当前位置:网站首页>Convergence by probability
Convergence by probability
2022-06-25 11:41:00 【herbie】
One mountain, one water, one city , One person, one pen, one world . Hello! , I am a Herbie, Welcome to my official account !
Convergence by probability
1. background
Suppose we check whether the products are qualified one by one on the production line . remember For the first time The quantity of unqualified products in this inspection , It can only take 0 and 1, And , among Is the unqualified rate of the product . This is a Bernoulli experiment sequence , It corresponds to an independent identically distributed ( The binomial distribution ) A sequence of random variables :, Write it down as . If you consider before The number of nonconforming products in each inspection Be situated between And What is the probability between ? namely
Of course , from This probability can be calculated , But when The larger the ( Such as or ) It is difficult to calculate . Can we find a simple random variable , Use its distribution ( stay large ) The approximate value of the above probability can be easily calculated , namely So under what conditions and in what sense , A sequence of random variables It can converge to random variablesAnother example is in the above Bernoulli experiment sequence , front Frequency of nonconforming products in this inspection Rate of nonconforming products The deviation of Can it be arbitrarily small ? When I'm sure I can't when I'm young ; But when What happens when it's very big ? So we will study random sequences Limit state of .
2. Definition
Definition : set up Is a sequence of random variables , Is a random variable , If to any , Yes
It's called sequence Converges in probability to , Write it down as .
The meaning of probability convergence is : Yes The probability that the absolute deviation of is not less than any given quantity will increase with Increase and decrease . Or say , Absolute deviation The probability of being less than any given quantity will increase with Increase and become closer to 1, That is to say (1) Equivalent to
Special When the distribution is deterministic , namely , It's called sequence Converges in probability to , namely
3. Theorem
3.1 Definition
Definition : set up Is a sequence of two random variables , It's two constants . If
Then there are3.2 prove
prove : (1) because
therefore
namely
It can be obtained. . Similar verifiable
(2) In order to prove , We do it in a few steps :
i) if , Then there are This is because for any Yes
ii) if , Then there are This is because in the when , Yes
And when when , The conclusion is clear .iii) if , Then there are . This is because there are a series of conclusions :,,,, namely iv) from iii) And (1) know ,, Thus there are
(3) In order to prove , Let's prove it first :. This is because for any , Yes
This proves , And again combination , utilize (2) Immediate . From this theorem we can see , The limit of random variable sequence in the sense of probability ( That is, it converges to a constant in probability a) It still holds under four operations .
4. reference
[1] Mao Shisong , Cheng Yiming , Pu Xiaolong . Probability theory and mathematical statistics course ( The second edition )[M]. Higher Education Press , 2019.
边栏推荐
- Jincang KFS data cascade scenario deployment
- Sentinel integrated Nacos data source
- Spannable 和 Editable、SpannableString 和 SpannableString
- Jincang database kingbasees plug-in identity_ pwdexp
- 西山科技冲刺科创板:拟募资6.6亿 郭毅军夫妇有60%表决权
- 贝叶斯
- Big endian and little endian
- 牛客网:分糖果问题
- 基于SSH的高校实验室物品管理信息系统的设计与实现 论文文档+项目源码及数据库文件
- An interesting logic SRC mining
猜你喜欢
按钮多次点击造成结果
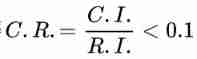
Application of analytic hierarchy process in college teaching evaluation system (principle + example + tool)

Spark runs wordcount (case 2)

基于C语言的图书信息管理系统 课程论文+代码及可执行exe文件

What is the development history, specific uses and structure of the chip

Crawler scheduling framework of scratch+scratch+grammar

杭州/北京内推 | 阿里达摩院招聘视觉生成方向学术实习生(人才计划)

Nacos installation and use

Translation of meisai C topic in 2022 + sharing of ideas

Jincang KFS data centralized scenario (many to one) deployment
随机推荐
Comment TCP gère - t - il les exceptions lors de trois poignées de main et de quatre vagues?
Idea local launch Flink task
Detection and analysis of simulator in an app
Yisheng biological sprint scientific innovation board: 25% of the revenue comes from the sales of new crown products, and it is planned to raise 1.1 billion yuan
Recommend a virtual machine software available for M1 computer
牛客网:分糖果问题
PHP如何提取字符串中的图片地址
Arrays. asList()
兴业证券是国企吗?在兴业证券开户资金安全吗?
Countdownlatch source code analysis
Whole process of web page request
wait()、notify()和notifyAll()、sleep()、Condition、await()、signal()
剑指 Offer II 091. 粉刷房子 : 状态机 DP 运用题
What is the development history, specific uses and structure of the chip
GC
Evaluating the overall situation of each class in a university based on entropy weight method (formula explanation + simple tool introduction)
Spannable 和 Editable、SpannableString 和 SpannableString
Golden sun education listed in the U.S.: a small cap medium cap stock with a market value of USD 360million
Introduction to JVM principle
CMU puts forward a new NLP paradigm - reconstructing pre training, and achieving 134 high scores in college entrance examination English