当前位置:网站首页>Handwritten common interview questions
Handwritten common interview questions
2022-06-12 10:37:00 【dralexsanderl】
Handwritten common interview questions
Handwritten common interview questions
Shake proof
Anti shake function principle : When the event is triggered n Seconds before the callback , If in this n It's triggered in seconds , Then the time will be counted again .
There are two situations :
- Click to execute immediately
- Click not to execute immediately
// Non immediate execution
const debounce1 = (fn, delay) => {
let timer = null;
return (...args) => {
if(timer) clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args);
}, delay)
}
}
// Execute now
const debounce2 = (fn, delay) => {
let timer = null;
let emitNow = true;
return (...args) => {
if(timer) clearTimeout(timer);
if(emitNow) {
fn.apply(this, args);
emitNow = false;
} else {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args);
emitNow = true;
}, delay)
}
}
}
// Whether to execute immediately is controlled by parameters
const debounce3 = (fn, delay, isImmediate) => {
let timer = null;
let emitNow = true;
return (...args) => {
if(timer) clearTimeout(timer);
if(isImmediate) {
if(emitNow) {
fn.apply(this, args);
emitNow = false;
} else {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args);
emitNow = true;
}, delay)
}
} else {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args);
}, delay)
}
}
}
throttle
Anti shake function principle : Within one unit time , Function can only be triggered once . If multiple functions are triggered in this unit time , Only once .
There are two situations :
- Click to execute immediately
- Click not to execute immediately
// Non immediate execution
const throttle1 = (fn, delay) => {
let isEmit = false;
return (...args) => {
if(isEmit) return;
isEmit = true;
setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args);
isEmit = false;
}, delay);
}
}
// Execute now
const throttle2 = (fn, delay) => {
let isEmit = false;
return (...args) => {
if(isEmit) return;
isEmit = true;
fn.apply(this,args);
setTimeout(() => {
isEmit = false;
},delay);
}
}
// Whether to execute immediately is controlled by parameters
const throttle3 = (fn, delay, isImmediate) => {
let isEmit = false;
return (...args) => {
if(isEmit) return;
isEmit = true;
if(isImmediate) {
fn.apply(this, args);
setTimeout(() => {
isEmit = false;
},delay);
} else {
setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args);
isEmit = false;
}, delay);
}
}
}
A deep clone
function deepCopy(obj) {
if(typeof obj !== 'object') {
return obj;
};
let cloneObj = obj.constructor=== Array ? [] : {
};
for(let property in obj) {
cloneObj[property] = typeof obj[property] === 'object' ? deepCopy(obj[property]) : obj[property];
}
return cloneObj;
}
instanceOf
according to Prototype chain Knowledge , We can soon know that according to the object __proto__ Property to find its constructor .
const instanceOf = function(object, target) {
// Take the prototype object of the target
const instance = target.prototype;
// Take the implicit prototype of the object to be tested
object = object.__proto__;
while(true) {
if(!object) return false;
if(object === instance) return true;
object = object.__proto__;
}
}
new The operator
new The role of :
- Create a new object
- take
thisExecute the new object created - The new object created will be linked to the function
prototypeOn the object ( New object__proto__Property points to the functionprototype); - Using function call Method , Point the original to window Binding object of this Yes obj.( thus , When we pass the arguments to the function again , The properties of the object are mounted to obj On .)
function createObject() {
// Create a new object
const obj = {
};
// Get constructor , use call The method makes arguments Able to use shift Method takes the first parameter ( Constructors ) Take it out
const Constructor = [].shift.call(arguments);
// Put the object __proto__ Property is linked to the constructor prototype Properties of the
obj.__proto__ = Constructor.prototype;
// In the constructor this Point to an object and pass arguments
const result = Constructor.apply(obj, arguments);
// Make sure the return value is an object
return typeof ret === "object" ? result : obj;
}
Realization call Method
We all know call This method is used to modify this Point to , But some students may not understand the principle , Let's write one call Methods help to gain insight into how it works .
Function.prototype.mycall = function(context) {
// The default context is window
context = context || window;
// Add a property to hold the current call call Function of
context.fn = this;
// take arguments Convert to an array and remove the first parameter ( Context )
const args = [...arguments].slice(1);
// When a function is called in this way, the function's internal this It points to the caller (context);
const result = context.fn(...args);
delete context.fn;
return result;
}
Realization apply Method
apply Principle and call Very similar , The only difference is the problem of parameter transmission ,apply The second parameter of the method is an array of all the parameters , and call Method except that the first parameter is context Outside , Other parameters are passed in .
Function.prototype.myapply = function(context, arr) {
// The default context is window
context = context || window;
// Add a property to hold the current call call Function of
context.fn = this;
// take arguments Convert to an array and remove the first parameter ( Context )
let result;
if(!arr) {
result = context.fn();
} else {
result = context.fn(arr);
}
delete context.fn;
return result;
}
Realization bind Method
be relative to call and apply for ,bind The return value of the method is a change this Function of ( That is, it is not called immediately ). When the returned function is used as a constructor ,this invalid , But the parameters passed in are still valid .
bind() Method creates a new function . When this new function is called ,bind() The first parameter of will be the this, The following sequence of parameters will be passed in as its parameters before the passed arguments .
Function.prototype.mybind = function(context) {
if(typeof this !== 'function') {
throw new Error('Uncaught TypeError: not a function')
}
const args = [...arguments].slice(1);
// Used to record the current incoming function prototype;
let Transit = function() {
};
const _ = this;
const FunctionToBind = function() {
const bindArgs = [...arguments];
return _.apply(this instanceof Transit ? this : context, args.concat(bindArgs));
}
// Record the... Of the currently passed in function prototype;
Transit.prototype = this.prototype;
FunctionToBind.prototype = new Transit();
return FunctionToBind;
}
Realization Object.create Method
Object.create() Method creates a new object , Using an existing object to provide a newly created object __proto__.
grammar :
Object.create(proto[, propertiesObject])proto: must . Represents the prototype object of the new object , That is, the parameter will be assigned to the target object ( That is, the new object , Or the last returned object ) On the prototype of . The parameter can benull, object , Functionalprototypeattribute ( When creating an empty object, you need to passnull, Otherwise it will throwTypeErrorabnormal )propertiesObject: Optional . Enumerable properties added to the newly created object ( That is, its own properties , Instead of enumerating properties on the prototype chain ) The property descriptor of the object and the corresponding property name . These attributes correspond toObject.defineProperties()Second parameter of , The default attribute descriptor for creating non empty objects isfalseOf , The descriptor of an object property created by a constructor or literal method is assumed by default to betrue.
new The key word is to create objects through constructors , The added attribute is under its own instance .Object.create() Another way to create objects , It can be understood as inheriting an object , The added attribute is under the prototype .
// new Object() Way to create
var a = {
rep : 'apple' }
var b = new Object(a)
console.log(b) // {rep: "apple"}
console.log(b.__proto__) // {}
console.log(b.rep) // {rep: "apple"}
// Object.create() Way to create
var a = {
rep: 'apple' }
var b = Object.create(a)
console.log(b) // {}
console.log(b.__proto__) // {rep: "apple"}
console.log(b.rep) // {rep: "apple"}
So much for that Object.create Knowledge , Let's implement this method :
Object.prototype.mycreate = function(proto, propertiesObject) {
function F() {
};
F.prototype = proto;
const obj = new F();
if(propertiesObject) {
Object.defineProperties(obj, propertiesObject);
}
return obj
}
The implementation principle is to create an empty constructor and prototype Point to the incoming object , Finally, an instance of the constructor is returned .
Realization promise
const statusMap = {
PENDING: "pending",
FULFILLED: "fulfilled",
REJECTED: "rejected"
}
class MyPromise{
constructor(handler) {
if(Object.prototype.toString.call(handler) !== '[object Function]') {
throw new Error('the first parameter should be a function');
}
this.status = statusMap.PENDING;
this.result = null;
// Used to perform then Method
this.fulfilledQueues = [];
this.rejectedQueues = [];
try{
// Execute two methods
handler(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
} catch(err) {
this._reject(err);
}
}
_resolve(val) {
if(this.status !== statusMap.PENDING) return;
const run = () => {
this.status = statusMap.FULFILLED;
this.result = val;
let cb;
while(cb = this.fulfilledQueues.shift()) {
cb(val);
}
}
setTimeout(() => run(), 0);
}
_reject(err) {
if(this.status !== statusMap.PENDING) return;
const run = () => {
this.status = statusMap.REJECTED;
this.result = err;
let cb;
while(cb = this.rejectedQueues.shift()) {
cb(err);
}
}
setTimeout(() => run(), 0);
}
}
MyPromise.prototype.then = function(onFulfilled, onRejeceted) {
const {
status, result } = this;
return new MyPromise((onFulfilledNext, onRejecetedNext) => {
let fulfilled = value => {
try {
if(Object.prototype.toString.call(onFulfilled) !== '[object Function]') {
onFulfilledNext(value);
} else {
let res = onFulfilled(value);
// The return result is MyPromise Example
if(res instanceof MyPromise) {
res.then(onFulfilledNext, onRejecetedNext);
} else {
onFulfilledNext(res);
}
}
} catch(e) {
onRejecetedNext(e);
}
}
let rejected = error => {
try {
if(Object.prototype.toString.call(onRejeceted) !== '[Object Function]') {
onRejecetedNext(error);
} else {
let res = onRejeceted(error);
// The return result is MyPromise Example
if(res instanceof MyPromise) {
res.then(onFulfilledNext, onRejecetedNext);
} else {
onFulfilledNext(res);
}
}
} catch(e) {
onRejecetedNext(e);
}
}
switch(status) {
case statusMap.PENDING:
this.fulfilledQueues.push(fulfilled);
this.rejectedQueues.push(rejected)
break;
case statusMap.FULFILLED:
this.fulfilledQueues.push(fulfilled);
break;
case statusMap.REJECTED:
this.rejectedQueues.push(rejected);
break;
}
})
}
Flattening arrays
Array Methods flat Many browsers have not yet implemented , And the browser supports flat Method cannot handle nested arrays . Write a flat Method , Flat nested arrays .
// The simplest solution
Array.prototype.flat = function (arr) {
return arr
.toString()
.split(',')
.map((item) => +item);
};
Array.prototype.flat = function (arr) {
return arr.reduce((prev, item) => {
return prev.concat(Array.isArray(item) ? flatten(item) : item);
}, []);
};
Array weight removal
For removal 1 Repeat more than times item, have access to Set.
function delRepeat(arr) {
return Array.from(new Set(arr));
}
But remove 2 You can't use it more than times set 了 .
// Known array
var arr = [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,3,3,3,3,3,5,5];
// Method 1
function delRepeat(arr) {
arr = arr.sort();
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == arr[i + 2]) {
arr.splice(i, 1);
i--;
}
}
return arr;
}
// Method 2
function delRepeat(arr) {
var newArr = [];
var obj = {
};
arr.map((item) => {
if (obj[item]) {
obj[item] += 1;
} else {
obj[item] = 1;
}
obj[item] <= 2 ? newArr.push(item) : '';
});
return newArr;
}
Code address :https://github.com/leopord-lau/EasyPresentation
边栏推荐
- JS obtains the time period of this week and last week (one time period is from Monday to Sunday)
- Class selectors and using pseudo class selectors with
- PHP occupies memory
- Leetcode 2169. Get operands of 0
- The name of a great man
- Chromebook system without anti-virus software
- Error during session start; please check your PHP and/or webserver log file and configure your PHP
- 2022京東618預售定金怎麼退?京東618定金能退嗎?
- ID obfuscation
- CTF freshman cup PHP deserialization question - EzPop
猜你喜欢

使用cpolar远程办公(2)

The most detailed explanation of the top ten levels of sqli labs platform

人脸识别pip 安装dlib库失败
CONDA install tensorflow test tensorflow

Remote desktop cannot copy and paste solution

How to refund the pre-sale deposit of JD 618 in 2022? Can JD 618 deposit be refunded?

2022 Taobao 618 Super Cat Games introduction 618 super cat games playing skills
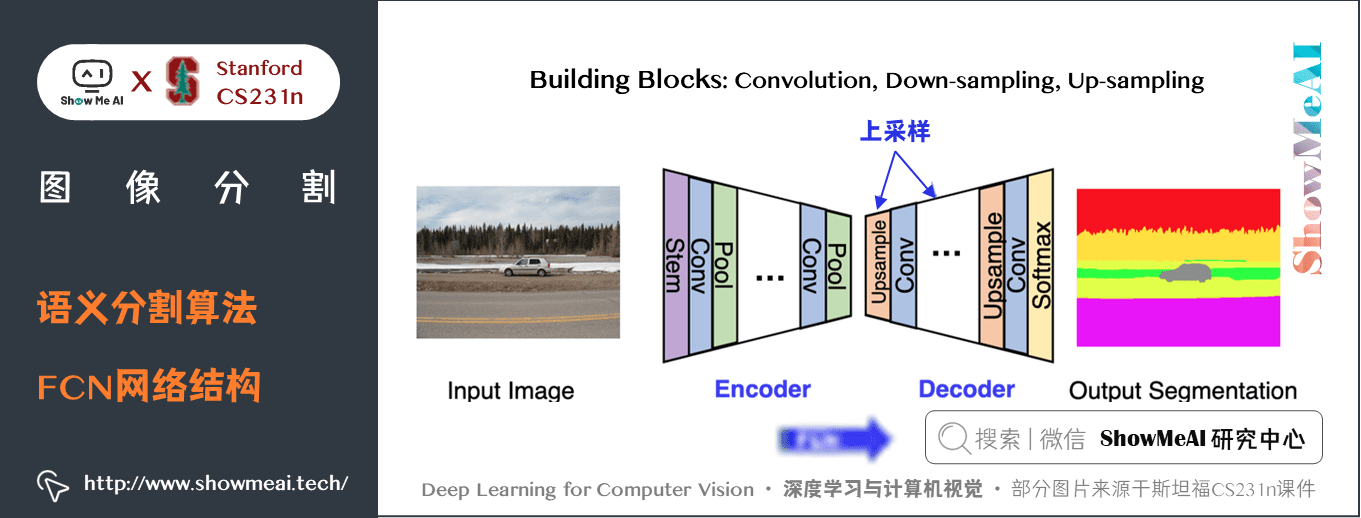
深度学习与CV教程(14) | 图像分割 (FCN,SegNet,U-Net,PSPNet,DeepLab,RefineNet)

2022淘宝618超级喵运会怎么玩?2022淘宝618喵运会玩法技巧

4. creator mode
随机推荐
Love and hate in the Jianghu
ASP. Net core permission system practice (zero)
Malicious code analysis practice -- using apatedns and inetsim to simulate network environment
Leetcode2154. 将找到的值乘以 2(二分查找)
Chromebook system without anti-virus software
Valentina Studio Pro for Mac(mac数据库管理软件)
Tp6+memcached configuration
93. obtain all IP addresses of the Intranet
MySQL implements split method
浅谈调和形状上下文特征HSC对3DSC的改进
Malicious code analysis practice - lab03-03 Exe basic dynamic analysis
93. Obtenir toutes les adresses IP de l'Intranet
Class. Forname connection MySQL driver keeps throwing classnotfoundexception exception solution
properties中文乱码
Solution to the problem that the applet developer tool cannot input simplified Chinese
conda 安装tensorflow 测试tensorflow
The difference between static method locking and non static method locking
PHP occupies memory
JS open common application market
Leetcdoe 2037. Make each student have the minimum number of seat movements (yes, once)