当前位置:网站首页>Configuration and optimization of redis cache database
Configuration and optimization of redis cache database
2022-06-22 03:05:00 【A thought of going to war】
List of articles
One 、 What is caching
Cache is to adjust the speed of two or more different substances with inconsistent speed , In the middle, it accelerates the slower side , such as CPU The first level of 、 The L2 cache is saved CPU Recently frequently accessed data , Memory is saved CPU Frequently access hard disk data , And the hard disk also has different sizes of cache , Even physical servers raid The card has a cache , All to accelerate CPU Purpose of accessing hard disk data , because CPU It's too fast ,CPU The required data can not be met in a short time due to the hard disk CPU The needs of , therefore CPU cache 、 Memory 、Raid Card cache and hard disk cache meet the requirements to a certain extent CPU Data requirements for , namely CPU Reading data from the cache can greatly improve CPU Work efficiency .
1.1 buffer And cache
buffer And cache All data system caches
- buffer: Buffer is also called write buffer , Generally used for write operations , You can write data to memory first and then to disk ,buffer Generally used for write buffer , Buffer used to solve the speed inconsistency of different media , First, temporarily write the data to the nearest place in the , To improve write speed ,CPU The data will be written to the disk buffer in memory first , Then it is considered that the data has been written. Look , Then the kernel writes to the disk at a subsequent time , So if the server suddenly loses power, some data in memory will be lost .
- cache: Cache is also called read cache , Generally used for read operations ,CPU Read file read from memory , If there is no memory, first read the memory from the hard disk, and then read CPU, Put the data that needs to be read frequently in its nearest cache area , The next time you read, you can quickly read .
1.2 Location of each layer cache
- The physical layer : disk Cache,RAID Cache
- System level :OS Of Cache
- The data layer : database 、 Distributed cache
- application layer : Static page caching
- Web layer :Web Server cache
- Broker layer : Content distribution network CDN, Reverse proxy cache
- User level :DNS cache
Two 、 Relational database and non relational database
2.1 Relational database
- Relational database is a structured database , Create in a relational model ( Two dimensional table model ) On the basis of , Generally oriented to records .
- SQL sentence ( Standard data query language ) It's a language based on relational database , Used to perform retrieval and operation of data in relational database .
- Mainstream relational databases include Oracle、 MySQL、SQL Server、Microsoft Access、 DB2、PostgreSQL etc. .
- When using the above databases, you must first build the database, build the table and design the table structure , Then, when storing data, store it according to the table structure , If the data does not match the table structure, the storage will fail .
2.2 Non relational database
- NoSQL(NoSQL=NotonlysQL), intend “ not only SQL", Is the general name of non relational database .
- In addition to the mainstream relational databases , They all think it's non relational .
- There is no need to build a database and table in advance to define the data storage table structure , Each record can have different data types and number of fields ( For example, the text in wechat group chat 、 picture 、 video 、 Music, etc ).
- Mainstream NOSQL The database has Redis、MongBD、 Hbase( Distributed non relational database , Big data use )、Memcached、ElasticSearch( abbreviation ES, Index database )、TSDB( Continuous database ) etc. .
2.3 The difference between the two
Data storage is different : The main difference between relational and non relational databases is the way data is stored .
- Relational data is naturally tabular , Therefore, it is stored in the rows and columns of the data table . Data tables can be associated with each other and stored cooperatively , It's also easy to extract data .
- On the contrary , Non relational data is not suitable to be stored in rows and columns of the data table , It's big pieces together . Non relational data is usually stored in a dataset , It's like a document 、 Key value pairs or graph structures . Your data and its characteristics are the primary factors in choosing how to store and extract data .( It's easy to switch data types , There are multiple data types in a dataset )
Different expansion methods :SQL and NoSQL The biggest difference between databases may be in the way they are extended , To support growing demand, of course, expand .
- To support more concurrency ,SQL The database is vertically extended , In other words, improve processing capacity , Use a faster computer , This makes it faster to process the same data set . Because the data is stored in relational tables , The performance bottleneck of the operation may involve many tables , This needs to be overcome by improving computer performance . although SQI The database has a lot of room for exhibition , But it will eventually reach the upper limit of vertical expansion .( Data is usually stored in the local file system . Reading can be separated by reading and writing 、 Load balancing to share performance , But reading and writing are still expensive IO performance )
- and NoSQL The database is scalable . Because non relational data storage is naturally distributed ,NoSQL The database can be expanded by adding more common database servers to the resource pool ( node ) To share the load .( Data is distributed and stored on different servers , Can read and write concurrently , Speed up efficiency )
Support for transactional is different
- If the data operation needs high transaction or complex data query needs to control the execution plan , So traditional SQL Database is your best choice in terms of performance and stability .SQL The database supports fine-grained control over the atomicity of transactions , And it's easy to roll back transactions .
- although NoSQL Databases can also use transactional operations , But it can't compare with relational database in terms of stability , So their real value is in the scalability of operation and large amount of data processing .
- Non - relational database in transaction processing and stability , Not as good as relational databases . But the reading and writing performance is good 、 extensible , Advantages in handling big data .
Summary :
Horizontal scaling : Add servers .( Cheaper )
Vertical expansion : Improve hardware configuration , For example, change to a higher performance one CPU、 Add CPU Check the number 、 Hard disk 、 disk IO、 Memory module .( Except the hard disk , Others need to be shut down before adding )
Relational database : It is especially suitable for tasks with high transactional requirements and the need to control the implementation plan , Transaction fine-grained control is better .
Non relational database : Transaction control will be slightly weak , Its value lies in high scalability and large amount of data processing .
2.4 The background of non relational database
Can be used to deal with Web2.0 Three high problems of pure dynamic website type .
High performance— High concurrent read and write requirements for the database
Huge Storage— Requirements for efficient storage and access of massive data
High Scalability s&High Availability A pair of database high scalability and high availability requirements
Relational database and non relational database have their own characteristics and application scenarios , The close combination of the two will give Web2.0 The development of database brings new ideas . Give Way Relational databases focus on the relationship and the consistency of data , Non relational databases focus on storage and efficiency . for example , In the separation of reading and writing MysQL In the database environment , You can store frequently accessed data in a non relational database , Improve access speed .
2.5 Stage summary
Relational database :
- Vertical expansion : Improve hardware configuration , For example, change to a higher performance one CPU、 Add CPU Check the number 、 Hard disk 、 disk IO、 Memory module .( Except the hard disk , Others need to be shut down before adding )
- It is especially suitable for tasks with high transactional requirements and the need to control the implementation plan , Transaction fine-grained control is better .
- example –> database –> surface (table)–> Record line (row)、 Data field (column)
Non relational database :
- Horizontal scaling : Add servers .( Cheaper )
- Transaction control will be slightly weak , Its value lies in high scalability and large amount of data processing .
- example –> database –> aggregate (collection) --> Key value pair (key-value)
- Non relational databases do not need to build databases and collections manually ( surface ).
3、 ... and 、 Cached database Redis
3.1 Redis brief introduction
- Redis( Remote dictionary server ) It's an open source 、 Use c language-written NoSQL database .
- Redis Run based on memory and support persistence , use key-value( Key value pair ) Storage form of , It is an indispensable part of the current distributed architecture .
- Redis The server program is a single process model , That is, multiple servers can be started at the same time on one server Redis process ,Redis The actual processing speed depends entirely on the execution efficiency of the main process .
- If you run only one on the server Redis process , When multiple clients access at the same time , The processing capacity of the server will decline to a certain extent .
- If you open multiple servers on the same server Redis process ,Redis While improving the concurrent processing ability, it will give the server CPU Cause a lot of pressure .
- In the actual production environment , You need to decide how many... To open according to the actual needs Redis process . If the requirements for high concurrency are higher , You may consider starting multiple processes on the same server . if CPU Resources are tight , A single process can be used .

3.2 Redis The advantages of
- It has very high data reading and writing speed : The speed of data reading can be as high as 110000 Time /s, Data write speed can be as high as 81000 Time /s.
- Supported data structures : key-value, Support rich data types :Strings( character string )、 Lists( list )、Hashes( Hash )、 Sets( unordered set ) And Sorted Sets( Ordered set ) And so on .
- Support data persistence : The data in memory can be saved on disk , When you restart, you can load it again for use .
- Atomicity : Redis All operations are atomic .( Support transactions , All operations are treated as transactions )
- Support data backup : namely master-salve Mode data backup .( Support master-slave replication )
3.3 Redis The shortcomings of
- Cache and database write consistency problem
- Cache avalanche problem
- Cache breakdown problem
- Concurrent contention of cache
3.4 Redis Applicable scenario
- Redis As a memory based database , Is a high-performance cache , General application in session cache 、 queue 、 Ranking List 、 Counter 、 The hottest article recently 、 The hottest comment recently 、 Publish, subscribe, etc .
- Redis It is suitable for data with high real-time requirements 、 Data storage is characterized by expiration and obsolescence 、 There is no need for persistence or only weak consistency 、 A scenario with simple logic .
3.5 Redis Why so soon?
- Redis Is a pure memory structure , Avoid disk I/O Wait for time-consuming operations .( Run based on memory )
- Redis The core module of command processing is single thread , Reduced lock competition , And the cost of creating and destroying threads frequently , Reduces the consumption of thread context switching .( Single thread model )
- Adopted I/O Multiplexing mechanism , Greatly improve the concurrency efficiency .(epoll Pattern )
notes : stay Redis6.0 The newly added multithreading is only for the process of processing network requests , And the data read and write command , It's still single threaded .
3.6 Redis And memcached Compare
| Redis | Memcached | |
|---|---|---|
| type | KV Type database | KV Type database |
| Expiration strategy | Support | Support |
| data type | Five data types | Single data type |
| Persistence | Support | I won't support it |
| Master slave copy | Support | I won't support it |
| Virtual memory | Support | I won't support it |
Four 、Redis Installation and deployment
-------------------- Early environmental preparation -----------------------
# Close the firewall and SELINUX
systemctl stop firewalld && setenforce 0
# Install dependent environment
yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ make
# take Redis Upload the package to opt Directory and extract
cd /opt
tar zxvf redis-5.0.7.tar.gz
----------------------- install Redis----------------------
# Compile the installation and specify the installation path as /usr/local/redis
cd /opt/redis-5.0.7/
make -j2 && make PREFIX=/usr/local/redis install
# because Redis The source package directly provides Makefile file , So after unpacking the package , You don't have to do it first ./configure To configure , It can be executed directly make And make install Command to install .
# Execute the... Provided by the software package install_server.sh Script files , Set up Redis Relevant configuration files required by the service
cd /opt/redis-5.0.7/utils
./install_server.sh
Just go straight back
Please select the redis executable path [] /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server
# I think so /usr/local/bin/redis-server, You need to manually change it to /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server, Be careful to input correctly at one time
#install_server.sh After the script runs ,Redis The service has started , The default listening port is 6379
netstat -natp | grep redis
# Optimize file path , Facilitate system management
ln -s /usr/local/redis/bin/* /usr/local/bin/
--------------------Redis Service management command ------------------
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 stop # stop it
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 start # start-up
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 restart # restart
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 status # Check the status
-------------------- Profile parameters ----------------------
vim /etc/redis/6379.conf
#70 That's ok
bind 127.0.0.1 192.168.41.43 # Monitoring IP Address ,127.0.0.1 Is the loopback network card address of this computer ,43 Is the physical network card address , monitor 43 Convenient for remote connection
#93 That's ok
port 6379 # Listening port
#137 That's ok
daemonize yes # Start using a daemon , That is, the background starts
#159 That's ok
pidfile /var/run/redis_6379.pid #Redis Process number file · Save the location
#172 That's ok
logfile /var/log/redis_6379.log # Where the log is saved
#187 That's ok
databases 16 # Number of listening Libraries ( Number 0-15)
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 restart # After changing the configuration file , restart redis
notes : If you want to remotely connect one host to another host redis, First
Make sure that both servers are redis already installed , Then, in the configuration files of the two machines
bind All parameters listen to the address of the local physical network card







5、 ... and 、Redis Command tool
| Tools | effect |
|---|---|
| redis-server | Used to start redis Tools for |
| redis-benchmark | Used to detect redis The operating efficiency of the machine |
| redis-check-aof | Repair AOF Persistent files |
| redis-check-rdb | Repair RDB Persistent files |
| redis-cli | redis Command line tools |
5.1 Redis-cli Command line tools
-------------------redis Database command -------------------
grammar :redis-cli [-h host -p port -a password]
-h: Designated host
-p: Appoint redis Port number
-a: Specified password , If no password is set , It can be omitted
redis-cli If you do not add any options, you will log in to this computer by default redis, Default port
Number 6379

5.2 redis-benchmark Testing tools
redis-benchmark It's official Redis Performance testing tools , Can effectively test Redis Service performance .
grammar :redis-benchmark [ Options ] [ Option value ]
-h: Specify the server host name
-p: Specify the server port
-s: Specify the server socket
-c: Specify the number of concurrent connections
-n: Specify the number of requests
-d: Specify... In bytes SET/GET Data size of value
-k:l=keep alive 0=reconnect
-r:SET/GET/INCR Use random key,SADD Use random values
-P: To transmit through pipes <numreg> request
-q: Forced exit redis, Show only query/sec value
--csv: With CSV Format output
-l: Generate a cycle , Perform tests permanently
-t: Run only comma separated list of test commands
-I:Idle Pattern , Just open N individual idle Connect and wait
1. towards IP The address is 192.168.41.43( This machine ), Port is 6379 Of Redis Server send 100 Multiple concurrent connections and 100000 Requests to test performance .
redis-benchmark -h 192.168.41.43 -p 6379 -c 100 -n 100000
perhaps
redis-benchmark -c 100 -n 100000
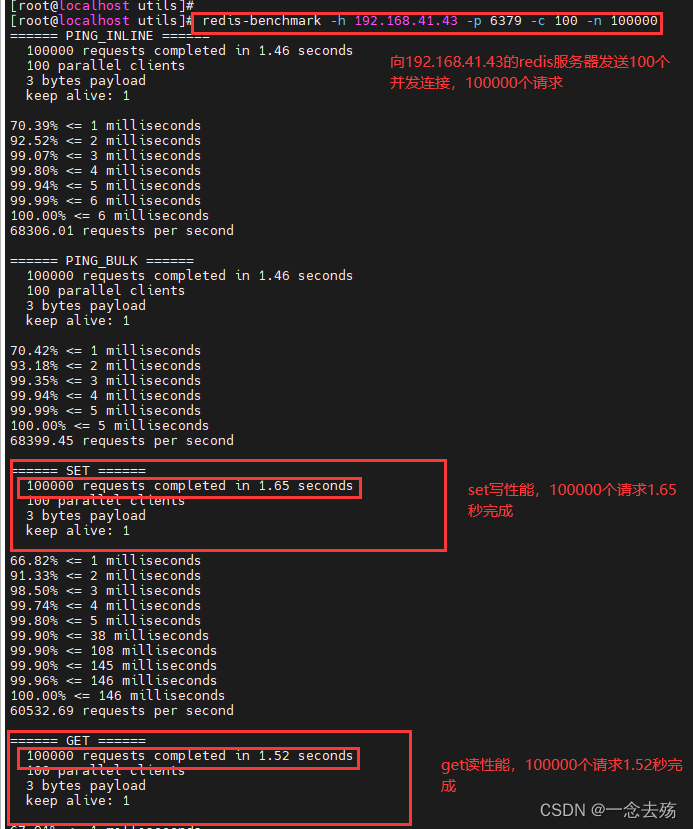
2. The test access size is 100 Byte packet performance
redis-benchmark -h 192.168.41.43 -p 6379 -q -d 100

3. Test on this machine Redis The service is in progress set And lpush Performance during operation
redis-benchmark -t set,lpush -n 100000 -q

6、 ... and 、Redis Operation commands in the database
| command | effect |
|---|---|
| set | Access data |
| get | Storing data |
| keys * | Look at all the keys |
| keys k? | see k Data of any position after the beginning |
| exist | Judge whether the key exists ,1 For existence ,0 For there is no such thing |
| del | Delete key |
| type | View key value Value type ( Five types ) |
| rename k1 k2 | Name it k1 The key of is renamed k2, No matter what k2 Whether it exists or not will succeed , There is k2,k1 The value of is overridden k2 Value ; non-existent , Will directly k1 Change it to k2,k1 It doesn't exist |
| renamenx | Same as rename It works the same , Just if k2 There is , It won't be implemented , It is recommended to use renamenx, To prevent important data from being overwritten |
| dbsize | View the current database key Number of |
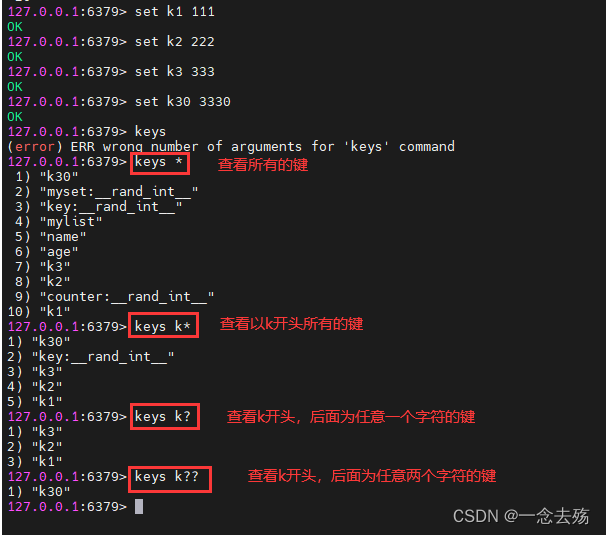
6.1 set、get、keys
Format :set Key name value # Save the data
get Key name # Check data
keys * # View all keys in the current database
keys k* # View the current database to k Key at the beginning
keys k? # View the current database to k start , A key followed by any one character
keys k?? # View the current database to k start , A key followed by any two characters


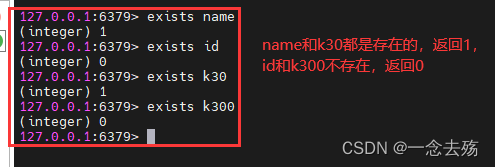
6.2 exists
exists Used to determine whether the key exists , There is returned 1, There is no return 0
grammar :exists Key name
6.3 del
del Used to delete keys
grammar :del Key name

6.4 type
type Used to view the data type stored by the key
grammar :type Key name

6.5 rename and renamenx
rename and renamenx Are used to rename , The difference lies in renamenx When the modified new key name exists , Don't execute ; and rename Whether the new key name exists or not , All changed
grammar :rename Old key name New key name
renamenx Old key name New key name



6.6 dbsize
dbsize Used to view the current database key Number of
grammar :dbsize

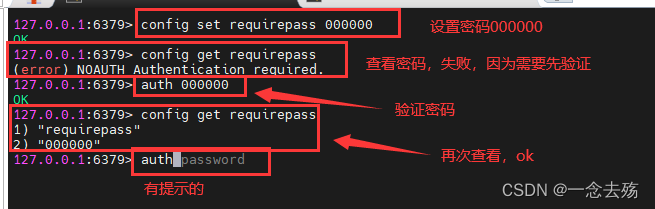
6.7 Set and clear passwords
grammar :config set requirepass XXXXXX
# Once the password is set , You have to verify the password first , Otherwise, all operations are not available
auth XXXXXX
# Verify password
config get requirepass
# Verify first , To view passwords and other operations , One time verification only supports this session , sign out redis Re entry requires re auth
redis-cli -a 000000
# Log in directly -a XXXXXX Password authentication , Subsequent operations do not require password verification
config set requirepass ''
# Empty password , Is to set the null character
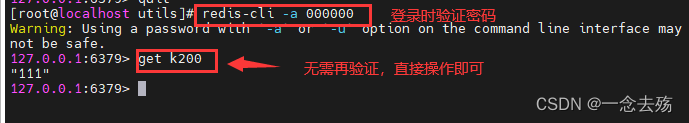

6.8 select
select For switching redis Database in , Default includes 16 individual , Number 0-15, By default 0
Use redis-cli Connect Redis After the database , The default sequence number is 0 The database of .
The databases are independent of each other , Mutual interference .
grammar :select Number


Move data between libraries
grammar :move Key name Library number

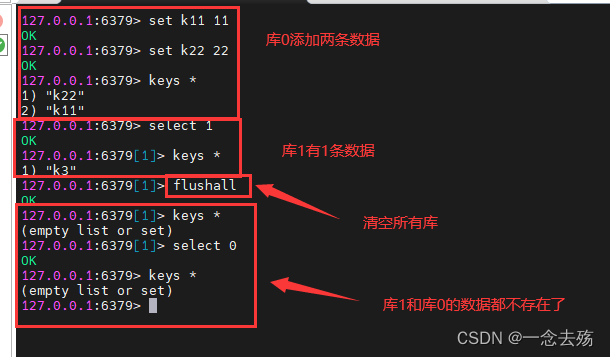
6.9 flushdb and flushall
flushdb: Clear the current database data
flushall: Clear all database data ... The so-called deleting databases and running away , Use with caution !!!

summary
- Common relational databases :oracle、MySQL、SQL Server、Microsoft Access、DB2、PostgreSQL
- Common non relational databases :Redis、MongBD、Hbase、Memcached、ElasticSearch( Index database )、TSDB( Time series database )
- Redis Default data type :string
- Redis Why so soon? :
- Redis Is a pure memory structure , Avoid disk I/O Wait for time-consuming operations .( Run based on memory )
- Redis The core module of command processing is single thread , Reduced lock competition , And the cost of creating and destroying threads frequently , Reduces the consumption of thread context switching .( Single thread model )
- Adopted I/O Multiplexing mechanism , Greatly improve the concurrency efficiency .(epoll Pattern )
- Redis Database common commands :set、get、keys、exists、dbsize、rename、renamenx、select
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

fastdfs-5.0.5安装

web框架概述与程序开发
ACL 2022 | multilingual knowledge map reasoning based on self supervised graph alignment
![[summary of leetcode weekly competition] summary of the 298th weekly competition of leetcode (6.19)](/img/72/d3e46a820796a48b458cd2d0a18f8f.png)
[summary of leetcode weekly competition] summary of the 298th weekly competition of leetcode (6.19)

What is an SSL certificate and what are the benefits of having an SSL certificate?

Day16QtQLabel2021-10-22

【 thesis 】 zero reference depth curve estimation for low light image enhancement

360edr planing

Project Management-软件开发之项目管理

【2. 归并排序】
随机推荐
Implementation of epoll+threadpool high concurrency network IO model
360edr planing
【1. 快速排序】
Figure data platform solution: single node deployment
Deep Copy
fastdfs-5.0.5安装
Overview of web framework and program development
C mapster object mapper learning
Li Kou today's question 1108 IP address invalidation
[crawler notes 2] mouse events, screenshots and common attack methods
Figure database ongdb release v-1.0.2
Sword finger offer 37 Serialized binary tree
你是一名技术管理者还是项目管理者?
The latest official product of domestic brand oppo! This ppt report! It really refreshes my understanding of it
fatal error: png++/png. Hpp: no that file or directory
Architecture and practice of vivo container cluster monitoring system
Using open source software to save an enterprise level map data platform solution
Force buckle 239 Sliding window Max
Database interview summary
Using JMeter for web side automated testing