当前位置:网站首页>0 basic self-study STM32 (wildfire) -- what is a register?
0 basic self-study STM32 (wildfire) -- what is a register?
2022-06-22 08:04:00 【Fecter11】
a key :
Memory mapping
Register mapping
First, learn to distinguish the components 1 Pin No , Note counterclockwise rotation .
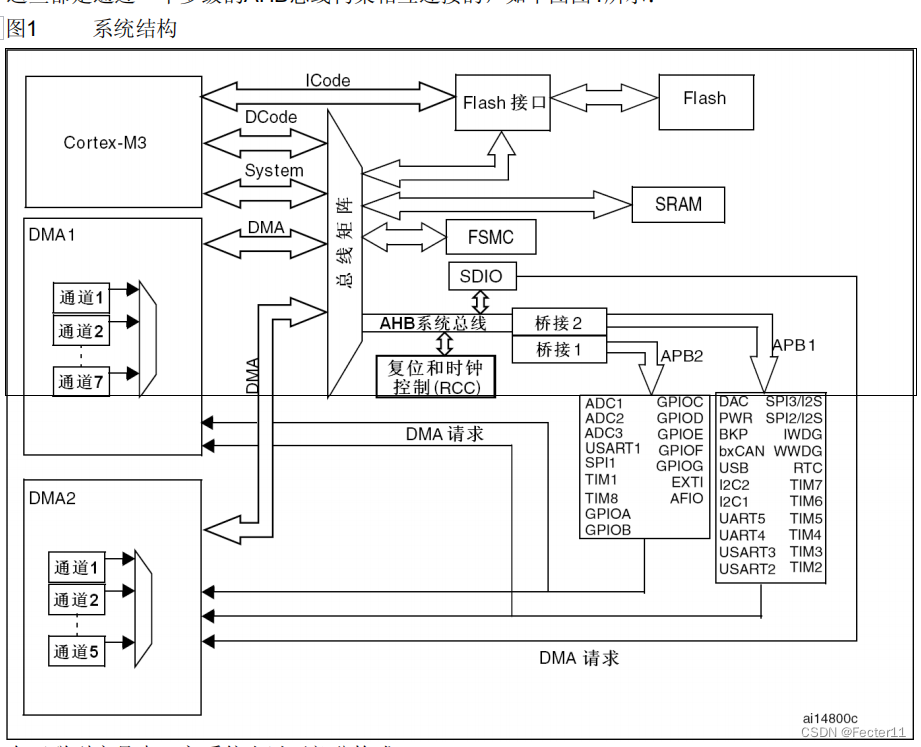
## First figure out the internal structure of the chip 

“AHB, yes Advanced High performance Bus Abbreviation , Advanced high performance bus ;
APB, yes Advanced Peripheral Bus Abbreviation , Advanced peripheral bus .”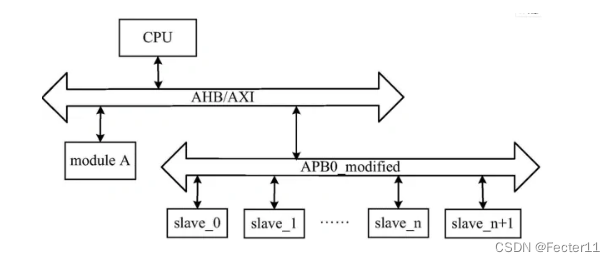


Drive unit :


Passive unit :




Next, check out the official data book ( English version )

ARM The kernel is 32 position , That's it 2 Of 32 Power , That is to say 4294967296byte( byte ),1kb=1024byte, That is, that is 4194304kB,1mb =1024kb, That is to say 4096mb, and 1gb=1024mb , In the end is 4gb
therefore arm The kernel can access 4gb Content ,arm Then we will 4g The memory is divided into eight blocks .
512mb*8=4096mb=4g

flash It's in the first piece 
We can see from the external package of the chip that the chip used by wildfire is stm32f103zet6
Among them e On behalf of 512k Of flash
Obviously, only a small part is used 
The point is block2 Peripheral part

Memory mapping ( a key )
What is memory mapping ?
The memory itself does not have address information , His address is assigned by the game film manufacturer or user , The process of assigning addresses to memory is memory mapping 
Register mapping
With stc51 For example
# include <stdio.h>
sbit LED = P0^0;
void main (void)
{
P0 = 0xfe;
LED =0;
}
Pay attention to the... We use P0, It is contained in the header file , The header file uses sfr Keyword let P0 Corresponding to the address of the corresponding register .
And in the stm32 Middle yield GPIOB Port of 16 Pin outputs high level , How to do that ??
Access memory units through absolute addresses
//GPIOB All ports output High level
*(unsigned int*)(0x40010C0C) = 0xFFFF;
We find GPIOB Register start address of 
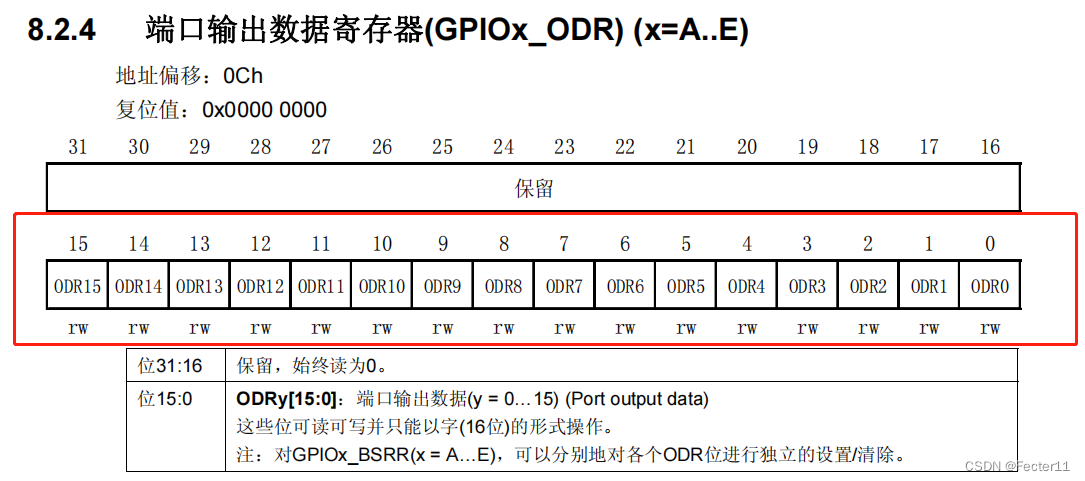
We see the ODR The address offset of :0x0C, The offset here is the offset from the base address of the register just found . because GPIOB There is more than one register for .
that GPIOB The address of the port is :GPIOB The base address + Address offset
We can be right IO To operate
*(unsigned int*)(0x40010C0C) = 0xFFFF;
among 0x40010C0C Is the address of the register
For the above, we need to grasp several key points :
1:0x40010C0C As GPIOB Output data register ODR How do people find your address ?
2:(unsigned int) What is the role of ?
3: Learn how to use c Linguistic “*” Number *
*(unsigned int*)(0x40010C0C) = 0xFFFF;
Let's first cast 0x40010C0C As address .
If we write it directly as 0x40010C0C = 0xFFFF; The compiler doesn't know 0x40010C0C It's the address , So I can't use it . We need to force conversion .
Obviously, the above method is troublesome .
Access memory unit by register alias :
//GPIOB All ports output high level
# define GPIOB_ODR (unsigned int*)(0x40010C0C) ;
* GPIOB_ODR = 0xFF;
For the convenience of operation, you can also “*” Also defined in the alias of the register
//GPIOB All ports output high level
# define GPIOB_ODR *(unsigned int*)(0x40010C0C) ;
GPIOB_ODR = 0xFF;
边栏推荐
- Mt4/mql4 getting started to mastering EA tutorial lesson 3 - common functions of MQL language (III) - common functions of K-line value taking
- Model electricity experiment -- Experiment 2 JFET common source amplifier circuit
- Mt4-mql4 language EA automatic transaction programming introduction to proficiency
- Mt4/mql4 getting started to mastering EA tutorial lesson 4 - common functions of MQL language (IV) - common functions of K-line value
- DTD约束
- Mt4/mql4 getting started to mastering EA tutorial lesson 8 - common functions of MQL language (VIII) - common time function
- navicat如何查询已连接的数据库密码信息
- Usage and understanding of async/await in JS
- 《守望先锋》阵亡镜头、全场最佳和亮眼表现是如何设计
- JS to assign values to two objects with the same attributes
猜你喜欢

Relative positioning, absolute positioning, fixed positioning

Qt 错误提示1: invalid use of incomplete type ‘***‘

Use of keepalived high availability cluster

What is distributed transaction

Excellent cases of data visualization

QT combox的使用示例

(7)双向链表
![[Oracle database] mammy tutorial day13 date function](/img/ca/90aaa682ec393b1531060377276ca6.png)
[Oracle database] mammy tutorial day13 date function

Problems caused by canvas palette width and height and canvas width and height
QT 自定义组合控件(类提升功能)
随机推荐
Use js to download the current image
C#实现语音朗读功能
Modular import and export collation in JS
Runloop detail summary
模電實驗——實驗二 JFET共源極放大電路
Model electricity experiment -- Experiment 1 transistor common emitter single transistor amplifier
Leetcode 172 Zero after factorial (2022.06.21)
Design skills of common table structure in database design
【Oracle 数据库】奶妈式教程 day12 字符函数
How to handle root password forgetting in MySQL
How to create an index
Stored procedures and functions of MySQL
DTD constraints
Model electricity experiment -- Experiment 2 JFET common source amplifier circuit
The jdbcurl is configured correctly in the project, but the jdbcurl is the wrong path after the project is started
Invalid applet margin right, text overflow?
模板代码概述
XMIND 2022 mind map active resources?
Layer drawing method
Easyui数据表实现增删改