当前位置:网站首页>学会使用LiveData和ViewModel,我相信会让你在写业务时变得轻松
学会使用LiveData和ViewModel,我相信会让你在写业务时变得轻松
2022-07-01 13:19:00 【InfoQ】
前言:
介绍
LiveData和ViewModel的关系:

LiveData
使用 LiveData 具有以下优势:
- UI与数据状态匹配
- LiveData 遵循观察者模式。当底层数据发生变化时,LiveData 会通知
Observer对象。您可以整合代码以在这些Observer对象中更新界面。这样一来,您无需在每次应用数据发生变化时更新界面,因为观察者会替您完成更新。
- 提高代码的稳定性
- 代码稳定性在整个应用程序生命周期中增加:
- 活动停止时不会发生崩溃。如果应用程序组件处于非活动状态,则这些更改不受影响。因此,您在更新数据时无需担心应用程序组件的生命周期。对于后台堆栈中的活动,它不会接受任何LiveData事件
- 内存泄漏会减少,观察者会绑定到Lifecycle对象,并在其关联的生命周期遭到销毁后进行自我清理
- 取消订阅任何观察者时无需担心
- 如果由于配置更改(如设备旋转)而重新创建了 Activity 或 Fragment,它会立即接收最新的可用数据。
- 不再需要手动处理生命周期
- 界面组件只是观察相关数据,不会停止或恢复观察。LiveData 将自动管理所有这些操作,因为它在观察时可以感知相关的生命周期状态变化。
- 数据始终保持最新状态
- 如果生命周期变为非活跃状态,它会在再次变为活跃状态时接收最新的数据。例如,曾经在后台的 Activity 会在返回前台后立即接收最新的数据。
- 共享资源
- 像单例模式一样,我们也可以扩展我们的LiveData对象来包装系统服务,以便它们可以在我们的应用程序中共享。一旦LiveData对象连接到系统服务,任何需要资源的观察者可以轻松地观看LiveData对象。
在以下情况中,不要使用LiveData:
- 您需要在信息上使用大量运算符,尽管LiveData提供了诸如转换之类的工具,但只有Map和switchMap可以帮助您
- 您没有与信息的UI交互
- 您有一次性的异步操作
- 您不必将缓存的信息保存到UI中
如何使用LiveData
基础使用流程:
class MainViewModel : ViewModel() {
var mycount: MutableLiveData<Int> = MutableLiveData()
}
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
lateinit var viewModel: MainViewModel
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
...
/**记住绝对不可以直接去创建ViewModel实例
一定要通过ViewModelProvider(ViewModelStoreOwner)构造函数来获取。
因为每次旋转屏幕都会重新调用onCreate()方法,如果每次都创建新的实例的话就无法保存数据了。
用上述方法后,onCreate方法被再次调用,
它会返回一个与MainActivity相关联的预先存在的ViewModel,这就是保存数据的原因。*/
viewModel = ViewModelProvider([email protected],ViewModelProvider.
NewInstanceFactory()).get(MainViewModel::class.java)
}
}
/**
* 订阅 ViewModel,mycount是一个LiveData类型 可以观察
* */
viewModel.mycount.observe([email protected]) {
countTv.text = viewModel.mycount.value.toString()
}
// LiveData onchange会自动感应生命周期 不需要手动
// viewModel.mycount.observe(this, object : Observer<Int> {
// override fun onChanged(t: Int?) {
//
// }
// })
进阶用法:
//实体类
data class User(var name: String)
...
//Transformations.map接收两个参数,第一个参数是用于转换的LiveData原始对象,第二个参数是转换函数。
private val userLiveData: MutableLiveData<User> = MutableLiveData()
val userNames: LiveData<String> = Transformations
.map(userLiveData) { user ->
user.name
}
data class Student
(var englishScore: Double, var mathScore: Double, val scoreTAG: Boolean)
.....
class SwitchMapViewModel:ViewModel {
var studentLiveData = MutableLiveData<Student>()
val transformationsLiveData = Transformations.switchMap(studentLiveData) {
if (it.scoreTAG) {
MutableLiveData(it.englishScore)
} else {
MutableLiveData(it.mathScore)
}
}
}
//使用时:
var student = Student()
person.englishScore = 88.2
person.mathScore = 91.3
//判断显示哪个成绩
person.condition = true
switchMapViewModel.conditionLiveData.postValue(person)
class MediatorLiveDataViewModel : ViewModel() {
var liveDataA = MutableLiveData<String>()
var liveDataB = MutableLiveData<String>()
var mediatorLiveData = MediatorLiveData<String>()
init {
mediatorLiveData.addSource(liveDataA) {
Log.d("This is livedataA", it)
mediatorLiveData.postValue(it)
}
mediatorLiveData.addSource(liveDataB) {
Log.d("This is livedataB", it)
mediatorLiveData.postValue(it)
}
}
}
解释:
- MutableLiveData的父类是LiveData
- LiveData在实体类里可以通知指定某个字段的数据更新
- MutableLiveData则是完全是整个实体类或者数据类型变化后才通知.不会细节到某个字段。
原理探究:
- LiveData的工作原理
- LiveData的observe方法源码分析
- LifecycleBoundObserver源码分析
- activeStateChanged源码分析(用于粘性事件)
- postValue和setValue
- considerNotify判断是否发送数据分析
- 粘性事件的分析
ViewModel
官方简介
生命周期

基础使用流程:
class MainViewModel : ViewModel() {
...
}
//第一种 ViewModelProvider直接获取
ViewModelProvider([email protected]).get(MainViewModel::class.java)
//第二种 通过 ViewModelFactory 创建
class TestViewModelFactory(private val param: Int) : ViewModelProvider.Factory {
override fun <T : ViewModel> create(modelClass: Class<T>): T {
return TestViewModel(param) as T
}
}
ViewModelProvider([email protected],TestViewModelFactory(0)).get(TestViewModel::class.java)
ViewModel常见的使用场景
- 使用ViewModel,在横竖屏切换后,Activity重建,数据仍可以保存
- 同一个Activity下,Fragment之间的数据共享
- 与LiveData配合实现代码的解耦
ViewModel和onSaveInstanceState的区别
ViewModel和Context
案例一:计数器 — 两个Activity共享一个ViewModel

import androidx.lifecycle.LiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.MutableLiveData
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
class MainViewModel : ViewModel() {
private var _mycount: MutableLiveData<Int> = MutableLiveData()
//只暴露不可变的LiveData给外部
val mycount: LiveData<Int> get() = _mycount
init {
//初始化
_mycount.value = 0
}
/**
* mycount.value若为空就赋值为0,不为空则加一
* */
fun add() {
_mycount.value = _mycount.value?.plus(1)
}
/**
* mycount.value若为空就赋值为0,不为空则减一,可以为负数
* */
fun reduce() {
_mycount.value = _mycount.value?.minus(1)
}
/**
* 随机参数
* */
fun random() {
val random = (0..100).random()
_mycount.value = random
}
/**
* 清除数据
* */
fun clear() {
_mycount.value = 0
}
}
import androidx.lifecycle.*
/**
* 用于标记viewmodel的作用域
*/
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
@Target(AnnotationTarget.FIELD)
annotation
class VMScope(val scopeName: String) {}
private val vMStores = HashMap<String, VMStore>()
fun LifecycleOwner.injectViewModel() {
//根据作用域创建商店
this::class.java.declaredFields.forEach { field ->
field.getAnnotation(VMScope::class.java)?.also { scope ->
val element = scope.scopeName
var store: VMStore
if (vMStores.keys.contains(element)) {
store = vMStores[element]!!
} else {
store = VMStore()
vMStores[element] = store
}
val clazz = field.type as Class<ViewModel>
val vm = ViewModelProvider(store, ViewModelProvider.NewInstanceFactory()).get(clazz)
field.set(this, vm)
}
}
}
class VMStore : ViewModelStoreOwner {
private var vmStore: ViewModelStore? = null
override fun getViewModelStore(): ViewModelStore {
if (vmStore == null)
vmStore = ViewModelStore()
return vmStore!!
}
}
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
@VMScope("count") //设置作用域
lateinit var viewModel: MainViewModel
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
injectViewModel()
initEvent()
}
private fun initEvent() {
val cardReduce: CardView = findViewById(R.id.card_reduce)
.....
cardReduce.setOnClickListener {
//调用自定义ViewModel中的方法
viewModel.reduce()
}
.....
/**
* 订阅 ViewModel,mycount是一个LiveData类型 可以观察
* */
viewModel.mycount.observe([email protected]) {
countTv.text = viewModel.mycount.value.toString()
}
}
在第二个Activity中也是类似...
案例二:同一个Activity下的两个Fragment共享一个ViewModel
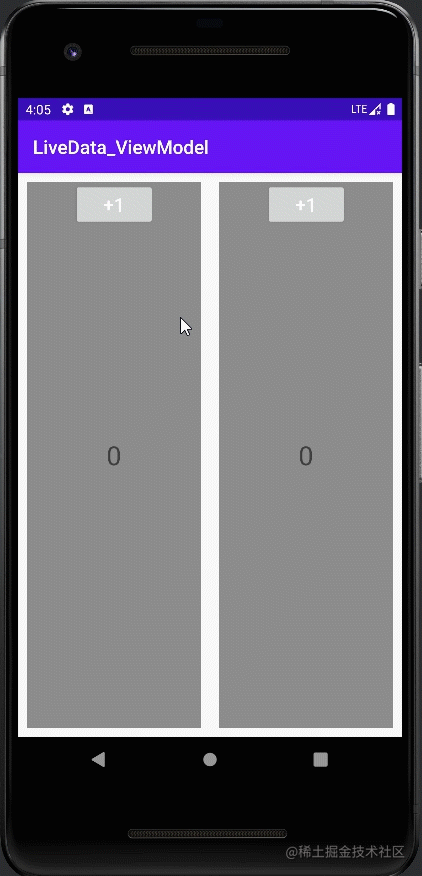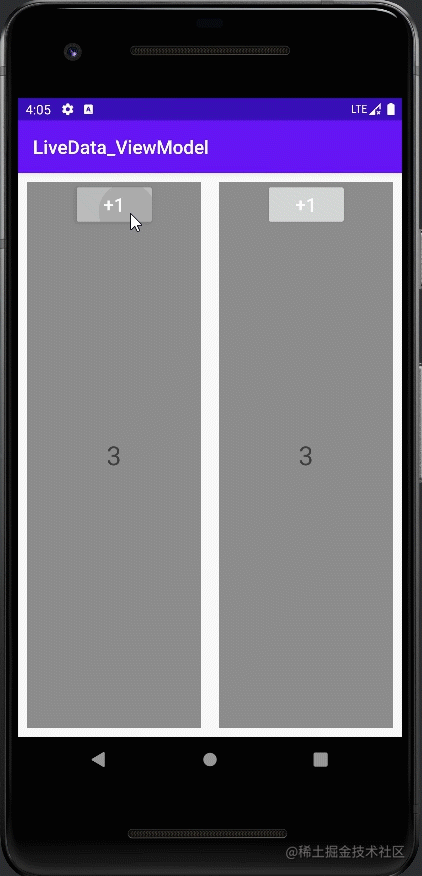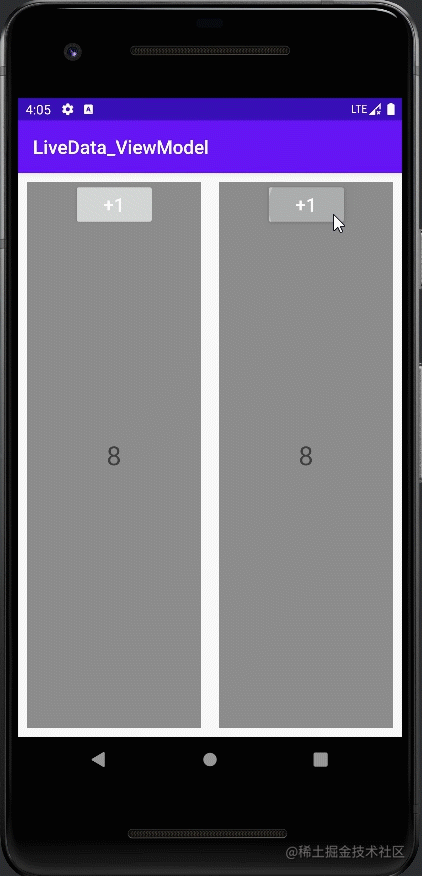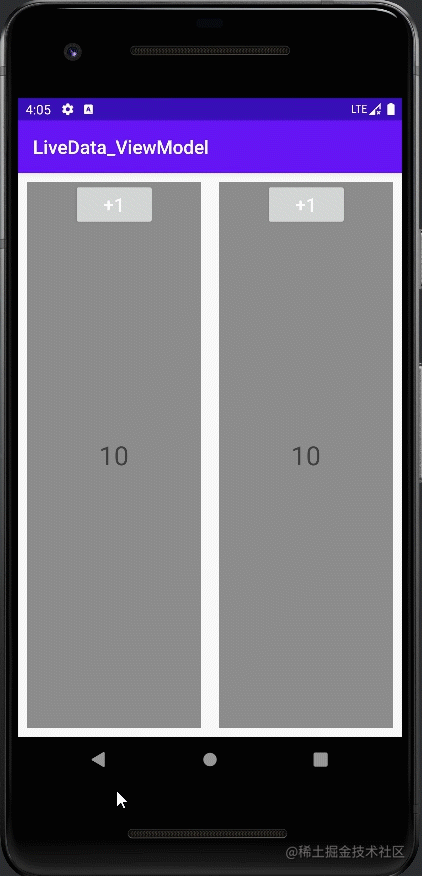
class BlankViewModel : ViewModel() {
private val numberLiveData = MutableLiveData<Int>()
private var i = 0
fun getLiveData(): LiveData<Int> {
return numberLiveData
}
fun addOne(){
i++
numberLiveData.value = i
}
}
//左Fragment
class LeftFragment : Fragment() {
private val viewModel:BlankViewModel by activityViewModels()
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_left, container, false)
}
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState)
//对+1按钮监听
left_button.setOnClickListener {
viewModel.addOne()
}
activity?.let {it ->
viewModel.getLiveData().observe(it){
left_text.text = it.toString()
}
}
}
}
//右Fragment
class RightFragment : Fragment() {
private val viewModel: BlankViewModel by activityViewModels()
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_right, container, false)
}
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState)
right_button.setOnClickListener {
viewModel.addOne()
}
activity?.let { it ->
viewModel.getLiveData().observe(it) {
right_text.text = it.toString()
}
}
}
}
尾述
关于我
边栏推荐
- 面试题目总结(1) https中间人攻击,ConcurrentHashMap的原理 ,serialVersionUID常量,redis单线程,
- 陈宇(Aqua)-安全-&gt;云安全-&gt;多云安全
- La taille de la pile spécifiée est petite, spécifiée à la sortie 328k
- ArrayList扩容机制以及线程安全性
- 1.8新特性-List
- Grafana reports an error: error= "failed to send notification to email addresses: [email protected] : 535 Error:
- 6. Wiper part
- Yarn restart applications record recovery
- Introduction to reverse debugging PE structure input table output table 05/07
- 1.8 new features list
猜你喜欢

Detailed explanation of OSPF LSA of routing Foundation

Anti fraud, refusing to gamble, safe payment | there are many online investment scams, so it's impossible to make money like this

5G工业网关的科技治超应用 超限超重超速非现场联合执法
![[Niu Ke's questions -sql big factory interview real questions] no2 User growth scenario (a certain degree of information flow)](/img/a0/e9e7506c9c34986dc73562539c8410.png)
[Niu Ke's questions -sql big factory interview real questions] no2 User growth scenario (a certain degree of information flow)

Jenkins+webhooks-多分支参数化构建-

JS discolored Lego building blocks

04 redis source code data structure dictionary

香港科技大学李泽湘教授:我错了,为什么工程意识比上最好的大学都重要?

详细讲解面试的 IO多路复用,select,poll,epoll

Chen Yu (Aqua) - Safety - & gt; Cloud Security - & gt; Multicloud security
随机推荐
Apache-Atlas-2.2.0 独立编译部署
Declare an abstract class vehicle, which contains the private variable numofwheel and the public functions vehicle (int), horn (), setnumofwheel (int) and getnumofwheel (). Subclass mot
Terminal identification technology and management technology
The 14th five year plan of China's environmental protection industry and the report on the long-term goals for 2035 Ⓖ 2022 ~ 2028
Detailed explanation of OSPF LSA of routing Foundation
洞态在某互联⽹⾦融科技企业的最佳落地实践
商汤科技崩盘 :IPO时已写好的剧本
Global and Chinese n-butanol acetic acid market development trend and prospect forecast report Ⓧ 2022 ~ 2028
Meta enlarge again! VR new model posted on CVPR oral: read and understand voice like a human
【大型电商项目开发】性能压测-压力测试基本概念&JMeter-38
学历、长相、家境普通的人,未来的发展方向是什么?00后的职业规划都已经整得明明白白......
leetcode 322. Coin Change 零钱兑换(中等)
spark源码(五)DAGScheduler TaskScheduler如何配合提交任务,application、job、stage、taskset、task对应关系是什么?
内容审计技术
运行游戏时出现0xc000007b错误的解决方法[通俗易懂]
Different test techniques
arthas使用
word2vec训练中文词向量
Several models of IO blocking, non blocking, IO multiplexing, signal driven and asynchronous IO
Reasons for MySQL reporting 1040too many connections and Solutions