当前位置:网站首页>2021-02-27image processing of MATLAB
2021-02-27image processing of MATLAB
2022-06-11 01:47:00 【Captain xiaoyifeng】
The image processing
imread
I=imread("path")
I It becomes a picture unit
imshow(I)
display picture
Original size 、 Borderless display :
imshow(i,'border','tight')
imshow(I,[low high])
Less than low It's black 、 Greater than high It's white , It should mean , Set a threshold to prevent overflow , If it is [],low、high Is the minimum and maximum
If you specify an empty matrix ([]), then imshow uses a display range of [min(I() max(I()]
size(I)
Size
We can find that the output of the color map is Long wide 3(rgb Tricolor )
imresize
i=imresize(i,[m,n]);
Resize the image
Image conversion function
• gray2ind(I,8) - intensity image to index image
• im2bw(I,0.5) - image to binary
• im2double - image to double precision
• im2uint8 - image to 8-bit unsigned integers
• im2uint16 - image to 16-bit unsigned integers
• ind2gray - indexed image to intensity image
• mat2gray - matrix to intensity image
• rgb2gray - RGB image to grayscale
• rgb2ind - RGB image to indexed image
im=image picture
gray=intensity Intensity diagram , The grayscale is 256 Bit intensity diagram ( Can that be understood )
bw=binary It's a binary graph , A threshold value is required in the parameter (0-1 representative 0-256)
ind=index
Image addition
In order to preserve the accuracy, the addition of images needs to be transformed into double
mI=uint8(double(I1)+double(I2)+double(I3));
A1 = imread('rice.png');
A2 = imread('cameraman.tif');
K = imadd(A1,A2,'uint16');% Image addition , Prevent pixel values from exceeding 255, So save the result as 16 position
%K = imlincomb(0.5,A1,0.5,A2); Used to adjust the scale of addition
figure;
subplot(1,3,1);imshow(A1);title('rice original image ');
subplot(1,3,2);imshow(A2);title('cameraman original image ');
subplot(1,3,3);imshow(K,[]);title(' Additive image ');% Pay attention to imshow Function time , To add [], So that the pixel value is compressed to 0—255
Image segmentation
mat2cell
mat2cell(i,[x1,x2,…],[y1,y2,…],…) How many dimensions are there , How many vectors are there , At the same time, the sum of the elements in the vector and the value of that dimension should be equal , So before using, adjust the size of the picture to an integer multiple of the size to be cut .
Intensity conversion
>> aI2=imadjust(I0,[],[],0.5);
>> aI1=imadjust(I0,[0,1],[1,0]);
The first line of code adjusts the intensity of the image through the following parameters , The default is 1, This is a linear mapping
The middle two parameters represent
[low_in;high_in],[low_out;high_out]
Indicates the range of gray scale before and after conversion
Statistical histogram
Statistics of color distribution
imhist(I0)
Image cropping
b = imcrop(I,[403,0,810,1080]);
Image opening and closing operation
Anyway, corrosion is less white , Expansion is the increase of whiteness
It is considered as corrosion before expansion , Used to eliminate small objects ; Closed operation is to expand first and then corrode , Used to connect small gaps .
i=imread('image.jpg');
i1=rgb2gray(i); % Grayscale image
i2=im2bw(i1); % Binary search
i3 = bwmorph(i2,'close'); % Closed operation
imshow(i3)
i4 = bwmorph(i2,'open'); % Open operation
figure, imshow(i4)
Image rotation and distortion
Using affine plus twist function , Commonly used to enhance image data
tform = affine2d([1 0 0; .5 1 0; 0 0 1])
J = imwarp(I,tform);
figure
imshow(J)
I = imread('kobi.png');
imshow(I)
tform1 = randomAffine2d('Rotation',[35 55]);% stay 35° and 55° Random rotation between
J = imwarp(I,tform1);
imshow(J)
Image zoom
Nearest neighbor resampling
Find the nearest one to interpolate , There will be a lot of noise
Bilinear interpolation
Maintain the interpolation of the two dimensions
I=imread('pic1.png');
I=I0;
I0=double(I0);
I1=zeros(size(I0,1)*2,size(I0,2)*2,3);
[r,c]=meshgrid(1:size(I0,2),1:size(I0,1));
rc=linspace(1, size(I,1), size(I,1)*2);
cc=linspace(1, size(I,2), size(I,2)*2);
[r_new,c_new]=meshgrid(cc,rc);
rc=linspace(1, size(I0,1), size(I0,1)*2);
cc=linspace(1, size(I0,2), size(I0,2)*2);
[r_new,c_new]=meshgrid(cc,rc);
I1(:,:,1)=interp2(r,c,I0(:,:,1),r_new,c_new,'spline');
I1(:,:,2)=interp2(r,c,I0(:,:,2),r_new,c_new,'spline');
I1(:,:,3)=interp2(r,c,I0(:,:,3),r_new,c_new,'spline');
imshow(uint8(I1))
size(I1)
interp2 Is a bilinear interpolation function
If the magnification is a fraction , The size is written like this round(size(I0,1)*p/q)
Image denoising
The noise contains white Gaussian noise 、 Salt and pepper noise
Add noise
nI = imnoise(I0, 'gaussian', 0, 0.01);
nI = imnoise(I0, ‘salt & pepper', 0.01);
Gaussian noise and salt and pepper noise
I0=imread('pic3.png');
I0(100:105,800:808,:)=0;
figure,imshow(I0)
Addition of outliers
Noise reduction 、 wave filtering
Nonlinear filtering and noise reduction : median filtering
k=medfilt2(spl,[5,5]);
Incoming picture and filter operator size , The image should be grayscale
The filter operator defaults to 3*3
filt: filter
Baidu for more filters
The use of filters , Edge detection
The principle of the filter is a convolution operation between the characteristic matrix and the image ( Equivalent to sliding on the surface of the image , If noise is detected , Will keep )
Abnormal point detection
Point detection operator
-1 -1 -1
-1 8 -1
-1 -1 -1
w=[-1 -1 -1;-1 8 -1;-1 -1 -1]
g=abs(imfilter(I0,w));
T=max(g(:));
g=(g>=T);
imshow(uint8(g))
Straight line detection
Horizontal line detection operator
-1 -1 -1
2 2 2
-1 -1 -1
Others in the same way , But there are too few kinds of straight lines that can be detected
Edge detector
Commonly used canny operator
I=imread('pic4.png');
I0=rgb2gray(I);
subplot(231);
imshow(I);
BW1=edge(I0,'Roberts',0.16);
subplot(232);
imshow(BW1);
title('Roberts')
BW2=edge(I0,'Sobel',0.16);
subplot(233);
imshow(BW2);
title('Sobel')
BW3=edge(I0,'Prewitt',0.16);
subplot(234);
imshow(BW3);
title('Prewitt');
BW4=edge(I0,'LOG',0.012);
subplot(235);
imshow(BW4);
title('LOG')
BW5=edge(I0,'Canny',0.2);
subplot(236);
imshow(BW5);
title('Canny');
Add text to picture
text function
Feeling MATLAB The function of is amazing , Below text Add dimensions to
x = 0:pi/20:2*pi;
y = sin(x);
plot(x,y)
text(pi,0,'\leftarrow sin(\pi)')
\leftarrow Is the left arrow ,pi 0 Such a point can be changed into a vector , Represents a multipoint dimension
The results are as follows 
plot(1:10)
str = {
{
'A simple plot','from 1 to 10'},'y = x'};
text([2 8],[7 7],str)
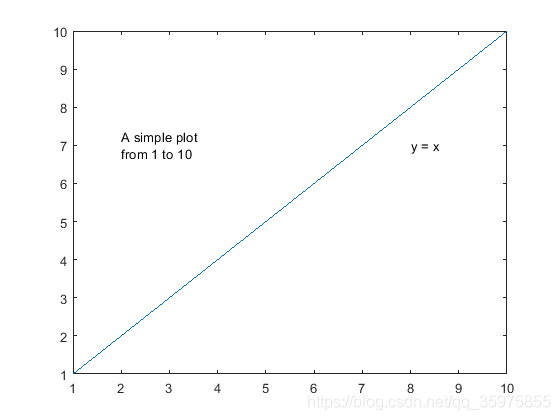
It is worth noting that , use text Not only can you write words , You can also draw spot 、 asterisk Wait for the pattern .
getframe function
This function is used to intercept the state of the window ( Screenshot ), Achieve the effect of writing on the picture
F = getframe(figure(1));
figure(2)
imshow(F.cdata)
Digression :getframe Related animation production
[X, Y, Z] = peaks(30);
% surf Draw a three-dimensional surface
surf(X,Y,Z);
axis([-3,3,-3,3,-10,10]);
% Close the mark on the coordinate axis used 、 Grating and unit marking . But reserved by text and gtext Set object
axis off;
shading interp;
colormap(hot);
M = moviein(20);% Build a 20 Large matrix of columns
for i = 1:20
view(-37.5+24*(i-1),30);% Change viewpoint
M(i) = getframe;% Save the drawing to M matrix
end
movie(M,2);% Play picture 2 Time
Reference links for animation :https://blog.csdn.net/qq_32892383/article/details/79553001
Add a box to the picture 、 rectangular
rectangle('Position',[100 100 100 100],'LineWidth',4,'EdgeColor','r');
The four coordinates of the vector are the coordinates of the top left corner vertex and the length and width of the matrix
Adjust the parameters to draw a solid rectangle
rectangle('Position',[1,2,5,10],'FaceColor','w','EdgeColor','w',...
'LineWidth',3)
You can even draw rounded rectangles and circles
rectangle('Position',[3 0 2 4],'Curvature',1)
pos = [2 4 2 2];
rectangle('Position',pos,'Curvature',[1 1])
axis equal
Draw a grid on the picture
p = imread('path'); % Read images
[mm,nn,~] = size(p); % Gets the size of the image
x = 0:nn/10:nn; % Suppose the level is divided into 10 grid
y = 0:mm/20:mm; % Let's say we split it vertically 20 grid
M = meshgrid(x,y); % Generating grids
N = meshgrid(y,x); % Generating grids
imshow(p); % First draw the original picture
hold on % Keep the original picture , As a canvas, add a grid on it
plot(x,N,'y'); % Draw a horizontal line . there 'y' The color of the line is yellow
%plot(M,y,'r'); % Draw a vertical line .'r' Indicates green red
Draw... On the original
This method may not require getframe function , Operate directly on the original drawing
I = imread('peppers.png');
RGB = insertShape(I,'circle',[150 280 35],'LineWidth',5);
pos_triangle = [183 297 302 250 316 297];
pos_hexagon = [340 163 305 186 303 257 334 294 362 255 361 191];
RGB = insertShape(RGB,'FilledPolygon',{
pos_triangle,pos_hexagon},...
'Color', {
'white','green'},'Opacity',0.7);
imshow(RGB);

边栏推荐
- 小鱼儿的处理
- Leetcode 665 non decreasing array (greedy)
- Using MySQL database in nodejs
- ROS parameter server
- Kubernetes binary installation (v1.20.15) (VII) plug a work node
- 2021-02-03美赛前MATLAB的学习笔记(灰色预测、线性规划)
- Is the SQL query result different from what you expected? Mostly "null" is making trouble
- From "0" to "tens of millions" concurrency, 14 technological innovations of Alibaba distributed architecture
- 多兴趣召回模型实践|得物技术
- Uninstall mavros
猜你喜欢

今日睡眠质量记录80分

1.5、PX4载具选择

关于概率统计中的排列组合

Using MySQL database in nodejs

关于CS-3120舵机使用过程中感觉反应慢的问题

Detailed explanation of classic papers on OCR character recognition

Leetcode linked list queue stack problem

Leetcode 2054 two best non overlapping events

Px4 from abandonment to mastery (twenty four): customized model

Yanrong looks at how to realize the optimal storage solution of data Lake in a hybrid cloud environment
随机推荐
LeetCode 1029 Two City Scheduling (dp)
数据库概述
Multi interest recall model practice | acquisition technology
MATLAB随机函数汇总
MultipartFile和File互转工具类
2021-3-1MATLAB写cnn的mnist数据库训练
Makefile:1860: recipe for target ‘cmake_ check_ build_ system‘ failed make: *** [cmake_check_build_syst
Implementing MySQL fuzzy search with node and express
CLIP论文详解
PX4从放弃到精通(二十四):自定义机型
kubernetes 二进制安装(v1.20.15)(七)加塞一个工作节点
[path planning] week 1: Path Planning open source code summary (ROS) version
Yunna provincial administrative unit fixed assets management system
1.5、PX4载具选择
“看似抢票实际抢钱”,别被花式抢票产品一再忽悠
Sealem finance builds Web3 decentralized financial platform infrastructure
Leetcode divide and conquer method
[leetcode] reverse linked list II
数字ic设计自学ing
Tencent cloud database tdsql- a big guy talks about the past, present and future of basic software