当前位置:网站首页>NDK learning notes (IX) POSIX sockect connection oriented communication
NDK learning notes (IX) POSIX sockect connection oriented communication
2022-06-11 05:34:00 【Come and go】
List of articles
1.sockect Function introduction
__af: Specify the... That will generate communication socket Domain , And select the protocol cluster to be used .
android Protocol clusters supported by the platform :
PF_LOCAL: Host internal communication protocol cluster
PF_INET:internet The first 4 Version protocol cluster , Corresponding ipv4
__type:
SOCK_STREAM: Provide use TCP Agreed 、 Connection oriented communication Stream socket type .
SOCK_DGRAM: Provide use UDP Agreed 、 Connectionless communication Datagram socket type .
__protocol: Specify the protocol to be used . Select the default protocol , This parameter can be set to zero .
If created successfully , Returns the relevant socket The descriptor ; Failure returns -1
__socketcall int socket(int __af, int __type, int __protocol);
__fd: Specifies the... That will be bound to the specified address socket example
__addr: Specify the protocol address
__addr_length: Specifies the size of the protocol address structure passed to the function
Bind address successfully , return 0, Otherwise return to -1
__socketcall int bind(int __fd, const struct sockaddr* __addr, socklen_t __addr_length);
Network byte sort
On the hardware layer , Different machine architectures use different data ordering and presentation rules , This is called machine byte ordering or byte ordering .
- BIG-endian Byte order stores the most important bytes first .
- Little-endian Byte order stores the least important bytes first .
To enable machines with different byte ordering rules to communicate over the Internet ,IP take big-endian Byte sorting is declared as the official data transmission network byte sorting rule .
java Virtual machines do not execute native components , Use machine byte sorting .
- ARM and x86 The machine structure uses little-endian Byte sort
- MIPS The machine structure uses big-endian Byte sort
In network communication , Native code needs to do the necessary conversion between machine byte sorting and network byte sorting .
endian.h Enables native applications to transparently handle byte sort conversions .
#include <sys/endian.h>
endian.h Function introduction in :
htons() take unsigned short Convert from host byte sort to network byte sort .
ntohs() and htons The function is the opposite , take unsigned short Convert from network byte sort to host byte sort .
htonl() take unsigned integer Convert from host byte sort to network byte sort .
ntohl() and htonl The function is the opposite , take unsigned integer Convert from network byte sort to host byte sort .
Listen for incoming connections
__fd: Specify the input connections that the application wants to listen on socjet example
__backlog: Specifies the size of the queue that holds the pending input connections .
success , return 0, Failure to return -1
__socketcall int listen(int __fd, int __backlog);
Accept incoming connections
accept It's a blocking function .
__fd:socket example
__addr: Address structure , Fill in the structure with connected kehu Customer agreement address , If the application does not need to change the information , It can be set to null.
__addr_length: The connection client protocol address provides a specified size of memory space . If this information is not required , It can be set to NULL.
If accept Ask Chen Gong , This function returns the client that will be used when interacting with the connection instance socket The descriptor ; otherwise , return -1
__socketcall int accept(int __fd, struct sockaddr* __addr, socklen_t* __addr_length);
Receive data
recv Function is a blocking function
__fd:socket example
__buf: Pointer to memory address , This memory is used to store data from socket Data received .
__n: Specifies the size of the buffer
__flags: Specify the additional flags required for acceptance
success , Return from socket The number of bytes received there , Otherwise return to -1.
return 0 Express socket The connection fails
ssize_t recv(int __fd, void* __buf, size_t __n, int __flags);
send data
Blocking function
__fd:socket example
__buf: Points to the memory address buffer The pointer ,
__n: Specifies the size of the buffer
__flags: Additional signs
Send successfully ,send The function returns the number of bytes transferred , Otherwise return to -1. return 0 The connection fails
ssize_t send(int __fd, const void* __buf, size_t __n, int __flags);
client
Connect
__fd:socket example
__addr: Address
__addr_length: Address structure length
success 0, Failure -1
__socketcall int connect(int __fd, const struct sockaddr* __addr, socklen_t __addr_length);
2.Socket Example
Because the amount of code is not easy to show in the blog , So it was put in gitee On .
https://gitee.com/xd_box/NDK_Socket
This example needs to be run with two simulators to see the effect .
After starting the simulator , A running EchoServerActivity Interface , A running EchoClientActivity Interface .
Connectivity simulator :
emulator-5554 Is to run EchoServerActivity Interface simulator
adb -s emulator-5554 forward tcp:12345 tcp:12346
The operation effect is as follows 
边栏推荐
- WinForm (II) advanced WinForm and use of complex controls
- Zed2 camera manual
- Wechat applet, automatic line feed for purchasing commodity attributes, fixed number of divs, automatic line feed for excess parts
- Combination sum Ⅳ -- leetcode exercise
- wxParse解析iframe播放视频
- mysql字符串转数组,合并结果集,转成数组
- 6 questions to ask when selecting a digital asset custodian
- 推荐一款免费的内网穿透开源软件,可以在测试本地开发微信公众号使用
- QT Road (1) -- Introduction to pro file
- 微信小程序,购买商品属性自动换行,固定div个数,超出部分自动换行
猜你喜欢

Analyze while doing experiments -ndk article -jni uses registernatives for explicit method registration

How to make lamps intelligent? How to choose single fire and zero fire intelligent switches!

Deep search + backtracking
微信自定义组件---样式--插槽

In the future, how long will robots or AI have human creativity?

jvm调优五:jvm调优工具和调优实战

Games101 job 7-path tracing implementation process & detailed interpretation of code

How much current can PCB wiring carry

深度学习分布式训练
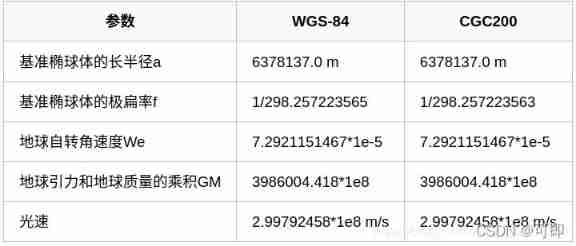
Conversion relationship between coordinate systems (ECEF, LLA, ENU)
随机推荐
使用acme.sh自动申请免费SSL证书
[project - what are the supporting materials in the annexes? (18 kinds of 2000 word summary)] project plan of innovation and entrepreneurship competition and supporting materials of Challenge Cup entr
35. search insertion position
KD-Tree and LSH
Section II: structural composition characteristics of asphalt pavement (2) structural layer and performance requirements
Opencv learning path (2-2) -- Deep parsing namedwindow function
Deep learning distributed training
How to make lamps intelligent? How to choose single fire and zero fire intelligent switches!
getBackgroundAudioManager控制音乐播放(类名的动态绑定)
Minimize maximum
wxParse解析iframe播放视频
截取文件扩展名
Preliminary test of running vins-fusion with zed2 binocular camera
Multi threading tutorial (XXIV) cas+volatile
Some details about memory
Zed2 camera manual
工具类ObjectUtil常用的方法
Section V: Recycling Application of asphalt pavement materials
Recherche sur l'optimisation de Spark SQL basée sur CBO pour kangourou Cloud Stack
The programmers of a large factory after 95 were dissatisfied with the department leaders, and were sentenced for deleting the database and running away