当前位置:网站首页>High level application of SQL statements in MySQL database (I)
High level application of SQL statements in MySQL database (I)
2022-06-24 22:46:00 【The strongest flying thunderobot Watergate】
One 、 Get ready
1. Source code compilation and installation MySQL
Mysql service ( One key deployment )
2. Create two tables as examples
mysql -uroot -p123123
create database train_ticket;
# Create a library
use train_ticket;
create table REGION(region varchar(10),site varchar(20));
create table FARE(site varchar(20),money int(10),date varchar(15));
# Create table
desc REGION;
desc FARE;
# View table structure 
insert into REGION values (‘south’,‘shenzhen’);
insert into REGION values (‘south’,‘hongkong’);
insert into REGION values (‘north’,‘beijing’);
insert into REGION values (‘north’,‘tianjin’);
# Insert data in Table 1
select * from REGION;
# View all data in the table 
insert into FARE values (‘shenzhen’,1000,‘2021-01-30’);
insert into FARE values (‘hongkong’,1500,‘2021-01-30’);
insert into FARE values (‘beijing’,800,‘2021-01-30’);
insert into FARE values (‘tianjin’,500,‘2021-01-30’);
insert into FARE values (‘hongkong’,2000,‘2021-02-05’);
select * from FARE;
Two 、SQL Statement high-level use
1.SELECT
Display all the data of one or more fields in the table
usage :
SELECT Field FROM Table name
example :
select region from REGION;
select money from FARE;
2.DISTINCT
Don't show duplicate data , And weight removal
usage :
ELECT DISTINCT Field FROM Table name
example :
select distinct region from REGION;
select distinct date from FARE;

3.WHERE
Conditional query
usage :
SELECT Field FROM Table name WHERE Conditions
example :
select site from FARE where money > 1000;
select site from FARE where money = 1000;
select site from FARE where money < 1000;
4.AND、OR
And or
usage :
SELECT Field FROM Table name WHERE Conditions 1 [AND|OR] ( Conditions 2);
example :
select site from FARE where money > 800 and (money < 2000);
select site,money from FARE where money < 600 or (money < 2100 and money >700);
select site,money,date from FARE where money >= 500 and (date < ‘2021-02-07’ and money < 1000);
5.IN
Show known data
usage :
SELECT Field FROM Table name WHERE Field IN (‘ value 1’,‘ value 2’,…);
example :
select site,money from FARE where money in (1500,500);
select money,date from FARE where money in (800,2000);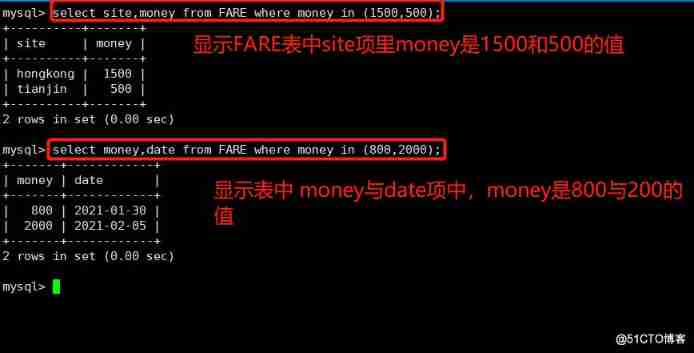
6.BETWEEN
Displays data in two ranges
usage :
SELECT Field FROM Table name WHERE Field BETWEEN ‘ value 1’ and ‘ value 2’;
example :
select * from FARE where money between 500 and 2000;
select * from FARE where money between 666 and 1888;

7. wildcard (LIKE)
Usually, wildcards are used with LIKE Use it together
%: A percent sign means zero 、 One or more characters
_: The underline represents a single character
LIKE: Used to match patterns to find data
usage :
SELECT Field FROM Table name WHERE Field LIKE ‘ Pattern ’;
example :
select * from FARE where site LIKE ‘be%’;
select * from FARE where site LIKE ‘ho%’;
select site,money from FARE where site LIKE ‘%jin_’;
select site,money from FARE where site LIKE ‘%kon_’;

8.ORDER BY
Sort by keyword
usage :
SELECT Field FROM Table name [WHERE Conditions ] ORDER BY Field [ASC,DESC];
#ASC: Sort in ascending order , The default sorting method
#DESC: Sort in descending order
example :
select * from FARE order by money desc;
select * from FARE order by money asc;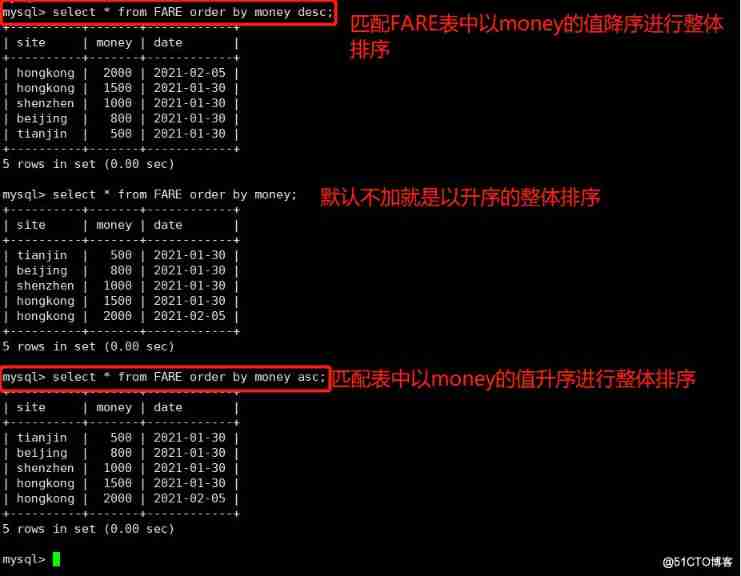
select date,money from FARE order by money desc;
select date,money from FARE where money > 999 order by money asc;
3、 ... and 、 function
1. Mathematical functions
The specific usage is shown in the table below :
function explain
abs(x) return x The absolute value of
rand() return 0 To 1 The random number
mod(x,y) return x Divide y The remainder after
power(x,y) return x Of y Power
round(x) Return from x The nearest integer
round(x,y) Retain x Of y The rounded value of a decimal place
sqrt(x) return x The square root of
truncate(x,y) Return to digital x Truncated to y A decimal value
ceil(x) Returns greater than or equal to x Minimum integer of
floor(x) Returns less than or equal to x Maximum integer for
greatest(x1,x2…) Returns the maximum value in the collection
east(x1,x2…) Returns the smallest value in the set
example :
select abs(-1),rand(),mod(5,3),power(2,3),round(1.567);
select sqrt(9),truncate(1.2345,2),ceil(1.3);
floor(1.7),greatest(1,2,3,4,5),least(1,2,3,4,5);
2. Aggregate functions
The specific usage is shown in the table below :
function explain
avg() Returns the average value of the specified column
count() Returns the value of the specified column NULL The number of values
min() Returns the minimum value of the specified column
max() Returns the maximum value of the specified column
sum(x) Returns the sum of all values in the specified column
example :
select avg(money) from FARE;
select count(money) from FARE;
select min(money) from FARE;
select max(money) from FARE;
select sum(money) from FARE;
3. String function
function explain
trim() Returns a value with the specified format removed
concat(x,y) The parameters that will be provided x and y Concatenate into a string
substr(x,y) Get from string x No y A string starting at a position , Follow substring() Functions work the same
substr(x,y,z) Get from string x No y The starting length of a position is z String
length(x) Return string x The length of
replace(x,y,z) The string z Alternative string x String in y
upper(x) The string x All of the letters of the alphabet become capital letters
lower(x) The string x All of the letters of the are changed into lower case letters
left(x,y) Return string x Before y Characters
right(x,y) Return string x After y Characters
repeat(x,y) The string x repeat y Time
space(x) return x A space
strcmp(x,y) Compare x and y, The value returned can be -1,0,1
reverse(x) The string x reverse
[ Location ]: The value of can be LEADING ( At first ), TRAILING ( ending ), BOTH ( The beginning and the end )
[ The string to remove ]: From the beginning of the string 、 ending , Or a string removed from the beginning and end ; The default is space
example :
select trim(leading ‘be’ from ‘beijing’);
select trim(trailing ‘–’ from ‘beijing–’);
select trim(both ‘–’ from ‘–shenzhen–’);
select concat(region,site) from REGION where region = ‘south’;
select concat(region,’ ',site) from REGION where region = ‘south’;
select substr(money,1,2) from FARE;
select substr(money,1,3) from FARE;
select length(site) from FARE;
select length(date) from FARE;
select replace(site,‘zhen’,‘–’) from FARE;
select replace(site,‘on’,‘–’) from FARE;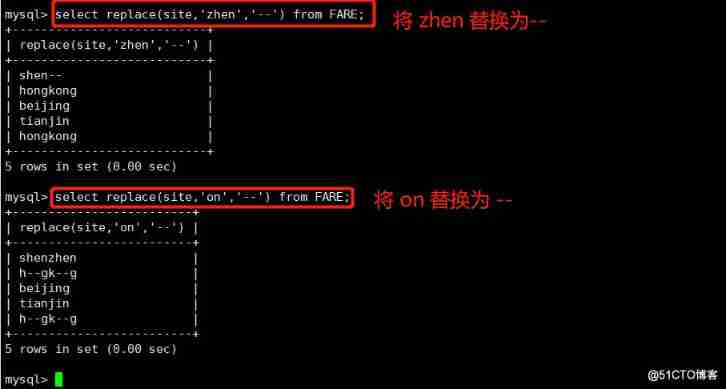
select upper(site) from FARE;
select upper(region) from REGION;
select lower(‘ABCDERG’);
select left(site,2) from FARE;
select right(site,3) from FARE;
select repeat(site,2) from FARE;
select repeat(region,3) from REGION;
select space(2);
select strcmp(100,200);
select strcmp(200,100);
select strcmp(200,200);
select reverse(site) from FARE;
select reverse(date) from FARE;

4.'||' Connector
If in mysql In the configuration file ,sql_mode Open... Open PIPES_AS_CONCAT, be "||" Treat as the concatenation operator of a string, not as the or operator
And string splicing function Concat Similar , This sum Oracle The database is used in the same way 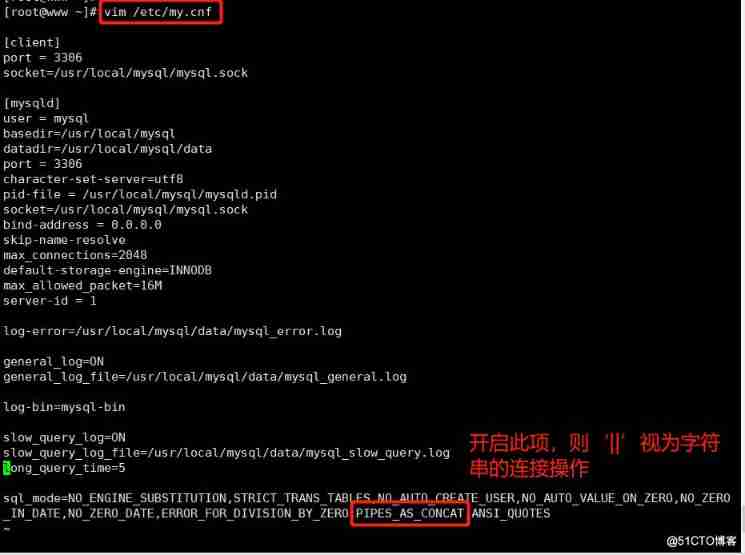
mysql -uroot -p123123
use train_ticket;
select region || ’ ’ || site from REGION where region = ‘north’;
select site || ’ ’ || money || ’ ’ || date from FARE;

5.GROUP BY
BY Summarize and group the query results in the following fields , Usually used in combination with aggregate functions
GROUP BY There is a principle , Namely SELECT In all the following columns , Columns that do not use aggregate functions , Must appear in GROUP BY Back
usage :
select site,sum(money) from FARE group by site;
select site,sum(money),date from FARE group by site order by money desc;
select site,count(money),sum(money),date from FARE group by site order by money desc;

6.HAVING
Used to filter by GROUP BY Statement returned recordset , Usually with GROUP BY Statements are used in conjunction with
HAVING The existence of sentences makes up for WHERE Keywords cannot be combined with aggregate functions
If you are SELECT Only the function bar , Then there is no need for GROUP BY Clause
usage :
SELECT Field 1,SUM( Field 2) FROM Table name GROUP BY Field 1 HAVING( Function conditions );
example :
select site,count(money),sum(money),date from FARE group by site having sum(money) >=800;
7. Alias
Used for field alias and table alias
usage :
SELECT “ Table alias ”.“ Field 1” [AS] “ Field 1 alias ” FROM “ Table name ” [AS] “ Table alias ”;
example :
select RE.region AS reg, count(site) from REGION AS RE group by reg;
select FA.site AS si,sum(money),count(money),date AS da from FARE AS FA group by si;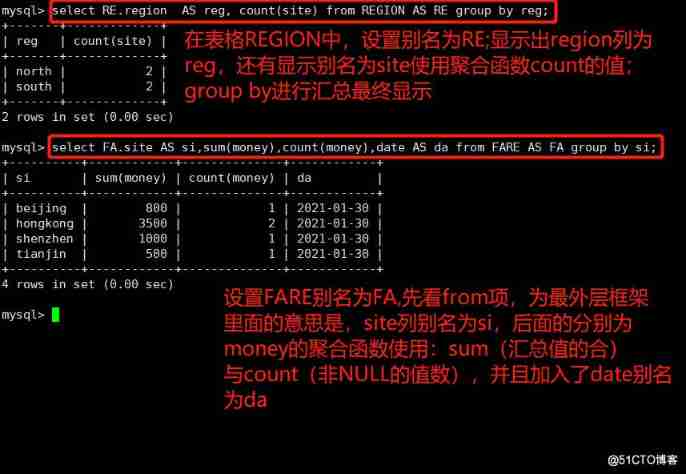
8. Subquery
Connect tables , stay WHERE Clause or HAVING Clause to insert another SQL sentence
# Can be symbolic operators
# example :=、>、<、>=、<=
# It can also be a literal operator
# example :LIKE、IN、BETWEEN
example :
select A.site,region from REGION AS A where A.site in(select B.site from FARE AS B where money<2000);
select B.site,money,date from FARE AS B where site in(select A.site from REGION AS A where region = ‘north’);
9.EXISTS
It is used to test whether the inner query produces any results , Whether Boolean value is true or not
If any , The system will execute the SQL sentence
If it were not so , The whole SQL Statement will not produce any results
usage :
SELECT Field 1 FROM surface 1 WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM surface 2 WHERE Conditions );
example :
use train_ticket;
select region from REGION where exists (select * from FARE where money = ‘800’);
select site from REGION where exists (select * from FARE where money = ‘801’);
select * from FARE where money = ‘800’;
select * from FARE where money = ‘801’;
select site from REGION;
10. Link query
10.1 inner join—— It's equivalent
Returns only rows with equal join fields in two tables
usage :
SELECT Field FROM surface 1 INNER JOIN surface 2 ON surface 1. Field = surface 2. Field ;
example :
select * from REGION AS A inner join FARE AS B on A.site = B.site;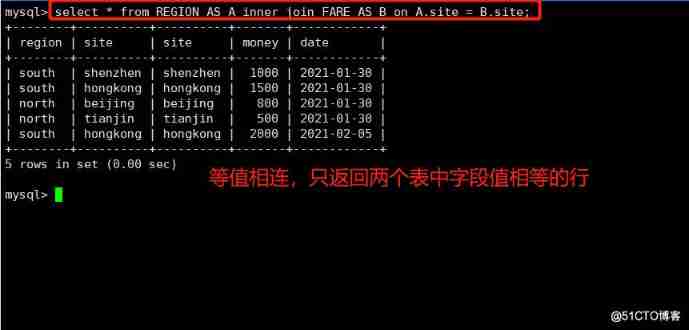
10.2 left join—— Left join
Returns records that include all records in the left table and join fields in the right table
example :
SELECT Field FROM surface 1 LEFT JOIN surface 2 ON surface 1. Field = surface 2. Field ;
example :
select * from REGION AS A left join FARE AS B on A.site = B.site;
10.3 right join—— Right link
Returns records including all records in the right table and the same join field in the left table
example :
SELECT Field FROM surface 1 RIGHT JOIN surface 2 ON surface 1. Field = surface 2. Field ;
example :
update FARE set site=‘nanjing’ where money=‘2000’;
select * from REGION AS A right join FARE AS B on A.site = B.site;
边栏推荐
- 04A interrupt configuration
- Combine pod identity in aks and secret in CSI driver mount key vault
- Huada 4a0gpio settings
- Creating files, recursively creating directories
- Programmers become gods by digging holes in one year, carrying flags in five years and becoming gods in ten years
- Idea close global search box
- Leetcode algorithm refers to offer II 027 Palindrome linked list
- Fanuc robot_ Introduction to Karel programming (1)
- 使用Aggregated APIServer扩展你的kubernetes API
- 堆内存分配的并发问题
猜你喜欢
CA Zhouji - the first lesson in 2022 rust

NiO, bio, AIO

大厂面试必问:如何解决TCP可靠传输问题?8张图带你详细学习

FANUC机器人_KAREL编程入门学习(1)

Redis hop table

Genesis public chain and a group of encryption investors in the United States gathered in consensus 2022

YGG recent game partners list

NIO、BIO、AIO
【个人实验报告】
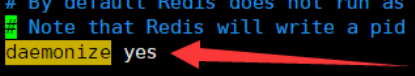
Docker installs redis-5.0.12. Detailed steps
随机推荐
Problem solving - nested lists
Environment configuration | vs2017 configuring openmesh source code and environment
Based on the codeless platform, users deeply participated in the construction, and digital data + Nanjing Fiberglass Institute jointly built a national smart laboratory solution
nuScenes——数据集配置过程中遇到图像文件缺失或大小为0时的补救方法
Dynamic memory management (1)
Pinduoduo updates the merchant live broadcast service agreement and strictly punishes the illegal merchants
CSRF and SSRF for web attacks
问题求解——嵌套列表
Can AI chat robots replace manual customer service?
软件设计的七大原则
How to solve the problem that the computer suddenly can't connect to WiFi
STP spanning tree protocol Foundation
双亲委派机制
YGG recent game partners list
VRRP skills topic
大厂面试必问:如何解决TCP可靠传输问题?8张图带你详细学习
Heavyweight! Fada is listed as a "specialized and new" enterprise
Seven principles of software design
Rip protocol of dynamic routing protocol
Technology Review: what is the evolution route of container technology? What imagination space is there in the future?
