当前位置:网站首页>Principle and application of user mode hot patch
Principle and application of user mode hot patch
2022-06-21 21:20:00 【51CTO】
author : Tianyi cloud Jiangshaotao
key word : hotfixes 、ELF、 relocation
( One )ELF brief introduction
Before understanding the principle of user mode hot patch , We have to be right ELF Simple understanding and analysis of documents , So the beginning , Let's talk to you first ELF.
stay Linux In the system , Most binary files use ELF Format . From the producer's point of view , This format consists of a set of files named sections The sections of .sections Can contain data (.rodata, .data)、text adopt symbols Symbolic mechanism to implement code 、 data 、 References to variables . for example ,C In program main It's a special symbol , After completing the required initialization ,C runtime Will transfer control to main..symtab Section lists the symbols that need to be used . Executable code ( Usually called .text) And some auxiliary data . The following simple c Program :

After compilation , Can pass readelf -S Binary name see ELF Of Sessions

ELF The format file mainly includes three types :
· Share used dynamic library files , It is mainly used to store public code ;
· Binary executable , It mainly includes applications ;
· Relocatable target file , It is mainly compiled from assembly files ;
stay GNU C compiler During compilation of , In fact, the assembly step is hidden . These are different ELF Type of format file , The main difference between them is whether the relocation type is included .
What is this relocation ? Relocation technology is a technology that allows the address to be changed in the binary object file . This technology is the key to realize user mode hot patch , So let's start by explaining . for example , When we put a series of .o When a file is linked to an executable , The linker will link each .o In the document .text、.data Sections are merged into one .text、.data In the festival , The linker will then adjust the relocation information , For example, the position of repositioning ( be called r_offset, For relocating files , This value is the byte offset of the storage unit affected by relocation in the section ; For executables or shares ELF The file is , This value is the virtual address of the storage unit affected by relocation )、 Target symbol and its address , Or the addend relative to the sign value ( be called r_addend). Some types of relocation , It is also allowed to appear in the final binary object , And resolve when the dynamic linker is loaded .
Take the following two pieces of code for example :


Compile the two source files into binary files :gcc -c a.c b.c
Disassemble the object file :

Through the command : readelf -r a.o Check if there is a redirect file
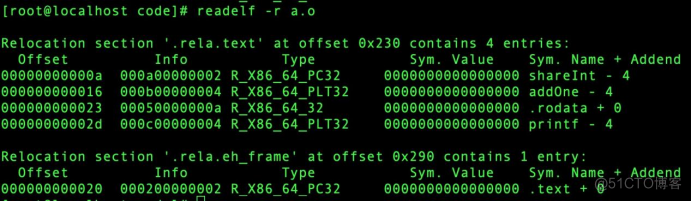
These are a.o This binary redirects the entry , We use addOne For example , You can see from the query results ,addOne Of r_offset by :000000000016,r_info by :000b00000004,
Now let's see b.o Disassembly result of

Then we compile these two binary files into executable files :gcc a.o b.o -o ab
Then check it out ab Disassembly result of , As described above ,ab China Council merge a.o and b.o Of .text .data Content , Because there is more content , Let's just look at the key points

Let's compare a.o b.o ab The executable file can be found from the disassembly result of ab The address of is obviously changed . This is the logic of redirection . The dynamic target contains all the necessary data to load it to a random base address . The use of random base addresses in such loading will randomize the addresses loaded by functions in the library , Thus, it is difficult for intruders to exploit loopholes to attack - blow , And it will not interfere with each other when loading multiple libraries . Because the address of the variable cannot be determined at compile time , Therefore, when referring to data objects in the dynamic library, use GOT surface . This table contains the addresses of variables , So accessing variables requires two steps : First load GOT Table entry , Then find the entry corresponding to accessing a variable in the table , To find the address to visit .GOT Entries in the table are dynamic linkers ( for example ld-linux) Through analysis .rela.dyn Section to complete the filling , Only a few types of relocation are allowed , For example, in x86-64 Under the architecture , Supported relocation types are R_X86_64_RELATIVE、R_X86_64_64 and R_X86_64_GLOB_DATA. The symbols provided in the dynamic library are listed in .dynsym In the festival , Symbol names are stored in .dynstr In the festival ..dynamic This special section contains all the data needed to load the library , For example, a list of required libraries 、 A pointer to a relocation entry, etc .
Variables in the executable target 、 Symbols are usually linked to a fixed address , And does not contain relocation information . The kernel just needs to know how to load this type of object with the interpreter . If there is no special designation , Most binaries use dynamic linkers ld-linux As an interpreter . It is loaded by the kernel and control is transferred here . The responsibility of the dynamic loader is to load all the necessary Libraries 、 Parse the symbols and transfer control to the application code .
Any relocation type is allowed in the relocatable target file . Static linker , for example ld, Link them into an executable target or a dynamic target . Relocatable object files can be seen as a simple transformation from assembly files to binary files , It contains an appropriate notation for symbolic references . That is, every symbol reference in the assembly file , In relocatable ELF There are corresponding symbols and relocation references to this symbol in the file . For each defined symbol , Will be added to .symtab In the festival . With ’\0’ The ending string identifies the symbol name , Stored in .strtab In the festival . then , The static linker uses symbols defined in other target files or dynamically shared target files to resolve symbol references in the target files .
边栏推荐
- Leecode198 looting
- Redis HyperLogLog 是什么?这些场景使用让我枪出如龙一笑破苍穹
- [parallel and distributed computing] 10B_ MapReduce GFS Implementation
- 这套实时监控方案,真的太顶了!
- 全新混合架构iFormer!将卷积和最大池化灵活移植到Transformer
- AXI_ Bus_ Matrix_ 4x4 design - logic design
- 【owt】p2p Signaling Server 运行
- Vertical and horizontal network shooting range community Modbus Protocol
- 欢迎使用Markdown编辑器
- MySQL learning (from getting started to mastering 1.2)
猜你喜欢
![[Patents and papers-19]: Notice on electronic information application of Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province in 2022 (medium and advanced)](/img/a5/47c1b189cfd4bee6edb68c266a3816.png)
[Patents and papers-19]: Notice on electronic information application of Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province in 2022 (medium and advanced)

向量與平面交點

【CTF】攻防世界 MISC

行业首家!极氪APP获中国网络安全审查技术与认证中心权威认证
![[OWT] P2P signaling server running](/img/92/bc2c364523a1bbfa2bb1c742827eec.png)
[OWT] P2P signaling server running

MySQL learning (from getting started to mastering 1.2)

【MySQL·水滴计划】第三话- SQL的基本概念

Redis HyperLogLog 是什么?这些场景使用让我枪出如龙一笑破苍穹

What is the C language callback function?

2016 ICLR | Adversarial Autoencoders
随机推荐
Several common device communication protocols in embedded development are summarized
#夏日挑战赛# 用OpenHarmony eTS 实现一个Huawei app标准布局
Cluster I -- LVS load balancing cluster NAT mode and LVS load balancing actual deployment
向量与平面交点
获取OpenHarmony源码:从DevEco Marketplace获取(1)
如何有序协同和管理多个研发项目?
向量與平面交點
About n before variables in SQL server and other usage analysis
Asynchronous method understanding (demo with code)
【服务器数据恢复】EMC某型号服务器raid5数据恢复案例
2022年最新河南建筑施工电工(建筑特种作业)模拟试题及答案
AB打包有的Shader没有触发IPreprocessShaders的回调
Mysql database - storage engine
PLC功能块系列之气缸功能块(FB)
Common cases of hybrid cloud exercises
Multithreaded instance code (Demo)
The final scheme of adding traceid at the C end
如何解决织梦文章列表自动更新点击次数
Intersection of vector and plane
2016 ICLR | Adversarial Autoencoders