当前位置:网站首页>Reading notes of CLR via C -clr boarding and AppDomain
Reading notes of CLR via C -clr boarding and AppDomain
2022-06-29 10:31:00 【zlbcdn】
1、CLR Lodging
stay Window There are two types of calls between programs on the platform : Managed program calls unmanaged program and unmanaged program calls managed program . The former usually uses P/Invoke Way to call , The most used is Win32 Programming interface . for instance :
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
......
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")]
public static extern int WinExec(string exeName, int operType);
WinExec(@"C:\**\ctsetdg.exe", 5);advantage : Many functions have been implemented , No need for redevelopment . shortcoming :1、 Out of control .2、API Lots of interfaces . Here is a API Documentation of . The specific website is here : API Description document
But when an unmanaged program calls a managed program , It needs to be used CLR Boarding . We know , A managed application is first started by the operating system , Then the operating system calls CLR To host the program .CLR The essence of is a being “ packing ” To DLL One of the COM The server . Therefore, unmanaged programs can call according to the interface CLR To run managed programs . We call this approach CLR Lodging . Make the unmanaged program the host .
Host program “ Have ”CLR after , You can use CLR Memory management 、 Garbage collection 、 Strategic management 、 Event management, etc
CLR adopt XX The header file declares how to call CLR Interface content of . There are too many methods , Don't look ( ha-ha , Actually, I can't understand ), Here is a blog post , In detail CLR Boarding of , recommend : The website is here . Although I don't understand , But it can be based on 《CLR via C#》 First sort out the general framework . As follows :
First step : establish COM The server . There are two ways to create a server :1、 adopt CoCreateInstance;2、 adopt CLRCreateInstance.《CLR via C#》 The author of suggests using the latter .
The second step :CLRCreateInstance return ICLRMetaHost Interface . Through this interface GetRuntime function , Can return ICLRRuntimeInfo The pointer to .
The third step : Pass the first 2 The pointer from step , Can its GetInterface Method , obtain ICLRRuntimeHost Interface .
Step four : You can get the interface through the third step , Complete calling assembly , And execute the code .( Actually , Through this interface, you can also complete : Set up the host Manager 、 obtain CLR Manager 、 Initialize and load the specific CLR、 stop it CLR etc. ).
Let's talk about personal understanding :
1、CLR The main function of hosting is to provide a way for programmers writing unmanaged code to execute managed code . therefore ,C# Programmers don't have to pay too much attention to this topic , If it needs to be connected with the outside , It's not too late to study .
2、 stay CLR The essence of boarding , It's reflex . establish CLR The server 、 Load the managed code that needs to be executed 、 Call the related methods through reflection . This is a CLR The basic idea of boarding . In this process, there are several small concepts :
2.1、MSCorEE.DLL. This DLL It's called “shim” shim . It is equivalent to 《 The matrix 》 To protect the Prophet (Oracle) My bodyguard . No matter how the prophet's face changes , This bodyguard can always find and protect the Prophet . This DLL It's the same thing . It can be based on the needs of users , Find the Executive CLR Version of .
2.2、GUID.GUID Is an all class 、 Interface 、 The type is unique in the world ID. Its 128 Bit length , Guaranteed by algorithm . and COM The creation of the server , Will register in the registry GUID, So the program just needs to pass GUID You can find it DLL, And there's no need to worry about DLL The name of 、 Specific location and other information . therefore , You can update the relevant contents in the registry , You can complete the program update without being aware of it .
That's all CLR After reading the boarding chapter .
in addition , In the process of searching for information , There are a few good technical blogs , We recommend :1、 Introduce MSCorEE.DLL The blog of : MSCorEE The function of .2、 Introduce CoCreateInstance 's blog post : CoCreateInstance
2、APPDomain
When an unmanaged program passes CLR Boarding when running managed programs , There are two ways :1、 Run managed programs without restrictions ;2、 Create a separate for the managed program “ The sandbox ”, Only managed programs are allowed in “ The sandbox ” Internal operation . Compare the two ways , The latter is safer . in addition , When the program itself is a managed code program ( for example :C# Written program ), Call the program of the third party as an extension program , To ensure safety , It is also possible to use the “ The sandbox ” The way . So ,.NET Provided in AppDomain, Its sole function is to isolate .
in addition , When an unmanaged program calls a managed program, the operation logic is as follows :
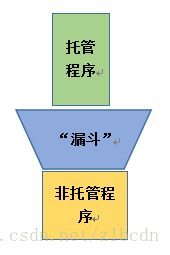
Between unmanaged and managed programs , You need to write a managed code , Used to call managed programs . As shown in the figure above “ funnel ” The role of . stay 《CLR via C#》 The author provides an example :
Through the example above , It can be learned that :
If you want to pass an object, you can use it in different AppDomain Passed between , There are two ways :1、 Pass a local instance's “ copy ”, Is the agent mentioned above ( You actually only have a remote reference to this object , Although you can call its methods , But in fact, these operations are all remote ).2、 Copy a full version , And pass it on . This is the following example .Demo1 That's the first case ,Demo2 That's the second case .
in addition , When an unmanaged program calls a managed program, the operation logic is as follows :

Between unmanaged and managed programs , You need to write a managed code , Used to call managed programs . As shown in the figure above “ funnel ” The role of . stay 《CLR via C#》 The author provides an example :
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Runtime.Remoting;
using System.Threading;
public sealed class Program {
public static void Main() {
Marshalling();
//FieldAccessTiming();
//AppDomainResourceMonitoring();
//UnloadTimeout.Go();
}
private static void Marshalling() {
// Get the default AppDomain
AppDomain adCallingThreadDomain = Thread.GetDomain();
// Show default name
String callingDomainName = adCallingThreadDomain.FriendlyName;
Console.WriteLine("Default AppDomain's friendly name={0}", callingDomainName);
// Show assembly name
String exeAssembly = Assembly.GetEntryAssembly().FullName;
Console.WriteLine("Main assembly={0}", exeAssembly);
// Define a local variable that can refer to an AppDomain
AppDomain ad2 = null;
// *** DEMO 1: By passing by reference AppDomain
Console.WriteLine("{0}Demo #1", Environment.NewLine);
// Create a new AppDomain, The first parameter represents the name , The second parameter represents AppDomain Safety decision setting for , The third parameter is zero AppDomain Basic settings of . by null,
// Represents the current default AppDomain identical
ad2 = AppDomain.CreateDomain("AD #2", null, null);
MarshalByRefType mbrt = null;
// Mount assembly , And create the specified instance , Then return
// here mbrt It's essentially a proxy
mbrt = (MarshalByRefType)ad2.CreateInstanceAndUnwrap(exeAssembly, "MarshalByRefType");
// The output here will be :MarshalByRefType,
Console.WriteLine("Type={0}", mbrt.GetType());
// But through the following sentence , You can get ,mbrt It's an agent
Console.WriteLine("Is proxy={0}", RemotingServices.IsTransparentProxy(mbrt));
// On the surface, , We called in the new AppDomain On mbrt Example method .
// But actually , The thread will jump to SomeMethod“ real ” Where defined , And carry out the implementation
mbrt.SomeMethod();
// uninstall
AppDomain.Unload(ad2);
//AppDomain After uninstalling , Proxy object mbrt There is still , however AppDomain Will no longer exist
// therefore , The following code calls again SomeMethod When the method is used , An exception will be thrown
try {
mbrt.SomeMethod();
Console.WriteLine("Successful call.");
}
catch (AppDomainUnloadedException) {
Console.WriteLine("Failed call.");
}
// *** DEMO 2: Pass by value
Console.WriteLine("{0}Demo #2", Environment.NewLine);
// Create new AppDomain (security & configuration match current AppDomain)
ad2 = AppDomain.CreateDomain("AD #2", null, null);
// Load our assembly into the new AppDomain, construct an object, marshal
// it back to our AD (we really get a reference to a proxy)
mbrt = (MarshalByRefType)
ad2.CreateInstanceAndUnwrap(exeAssembly, "MarshalByRefType");
// The object's method returns a COPY of the returned object;
// the object is marshaled by value (not be reference).
MarshalByValType mbvt = mbrt.MethodWithReturn();
// Prove that we did NOT get a reference to a proxy object
Console.WriteLine("Is proxy={0}", RemotingServices.IsTransparentProxy(mbvt));
// This looks like we're calling a method on MarshalByValType and we are.
Console.WriteLine("Returned object created " + mbvt.ToString());
// Unload the new AppDomain
AppDomain.Unload(ad2);
// mbvt refers to valid object; unloading the AppDomain has no impact.
try {
// We're calling a method on an object; no exception is thrown
Console.WriteLine("Returned object created " + mbvt.ToString());
Console.WriteLine("Successful call.");
}
catch (AppDomainUnloadedException) {
Console.WriteLine("Failed call.");
}
// DEMO 3: Cross-AppDomain Communication using non-marshalable type
Console.WriteLine("{0}Demo #3", Environment.NewLine);
// Create new AppDomain (security & configuration match current AppDomain)
ad2 = AppDomain.CreateDomain("AD #2", null, null);
// Load our assembly into the new AppDomain, construct an object, marshal
// it back to our AD (we really get a reference to a proxy)
mbrt = (MarshalByRefType)
ad2.CreateInstanceAndUnwrap(exeAssembly, "MarshalByRefType");
// The object's method returns an non-marshalable object; exception
NonMarshalableType nmt = mbrt.MethodArgAndReturn(callingDomainName);
// We won't get here...
}
}
// Instances can be marshaled-by-reference across AppDomain boundaries
public sealed class MarshalByRefType : MarshalByRefObject
{
public MarshalByRefType()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} ctor running in {1}",
this.GetType().ToString(), Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName);
}
public void SomeMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("Executing in " + Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName);
}
public MarshalByValType MethodWithReturn()
{
Console.WriteLine("Executing in " + Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName);
MarshalByValType t = new MarshalByValType();
return t;
}
public NonMarshalableType MethodArgAndReturn(String callingDomainName)
{
// NOTE: callingDomainName is [Serializable]
Console.WriteLine("Calling from '{0}' to '{1}'.",
callingDomainName, Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName);
NonMarshalableType t = new NonMarshalableType();
return t;
}
[DebuggerStepThrough]
public override Object InitializeLifetimeService()
{
return null; // We want an infinite lifetime
}
}
// Instances can be marshaled-by-value across AppDomain boundaries
[Serializable]
public sealed class MarshalByValType : Object
{
private DateTime m_creationTime = DateTime.Now; // NOTE: DateTime is [Serializable]
public MarshalByValType()
{
Console.WriteLine("{0} ctor running in {1}, Created on {2:D}",
this.GetType().ToString(),
Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName,
m_creationTime);
}
public override String ToString()
{
return m_creationTime.ToLongDateString();
}
}
// Instances cannot be marshaled across AppDomain boundaries
// [Serializable]
public sealed class NonMarshalableType : Object
{
public NonMarshalableType()
{
Console.WriteLine("Executing in " + Thread.GetDomain().FriendlyName);
}
}
Through the example above , It can be learned that :
If you want to pass an object, you can use it in different AppDomain Passed between , There are two ways :1、 Pass a local instance's “ copy ”, Is the agent mentioned above ( You actually only have a remote reference to this object , Although you can call its methods , But in fact, these operations are all remote ).2、 Copy a full version , And pass it on . This is the following example .Demo1 That's the first case ,Demo2 That's the second case .
边栏推荐
- Codeforces Round #641 Div2
- 如何快速完成磁盘分区
- 這個開源項目超哇塞,手寫照片在線生成
- Wandering -- the last programming challenge
- InnoDB in MySQL_ page_ Cleaners details
- MySQL中update一条record的过程
- Win32Exception (0x80004005): 组策略阻止了这个程序。要获取详细信息,请与系统管理员联系。
- Voir le classement des blogs pour csdn
- std::make_ shared<T>/std::make_ Unique < T> and std:: shared_ ptr<T>/std::unique_ The difference and relation between PTR < t >
- Call another interface button through win32API
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Codeforces Round #645 (Div. 2)
Weight recursion of complete binary tree -- the last programming challenge
C # use winexec to call exe program
如何快速完成磁盤分區
C语言库函数--strstr()
2019.11.20 training summary
Comment terminer rapidement une partition de disque
This open source project is super wow, and handwritten photos are generated Online
Nacos environmental isolation
在实践中学习Spark计算框架(01)
完全二叉树的权值 递归做法 ——最后的编程挑战
蛇形填数
2020-10-17:刷题1
How to quickly complete disk partitioning
HDU 6778 car (group enumeration -- > shape pressure DP)
1021 Deepest Root (25 分)
2019.10.30 learning summary
qgis制图
《CLR via C#》读书笔记-单实例应用程序
L2-025 分而治之 (25 分)