当前位置:网站首页>ROM of IP core
ROM of IP core
2022-07-27 06:10:00 【Three assassins】
ROM summary
ROM Read only memory (Read-Only Memory) For short , It is a solid-state semiconductor memory that can only read out the data stored in advance . Its characteristic is that once the data is stored, it can no longer be changed or deleted , And the data will not disappear because the power is turned off .

Single port ROM Interface signal

Dual port ROM Interface signal
Single port ROM Configuration of
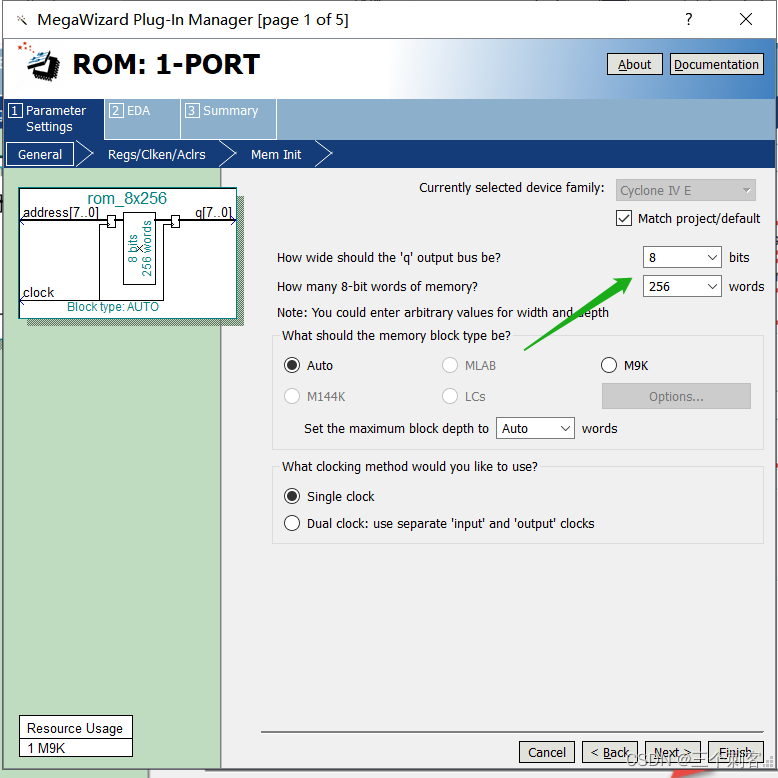
Select the clock mode to use , You can choose single clock or double clock . When selecting a single clock, use one clock to control all registers of the storage block , When double clock is selected, input clock control address register , Output clock control data output register .ROM Mode is not write enabled 、 Byte enable and data input registers . Here we choose the default option Single clock( Single clock ).

The figure above shows whether to output “q” register . Here we remove the register of the output port ( If not removed word , It will delay the output by one beat . If there is no special demand, we don't need to delay this shot ).
When not checked , The data output will delay the address input by one clock cycle , When checked , The clock signal will input a higher frequency , The data output will delay the address input for two clock cycles

The above figure shows adding a file path
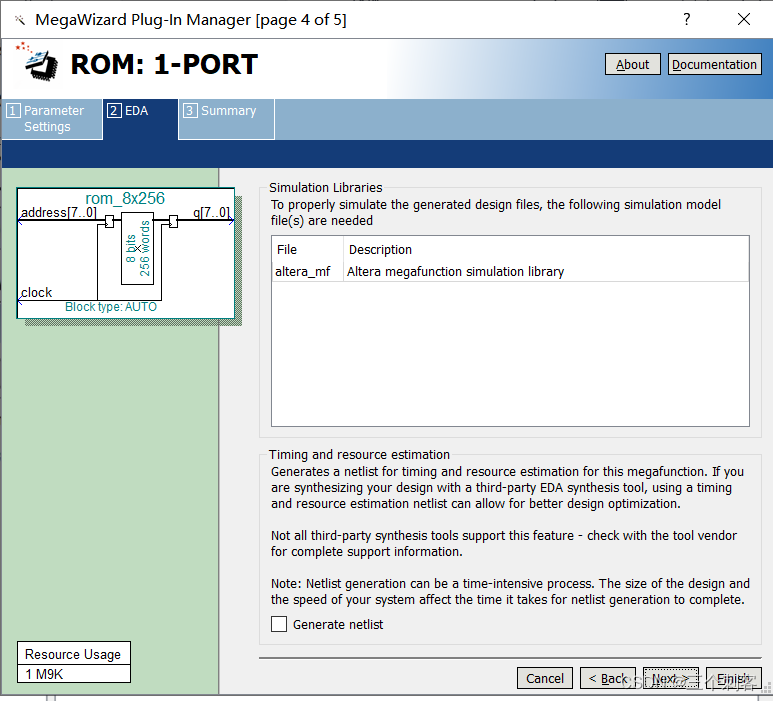

It reminds us that we need to add a third-party simulation tool named “altera_mf” The library of
Dual port ROM Configuration of

As a number of words” It is determined by the number of words ,“AS a number of bits” It is determined by the number of bits .
( Be careful : The selected capacity should be greater than the data volume of the data file we need to write

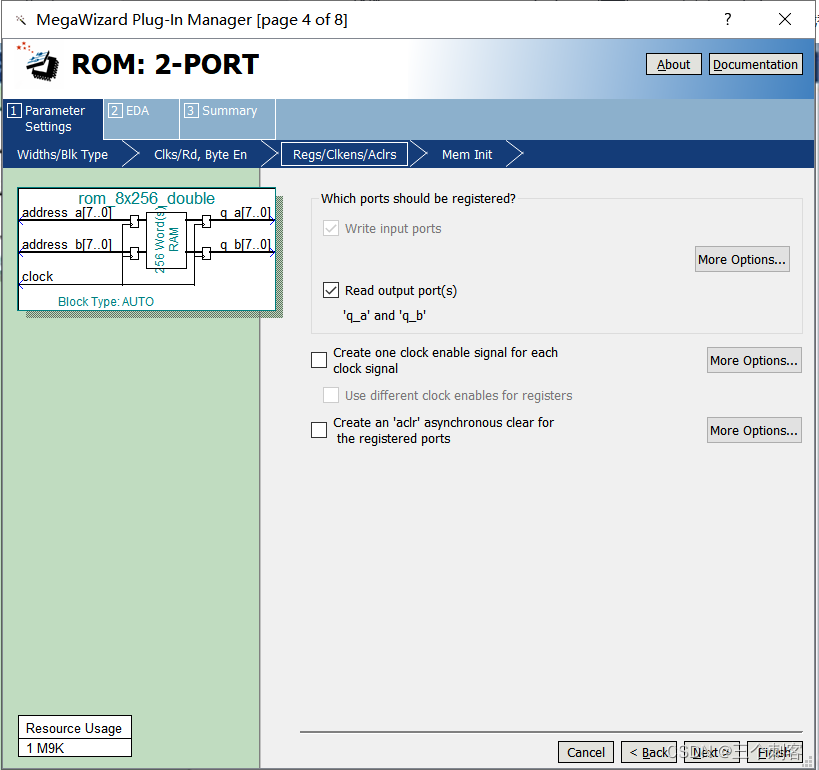

Single clock( Single clock ): Use a clock to control .
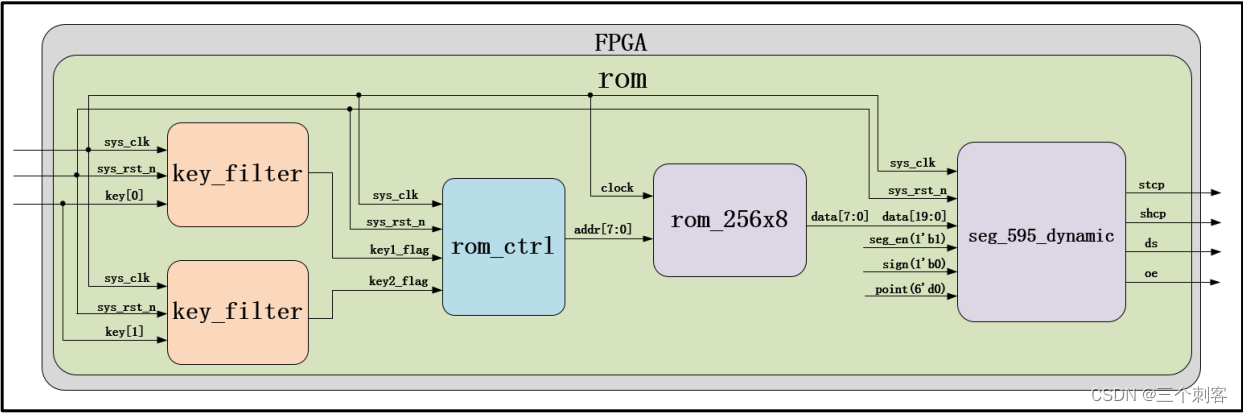

ROM IP Nuclear modules

ROM Control module


ROM Control module input and output signals
module rom_ctrl
#(
parameter CNT_MAX = 24'd9_999_999
)
(
input wire sys_clk ,
input wire sys_rst_n,
input wire key1 , // Key 1 Effective signal after chattering elimination
input wire key2 , // Key 2 Effective signal after chattering elimination
output reg [7:0] addr // Output read ROM Address
);
reg [23:0] cnt_200ms ;
reg key1_en; // Specific address 1 Sign signal
reg key2_en; // Specific address 2 Sign signal
//0.2s Cycle count
[email protected](posedge sys_clk or negedge sys_rst_n)
if(sys_rst_n == 1'b0)
cnt_200ms <= 24'd0;
else if(cnt_200ms == CNT_MAX || key1_en == 1'b1 || key2_en == 1'b1)
cnt_200ms <= 24'd0;
else
cnt_200ms <= cnt_200ms + 1'b1;
// Generate a specific address 1 Sign signal
[email protected](posedge sys_clk or negedge sys_rst_n)
if(sys_rst_n == 1'b0)
key1_en <= 1'b0;
else if(key2 == 1'b1)
key1_en <= 1'b0;
else if(key1 == 1'b1)
key1_en <= ~key1_en;
else
key1_en <= key1_en;
/ Generate a specific address 2 Sign signal
[email protected](posedge sys_clk or negedge sys_rst_n)
if(sys_rst_n == 1'b0)
key2_en <= 1'b0;
else if(key1 == 1'b1)
key2_en <= 1'b0;
else if(key2 == 1'b1)
key2_en <= ~key2_en;
else
key2_en <= key2_en;
// Let the address change from 0~255 loop , Two of the keys control the jump of two specific addresses
[email protected](posedge sys_clk or negedge sys_rst_n)
if(sys_rst_n == 1'b0)
addr <= 8'd0;
else if(addr == 8'd255 && cnt_200ms == CNT_MAX)
addr <= 8'd0;
else if(key1_en == 1'b1)
addr <= 8'd99;
else if(key2_en == 1'b1)
addr <=8'd199;
else if(cnt_200ms == CNT_MAX)
addr <= addr + 1'b1;
endmodule
Top level modules


module rom
(
input wire sys_clk,
input wire sys_rst_n,
input wire key1 ,
input wire key2 ,
output wire ds,
output wire oe,
output wire shcp,
output wire stcp
);
wire key1_flag; // Key 1 Dithering signal
wire key2_flag; // Key 2 Dithering signal
wire [7:0] addr;
wire [7:0] data; // read out ROM data
key_filter
#(
.CNT_MAX (20'd999_999)
)
key_filter_inst1
(
.sys_clk (sys_clk),
.sys_rst_n(sys_rst_n),
.key_in (key1),
.key_flag (key1_flag) //key_flag by 1 When, it means that the key is pressed after shaking elimination
);
key_filter
#(
.CNT_MAX (20'd999_999)
)
key_filter_inst2
(
.sys_clk (sys_clk),
.sys_rst_n(sys_rst_n),
.key_in (key2),
.key_flag (key2_flag) //key_flag by 1 When, it means that the key is pressed after shaking elimination
);
rom_ctrl
#(
.CNT_MAX (24'd9_999_999)
)
rom_ctrl_inst
(
.sys_clk (sys_clk),
.sys_rst_n(sys_rst_n),
.key1 (key1_flag), // Key 1 Effective signal after chattering elimination
.key2 (key2_flag), // Key 2 Effective signal after chattering elimination
.addr (addr) // Output read ROM Address
);
rom_8x256 rom_8x256_inst
(
.address ( addr ),
.clock ( sys_clk ),
.q ( data )
);
seg_595_dynamic seg_595_dynamic
(
.sys_clk (sys_clk),
.sys_rst_n(sys_rst_n),
.data ({12'b0,data}),
.point (6'b000_000), // Decimal point display , High active
.sign (1'b0), // Sign bit , The high level displays a negative sign
.seg_en (1'b1), // Nixie tube enable signal , High active
.ds (ds ), // Serial data input
.oe (oe ), // Output enable signal
.shcp (shcp), // Clock input of shift register
.stcp (stcp) // The output data is stored and sent to the clock
);
endmodule
RTL View

ROM IP Nuclear simulation
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module tb_rom();
reg sys_clk;
reg sys_rst_n;
reg key1;
reg key2;
wire ds;
wire oe;
wire shcp;
wire stcp;
initial
begin
sys_clk = 1'b1;
sys_rst_n <= 1'b0;
key1 <= 1'b1;
key2 <= 1'b1;
#20
sys_rst_n <= 1'b1;
#700000 // The simulation is 100 Clock cycles , One clock cycle 20ns, That's one
// The display time of the data is 100*20=2000ns,
//256 Data display time is 256*2000=512000ns, Therefore, the delay time needs to be greater than this value
//key1
key1 <= 1'b0;
#20
key1 <= 1'b1;
#20
key1 <= 1'b0;
#20
key1 <= 1'b1;
#20
key1 <= 1'b0;
#200 // The above is to simulate the jitter before pressing the key , The following is a simulation of the jitter after pressing a key
key1 <= 1'b1;
#20
key1 <= 1'b0;
#20
key1 <= 1'b1;
#20
key1 <= 1'b0;
#20
key1 <= 1'b1;
//key2
#20000
key2 <= 1'b0;
#20
key2 <= 1'b1;
#20
key2 <= 1'b0;
#20
key2 <= 1'b1;
#20
key2 <= 1'b0;
#200 // The above is to simulate the jitter before pressing the key , The following is a simulation of the jitter after pressing a key
key2 <= 1'b1;
#20
key2 <= 1'b0;
#20
key2 <= 1'b1;
#20
key2 <= 1'b0;
#20
key2 <= 1'b1;
//key2
#20000
key2 <= 1'b0;
#20
key2 <= 1'b1;
#20
key2 <= 1'b0;
#20
key2 <= 1'b1;
#20
key2 <= 1'b0;
#200 // The above is to simulate the jitter before pressing the key , The following is a simulation of the jitter after pressing a key
key2 <= 1'b1;
#20
key2 <= 1'b0;
#20
key2 <= 1'b1;
#20
key2 <= 1'b0;
#20
key2 <= 1'b1;
end
always #10 sys_clk = ~sys_clk;
//defparam rom_inst.key_filter_indt1.CNT_MAX = 9;
rom rom_inst
(
.sys_clk (sys_clk ),
.sys_rst_n(sys_rst_n),
.key1 (key1 ),
.key2 (key2 ),
.ds (ds ),
.oe (oe ),
.shcp (shcp ),
.stcp (stcp )
);
endmodule
Next, the simulation verifies
边栏推荐
- 判断是否为回文结构的三种方法
- [song] rebirth of me in py introductory training (9): exception handling
- Gbase 8C - SQL reference 6 SQL syntax (14)
- Summary of the use of C # Jason code in TCP communication
- [first song] rebirth of me in py introductory training (6): definition and application of functions
- 力扣 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- Baiwen driving Daquan learning (II) I2C driving
- [dynamic planning - steel bar cutting]
- 2022.6.10 stm32mp157 serial port clock learning
- 根据SQL必知必会学习SQL(MYSQL)
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
编程学习记录——第7课【函数】
力扣每日一题(链表模拟)
力扣题解 二叉树(5)
非重叠矩形中的随机点(力扣每日一题)
遥感影像识别-多类识别下的错分问题
PS 2022 updated in June, what new functions have been added
Code implementation and introduction of all commonly used sorting
[first song] rebirth of me in py introductory training (6): definition and application of functions
编程学习记录——第3课【初识C语言】
哈希表的原理及哈希冲突的解决方法
WebODM win10安装教程(亲测)
Li Kou daily question sword finger offer II 091. paint the house
pycharm安装及导入项目注意事项
力扣每日一题 剑指 Offer II 091. 粉刷房子
Kaggle调用自定义模块方法
SQL novice
剪枝-量化-转onnx中文系列教程
socket 长链接
[first song] rebirth of me in py introductory training (3): if conditional sentence
人月神话阅读笔记








![[5.20 special] MATLAB, I'm confessing to you](/img/ce/ea8697db3e10a216efc9ac5e0fad8d.png)
