当前位置:网站首页>In-depth understanding of JVM-memory structure
In-depth understanding of JVM-memory structure
2022-08-03 19:42:00 【Horse stepping on flying swallows & lin_li】
深入理解JVM-内存结构
[视频链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1yE411Z7AP
什么是JVM?
Java Virtual Machine - java程序的运行环境(java二进制字节码的运行环境)
JVM好处?
- 一次编写,到处运行的基石【重点】
- 自动内存管理,垃圾回收功能【重点】
- 数据下标越界检查
- 多态,面向对象编程
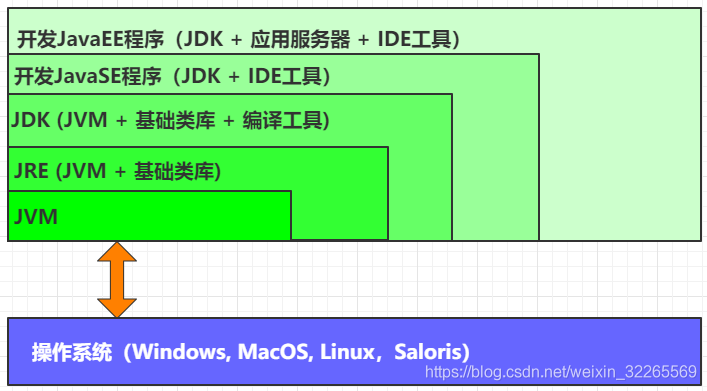
JVM、JRE、JDK三者比较:

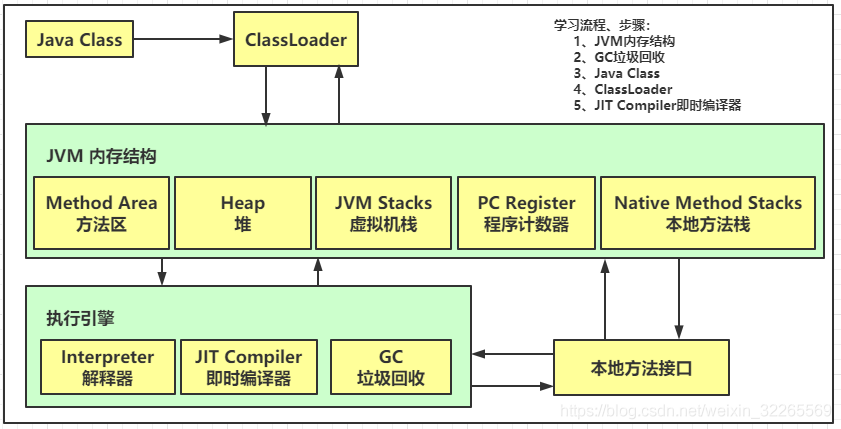
JVM组成有哪些?
常见的JVM
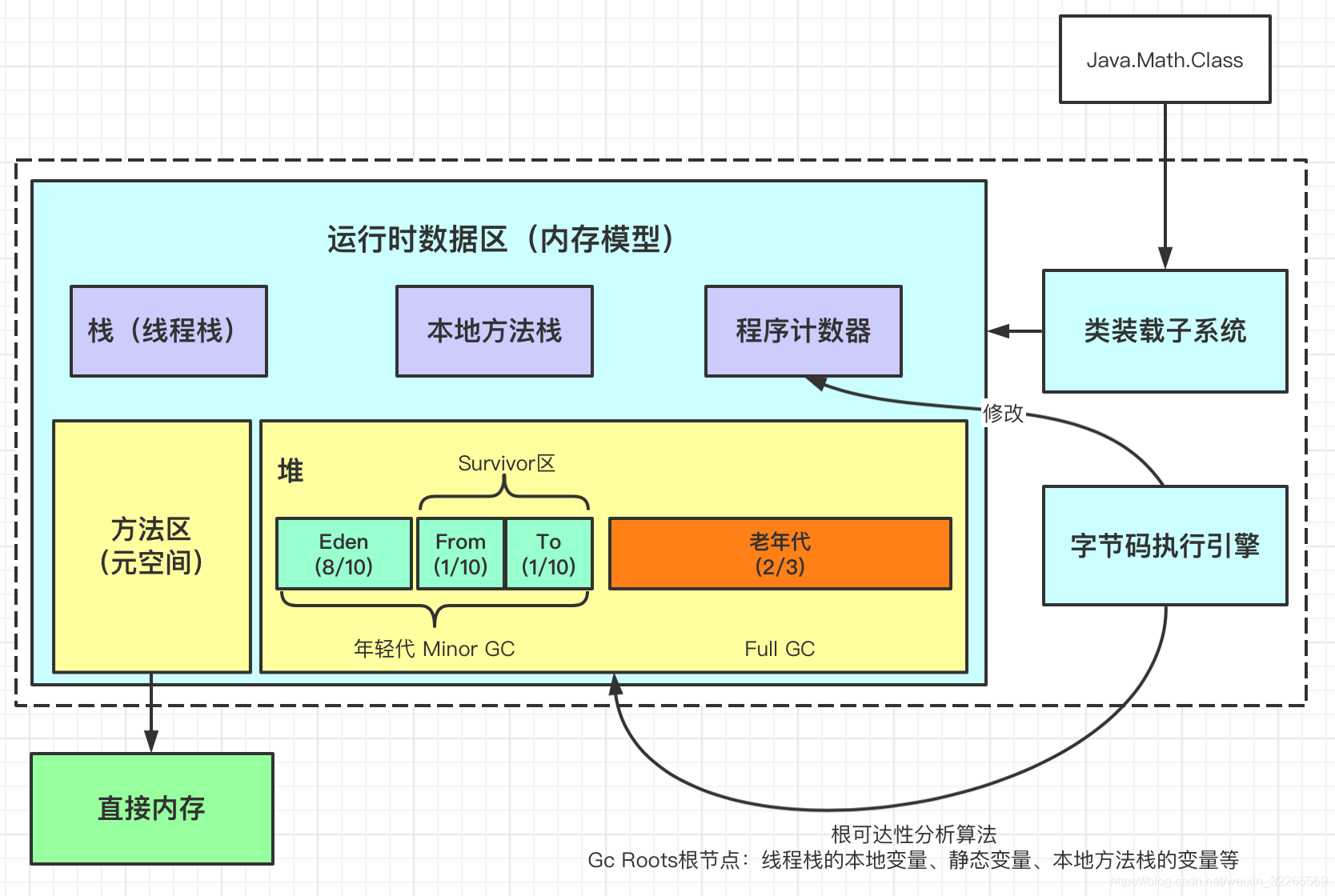
JAVA 内存结构组成
- 程序计数器
- 虚拟机栈
- 本地方法栈
- 堆
- 方法区
1、程序计数器
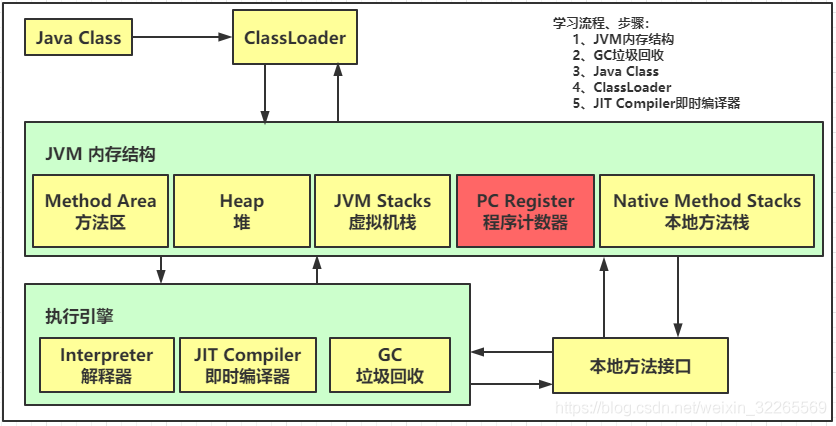
1.1 程序计数器定义
Program Counter Register程序计数器(寄存器)
1.2 程序计数器作用
作用:是记住下一条jvm指令的执行地址
特点:线程私有的; 不存在内存溢出,也是JVM规范中唯一没有OutOfMemoryError的区域
二进制字节码:JVM指令 —> 解释器 —> 机器码 —> CPU
程序计数器:记住下一条jvm指令的执行地址,硬件方面通过【寄存器】实现
示例: 二进制字节码:jvm指令 java 源代码
2、虚拟机栈(-Xss256k)
先了解一程数据结构
- 栈Stack,先进后出FILO
- 栈-线程运行需要的内存空间
- 栈帧-每个方法运行时需要的内存
2.1 栈定义
Java Virtual Machine Stacks (Java虚拟机栈)
- 每个线程运行时所需要的内存,称为虚拟机栈
- 每个栈由多个栈帧(Frame)组成,对应着每次方法调用时所占用的内存
- 每个线程只能有一个活动栈帧,对应着当前正在执行的那个方法
2.2 栈问题
- 垃圾回收是否涉及栈内存? 答案:栈内存不涉及垃圾回收
- 栈内存分配越大越好吗? 答案:栈内存不是越大越好,如果设置过大,会影响可用线程的数量;比如-Xss1m、-Xss2m,在总内存不变的情况下,可用线程数量会减少
- 方法内的局部变量是否线程安全? 答案:方法内的局部变量是线程安全,因为方法内的局部变量各自在自已独立的内存中;如果是static int 就是线程共享的,就不是线程安全;主要看变量是否是线程共享、还是线程私有
核心1:如果方法内局部变量没有逃离方法的作用范围,它是线程安全的
核心2:如果是局部变量引用了对象,并逃离方法的作用范围,需要考虑线程安全

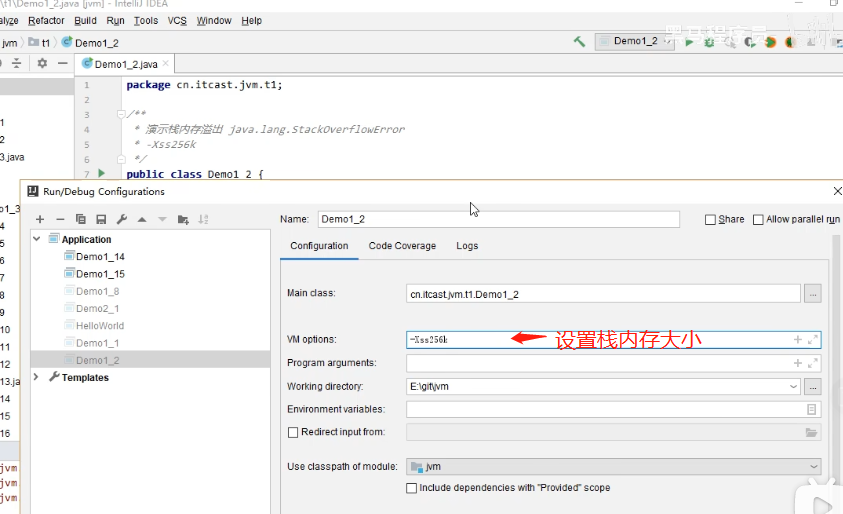
2.3 栈内存溢出(-Xss256k)
栈帧过多导致栈内存溢出,比如:递归,我们生产环境推荐尽量不使用递归
栈帧过大导致栈内存溢出
2.3 线程运行诊断(附案例)
2.3.1 cpu占用过高,如何诊断案例
1. 用top定位哪个进程对cpu的占用过高
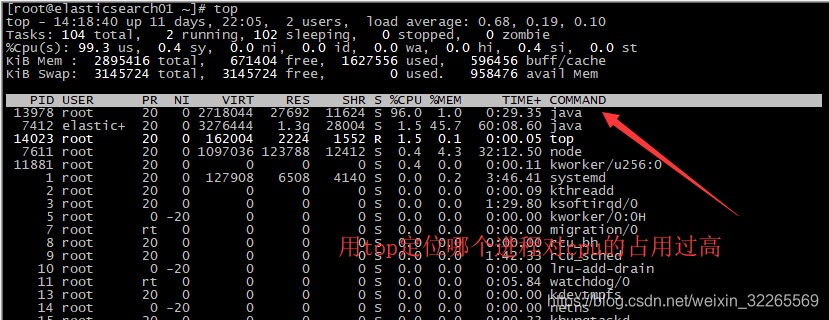
2. ps H -eo pid,tid,%cpu 查看linux所有进程、线程、CPU消耗情况

3. ps H -eo pid,tid,%cpu | grep 进程id 用ps命令进一步定位哪个线程引起的CPU占用过高
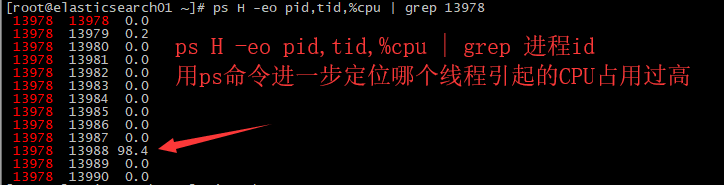
4. jstack 进程pid 需要将十进制的线程id转成16进制;可以根据线程id找到有问题的线程,进一步定位问题代码的源码行号
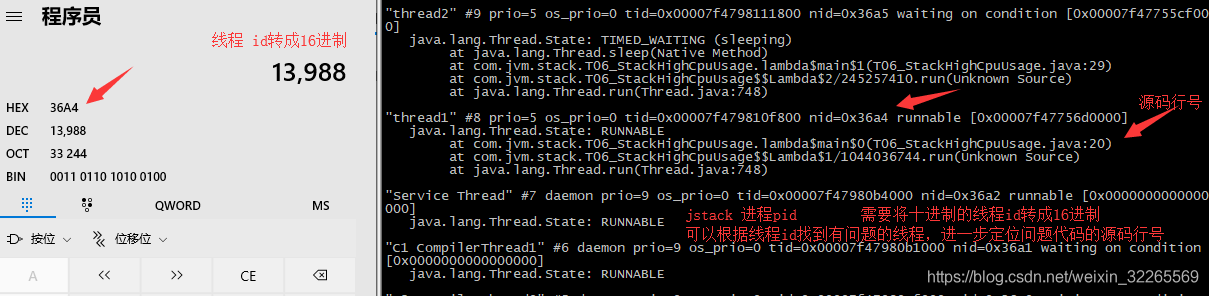
通过上述方式找到了源代码CPU消耗过高的文件及行号
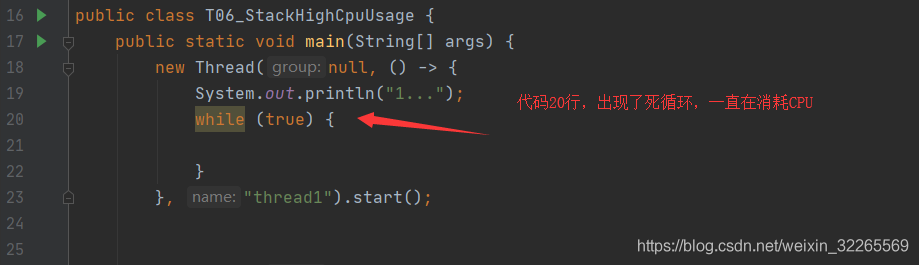
3、本地方法栈(不是Java编写的代码,通过C/C++)
给本地方法的运行提供内存空间
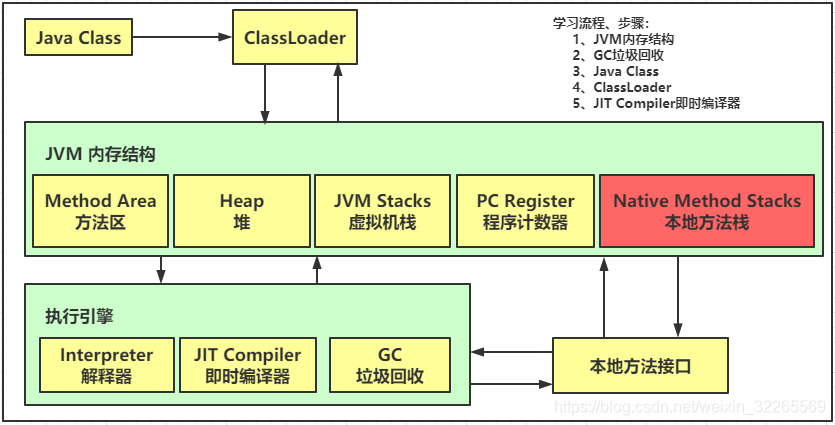
4、堆(-Xmx8m)
4.1 堆的定义
- 通过new 关键字,创建对象都会使用堆内存
- 特点:
- 它是线程共享的,堆中对象需要考虑线程安全的问题
- 有垃圾回收机制
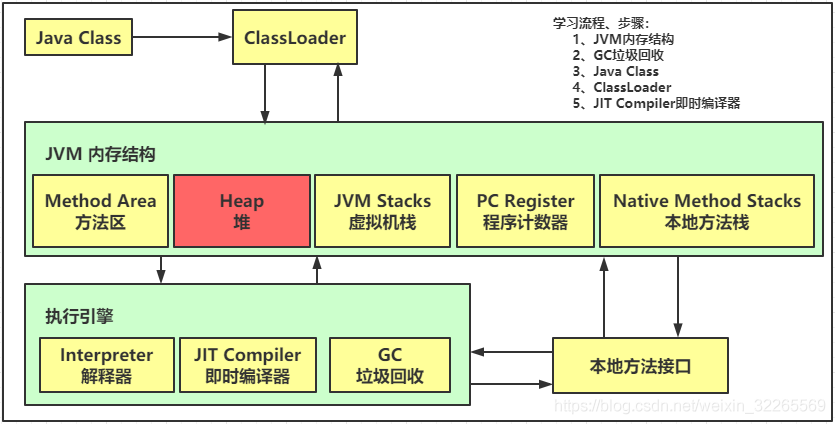
4.2 堆内存溢出问题及生产建议
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.heap;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/** * 演示堆内存溢出 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space * -Xmx8m */
public class Demo1_5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
try {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
String a = "hello";
while (true) {
list.add(a); // hello, hellohello, hellohellohellohello ...
a = a + a; // hellohellohellohello
i++;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
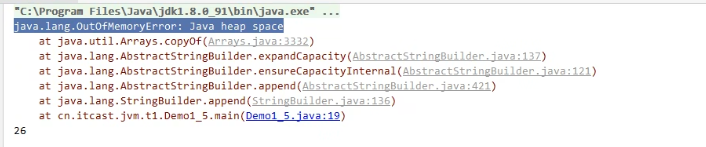
生产环境建议:如果内存比较大,内存溢出不会那么快的暴露;这时,我们可以将堆内存调小,让内存溢出尽早暴露
4.3 堆内存诊断工具介绍,及实操
- **jps工具:**查看当前系统中有哪些java进程
- jmap工具:查看堆内存占用情况 jmap -heap pid
- jstack 工具:线程监控
- **jconsole工具:**图形界面的,多功能的检测工具,可以连续监测
- **jvisualvm工具:**图形界面的,多功能的检测工具,可以连续监测;还有dump
/** * 演示堆内存 */
public class T02_HeapUseUpAndDown {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("1...");
Thread.sleep(30000);
byte[] array = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 10]; // 10 Mb
System.out.println("2...");
Thread.sleep(20000);
array = null;
System.gc();
System.out.println("3...");
Thread.sleep(1000000L);
}
}
- Jps
- Jmap -head pid 查看堆内存占用
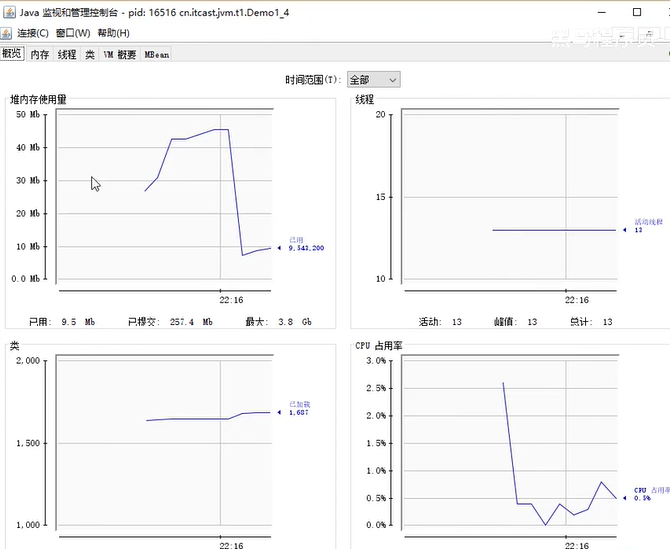
- 在控制台上使用 jconsole
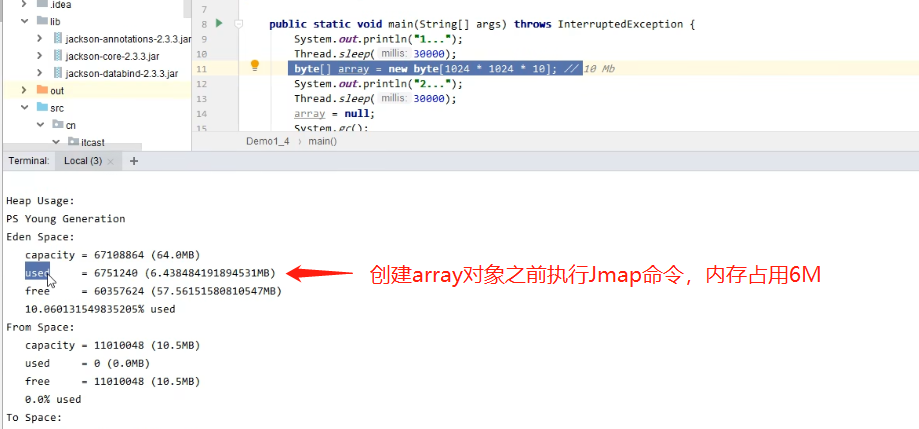
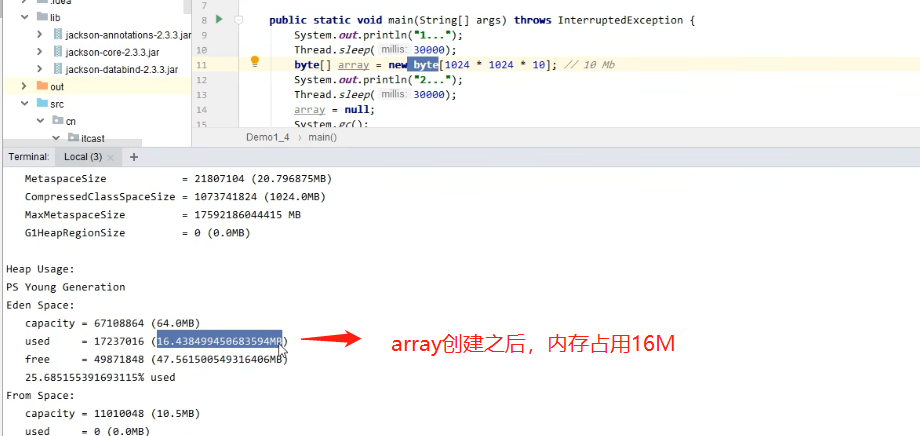

jconsole的使用
4.3.1 垃圾回收后,内存占用仍然很高,排查方式案例
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.heap;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/** * 演示查看对象个数 堆转储 dump */
public class Demo1_13 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
students.add(new Student());
// Student student = new Student();
}
Thread.sleep(1000000000L);
}
}
class Student {
private byte[] big = new byte[1024*1024];
}
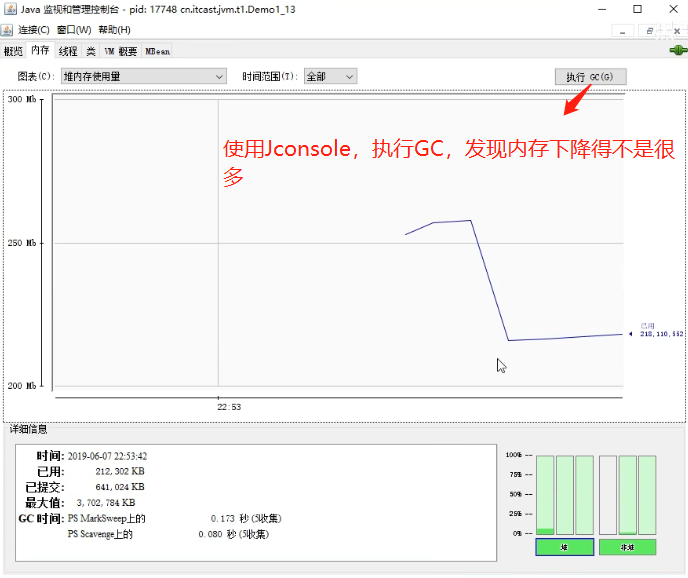
解决方式:jvisualvm 可以使用dump,查找最大的对象堆转储 dump(基于上述问题,使用工具进行查看); 在测试环境下,我们可以开启dump文件记录,然后将dump文件导入到jvisualvm工具查看,占用最多的内存的对象是哪些.
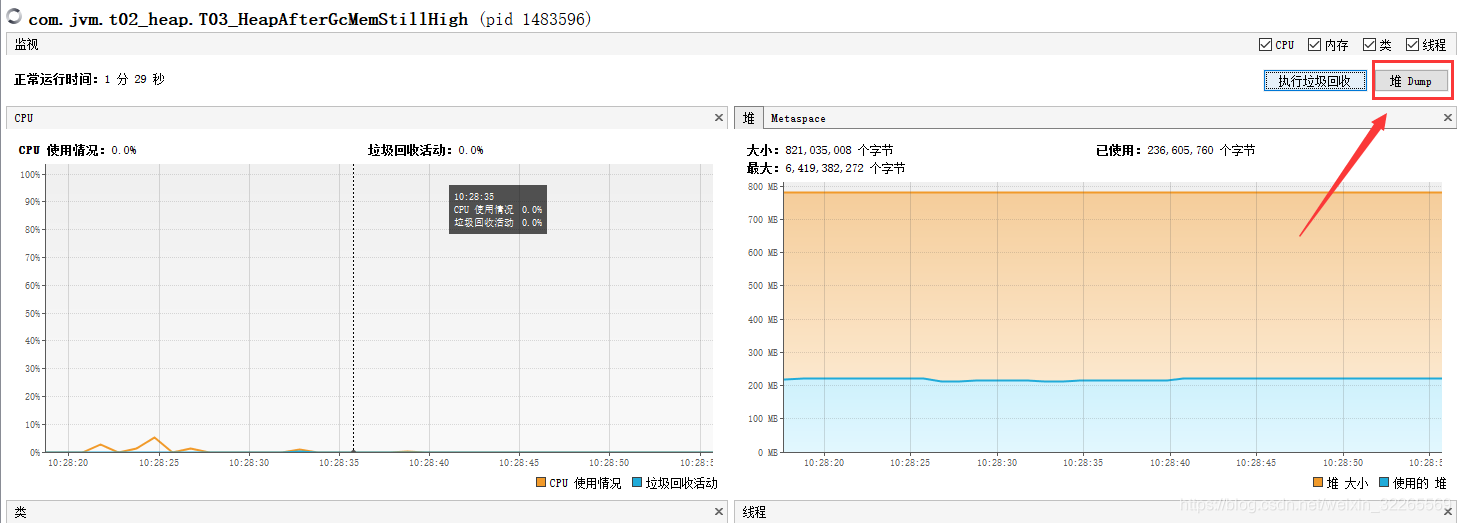
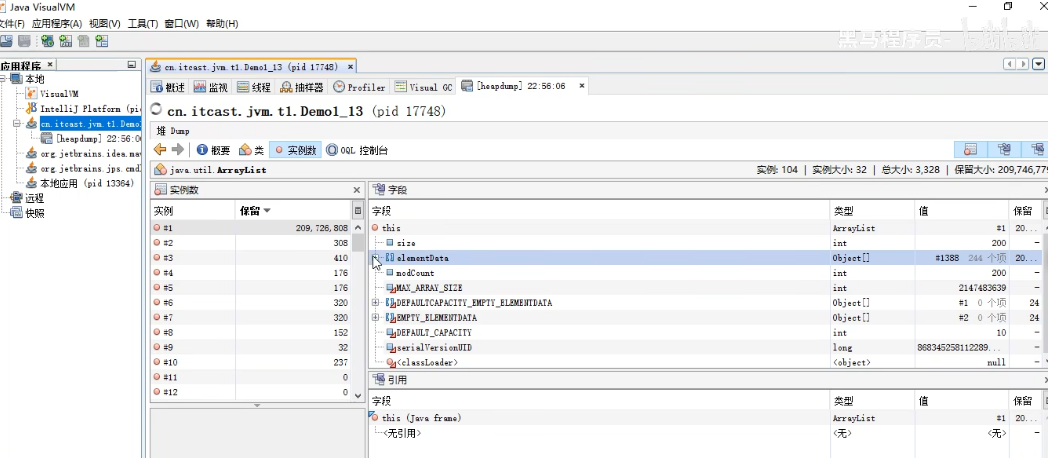
5、元空间/方法区(-XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=8m)
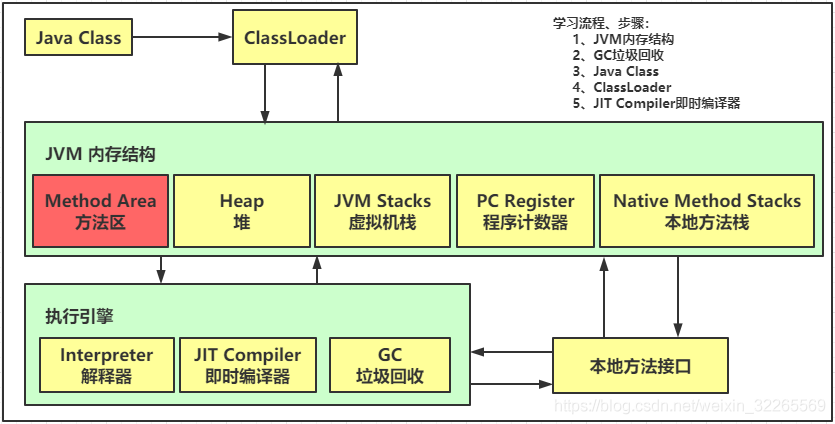
5.1 JVM方法区定义
- 线程共享
- 在JVM启动时创建,在逻辑上属于堆的一部分(看厂商实现)
- 方法区也可能会内存溢出
5.2 方法区组成
5.3 方法区内存溢出
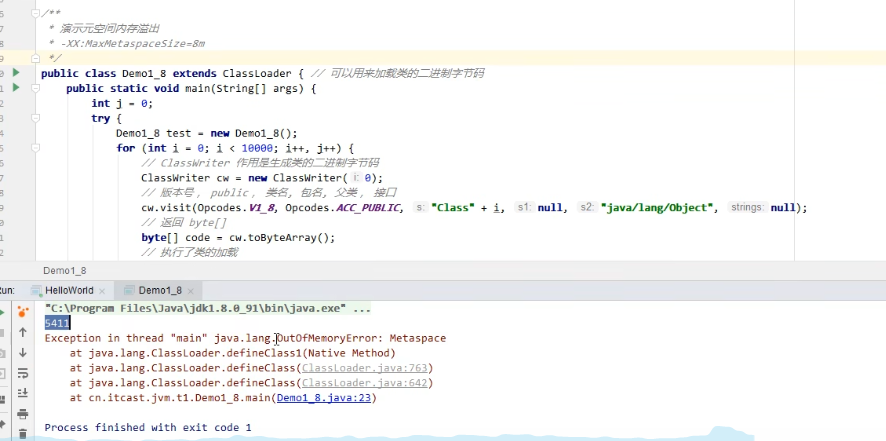
- 演示元空间内存溢出 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Metaspace
- -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=8m
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.metaspace;
import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.ClassWriter;
import jdk.internal.org.objectweb.asm.Opcodes;
/** * 演示元空间内存溢出 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Metaspace * -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=8m */
public class Demo1_8 extends ClassLoader {
// 可以用来加载类的二进制字节码
public static void main(String[] args) {
int j = 0;
try {
Demo1_8 test = new Demo1_8();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++, j++) {
// ClassWriter 作用是生成类的二进制字节码
ClassWriter cw = new ClassWriter(0);
// 版本号, public, 类名, 包名, 父类, 接口
cw.visit(Opcodes.V1_8, Opcodes.ACC_PUBLIC, "Class" + i, null, "java/lang/Object", null);
// 返回 byte[]
byte[] code = cw.toByteArray();
// 执行了类的加载
test.defineClass("Class" + i, code, 0, code.length); // Class 对象
}
} finally {
System.out.println(j);
}
}
}
5.3.2 生产环境出现元空间内存溢出问题,应该锁定这些方面
虽然我们自己编写的程序没有大量使用动态加载类,但如果我们在使用外部一些框架时,可能大量动态加载类,就可能会导致元空间内存溢出.
场景(动态加载类),If the framework is used unreasonably, it will also lead to memory overflow in the method area
- spring
- mybatis
5.4 运行时常量池
- 常量池,就是一张表,虚拟机指令根据这张常量表找到要执行的类名、方法名、参数类型、字面量等信息
- 运行时常量池,常量池是*.class 文件中的,当该类被加载,它的常量池信息就会放入运行时常量池,并把里面的符号地址变为真实地址

5.4.1 字符串常量池JVM字节码方面原理演示
// 二进制字节码(类基本信息,常量池,类方法定义,包含了虚拟机指令)
public class T02_StringHelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
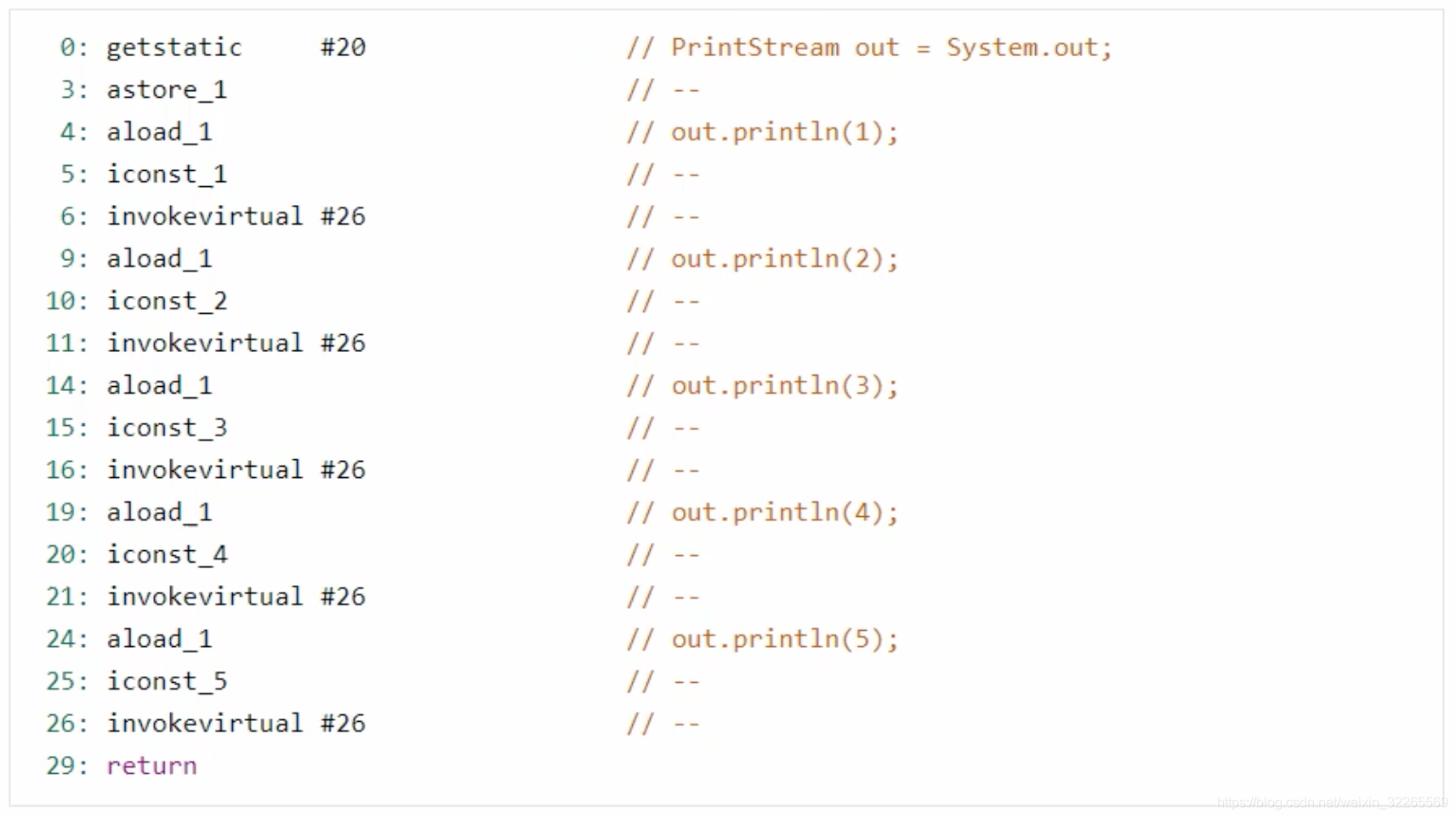
将上述编译好的class文件进行反汇编:Javap -v HelloWord.class 反编译结果如下:
D:\software\Java\jdk1.8.0_211\bin\javap.exe -v com.jvm.t03_metaspace.T02_MetaspaceConstantPool
Classfile /D:/lei_test_project/idea_workspace/Jvm_Learn/target/classes/com/jvm/t03_metaspace/T02_MetaspaceConstantPool.class
Last modified 2020-7-29; size 623 bytes
MD5 checksum 6b5272fbb2c0ca06c0e460818756710d
Compiled from "T02_MetaspaceConstantPool.java"
public class com.jvm.t03_metaspace.T02_MetaspaceConstantPool
minor version: 0
major version: 52
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SUPER
Constant pool:
#1 = Methodref #6.#20 // java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
#2 = Fieldref #21.#22 // java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#3 = String #23 // hello world!
#4 = Methodref #24.#25 // java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#5 = Class #26 // com/jvm/t03_metaspace/T02_MetaspaceConstantPool
#6 = Class #27 // java/lang/Object
#7 = Utf8 <init>
#8 = Utf8 ()V
#9 = Utf8 Code
#10 = Utf8 LineNumberTable
#11 = Utf8 LocalVariableTable
#12 = Utf8 this
#13 = Utf8 Lcom/jvm/t03_metaspace/T02_MetaspaceConstantPool;
#14 = Utf8 main
#15 = Utf8 ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
#16 = Utf8 args
#17 = Utf8 [Ljava/lang/String;
#18 = Utf8 SourceFile
#19 = Utf8 T02_MetaspaceConstantPool.java
#20 = NameAndType #7:#8 // "<init>":()V
#21 = Class #28 // java/lang/System
#22 = NameAndType #29:#30 // out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#23 = Utf8 hello world!
#24 = Class #31 // java/io/PrintStream
#25 = NameAndType #32:#33 // println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#26 = Utf8 com/jvm/t03_metaspace/T02_MetaspaceConstantPool
#27 = Utf8 java/lang/Object
#28 = Utf8 java/lang/System
#29 = Utf8 out
#30 = Utf8 Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#31 = Utf8 java/io/PrintStream
#32 = Utf8 println
#33 = Utf8 (Ljava/lang/String;)V
{
public com.jvm.t03_metaspace.T02_MetaspaceConstantPool();
descriptor: ()V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=1, locals=1, args_size=1
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
4: return
LineNumberTable:
line 11: 0
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 5 0 this Lcom/jvm/t03_metaspace/T02_MetaspaceConstantPool;
public static void main(java.lang.String[]);
descriptor: ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC
Code:
stack=2, locals=1, args_size=1
0: getstatic #2 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
3: ldc #3 // String hello world!
5: invokevirtual #4 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
8: return
LineNumberTable:
line 13: 0
line 14: 8
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 9 0 args [Ljava/lang/String;
}
SourceFile: "T02_MetaspaceConstantPool.java"
Process finished with exit code 0
5.5 StringTable
5.5.1 StringTable常量池与串池的关系
Only when a string is used, the symbol in the constant pool is taken to create a string object
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.stringtable;
// StringTable [ "a", "b" ,"ab" ] hashtable 结构,不能扩容 串池
public class Demo1_22 {
// 常量池中的信息,都会被加载到运行时常量池中, 这时 a b ab 都是常量池中的符号,还没有变为 java 字符串对象
// ldc #2 会把 a 符号变为 "a" 字符串对象
// ldc #3 会把 b 符号变为 "b" 字符串对象-
// ldc #4 会把 ab 符号变为 "ab" 字符串对象
public static void main(String[] args) {
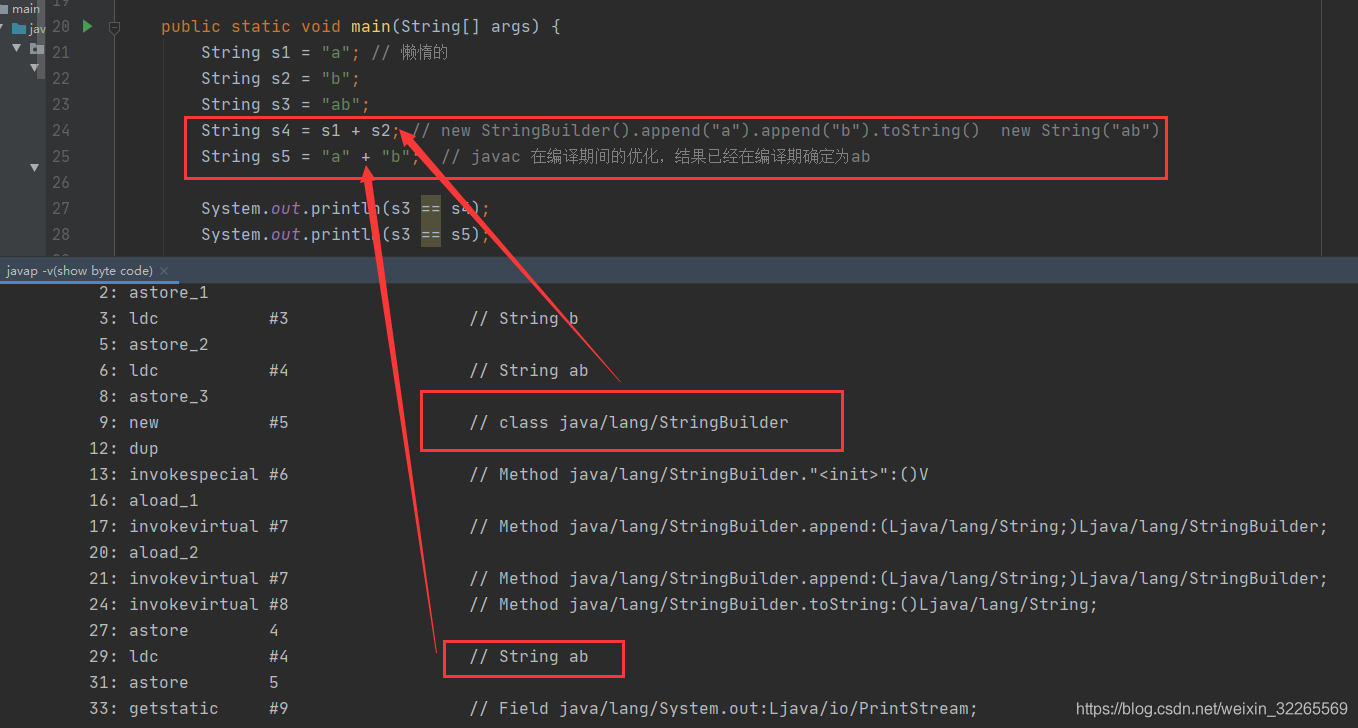
String s1 = "a"; // 懒惰的
String s2 = "b";
String s3 = "ab";
String s4 = s1 + s2; // new StringBuilder().append("a").append("b").toString() new String("ab")
String s5 = "a" + "b"; // javac 在编译期间的优化,结果已经在编译期确定为ab,No new string objects are created,Extends an object from an existing string pool
System.out.println(s3 == s4); //False
//s3是在串池中的,s4是newThe objects that come out are in the heap
System.out.println(s3 == s5); //True
//s3和s5All are in the pool
}
}
Concatenation of string variables
5.5.2 StringTable 字符串延迟加载
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.stringtable;
/** * 演示字符串字面量也是【延迟】成为对象的 */
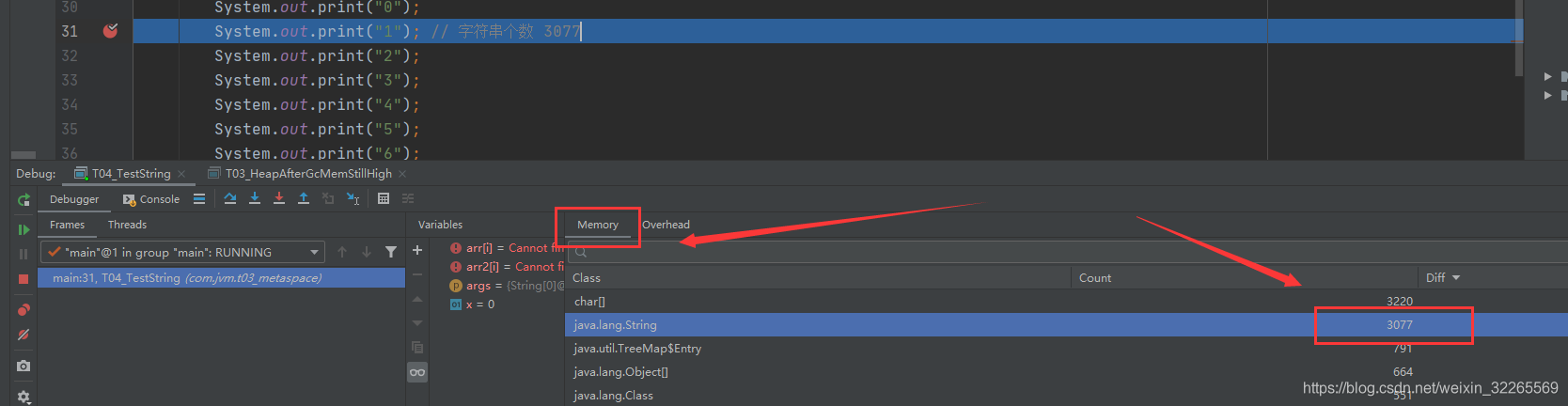
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = args.length;
System.out.println(); // 字符串个数 2275
System.out.print("1");
System.out.print("2");
System.out.print("3");
System.out.print("4");
System.out.print("5");
System.out.print("6");
System.out.print("7");
System.out.print("8");
System.out.print("9");
System.out.print("0");
System.out.print("1"); // 字符串个数 2285
System.out.print("2");
System.out.print("3");
System.out.print("4");
System.out.print("5");
System.out.print("6");
System.out.print("7");
System.out.print("8");
System.out.print("9");
System.out.print("0");
System.out.print(x); // 字符串个数 2285
}
}
5.6 StringTable特性
常量池中的字符串仅是符号,第一次用到时才变为对象
利用串池的机制,来避免重复创建字符串对象 HashTable
字符串变量拼接的原理是 StringBuilder (JDK1.8)
字符串常量拼接的原理是编译期优化
可以使用intern 方法,主动将串池中还没有的字符串对象放入串池
1.8 将这个字符串对象尝试放放串池,如果有则并不会放入,如果没有则放入串池,会把串池中的对象返回
1.6 将这个字符串对象尝试放入串池,如果有则并不会放入,如果没有会把对象复制一份,放入串池,会把串池中的对象返回
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.stringtable;
public class Demo1_23 {
// ["ab", "a", "b"]
public static void main(String[] args) {
String x = "ab";
String s = new String("a") + new String("b");
// 堆 new String("a") new String("b") new String("ab")
String s2 = s.intern(); // 将这个字符串对象尝试放入串池,如果有则并不会放入,如果没有则放入串池, 会把串池中的对象返回
System.out.println( s2 == x); //True
System.out.println( s == x ); //1.6 False 1.8 True
}
}
5.6.1 常见面试题
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.stringtable;
/** * 演示字符串相关面试题 */
public class Demo1_21 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "a";
String s2 = "b";
String s3 = "a" + "b"; // ab
String s4 = s1 + s2; // new String("ab")
String s5 = "ab";
String s6 = s4.intern();
// 问
System.out.println(s3 == s4); // false
System.out.println(s3 == s5); // true
System.out.println(s3 == s6); // true
String x2 = new String("c") + new String("d"); // new String("cd")
x2.intern();
String x1 = "cd";
// 问,如果调换了【最后两行代码】的位置呢,如果是jdk1.6呢
System.out.println(x1 == x2); //true
}
}
String x2 = new String("c") + new String("d"); // new String("cd")
String x1 = "cd";
x2.intern();
// 问,如果调换了【最后两行代码】的位置呢,如果是jdk1.6呢
System.out.println(x1 == x2); //false
5.7 StringTable位置
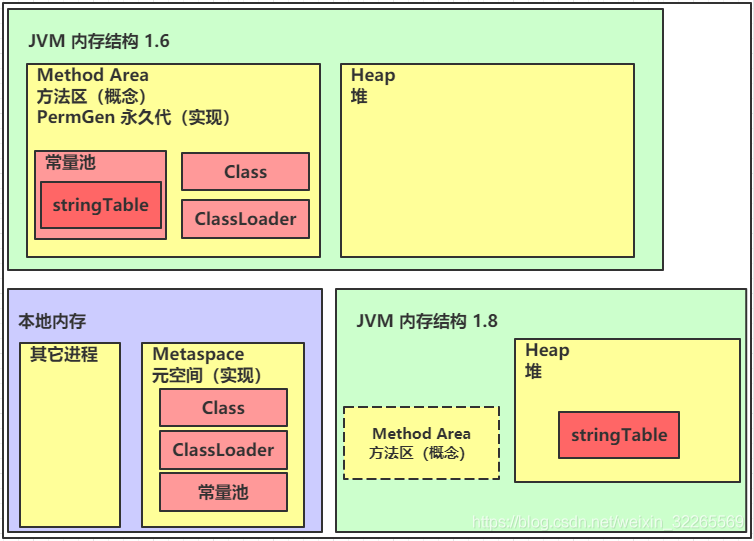
- JDK1.6版本,字符串常量池是在永久代中;
- JDK1.7 及之后版本的 JVM 已经将运行时常量池从方法区中移了出来,在 Java 堆(Heap)中开辟了一块区域存放运行时常量池.
- JDK1.8开始,取消了Java方法区,取而代之的是位于直接内存的元空间(metaSpace).
JDK1.6 与 JDK1.8字符串常量池对比
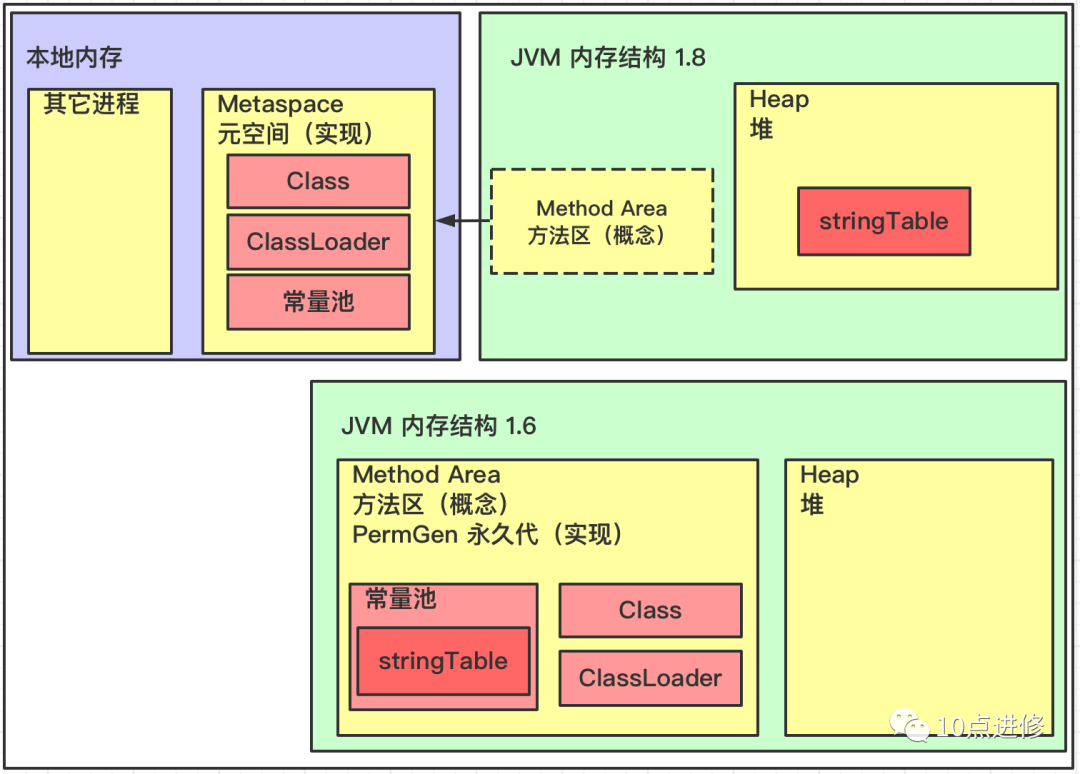
The permanent generation has less memory,GCRecycling has to wait for the old generation to run out of space before triggering,回收效率不高,所以Java 1.8 把StringTabletransfer to heap.
5.7.1 JDK1.8 字符串常量池在堆中实例验证
package cn.itcast.jvm;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/** * 演示 StringTable 位置 * 在jdk8下设置 -Xmx10m -XX:-UseGCOverheadLimit * 在jdk6下设置 -XX:MaxPermSize=10m */
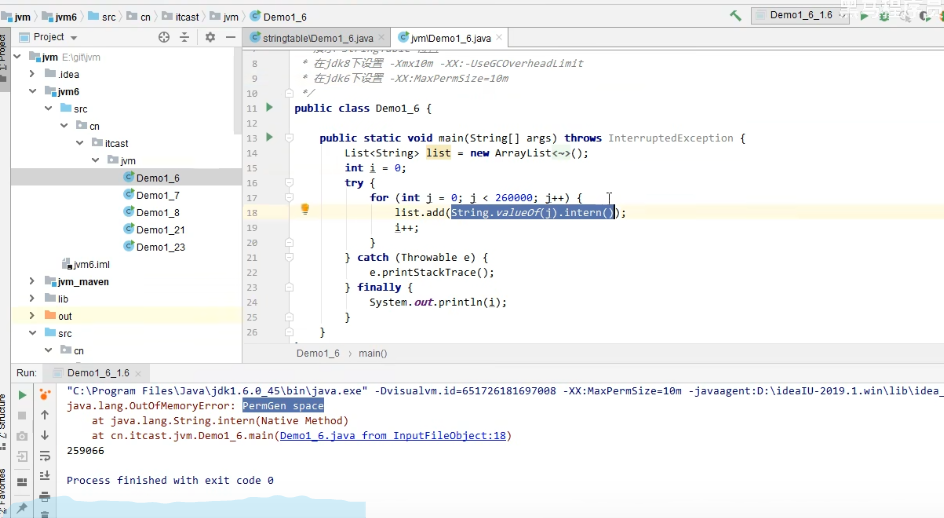
public class Demo1_6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
int i = 0;
try {
for (int j = 0; j < 260000; j++) {
list.add(String.valueOf(j).intern());
i++;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
JDK 1.6
JDK 1.8
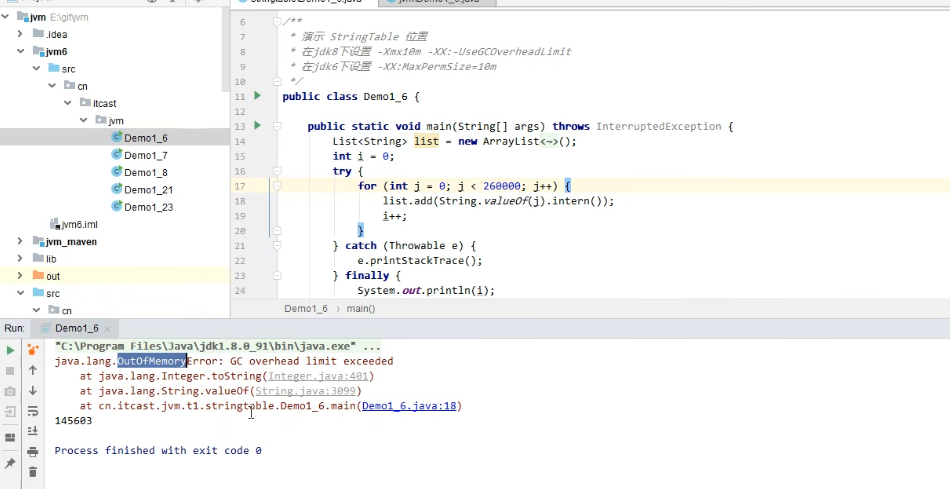
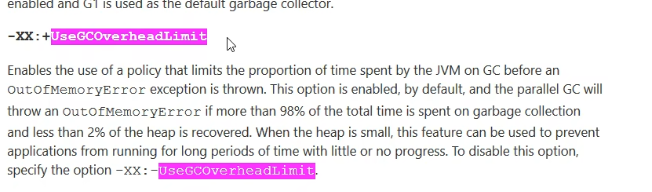
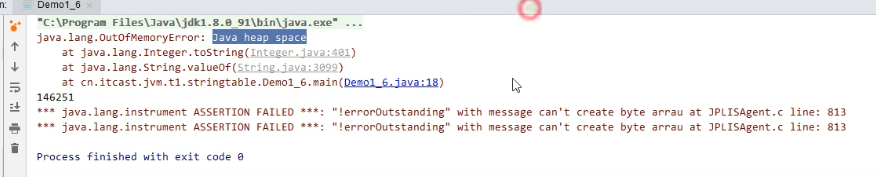
98%time spent on garbage collection,But only recycled2%的垃圾,加上-XX:-UseGCOverheadLimit
5.8 StringTable垃圾回收
因为在jdk1.8中,字符串常量池是放在堆中,如果堆空间不足,字符串常量池也会进行垃圾回收
-XX:+PrintStringTableStatistics Information about string instances in the string pool
-XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc 打印垃圾回收的详细信息
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.stringtable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/** * 演示 StringTable 垃圾回收 * -Xmx10m -XX:+PrintStringTableStatistics -XX:+PrintGCDetails -verbose:gc */
public class Demo1_7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int i = 0;
try {
for (int j = 0; j < 100000; j++) {
// j=100, j=10000
String.valueOf(j).intern();
i++;
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
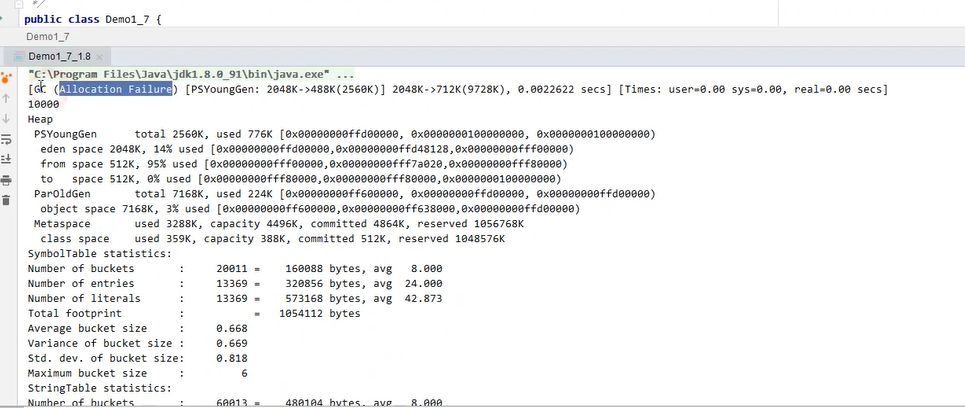
运行前:
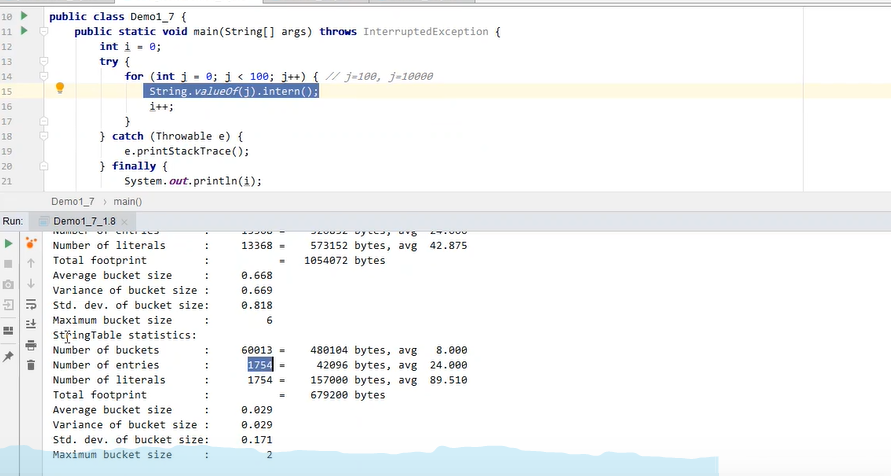
运行后:
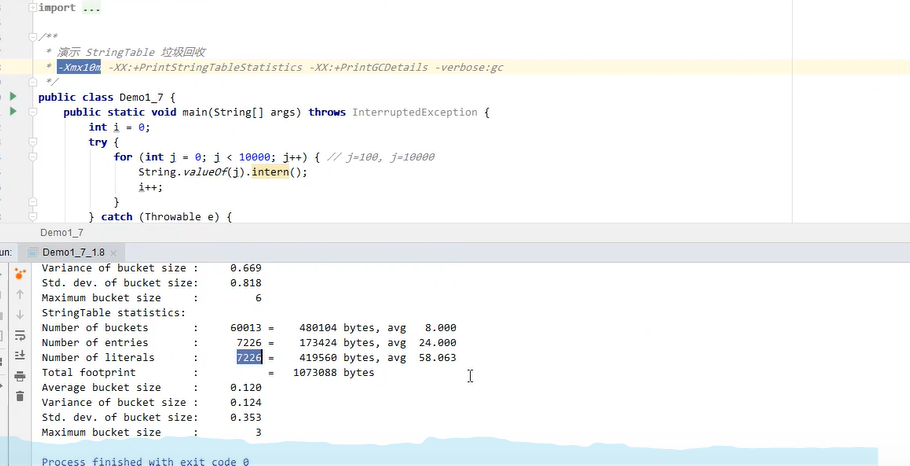
5.9 StringTable 性能调优(案例)
- 调整 -XX:StringTableSize=桶个数
- 考虑将字符串对象是否入池
5.9.1 使用-XX:StringTableSize=大小参数增加桶的数量使StringTable性能增加案例
| 序号 | StringTableSize大小 | 运行耗时(单位毫秒) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1009 | 11444  |
| 2 | 10009 | 1765  |
| 3 | 100009 | 430  |
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.stringtable;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/** * 演示串池大小对性能的影响 * -Xms500m -Xmx500m -XX:+PrintStringTableStatistics -XX:StringTableSize=1009 */
public class Demo1_24 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("linux.words"), "utf-8"))) {
String line = null;
long start = System.nanoTime();
while (true) {
line = reader.readLine();
if (line == null) {
break;
}
line.intern();
}
System.out.println("cost:" + (System.nanoTime() - start) / 1000000);
}
}
}
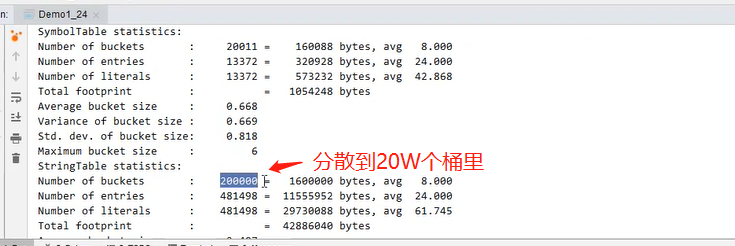
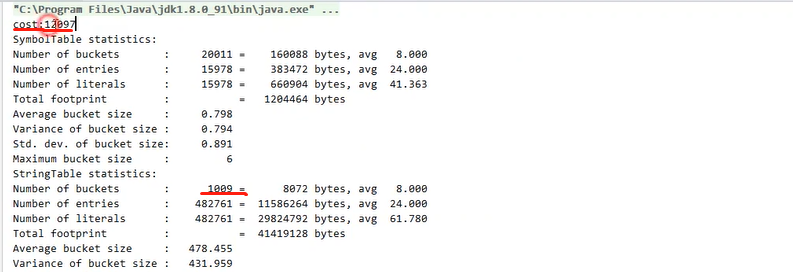
StringTableSize(桶)Size affects placementStringTable的时间,可以减少哈希冲突
5.9.2 使用字符串常量池对字符串较多的场景减少内存占用案例
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.stringtable;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/** * 演示 intern 减少内存占用 * -XX:StringTableSize=200000 -XX:+PrintStringTableStatistics * -Xsx500m -Xmx500m -XX:+PrintStringTableStatistics -XX:StringTableSize=200000 */
public class Demo1_25 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
List<String> address = new ArrayList<>(); //防止被垃圾回收
System.in.read();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("linux.words"), "utf-8"))) {
String line = null;
long start = System.nanoTime();
while (true) {
line = reader.readLine();
if(line == null) {
break;
}
address.add(line.intern());
}
System.out.println("cost:" +(System.nanoTime()-start)/1000000);
}
}
System.in.read();
}
}
输入jvisualvm命令,You can see the memory usage
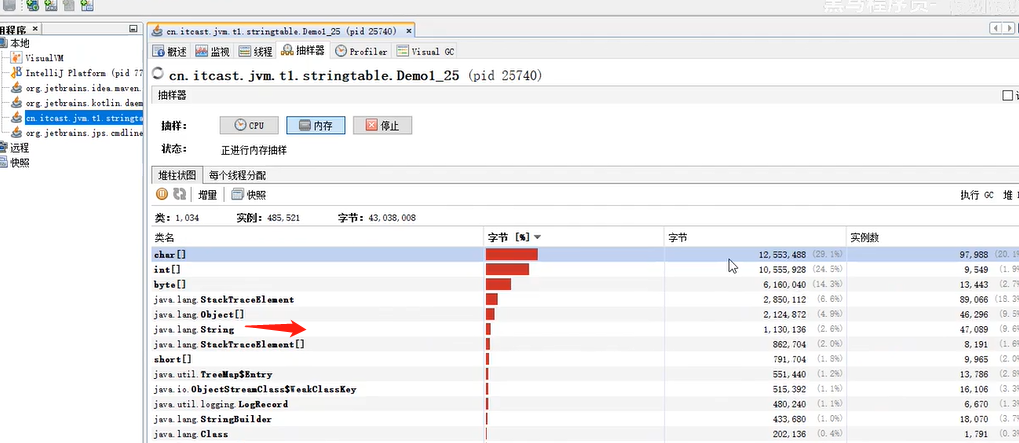
After starting to read data,内存占用情况
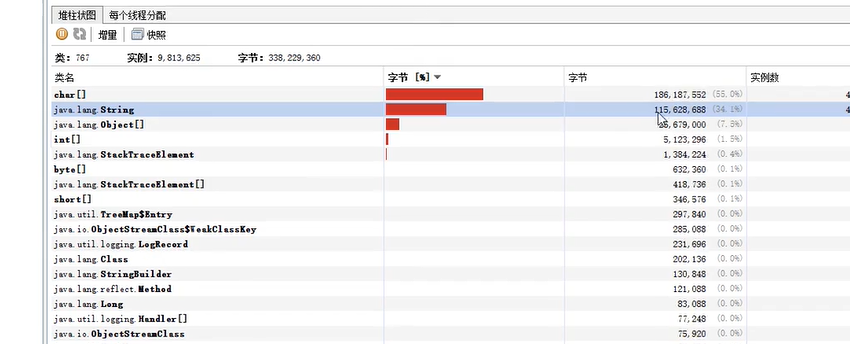
加上 address.add(line.intern()); 先入池,Then add the objects in the string pool to itaddress中,Those outside the pool will be recycled
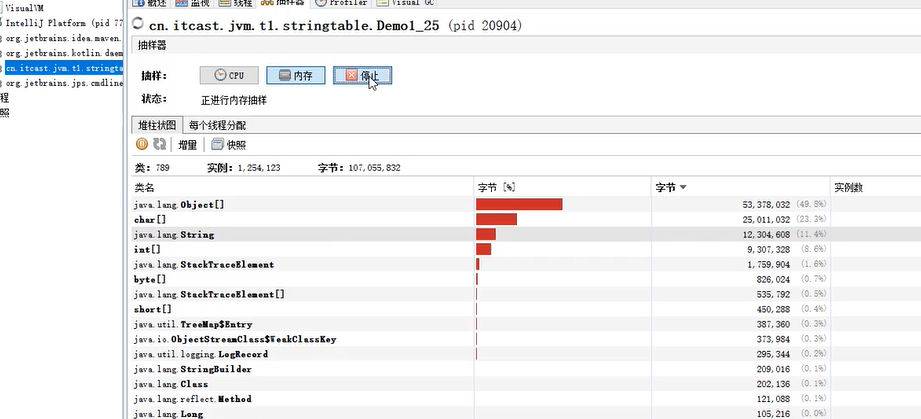
可以发现,String和CharThe memory footprint has been reduced a lot.
总结:If there are a lot of strings in the program,And the string repeats a lot,Heap memory usage can be reduced by pooling.
6、直接内存Direct Memory
6.1 直接内存定义
- 常见于NIO操作时,用于数据缓冲区
- 分配回收成本较高,但读写性能高
- 不受JVM内存回收管理
6.2 原理讲解
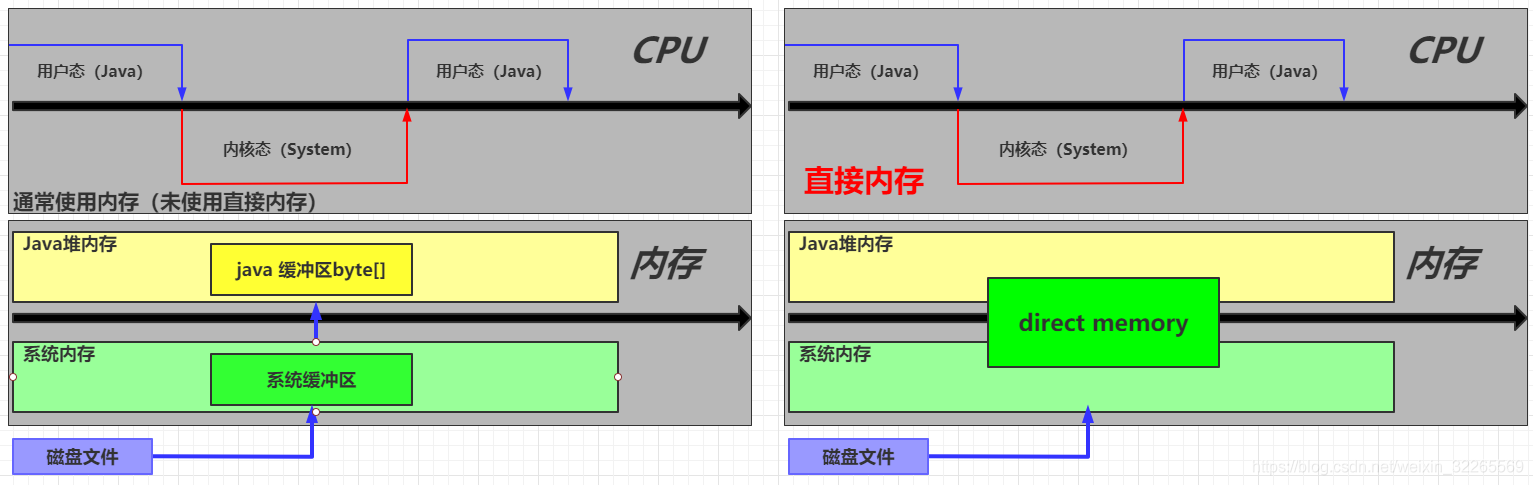
- 普通内存
- 需要从用户态向内核态申请资源,即用户态会创建一个java 缓冲区byte[],内核态会创建系统缓冲区.
- 直接内存
- 需要从用户态向内核态申请资源,即内核态会创建一块直接内存direct memory,这块direct memory内存可以在用户态、内核态使用.JAVACode and system memory can share this block area.
通常使用内存(未使用直接内存) VS 直接内存,原理对比图
6.3 直接内存与传统方式读取大文件耗时对比案例
接下来,我们将对一个大约1.29G大小的视频文件进行读取并写入指定文件中,即复制.代码如下:
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.direct;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
/** * 演示 ByteBuffer 作用 */
public class Demo1_9 {
static final String FROM = "E:\\编程资料\\第三方教学视频\\youtube\\Getting Started with Spring Boot-sbPSjI4tt10.mp4";
static final String TO = "E:\\a.mp4";
static final int _1Mb = 1024 * 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) {
io(); // io 用时:1535.586957 1766.963399 1359.240226
directBuffer(); // directBuffer 用时:479.295165 702.291454 562.56592
}
private static void directBuffer() {
long start = System.nanoTime();
try (FileChannel from = new FileInputStream(FROM).getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream(TO).getChannel();
) {
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1Mb);
while (true) {
int len = from.read(bb);
if (len == -1) {
break;
}
bb.flip();
to.write(bb);
bb.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("directBuffer 用时:" + (end - start) / 1000_000.0);
}
private static void io() {
long start = System.nanoTime();
try (FileInputStream from = new FileInputStream(FROM);
FileOutputStream to = new FileOutputStream(TO);
) {
byte[] buf = new byte[_1Mb];
while (true) {
int len = from.read(buf);
if (len == -1) {
break;
}
to.write(buf, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("io 用时:" + (end - start) / 1000_000.0);
}
}
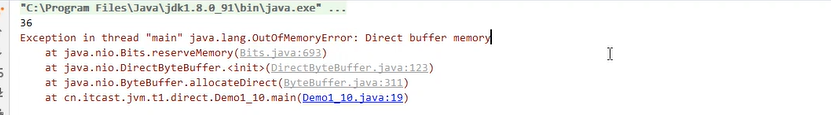
6.4 直接内存溢出案例
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.direct;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/** * 演示直接内存溢出 */
public class Demo1_10 {
static int _100Mb = 1024 * 1024 * 100;
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<ByteBuffer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0;
try {
while (true) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_100Mb);
list.add(byteBuffer);
i++;
}
} finally {
System.out.println(i);
}
// 方法区是jvm规范, jdk6 中对方法区的实现称为永久代
// jdk8 对方法区的实现称为元空间
}
}
6.5 Demo cases of distribution and usage principles
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.direct;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
/** * 禁用显式回收对直接内存的影响 */
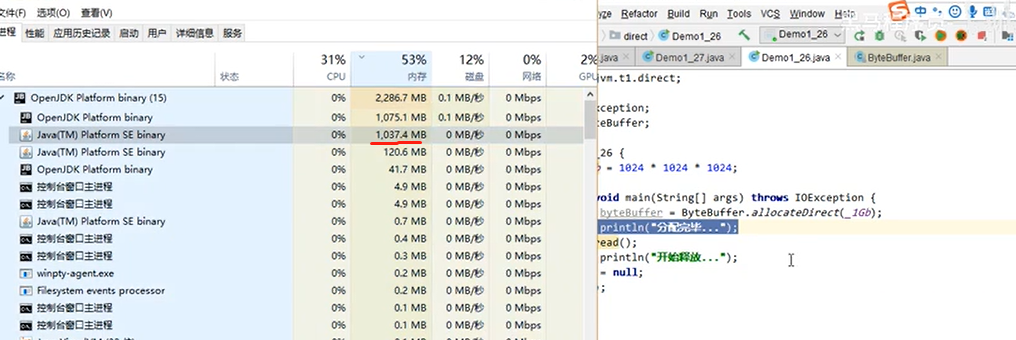
public class Demo1_26 {
static int _1Gb = 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
/* * -XX:+DisableExplicitGC 禁用显式的垃圾回收 */
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1Gb);
System.out.println("分配完毕...");
System.in.read();
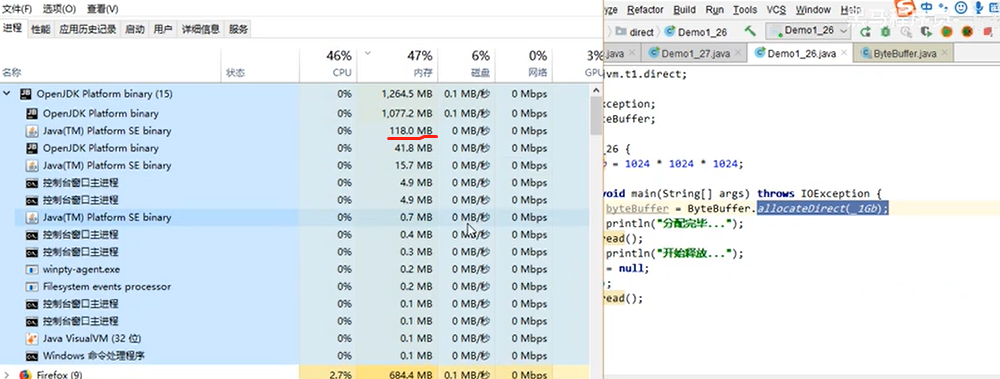
System.out.println("开始释放...");
byteBuffer = null;
System.gc(); // 显式的垃圾回收,Full GC
System.in.read();
}
}
分配时:
回收后:
6.6 分配和回收原理及案例演示
- 使用了UnSafe对象完成直接内存的分配回收,并且回收需要主动调用freeMemory方法
- ByteBuffer的实现类内部,使用了Cleaner(虚引用)来监测ByteBuffer对象,一旦ByteBuffer对象被垃圾回收,那么就会由ReferenceHandler线程通过Cleaner的clean方法调用freeMemory来释放直接内存
package cn.itcast.jvm.t1.direct;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/** * 直接内存分配的底层原理:Unsafe */
public class Demo1_27 {
static int _1Gb = 1024 * 1024 * 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Unsafe unsafe = getUnsafe();
// 分配内存
long base = unsafe.allocateMemory(_1Gb);
unsafe.setMemory(base, _1Gb, (byte) 0);
System.in.read();
// 释放内存
unsafe.freeMemory(base);
System.in.read();
}
public static Unsafe getUnsafe() {
try {
Field f = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
f.setAccessible(true);
Unsafe unsafe = (Unsafe) f.get(null);
return unsafe;
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
结论:The release of direct memory is passedUnsafe对象来完成的(需要主动调用),垃圾回收只能释放Java的内存.
6.7 直接内存_Disables showing the effect of reclamation on direct memory
-XX:+DisableExplicitGC 禁用显式的垃圾回收
如6.5代码所示,如果加上了-XX:+DisableExplicitGC 虚拟机参数,执行到System.gc()时,Direct memory cannot be reclaimed,It can only be collected when it is truly garbage collected,This leads to excessive direct memory,会导致内存溢出.可以使用Unsafe类的freememory方法,Manually free direct memory.
边栏推荐
- 2022 CCF中国开源大会会议通知(第三轮)
- Execute the mysql script file in the docker mysql container and solve the garbled characters
- net-snmp编译报错:/usr/bin/ld: cannot find crti.o: No such file or directory
- 开发即时通讯到底需要什么样的技术,需要多久的时间
- LeetCode 952. Calculate Maximum Component Size by Common Factor
- 京东云发布新一代分布式数据库StarDB 5.0
- 边缘盒子+时序数据库,美的数字化平台 iBuilding 背后的技术选型
- 宁德时代2号人物黄世霖辞任副董事长:身价1370亿
- Internet Download Manager简介及下载安装包,IDM序列号注册问题解决方法
- 开源教育论坛| ChinaOSC
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Radondb mysql installation problems
ScrollView嵌套RV,滑动有阻力不顺滑怎么办?
阿里二面:多线程间的通信方式有几种?举例说明
pytorch框架实现老照片修复功能详细演示(GPU版)
【统计机器学习】线性回归模型
图像超分——Real-ESRGAN快速上手
余弦距离介绍
Postgresql source code (64) Query execution - data structure and execution process before submodule Executor (2) execution
利用net-snmp的库实现snmpget,snmpset
Introduction to Cosine Distance
MySQL master-slave, 6 minutes you master!
awk语法-02-运算、数组、格式化输出
redis常用命令,HSET,XADD,XREAD,DEL等
Postgresql-xl全局快照与GTM代码走读(支线)
开源教育论坛| ChinaOSC
LeetCode 952. Calculate Maximum Component Size by Common Factor
Power button brush the topic of merging two orderly array
按需视觉识别:愿景和初步方案
ctfshow php特性
云图说丨初识华为云微服务引擎CSE