当前位置:网站首页>Talk about how to use redis to realize distributed locks?
Talk about how to use redis to realize distributed locks?
2022-07-26 19:40:00 【JavaMonsterr】
Today, I want to talk about two questions :
- How to use Redis Implement distributed locks ?
- Redis How to solve the reliability problem of distributed locks in the case of clusters ?
How to use Redis Implementation of distributed locks ?
Distributed lock is a mechanism for concurrency control in distributed environment , It is used to control that a resource can only be used by one application at the same time . As shown in the figure below :

Redis It can be shared and accessed by multiple clients , It happens to be a shared storage system , Can be used to hold distributed locks , and Redis High read and write performance , It can cope with high concurrency lock operation scenarios .
Redis Of SET The command has a NX Parameters can be implemented 「key Insert... Only if it doesn't exist 」, So it can be used to realize distributed locking :
- If key non-existent , Then the insertion is successful , It can be used to indicate the success of locking ;
- If key There is , Insert failed... Will be displayed , It can be used to indicate locking failure .
be based on Redis When nodes implement distributed locks , For lock operation , We need to meet three conditions .
- Locking includes reading lock variables 、 Check the lock variable value and set the lock variable value , But it needs to be done in an atomic way , therefore , We use SET Order to take NX Option to implement locking ;
- The lock variable needs to set the expiration time , To avoid exceptions after the client gets the lock , As a result, the lock cannot be released , therefore , We are SET Add... When the command is executed EX/PX Options , Set its expiration time ;
- The value of the lock variable needs to be able to distinguish lock operations from different clients , In case of releasing the lock , Incorrect release operation occurs , therefore , We use SET Command to set the value of the lock variable , The value set by each client is a unique value , Used to identify the client ;
The distributed commands that meet these three conditions are as follows :
SET lock_key unique_value NX PX 10000
- lock_key Namely key key ;
- unique_value Is a unique identifier generated by the client , Distinguish lock operations from different clients ;
- NX Representative only in lock_key When there is no , That's right lock_key Set up operation ;
- PX 10000 Presentation settings lock_key Expires on 10s, This is to avoid that the client cannot release the lock due to an exception .
The process of unlocking is to lock_key Key delete (del lock_key), But it can't be deleted randomly , Make sure that the client performing the operation is the locked client . therefore , When you unlock , We have to judge the lock first unique_value Whether it is a locked client , If yes , Only then lock_key Key delete .
You can see , Unlocking has two operations , It's time to Lua Script to ensure the atomicity of the unlock , because Redis In execution Lua Script time , Can be performed in an atomic manner , The atomicity of lock release operation is guaranteed .
// When releasing the lock , Compare first unique_value Whether it is equal or not , Avoid false release of lock
if redis.call("get",KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then
return redis.call("del",KEYS[1])
else
return 0
end
thus , Just by using SET Command and Lua Script in Redis The locking and unlocking of distributed locks are completed on a single node .
be based on Redis What are the advantages and disadvantages of implementing distributed locks ?
be based on Redis Implementation of distributed locks advantage :
- High performance ( This is the core starting point of choosing cache to implement distributed lock ).
- To achieve convenient . Many R & D engineers choose to use Redis To implement distributed locking , Largely because Redis Provides setnx Method , It is very convenient to implement distributed locks .
- Avoid single point of failure ( because Redis It is deployed across clusters , Naturally, a single point of failure is avoided ).
be based on Redis Implementation of distributed locks shortcoming :
The timeout is not easy to set . If the lock timeout is set too long , Will affect performance , If the timeout is set too short, shared resources will not be protected . For example, in some scenes , One thread A After getting the lock , Because the execution time of business code may be long , The timeout of the lock was exceeded , Automatic failure , Be careful A The thread is not finished , Subsequent threads B And accidentally held the lock , It means that shared resources can be operated , Then the shared resources between two threads cannot be protected .
- So how to reasonably set the timeout ? We can set the timeout based on renewal : First set a timeout for the lock , Then start a daemonic thread , Let the daemon thread after a period of time , Reset the timeout of this lock . The implementation method is : Write a daemon thread , Then judge the condition of the lock , When the lock is about to fail , Renew and lock again , When the main thread completes execution , Destroy the renewal lock , But this approach is relatively complex to implement .
Redis The data in the master-slave replication mode is asynchronously replicated , This leads to the unreliability of distributed locks . If in Redis After the master node obtains the lock , When there is no synchronization to other nodes ,Redis The primary node is down , Now the new Redis The master lock can still be acquired , Therefore, multiple application services can obtain locks at the same time .
Redis How to solve the reliability of distributed lock in cluster ?
In order to ensure the reliability of distributed locks in the cluster environment ,Redis Officials have designed a distributed lock algorithm Redlock( Red lock ).
It is based on multiple Redis Distributed locks for nodes , Even if a node fails , The lock variable still exists , The client can still complete the lock operation .
Redlock The basic idea of the algorithm , Is to let the client and multiple independent Redis Nodes request locking in turn , If the client can successfully complete the locking operation with more than half of the nodes , So we say , The client successfully obtained the distributed lock , Otherwise, locking fails .
thus , Even if there is one Redis Node failure , Because the locked data is also saved on other nodes , So the client can still lock normally , The data of the lock will not be lost .
Redlock There are three processes of algorithm locking :
The first step is to , The client gets the current time .
The second step is , The clients are sent to... In order N individual Redis The node performs locking :
- Use of locking operation SET command , close NX,EX/PX Options , And the unique identification of the client .
- If a Redis The node has failed , To ensure that in this case ,Redlock The algorithm can continue to run , We need to give 「 Lock operation 」 Set a timeout ( Not right 「 lock 」 Set timeout , It's right 「 Lock operation 」 Set timeout ).
The third step is , Once the client is finished and all Redis Node locking operation , The client needs to calculate the total time of the whole locking process (t1).
Successful locking requires two conditions to be met at the same time ( sketch : If there are more than half Redis The node successfully obtains the lock , And the total time does not exceed the effective time of the lock , Then it is the success of locking ):
- Conditions for a : Clients from more than half ( Greater than or equal to N/2+1) Of Redis The lock was successfully obtained on the node ;
- Condition 2 : The total time it takes for the client to acquire the lock (t1) The effective time of the lock is not exceeded .
After locking successfully , The client needs to recalculate the effective time of this lock , The result of the calculation is 「 The initial effective time of the lock 」 subtract 「 The total time taken by the client to acquire the lock (t1)」.
After the lock failed , Client to all Redis The node initiates the operation to release the lock , The operation of releasing the lock is the same as that of releasing the lock on a single node , Just execute the of releasing the lock Lua Scripts will do .
边栏推荐
- MySQL教程:MySQL数据库学习宝典(从入门到精通)
- Cannot find current proxy: Set ‘exposeProxy‘ property on Advised to ‘true‘ to make it available
- 2022/07/26 学习笔记 (day16) 抽象与接口
- What do indicators and labels do
- 测试人员必须知道的软件流程
- Onion group joined hands with oceanbase to realize distributed upgrading, and global data has achieved cross cloud integration for the first time
- Introduce the difference between @getmapping and @postmapping in detail
- 彻底关闭win10自动更新
- Linear algebra Chapter 4 linear equations
- Chapter 9 practical modeling technology
猜你喜欢

B站SRE负责人亲述 713事故后的多活容灾建设|TakinTalks大咖分享

服务发现原理分析与源码解读
![[yolov5] - detailed version of training your own dataset, nanny level learning, logging, hand-in-hand tutorial](/img/34/5ab529ff6d8d0fd3827c440299964d.png)
[yolov5] - detailed version of training your own dataset, nanny level learning, logging, hand-in-hand tutorial

线性代数第3章向量

Volatile keyword of JVM memory model

C # create and read dat file cases

测试面试题集-UI自动化测试

Advantages of advanced anti DDoS IP in Hong Kong and which industries are suitable for use

Turn off win10 automatic update completely
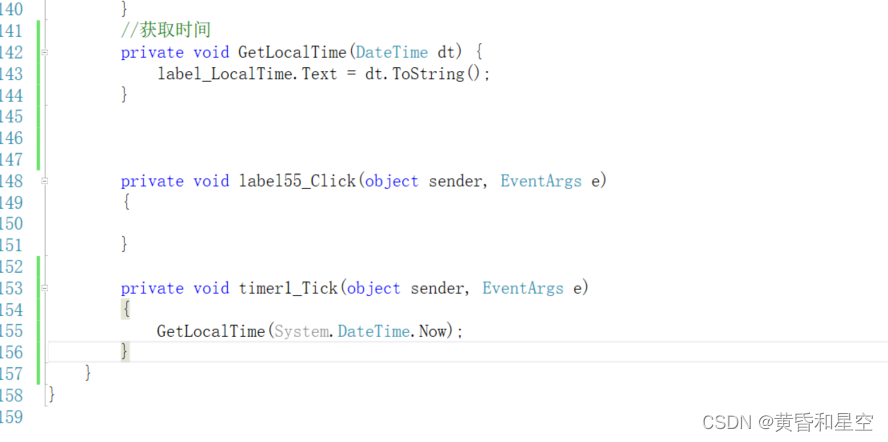
C # get local time / system time
随机推荐
微信小程序插件--wxml-to-canvas(生成图片)
MySQL tutorial: MySQL database learning classic (from getting started to mastering)
DDL,DQL,DML语句
YOLO V2详解
Advantages of advanced anti DDoS IP in Hong Kong and which industries are suitable for use
JS中的 作用域
Software process that testers must know
Selenium + case of Web Automation Framework
Pads draw 2.54mm row needle
2022/07/26 学习笔记 (day16) 抽象与接口
2022牛客多校联赛第三场 题解
【C语言实现】----动态/文件/静态通讯录
安全测试与功能测试、渗透测试你知道有什么区别吗?
文件深度监控策略
查看容器的几种方式
密码一致,总显示如下图
TB 117-2013美国联邦强制性法规
Adjust the array order so that odd numbers precede even numbers and their relative positions remain the same
Customer cases | focus on process experience to help bank enterprise app iteration
A case study of building an efficient management system for a thousand person food manufacturing enterprise with low code