当前位置:网站首页>Opencv feature extraction - hog
Opencv feature extraction - hog
2022-07-03 10:05:00 【Σίσυφος one thousand and nine hundred】
One 、HOG features
HOG(Histograms of Oriented Gradients) Gradient direction histogram
Two 、HOG Feature extraction process
1) Grayscale image transformation ( Think of the image as a x,y,z( Grayscale ) Three dimensional images of );
2) use Gamma The input image is normalized in color space by correction method ( normalization ); The purpose is to adjust the contrast of the image , Reduce the impact of local shadow and light changes in the image , At the same time, it can suppress the interference of noise ;

#if 1 // Image enhancement algorithm --gamma
int Gamma = 2;
int main(int args, char* arg)
{
Mat src = imread("C:\\Users\\19473\\Desktop\\opencv_images\\88.jpg");
if (!src.data)
{
printf("could not load image....\n");
}
imshow(" Original image ", src);
// Be careful : CV_32FC3
Mat dst(src.size(), CV_32FC3);
for (int i = 0; i < src.rows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < src.cols; j++)
{
// Yes bgr Each channel of is calculated
dst.at<Vec3f>(i, j)[0] = pow(src.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[0], Gamma);
dst.at<Vec3f>(i, j)[1] = pow(src.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[1], Gamma);
dst.at<Vec3f>(i, j)[2] = pow(src.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[2], Gamma);
}
}
// normalization
normalize(dst, dst, 0, 255, CV_MINMAX);
convertScaleAbs(dst, dst);
imshow(" Enhanced image ", dst);
waitKey(0);
return -1;
}
#endif3) Calculate the gradient of each pixel in the image ( Including size and direction ); The main purpose is to capture the contour information , At the same time, further weaken the interference of light
Mat non_max_supprusion(Mat dx, Mat dy) // What comes in is the difference matrix in two directions 3*3 Mask of
{
// Edge strength =sqrt(dx The square of +dy The square of )
Mat edge;
magnitude(dx, dy, edge);// Calculate the amplitude value
int rows = dx.rows;
int cols = dy.cols;
// Non maximum suppression of edge strength
Mat edgemag_nonMaxSup = Mat::zeros(dx.size(), dx.type());
// Use two steps to calculate And gradient direction And convert it to angleMatrix
for (int row = 1; row < rows - 1; row++)
{
for (int col = 1; col < cols - 1; col++)
{
float x = dx.at<float>(row, col);
float y = dx.at<float>(row, col);
// The direction of the gradient ---atan2f
float angle = atan2f(y, x) / CV_PI * 180;
// Edge strength of current position
float mag = edge.at<float>(row, col);
// Find the left and right directions
if (abs(angle) < 22.5 || abs(angle) > 157.5)
{
float left = edge.at<float>(row, col - 1);
float right = edge.at<float>(row, col + 1);
// Judge in two directions
if (mag > left && mag > right) {
edgemag_nonMaxSup.at<float>(row, col) = mag;
}
}
// Top left and bottom right
if ((abs(angle) >= 22.5 && abs(angle) < 67.5) || (abs(angle) < -112.5 && abs(angle) > 157.5))
{
float lefttop = edge.at<float>(row - 1, col - 1);
float rightbottom = edge.at<float>(row + 1, col + 1);
// Judge in two directions
if (mag > lefttop && mag > rightbottom) {
edgemag_nonMaxSup.at<float>(row, col) = mag;
}
}
// On Next Direction
if ((abs(angle) >= 67.5 && abs(angle) <= 112.5) || (abs(angle) >= -112.5 && abs(angle) <= -67.5))
{
float top = edge.at<float>(row - 1, col);
float down = edge.at<float>(row + 1, col);
// Judge in two directions
if (mag > top && mag > down) {
edgemag_nonMaxSup.at<float>(row, col) = mag;
}
}
// The upper right The lower left Direction
if ((abs(angle) > 122.5 && abs(angle) < 157.5) || (abs(angle) > -67.5 && abs(angle) <= -22.5))
{
float leftdown = edge.at<float>(row - 1, col + 1);
float rightup = edge.at<float>(row + 1, col - 1);
// Judge in two directions
if (mag > leftdown && mag > rightup) {
edgemag_nonMaxSup.at<float>(row, col) = mag;
}
}
}
}
return edgemag_nonMaxSup;
}
4) Divide the image into small cells( for example 8* 8 Pixels / cell); Work out each cell Gradient size and direction . Then set the gradient direction of each pixel in Within the interval ( Undirected :0-180, Directed :0-360) The average is divided into 9 individual bins, Every cell Pixels in the are represented by amplitude , Weighted voting for its gradient histogram .


5) Count each one cell The gradient histogram of ( The number of different gradients ), You can form each cell Of descriptor; Quick description seed
6) Will each several cell Form a block( for example 3 * 3 individual cell / block), One block All in cell Characteristics of descriptor In series, you get this block Of HOG features descriptor. Quickly describe seed normalization
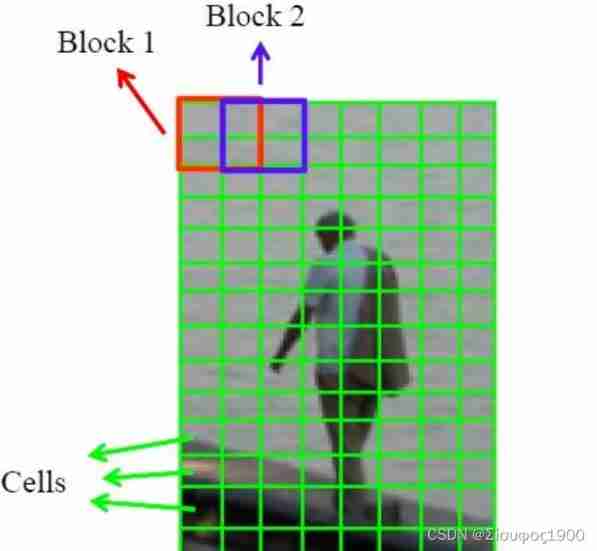
7) The image image In all of the block Of HOG features descriptor In series, you can get the image( The target you want to detect ) Of HOG features descriptor 了 . This is the final feature vector for classification Feature data and detection window
For size 128×64 Size image , use 8*8 Pixel sell,2×2 individual cell Composed of 16×16 Pixel block, use 8 Pixel block Move step , In this way, the detection window block There are ((128-16)/8+1)×((64-16)/8+1)=15×7. be HOG The dimension of the feature descriptor is 15×7×4×9.
8) Match method
HOG The shortcomings of :
Slow speed , Poor real-time performance ; Difficult to deal with occlusion
3、 ... and 、 Code demonstration
int main(int args, char* arg)
{
// Target image
src = imread("C:\\Users\\19473\\Desktop\\opencv_images\\153.jpg");
if (!src.data)
{
printf("could not load image....\n");
}
namedWindow(INPUT_TITLE, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
//namedWindow(OUT_TITLE, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow(INPUT_TITLE, src);
/*
// Resize the image
resize(src, dst,Size(64,128));
cvtColor(dst, src_gary, CV_BGR2GRAY);
HOGDescriptor detector(Size(64,128), Size(16,16), Size(8,8),Size(8,8),9);
vector<float> descripers;
vector<Point> locations;
detector.compute(src_gary, descripers, Size(0,0), Size(0, 0), locations);
printf("num of HOG: %d\n", descripers.size());
*/
//SVM classifier -- Narrator
HOGDescriptor hog = HOGDescriptor();
hog.setSVMDetector(hog.getDefaultPeopleDetector());
vector<Rect> foundloactions;
// Multiscale detection
hog.detectMultiScale(src, foundloactions, 0, Size(8, 8), Size(32, 32), 1.05, 2, false);
// if rects Nested , Then take the outermost rectangle and store it rect
for (size_t i = 0; i < foundloactions.size(); i++)
{
rectangle(src, foundloactions[i], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8.0);
}
namedWindow(OUT_TITLE, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow(OUT_TITLE, src);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
} 
边栏推荐
- (1) 什么是Lambda表达式
- 01仿B站项目业务架构
- Do you understand automatic packing and unpacking? What is the principle?
- Dynamic layout management
- The data read by pandas is saved to the MySQL database
- LeetCode - 703 数据流中的第 K 大元素(设计 - 优先队列)
- byte alignment
- Embedded systems are inherently flawed. Compared with the Internet, there are so many holes that it is simply difficult to walk away from
- 2021-01-03
- Serial communication based on 51 single chip microcomputer
猜你喜欢
干单片机这一行的时候根本没想过这么多,只想着先挣钱养活自己

当你需要使用STM32某些功能,而51实现不了时, 那32自然不需要学

Oracle database SQL statement execution plan, statement tracking and optimization instance

JS基础-原型原型链和宏任务/微任务/事件机制

Yocto technology sharing phase IV: customize and add software package support
pycharm 无法引入自定义包

For new students, if you have no contact with single-chip microcomputer, it is recommended to get started with 51 single-chip microcomputer

YOLO_ V1 summary

STM32 interrupt switch

yocto 技術分享第四期:自定義增加軟件包支持
随机推荐
[combinatorics] Introduction to Combinatorics (combinatorial idea 3: upper and lower bound approximation | upper and lower bound approximation example Remsey number)
Serial port programming
Toolbutton property settings
在三线城市、在县城,很难毕业就拿到10K
01 business structure of imitation station B project
Circular queue related design and implementation reference 1
Open Euler Kernel Technology Sharing - Issue 1 - kdump Basic Principles, use and Case Introduction
2020-08-23
(1) 什么是Lambda表达式
Getting started with JMX, MBean, mxbean, mbeanserver
The new series of MCU also continues the two advantages of STM32 product family: low voltage and energy saving
Vgg16 migration learning source code
The data read by pandas is saved to the MySQL database
Embedded systems are inherently flawed. Compared with the Internet, there are so many holes that it is simply difficult to walk away from
In third tier cities and counties, it is difficult to get 10K after graduation
openEuler kernel 技術分享 - 第1期 - kdump 基本原理、使用及案例介紹
There is no shortcut to learning and development, and there is almost no situation that you can learn faster by leading the way
Timer and counter of 51 single chip microcomputer
Adaptiveavgpool1d internal implementation
is_ power_ of_ 2 judge whether it is a multiple of 2