当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode interview question 02.07. Linked list intersection [knowledge points: Double pointers, stack]
Leetcode interview question 02.07. Linked list intersection [knowledge points: Double pointers, stack]
2022-07-28 21:30:00 【Hongyan Hongdou】
subject
source : Power button (LeetCode)
link : Interview questions 02.07. The list intersects
Copyright belongs to the network . For commercial reprint, please contact the official authority , Non-commercial reprint please indicate the source .
Here are two head nodes of the single linked list headA and headB , Please find out and return the starting node where two single linked lists intersect . If there is no intersection between two linked lists , return null .
Figure two linked lists at the node c1 Start meeting :
Subject data Guarantee In the whole chain structure There is no ring .
Be careful , Function returns the result , Linked list must Keep its original structure .
Example 1:
Input :intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output :Intersected at ‘8’
explain : The value of the intersection node is 8 ( Be careful , If two linked lists intersect, they cannot be 0).
Starting from the respective heads , Linked list A by [4,1,8,4,5], Linked list B by [5,0,1,8,4,5].
stay A in , There is... Before the intersection node 2 Nodes ; stay B in , There is... Before the intersection node 3 Nodes .
Example 2: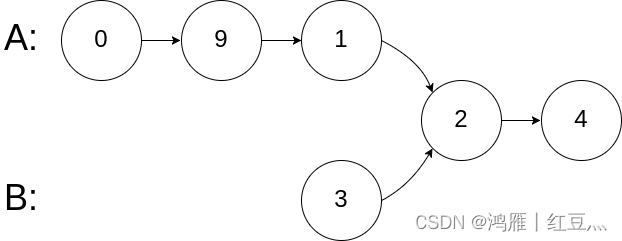
Input :intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output :Intersected at ‘2’
explain : The value of the intersection node is 2 ( Be careful , If two linked lists intersect, they cannot be 0).
Starting from the respective heads , Linked list A by [0,9,1,2,4], Linked list B by [3,2,4].
stay A in , There is... Before the intersection node 3 Nodes ; stay B in , There is... Before the intersection node 1 Nodes .
Example 3:
Input :intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output :null
explain : Starting from the respective heads , Linked list A by [2,6,4], Linked list B by [1,5].
Because these two linked lists don't intersect , therefore intersectVal It has to be for 0, and skipA and skipB It could be any value .
The two lists don't intersect , Therefore return null .
Tips :
- listA The number of nodes in is m
- listB The number of nodes in is n
- 0 <= m, n <= 3 * 104
- 1 <= Node.val <= 105
- 0 <= skipA <= m
- 0 <= skipB <= n
- If listA and listB There is no point of intersection ,intersectVal by 0
- If listA and listB There are intersections ,intersectVal == listA[skipA + 1] == listB[skipB + 1]
** Advanced :** Can you design a time complexity O(n) 、 Just use O(1) Memory solutions ?
Problem solving
Method 1 : Violence enumeration
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * }; */
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
struct ListNode *p,*q;
for(p=headA;p;p=p->next){
for(q=headB;q;q=q->next){
if(p == q){
goto HERE;
}
}
}
HERE: return p;
}
Time complexity O(m*n), Spatial complexity O(1)
Method 2 : Stack
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * }; */
#define MAXNUMS 30001
typedef struct _Stack{
struct ListNode* Array[MAXNUMS];
int Top;
}Stack;
void Push( Stack* S,struct ListNode* p )
{
S->Top++;
if(S->Top < MAXNUMS){
S->Array[S->Top] = p;
}
}
struct ListNode* Pop( Stack* S )
{
return S->Array[S->Top--];
}
bool isEmpty ( Stack* S )
{
return S->Top == -1 ? true : false;
}
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL){
return NULL;
}
Stack* A = malloc(sizeof(Stack));
A->Top = -1;
Stack* B = malloc(sizeof(Stack));
B->Top = -1;
struct ListNode *p,*q;
p = headA;
while(p){
Push( A,p );
p = p->next;
}
q = headB;
while(q){
Push( B,q );
q = q->next;
}
struct ListNode *ans;
p = q = NULL;
while( p == q && !isEmpty( A ) && !isEmpty( B ) ){
ans = p;
p = Pop( A );
q = Pop( B );
}
if((isEmpty( A ) || isEmpty( B )) && p == q){
ans = p;
}
return ans;
}
Method 3 : Front and rear double pointers ( Optimal solution of this problem )
Figure out first. 2 The length of the list , The pointer of the long linked list goes a few more steps first , Make sure the remaining length is equal to the other , then 2 The pointers move back at the same time , Judge whether it points to the same node ;
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * struct ListNode *next; * }; */
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
struct ListNode *p,*q;
int La,Lb;
La = Lb = 0;
for(p=headA;p;p=p->next,La++);
for(q=headB;q;q=q->next,Lb++);
p = headA;
q = headB;
int K;
if(La >= Lb){
K = La -Lb;
while(K--){
p = p->next;
}
}else{
K = Lb - La;
while(K--){
q = q->next;
}
}
while(p){
if(p == q){
break;
}else{
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
}
return p;
}
The great god NB Double pointer :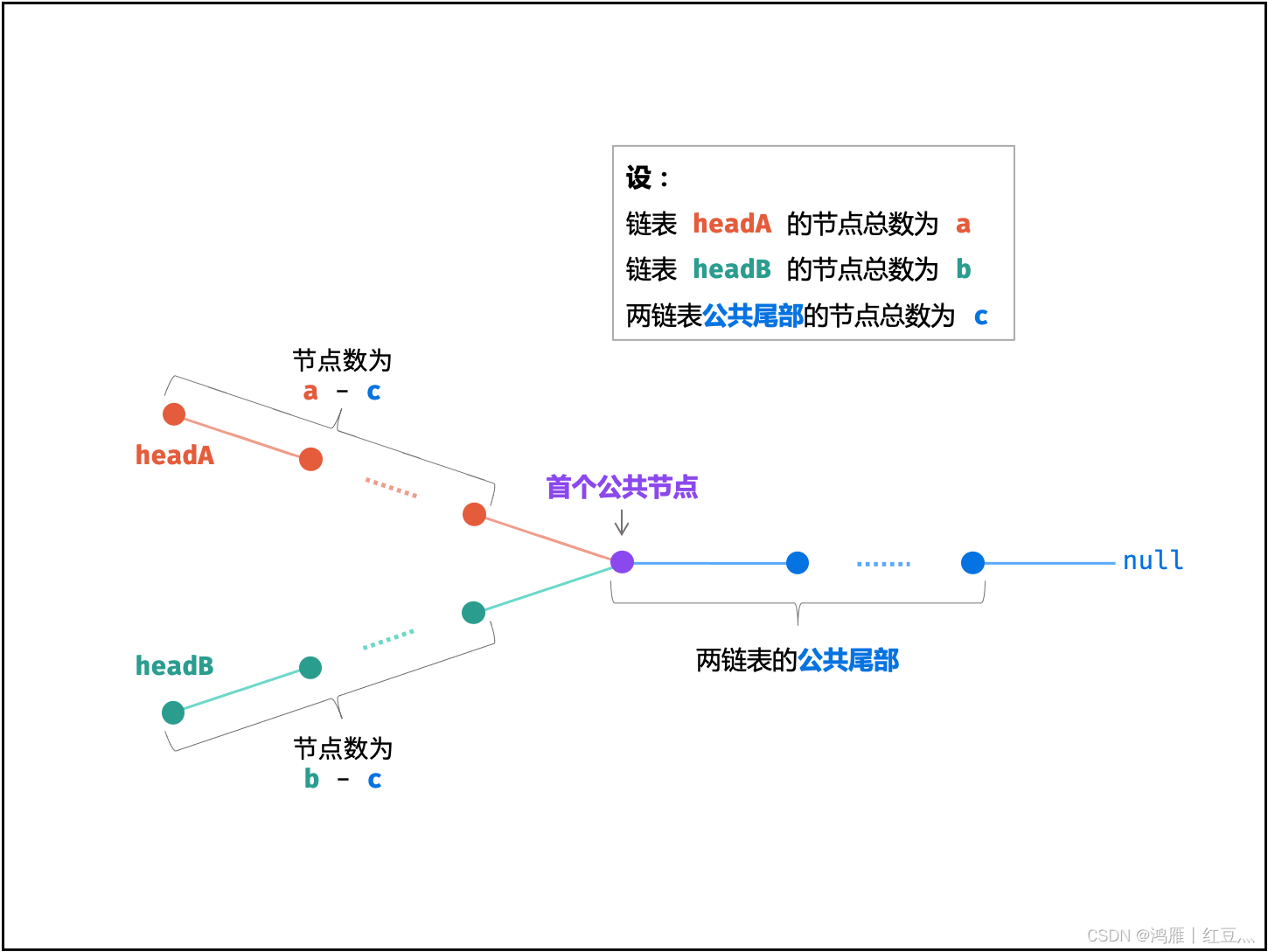
Consider building two node pointers A , B Point to the two chain header nodes respectively headA , headB , Do the following :
- The pointer A First traverse the linked list headA , Then start traversing the linked list headB , When go to node when , The total number of steps is :
a + (b - c) - The pointer B First traverse the linked list headB , Then start traversing the linked list headA , When go to node when , The total number of steps is :
b + (a - c)
It is shown in the following formula , Now the pointer A , B coincidence , And there are two situations :
a + (b - c) = b + (a - c)
- If two linked lists Yes The public tail ( namely c > 0c>0 ) : The pointer A , B At the same time point to 「 The first common node 」node .
- If two linked lists nothing The public tail ( namely c = 0c=0 ) : The pointer A , B At the same time point to nullnull .
Therefore return A that will do .
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
struct ListNode *A,*B;
A = headA;
B = headB;
while(A != B){
A = A==NULL ? headB : A->next;
B = B==NULL ? headA : B->next;
}
return A;
}
This code is so beautiful !!! A great god NB!!
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Nacos principle

Icml2022 | timing self-monitoring video transformer

证券企业基于容器化 PaaS 平台的 DevOps 规划建设 29 个典型问题总结

What functions does MySQL have? Don't look everywhere. Just look at this.

Ctfshow question making web module web11~web14

(turn) bubble sorting and optimization details

SSM-使用@Async和创建ThreadPoolTaskExecutor线程池

How to build a foreign environment for the self-supporting number of express evaluation? How much does it cost?

ctfshow 网络迷踪做题记录(1)

Discussion: if you want to land Devops, is it enough to only consider a good PAAS container platform?
随机推荐
Maxwell is an easy-to-use software for capturing MySQL data in real time
Study and use of cobalt strike
Study - 几何计算总结
4.1 various calling methods of member
Introduction to blue team: efficiency tools
实习日记第一周
Four methods of multi-threaded sequential operation. Ask casually during the interview
提前布局6G赛道!紫光展锐发布《6G无界 有AI》白皮书
Capture video by buffering
The ref value ‘xxx‘ will likely have changed by the time this effect function runs. If this ref......
1162. 地图分析-非递归法
高举5G和AI两面旗帜:紫光展锐市场峰会火爆申城
Applet container technology improves mobile R & D efficiency by 500%
Backup and recovery of SQL Server database
(PMIC)全、半桥驱动器CSD95481RWJ PDF 规格
Using El date picker to report errors in sub components
Maintenance of delta hot metal detector principle analysis of v5g-jc-r1 laser measurement sensor / detector
(turn) bubble sorting and optimization details
Automatic filling of spare parts at mobile end
quii cordova-plugin-telerik-imagepicker插件多图上传乱序