当前位置:网站首页>[day 7 of JUC learning] reentrantlock and reentrantreadwritelock
[day 7 of JUC learning] reentrantlock and reentrantreadwritelock
2022-06-11 23:55:00 【birdyson】
Thread lock
be located jucl Next , There are two main types of interface locks :
Lock:There are three types of locks :
- Fair lock : It is fair for different threads to acquire locks
- Not fair lock : The process of obtaining locks by different threads is unfair , Allow competition to gain .
- Reentrant lock : The same lock can be acquired multiple times by a thread , Avoid deadlocks .
ReadWhiteLock: Provide read lock and write lock , Read time lock sharing , Exclusive when modifying .
ReentrantLock
Mutexes or exclusive locks , yes Lock Implementation class of , It means that once the lock is obtained , Other threads are not allowed to operate ( Whether reading or writing ),synchronized It is also a mutex .
First observe ReentrantLock Source code :
package java.util.concurrent.locks;
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984872572414699L;
/** Synchronizer providing all implementation mechanics */
private final Sync sync;
}
Continue to grill Sync:
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5179523762034025860L;
}
Continue to grill AbstractQueuedSynchronizer:( This is it. JUC Another core :AQS)
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984972572414691L;
}
continue :
public abstract class AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {
AQS The essence of is an execution queue , All threads to be executed are stored in a queue , It can solve the deadlock problem . stay JUC Of AQS There is a CLH queue .CLH (Craig, Landin, and Hagersten) Lock is an extensible system based on linked list 、 High performance 、 Fair spin lock , The application thread spins only on local variables , It constantly polls the status of its predecessors , If you find that the precursor releases the lock, the spin ends .
/** JDK17 CLH Nodes */
abstract static class Node {
volatile Node prev; // initially attached via casTail
volatile Node next; // visibly nonnull when signallable
Thread waiter; // visibly nonnull when enqueued
volatile int status; // written by owner, atomic bit ops by others
}
The mechanism for obtaining locks is provided by AQS Subclasses of Sync Provided ,Sync There are also two subclasses :FairSync、NonfairSync.
ReentrantLock There are two situations in operation :
- Multiple threads preempt mutex resources :

- Mutex snatch and wait :
![[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-fShBnwgJ-1653492592222)(/Users/alexanderron/Library/Application Support/typora-user-images/image-20220525103823265.png)]](/img/44/0ba7f06287734179ee66b8f4990910.png)
The waiting thread will be saved in AQS Medium CLH Waiting in the queue , The mechanism of lock competition is determined by Sync Decisive , It can be found that the default is an unfair lock , Is more efficient than fair lock , It can also give full play to the performance of the computer .
private final Sync sync;
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();}
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();}
lock() And unlock()
public void lock() {
// It's abbreviated here
sync.acquire(1);
}
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
In the process of thread locking, the number of thread locks is controlled , The lock counting method will be called when locking :acquire(1), Whenever a thread is locked , This time the count will be +1,CLH It depends on whether the number of locks is 0 To determine if there are any locked threads , So as to solve the thread deadlock problem . It will call every time you unlock release(1) Release a lock .
Design a ticket grabbing system
class SaleSystem {
private int ticket;
private static final ReentrantLock LOCK = new ReentrantLock();
public SaleSystem() {
}
public SaleSystem(int ticket) {
this.ticket = ticket;
}
public void sale() {
LOCK.lock();
try {
if (this.ticket > 0) {
System.out.printf("【%s】 Ticket sales successful ! The number of votes left :%d\n",
Thread.currentThread().getName(), this.ticket --);
} else {
System.out.printf("【%s】 There are no tickets !\n", Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
LOCK.unlock();
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SaleSystem saleSystem = new SaleSystem(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i ++) {
new Thread(saleSystem::sale).start();
}
}
}
【Thread-0】 Ticket sales successful ! The number of votes left :5
【Thread-4】 Ticket sales successful ! The number of votes left :4
【Thread-1】 Ticket sales successful ! The number of votes left :3
【Thread-3】 Ticket sales successful ! The number of votes left :2
【Thread-5】 Ticket sales successful ! The number of votes left :1
【Thread-2】 There are no tickets !
【Thread-6】 There are no tickets !
【Thread-7】 There are no tickets !
ReentrantReadWriteLock
Non exclusive lock , Read lock belongs to shared lock , All read threads share a shared lock , When the write lock works , The entire shared lock will enter the pause phase , Wait for the write to complete before performing multiple concurrent reads .


public class ReentrantReadWriteLock
implements ReadWriteLock, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6992448646407690164L;
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readerLock;
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writerLock;
final Sync sync;
public ReentrantReadWriteLock() {
this(false);
}
public ReentrantReadWriteLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
readerLock = new ReadLock(this);
writerLock = new WriteLock(this);
}
public ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock() {
return writerLock; }
public ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock() {
return readerLock; }
}
边栏推荐
- Lake shore vnf series low temperature thermostat system - sample in flowing steam
- swiper
- Solr之基础讲解入门
- 使用 select 切换协程
- Sorting out app startup process
- Mingdeyang ADC series development board-ad9653 daughter board multi-channel high resolution and high sampling rate
- Ar helps brand stores achieve global data growth
- Dom Knowledge point Summary
- 多路查找树
- 2022 safety officer-a certificate test question simulation test platform operation
猜你喜欢

2022 high voltage electrician test question simulation test question bank and online simulation test

(linear DP | monotone queue) acwing 895 Longest ascending subsequence

sonarqube介紹和安裝步驟

(greedy + longest ascending subsequence) acwing 896 Longest ascending subsequence II

二叉排序树
Teach you to play with SSM framework
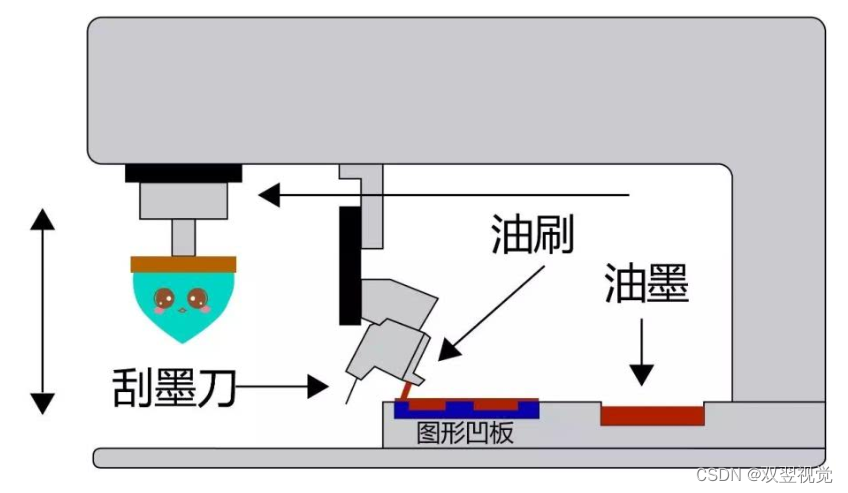
Pad printing process flow and application precautions
![将数组分成和相等的三个部分[问题分析]](/img/0b/856fcceb0373baa8acb46e9ae2c861.png)
将数组分成和相等的三个部分[问题分析]

Mysql5 and mysql8 are installed at the same time

HMS core shows the latest open capabilities in mwc2022, helping developers build high-quality applications
随机推荐
New Year Countdown JS case
Node version control tool NVM
How to achieve fair and equitable data access and service ecology?
(simple statistics) acwing 3404 Who are your potential friends
(dp) acwing 899. Edit distance
图及图的遍历
Here we go! Dragon lizard community enters PKU classroom
【juc学习之路第5天】引用原子类和属性修改器
Custom JSP tag - > concept - > lifecycle
移印工艺流程及应用注意事项
Read 5g RF terminal industry
05 classification learning notes lihongyi's in-depth study 2021
Flex flexible layout tutorial and understanding of the main axis cross axis: Grammar
Class. Getresource() and class Getresourceasstream() method
RF中使用reuqests的两种方式
Test case design method
MySQL 8.0 decompressed version installation tutorial
(dp+ group backpack) acwing 9 Group knapsack problem
Cisco private dynamic routing protocol: EIGRP
Antigen products enter the family, and Chinese medical device enterprises usher in a new blue ocean