当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to internet protocol -- five layer model
Introduction to internet protocol -- five layer model
2022-06-21 20:41:00 【Tan.] der】
zero 、 Preface
We use the Internet every day , Have you ever thought about , How it is realized ?
Billions of computers around the world , come together , Two to two correspondence . A network card in Shanghai sends out signals , Another network card in Los Angeles actually received , They don't actually know each other's physical location , Don't you think it's amazing ?
The core of the Internet is a series of protocols , It's called " Internet Protocol "(Internet Protocol Suite). How they connect and network computers , Made detailed rules . Understanding these agreements , I understand the principle of the Internet .
Because these agreements are so complicated 、 Too big . To make it easy to understand , A lot of simplification , Some places are not comprehensive and precise , But we should be able to explain the principle of the Internet .
One 、 summary
1.1 Five layer model
The realization of the Internet , It's divided into layers . Each layer has its own functions , It's like a building , Each layer is supported by the next layer .
What users are exposed to , It's just the top layer , I didn't feel the underlying layer at all . Understand the Internet , It has to start at the bottom , Understand the function of each layer from the bottom up .
How to layer has different models , Some models are divided into seven layers , Some are divided into four layers . I think , Divide the Internet into five layers , It's easier to explain .
As shown in the figure above , The bottom layer is called " Physical layer "(Physical Layer), The top layer is called " application layer "(Application Layer), The middle three layers ( Bottom up ) Namely " Link layer "(Link Layer)、“ The network layer ”(Network Layer) and " Transport layer "(Transport Layer). The lower layer , Closer to the hardware ; Over the top layer , Closer to the user .
What are their names , It doesn't matter . Just need to know , The Internet can be divided into several layers .
1.2 Layers and agreements
Each layer is to complete a function . To achieve these functions , We need to follow the same rules .
The rules that everybody follows , It's called " agreement "(protocol).
Every layer of the Internet , A lot of agreements are defined . The collective name of these agreements , It's called " Internet Protocol "(Internet Protocol Suite). They are the core of the Internet , The functions of each layer are described below , It mainly introduces the main protocols of each layer .
Two 、 Physical layer
We start from the bottom floor .
Computers need to be networked , What's the first thing ? Of course, connect the computers first , You can use fiber optic cables 、 cable 、 Twisted pair 、 Radio waves, etc .
This is called " Physical layer ", It's the physical means of connecting computers . It mainly specifies some electrical characteristics of the network , The function is to transmit 0 and 1 The electrical signal of .
3、 ... and 、 Link layer
3.1 Definition
pure 0 and 1 It doesn't make any sense , There has to be a way of reading : How many electrical signals are in a group ? What is the meaning of each signal bit ?
This is it. " Link layer " The function of , It's in " Physical layer " On top of , To determine the 0 and 1 In groups .
3.2 Ethernet protocol
In the early days , Each company has its own electrical signal grouping method . Gradually, , One is called " Ethernet "(Ethernet) The agreement , Take the lead .
Ethernet rules , A group of electrical signals constitutes a packet , be called " frame "(Frame). Each frame is divided into two parts : header (Head) And data (Data).

" header " Contains some instructions for the package , Like the sender 、 The recipient 、 Data types and so on ;" data " Is the specific content of the packet .
" header " The length of , Fixed for 18 byte ." data " The length of , The shortest is 46 byte , The longest is 1500 byte . therefore , Whole " frame " The shortest is 64 byte , The longest is 1518 byte . If the data is long , It must be divided into multiple frames for transmission .
3.3 MAC Address
above-mentioned , Ethernet packets " header ", Contains sender and receiver information . that , How are senders and receivers identified ?
Ethernet rules , All devices connected to the network , All must have " network card " Interface . The packet must be from a network card , Transfer to another network card . Address of network card , It is the sending address and receiving address of the packet , It's called MAC Address .

When each network card leaves the factory , There is a unique MAC Address , The length is 48 Binary bits , Usually use 12 Hexadecimal numbers mean .
front 6 A hexadecimal number is the manufacturer number , after 6 One is the serial number of the manufacturer's network card . With MAC Address , You can locate the network card and packet path .
3.4 radio broadcast
Defining an address is just the first step , There are more steps to follow .
First , How can a network card know another network card MAC Address ?
The answer is that there is a ARP agreement , Can solve this problem . This is left for later introduction , All we need to know here is , Ethernet packets must know the receiver's MAC Address , And then send .
secondly , Even if there is MAC Address , How can the system send the data package to the receiver accurately ?
The answer is that Ethernet uses a very " original " The way , It's not exactly sending packets to the receiver , But to all computers in the network , Let each computer judge by itself , Is it the receiver .

Above picture ,1 Computer No 2 Computer sent a packet , Of the same subnet 3 Number 、4 Number 、5 Computers will receive this package . They read the " header ", Find the receiver's MAC Address , And then with their own MAC Address compared to , If they are the same , Just accept this package , Do further processing , Otherwise, discard the package . This way of sending is called " radio broadcast "(broadcasting).
With the definition of packets 、 NIC MAC Address 、 The way of broadcasting ," Link layer " You can transfer data between multiple computers .
Four 、 The network layer
4.1 The origin of network layer
Ethernet protocol , rely on MAC Address sending data . Theoretically , Rely solely on MAC Address , Shanghai network card can find Los Angeles network card , Technically, it can be realized .
however , There is a major drawback to this . Ethernet uses broadcast mode to send data packets , All the members have one " package ", Not only is it inefficient , And it's limited to the sender's subnet . in other words , If two computers are not on the same subnet , The radio can't be transmitted . This design is reasonable , Otherwise, every computer on the Internet will receive all the packages , That would cause disaster .
The Internet is a huge network of numerous subnetworks , It's like imagining that computers in Shanghai and Los Angeles will be on the same subnet , It's almost impossible .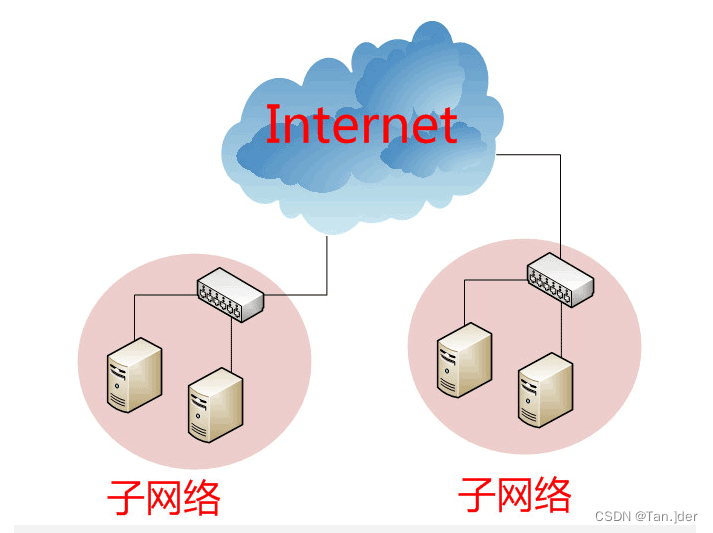
therefore , A way must be found , Be able to distinguish between MAC Address belongs to the same subnet , Which are not . If it's the same subnet , Just broadcast it , Otherwise, use " route " Mode sending .(" route " It means , It means how to distribute packets to different subnetworks , It's a big theme , This article does not cover .) Unfortunately ,MAC The address itself can't do that . It's only about the manufacturer , It has nothing to do with the network .
And that leads to this " The network layer " The birth of . Its purpose is to introduce a new set of addresses , It enables us to distinguish whether different computers belong to the same subnet . This set of addresses is called " network address ", abbreviation " website ".
therefore ," The network layer " After a , Each computer has two addresses , One is MAC Address , The other is the network address . There is no connection between the two addresses ,MAC The address is bound to the network card , The network address is assigned by the administrator , They're just random combinations .
The network address helps us to determine the subnet where the computer is located ,MAC The address sends the packet to the destination network card in the subnet . therefore , Logically, it can be inferred that , Must be dealing with the network address first , And then deal with MAC Address .
4.2 IP agreement
A protocol that specifies a network address , be called IP agreement . The address it defines , This is called IP Address .
at present , What is widely used is IP The fourth edition of the agreement , abbreviation IPv4. This version stipulates , The network address is 32 Binary bits make up .

5、 ... and 、 Transport layer
5.1 The origin of the transport layer
With MAC Address and IP Address , We can already establish communication on any two hosts on the Internet .
The next question is , There are many programs on the same host that need to use the network , such as , You're browsing the web , While chatting with friends online . When a packet comes from the Internet , how did you know? , It means the content of the web page , Or the content of online chat ?
in other words , We need another parameter , Indicates which program this packet is provided for ( process ) Use . This parameter is called " port "(port), It is actually the number of every program that uses the network card . Each packet is sent to a specific port of the host , So different programs can get the data they need .
" port " yes 0 To 65535 An integer between , Just right 16 Binary bits .0 To 1023 The port of is occupied by the system , The user can only choose greater than 1023 The port of . Whether it's browsing the web or chatting online , The application will randomly choose a port , Then contact the corresponding port of the server .
" Transport layer " The function of , It's about building " Port to port " Communication for . by comparison ,“ The network layer " The function of is to establish " Host to host " Communication for . Just determine the host and port , We can communicate between programs . therefore ,Unix The system puts the host + port , be called " Socket ”(socket). With it , Then we can develop network applications .
5.2 UDP agreement
Now? , We have to include port information in the packet , This requires a new agreement . The simplest implementation is called UDP agreement , Its format is almost in front of the data , Add the port number .
UDP Data packets , Also by " header " and " data " Two parts .
" header " Part of the main definition of the send port and receive port ," data " Part is the specific content . then , The whole UDP Put the packet in IP Packet " data " part , And I said before ,IP Packets are put in Ethernet packets , So the whole Ethernet packet is now like this :

UDP The packet is very simple ," header " Part of it is only 8 Bytes , The total length does not exceed 65,535 byte , Just put a IP Data packets .
5.3 TCP agreement
UDP The advantage of the protocol is that it's simpler , Easy to implement , But the disadvantage is poor reliability , Once the packet is sent , It's impossible to know if the other party has received .
To solve this problem , Improve network reliability ,TCP The agreement was born . This agreement is very complicated , But it can be approximated as , It has a confirmation mechanism UDP agreement , Every packet sent requires confirmation . If a packet is missing , You can't receive confirmation , The sender knows it's necessary to resend the packet .
therefore ,TCP The protocol ensures that data is not lost . Its disadvantage is that the process is complex 、 Difficult to achieve 、 Consume more resources .
TCP Packets and UDP The packets are the same , It's all embedded in IP Packet " data " part .TCP There is no length limit for packets , Theoretically, it can be infinitely long , But in order to ensure the efficiency of the network , Usually TCP The length of the packet will not exceed IP The length of the packet , To ensure that a single TCP Packets don't have to be split anymore .
6、 ... and 、 application layer
App received " Transport layer " The data of , The next step is to interpret . Because the Internet is an open architecture , There are various sources of data , The format must be specified in advance , Otherwise, it's impossible to interpret .
" application layer " The role of , It's about specifying the data format of the application .
for instance ,TCP Protocol can transfer data for various programs , such as Email、WWW、FTP wait . that , There must be a different protocol for email 、 Webpage 、FTP The format of the data , These application protocols make up " application layer ".
This is the highest level , Face users directly . Its data is in TCP Packet " data " part . therefore , Now the Ethernet packet is like this .
7、 ... and 、 A summary
The last article analyzed the general idea of the Internet , From bottom to top , The design idea of each layer protocol .
It's from the designer's point of view , Today I want to switch to the user's point of view , Look at how users go from top to bottom , Interacting with these agreements .
Let's start with the previous content , Make a summary .
We already know , Network communication is the exchange of packets . The computer A To the computer B Send a packet , The latter received , Reply to a packet , So as to realize the communication between two computers . Packet structure , It's basically the following :
Send this package , You need to know two addresses :
* The other person's MAC Address
* The other person's IP Address
With these two addresses , The packet can be delivered to the receiver accurately . however , As I said before ,MAC Address has limitations , If two computers are not on the same subnet , You can't know the other person's MAC Address , It has to go through the gateway (gateway) forward .
Above picture ,1 Computer number one is going to 4 Computer number one sends a packet . It first judges 4 Is computer No. 1 on the same subnet , It turns out it's not ( The following article introduces the judgment method ), So the packet is sent to the gateway A. gateway A Through routing protocols , Find out 4 Computer number one is on the subnet B, Send the packet to the gateway again B, gateway B Forwarding to 4 The computer no. .
1 Computer number one sends packets to the gateway A, You have to know the gateway A Of MAC Address . therefore , The destination address of the packet , There are actually two situations :
| scene | Packet address |
|---|---|
| The same subnet | The other person's MAC Address , The other person's IP Address |
| Not the same subnet | The gateway MAC Address , The other person's IP Address |
Before sending packets , The computer must determine whether the other party is on the same subnet , Then choose the appropriate MAC Address . Next , Let's see , In practice , How this process is accomplished .
8、 ... and 、 User's Internet settings
8.1 static state IP Address
You bought a new computer , Plug in the Internet cable , Turn it on , Can the computer access the Internet at this time ?
Usually you have to make some settings . Sometimes , Administrators ( perhaps ISP) I'll tell you the following four parameters , You put them in the operating system , The computer can be connected to the Internet :
Native IP Address
Subnet mask
The gateway IP Address
DNS Of IP Address
The picture below is Windows System settings window .
These four parameters are indispensable , I'll explain why you need to know them to get online . Because they are given , Every time the computer starts up , They all get the same IP Address , So this situation is called " static state IP Address online ".
however , It's a professional setting , Ordinary users are terrified , And if a computer's IP The address remains the same , Other computers can't use this address , inflexible . For these two reasons , Most users use " dynamic IP Address online ".
8.2 dynamic IP Address
So-called " dynamic IP Address ", When the computer is turned on , Will be automatically assigned to a IP Address , There's no need to set it up . It uses a protocol called DHCP agreement .
The agreement says , In every subnet , There is a computer in charge of all the IP Address , It's called "DHCP The server ". New computers join the network , You have to go to "DHCP The server " Send a "DHCP request " Data packets , apply IP Address and related network parameters .
As I said before , If two computers are on the same subnet , You have to know each other's MAC Address and IP Address , To send packets . however , The new computer doesn't know these two addresses , How to send packets ?
DHCP The agreement makes some clever rules .
8.3 DHCP agreement
First , It's an application layer protocol , Based on the UDP The agreement above , So the whole packet is like this :
(1) The front of " Ethernet header ", Set the sender ( This machine ) Of MAC Address and receiver (DHCP The server ) Of MAC Address . The former is the local network card MAC Address , The latter did not know at this time , Just fill in a broadcast address :FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF.
(2) hinder "IP header ", Set the sender's IP Address and receiver's IP Address . At this time , For both , This machine doesn't know . therefore , The sender's IP The address is set to 0.0.0.0, Receiving party IP The address is set to 255.255.255.255.
(3) final "UDP header ", Set the sender's port and the receiver's port . This part is DHCP The agreement stipulates that , The sender is 68 port , The receiver is 67 port .
After the packet is constructed , You can send out . Ethernet is broadcast transmission , Every computer on the same subnet receives this package . Because the receiver's MAC The address is FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF, I can't see who it was sent to , So every computer that receives this package , You have to analyze the IP Address , To determine if it was sent to you . When you see the sender IP The address is 0.0.0.0, The receiver is 255.255.255.255, therefore DHCP Server knows " This bag is for me ", And other computers can discard this package .
Next ,DHCP The server reads the data content of this package , Assign well IP Address , Send back one "DHCP Respond to " Data packets . The structure of this response package is similar , Ethernet header MAC Address is the network card address of both parties ,IP Head of IP The address is DHCP Server's IP Address ( From ) and 255.255.255.255( The receiving party ),UDP The port of the header is 67( From ) and 68( The receiving party ), Assigned to the requester IP The address and the specific parameters of the network are included in Data part .
The new computer received this response package , So I know my own IP Address 、 Subnet mask 、 default gateway 、DNS Server and so on .
With these values , The computer can access the Internet " surfing " 了 . Next , Let's look at an example , When a user visits a web page , How internet protocol works .
Nine 、 An instance : Access page
9.1 Local parameters
We assume that , Go through the steps in the previous section , Users set their own network parameters :
Native IP Address
Subnet mask
The gateway IP Address
DNS Of IP Address
Then he opens the browser , Want to visit baidu, In the address bar, I input the web address :www.baidu.com.
It means , The browser should be directed to Google Send a web request packet .
9.2 DNS agreement
We know , Send packet , You have to know the other person's IP Address . however , Now? , We only know the URL www.baidu.com, I don't know about it IP Address .
DNS Agreements can help us , Convert this URL to IP Address . It is known that DNS The server is 8.8.8.8, So we send this address a DNS Data packets (53 port ).
This machine has received HTTP After responding , You can display the web page , Complete a network communication .
So far for this example , Although simplified , But it basically reflects the whole communication process of internet protocol
边栏推荐
- Pfsense configurer le tutoriel de tunnel de site à site Tinc
- 高性能内网DNS系统介绍
- 大魚吃小魚小遊戲完整版
- Jenkins定时构建并传递构建参数
- 细节、MYSQL_DATE_FORMAT()_函数_详解(记得收藏)
- Anfulai embedded weekly report (issue 270): June 13, 2022 to June 19, 2022
- 国家认证--软件评测师考试要求
- Selected articles of the research paper | interpretation of the trend of McKinsey's China's Digital Innovation future
- 高等代数_第9章:线性映射
- Highly scalable, emqx 5.0 achieves 100million mqtt connections
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Whether MySQL has triggers
Goldfish rhca memoirs: do447 managing user and team access
Rongyun obtains token
Big fish eat small fish games full version
第十七届全国大学 RT-Thread创新专项奖
用户态热补丁原理与应用
Software testing office tools recommendation - Desktop Calendar
TC3608H高效率 1.2MHz DC-DC 升压器 IC
Servlet usage
贪吃蛇游戏项目完整版
Flutter PageView组件
Flutter 输入框组件
Rough reading of targeted supervised contractual learning for long tailed recognition
Sd6.20 summary of intensive training
Pfsense configuring tinc site to site tunneling tutorial
It is said that the price of the iPhone 14 will rise; TikTok US user data is transferred to Oracle, and bytes cannot be accessed; Seatunnel 2.1.2 releases geek headlines
IAR major upgrade, support vs code, St release the first sensor with processing unit
Functor
jmeter线程持续时间
Simple integration of client go gin IX create