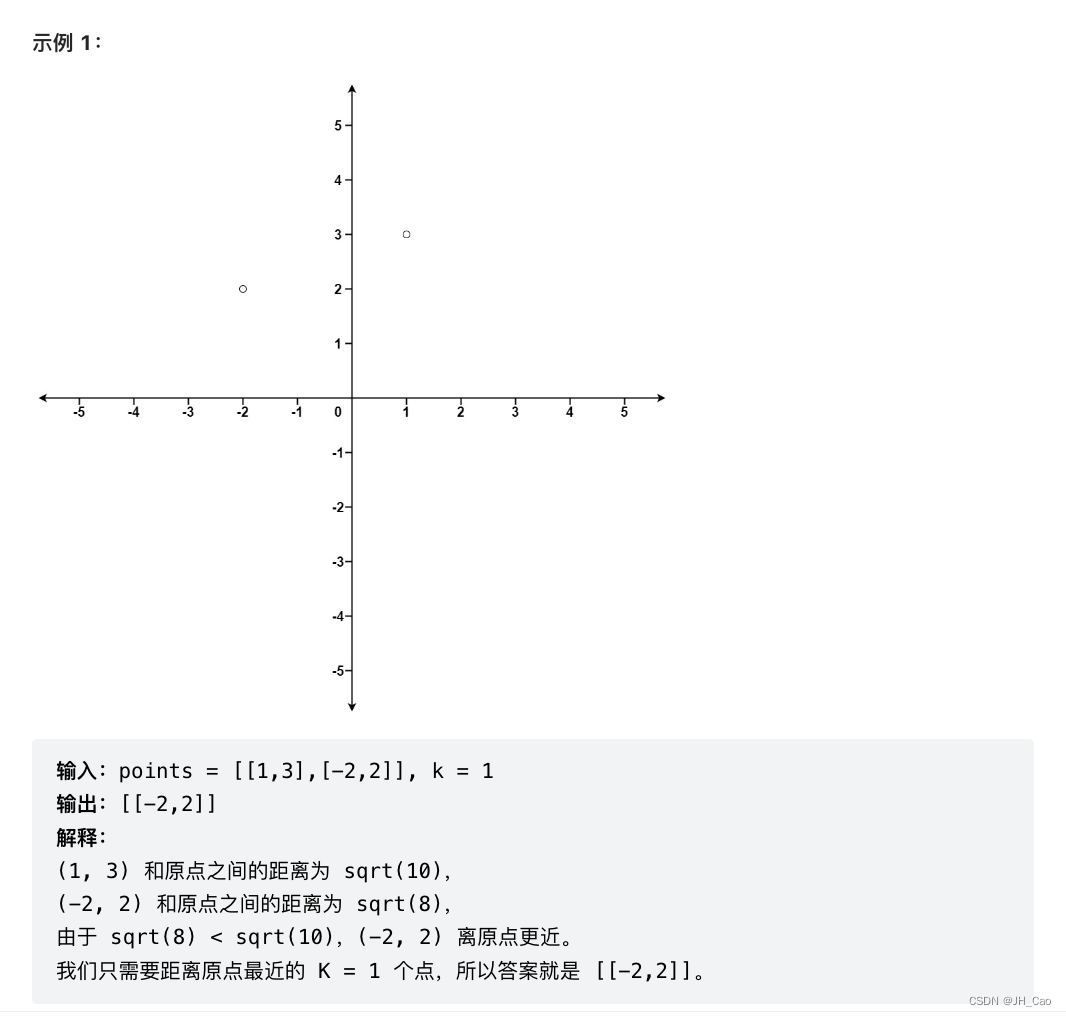
15 -- 最接近原点的 K 个点

ffmpeg protocol concat 进行ts流合并视频的时间戳计算及其音画同步方式一点浅析
【Try to Hack】vulnhub DC1

Introduction to flexible array

What moment makes you think there is a bug in the world?
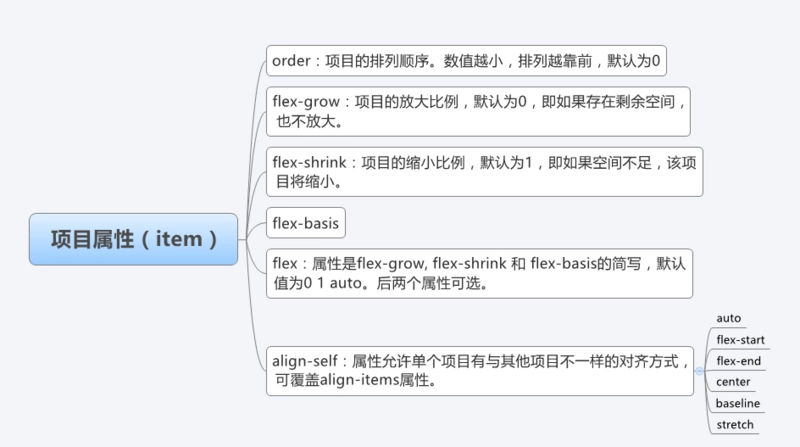
Flexible layout (display:flex;) Attribute details
随机推荐
(translation) json-rpc 2.0 specification (Chinese version)
搭建极简GB28181 网守和网关服务器,建立AI推理和3d服务场景,然后开源代码(一)
Jaspersoft studio installation
QT opens the print dialog box in a text editor
Custom structure type
Std:: vector minutes
Gif动图如何裁剪?收下这个图片在线裁剪工具
Basic knowledge of pointer
分饼干问题
开餐馆
Vs2019 scanf error
QT loading third-party library basic operation
14 -- 验证回文字符串 Ⅱ
iconv_ Open returns error code 22
In 2022, the score line of Guangdong college entrance examination was released, and several families were happy and several worried
How to cut the size of a moving picture? Try this online photo cropping tool
Biscuit distribution
Cross compilation correlation of curl Library
Add the resources directory under test in idea
Using Sphinx to automatically generate API documents from py source files