当前位置:网站首页>Lambda and filter, List 和 numpy array的索引,以及各种距离指标distance-metrics,拼接数组以及axis=0 and axis=1的区分
Lambda and filter, List 和 numpy array的索引,以及各种距离指标distance-metrics,拼接数组以及axis=0 and axis=1的区分
2022-06-12 11:35:00 【king52113141314】
Lambda
lambda 函数参数:函数表达式
# 函数定义
def add(x,y):
return x+y
# 上面函数使用lambda改写
lambda x,y: x+y
filter
如果第一个参数是函数:
将第二个参数(即可迭代数据)的每一个元素作为函数的参数进行计算,将返回true的值筛选出来以列表的形式返回。注意:这个函数的返回值只能要么是True, 要么是False。
filter(lambda x: x, [-1, 0, 1]) #[-1, 1] filter(lambda x: not x, [-1, 0, 1]) #[0] def f(x): return True if x == 1 else False filter(lambda x: f(x), [-1, 0, 1]) #[1]
如果第一个参数为None:
将第二个参数里面的true值筛选出来filter(None, (True, 1, 0, -1, False)) #(True, 1, -1)
想要使用filter后的结果,最好先将它转为list:
list(filter_return)
Python中filter与lambda的结合使用_肖哥shelwin的博客-CSDN博客
Python_lambda表达式_filter()过滤器_map映射_NUC_Dodamce的博客-CSDN博客_lambda map 过滤
List 和 numpy array的索引
Remove an item from a list in Python (clear, pop, remove, del)
l = list(range(10))
print(l)
# [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
l.clear()
print(l)
# []
print(l.pop(3))
# 4
print(l)
# [1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print(l.pop())#If the argument is omitted, the last item is deleted.
# 9
print(l)
# [1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7]
del l[-1]
print(l)
# [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
del l[2:5]
print(l)
# [0, 1, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
###Removing items that satisfy the condition
#is equivalent to extracting items that do not satisfy the condition.
print([i for i in l if i % 2 != 0])
# [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
l = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'Bob', 'Dave']
print(l)
# ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'Bob', 'Dave']
l.remove('Alice')
print(l)
# ['Bob', 'Charlie', 'Bob', 'Dave']
aaa=np.arange(10)
iii=[0,5,2]
np.delete(aaa, iii, None)
#array([1, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9])检查 a nested list or numpy array是否为空?
How to check if a nested list or numpy array is essentially empty?
#1, 推荐
#Use the any() function.
#This returns True if any list within the list is not empty.
alist = [[],[]]
if not any(alist):
print("Empty list!")
#2
l2 = []
if l2:
print("list is not empty")
elif not l2:
print("list is empty")
#3
if len(l2) == 0:
print("list is empty")
else:
print("list is not empty")
#4 不推荐
alist = [[],[]]
if not np.any(alist):
print("Empty list!")
#1
arr1 = np.array([])
ran = not np.any(arr1)
if ran:
print('Array is empty')
else:
print('Array is not empty')
#2
arr = np.array([])
flag = np.size(arr)
if flag:
print('Array is not empty')
else:
print('Array is empty')
#3 推荐
a = np.array([])
if a.size == 0:
print("Empty")
#4 不推荐 比如arr = np.array([[0],[]])
arr = np.array([[],[]])
if not np.any(arr):
print("Empty!")
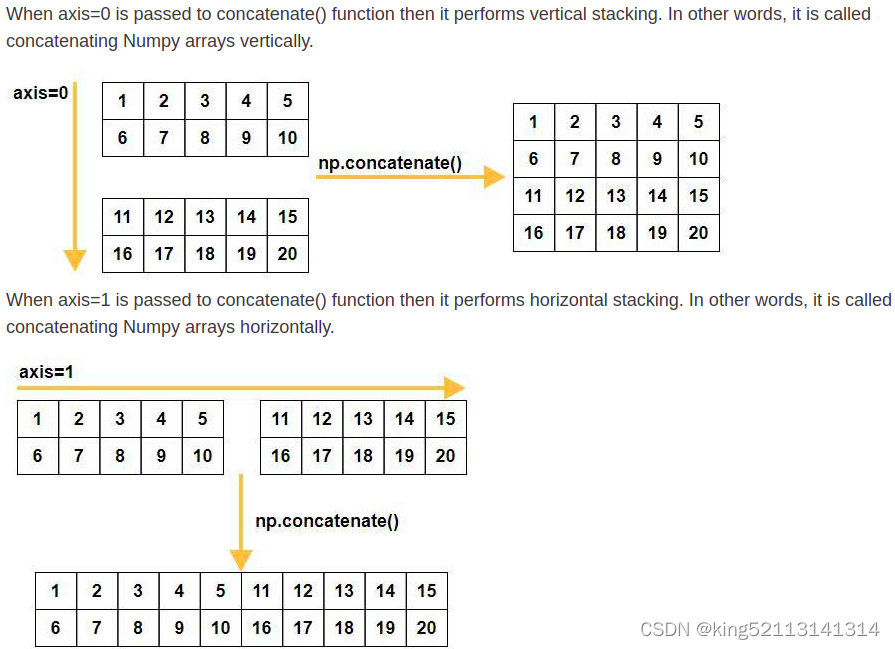
拼接数组以及axis=0 and axis=1的区分
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]])
b = np.array([[11, 12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19, 20]])
print('Concatenate along axis=0:\n', np.concatenate((a,b), axis=0))
print('Concatenate along axis=0:\n', np.concatenate((a,b)))
print('Vertically stacked array:\n', np.vstack((a,b)))
##pass tuple or list of Numpy arrays is OK
print('Concatenate along axis=1:\n', np.concatenate([a,b], axis=1))
print('Horizontally stacked array:\n', np.hstack((a,b)))
交换数组列 or Rearrange columns of a given array
import numpy as np
array_nums = np.arange(20).reshape(4,5)
print("Original array:",array_nums)
### swapping the column with index of original array
array_nums[:,[0,3]] = array_nums[:,[3,0]]
print("\nAfter swapping column1 with column4:",array_nums)
############# Rearrange columns of a given array by indexes
array1 = np.array([[11, 22, 33, 44, 55],
[66, 77, 88, 99, 100]])
print("Original arrays:",array1)
i = [1,3,0,4,2]
result = array1[:,i]
print("New array:",result)


所有distance-metrics
推荐使用 minkowski distance 和 the Mahalanobis distance。
使用scipy的函数
Distance computations (scipy.spatial.distance) — SciPy v1.8.1 Manual
scipy/distance.py at v1.8.1 · scipy/scipy · GitHub
GitHub - niranjanbsubramanian/distance-measures
数据科学中常见的9种距离度量方法_视学算法的博客-CSDN博客
https://towardsdatascience.com/9-distance-measures-in-data-science-918109d069fa
4 Distance Measures for Machine Learning
马氏距离和欧式距离详解_bluesliuf的博客-CSDN博客_欧式距离
import numpy as np
from math import sqrt
# Euclidean distance
def euclidean(x, y):
distance = 0
for a, b in zip(x, y):
distance += (sum([(pow((a-b),2))]))
return sqrt(distance)
print("Euclidean Distance:",euclidean([1,3,4,1],[3,2,1,1]))
#Calculate the Euclidean distance using linalg.norm()
# initializing points in
# numpy arrays
point1 = np.array((1, 2, 3))
point2 = np.array((1, 1, 1))
# calculating Euclidean distance
# using linalg.norm()
dist = np.linalg.norm(point1 - point2)
# using sum() and square()
sum_sq = np.sum(np.square(point1 - point2))# finding sum of squares
dist = np.sqrt(sum_sq)# Doing squareroot
# Manhattan distance
def manhattan(x, y):
distance=0
for a,b in zip(x,y):
distance += sum([abs(a-b)])
return distance
print("Manhattan Distance:",manhattan([1,3,4,1],[3,2,1,1]))
#chebyshev distance
def chebyshev(x,y):
distance = []
for a,b in zip(x,y):
distance.append(abs(a-b))
return max(distance)
print("Chebyshev Distance:",chebyshev([1,3,4,1],[3,2,1,1]))
#hamming distance
def hamming(x,y):
distance = 0
for a,b in zip(x,y):
if a != b:
distance += 1
return distance
print("Hamming Distance:",hamming("hello world","hallo warld"))
#cosine_similarity
def cosine_similarity(x,y):
numerator = 0
sum_x = 0
sum_y = 0
for a,b in zip(x,y):
numerator += sum([a * b])
sum_x += sum([a**2])
sum_y += sum([b**2])
denominator = round(sqrt(sum_x) * sqrt(sum_y))
return numerator / denominator
print("Cosine Similarity:", cosine_similarity([1,3,4,1],[3,2,1,1]))
#jaccard
def jaccard_similarity(x,y):
intersection = len(set(x).intersection(set(y)))
union = len(set(x).union(set(y)))
return (intersection / union)
print("Jaccard Similarity:",jaccard_similarity([0,1,2,5,6], [0,2,3,4,5,7,9]))
print("Jaccard Distance:", 1-jaccard_similarity([0,1,2,5,6],[0,2,3,4,5,7,9]))
#minkowski
# calculating minkowski distance between vectors
from math import sqrt
# calculate minkowski distance
def minkowski_distance(a, b, p):
'''
p=1, the distance measure is the Manhattan measure.
p=2, the distance measure is the Euclidean measure.
p = ∞, the distance measure is the Chebyshev measure.
'''
return sum(abs(e1-e2)**p for e1, e2 in zip(a,b))**(1/p)
# define data
row1 = [10, 20, 15, 10, 5]
row2 = [12, 24, 18, 8, 7]
# calculate distance (p=1)
dist = minkowski_distance(row1, row2, 1)
print(dist)
# calculate distance (p=2)
dist = minkowski_distance(row1, row2, 2)
print(dist)
#Mahalanobis
# Importing libraries
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import scipy as stats
# calculate Mahalanobis function to calculate
# the Mahalanobis distance
def calculateMahalanobis(y=None, data=None, cov=None):
y_mu = y - np.mean(data)
if not cov:
cov = np.cov(data.values.T)
inv_covmat = np.linalg.inv(cov)
left = np.dot(y_mu, inv_covmat)
mahal = np.dot(left, y_mu.T)
return mahal.diagonal()
# create new column in dataframe that contains
# Mahalanobis distance for each row
df['calculateMahalanobis'] = mahalanobis(x=df, data=df[['Price', 'Distance',
'Emission','Performance',
'Mileage']])GitHub - brando90/Normalized-Euclidean-Distance-and-Similarity-NED-NES-


边栏推荐
- SOT23(Small Outline Transistor)
- 890. find and replace mode
- UI自动化测试中比较少见的异常记录
- Pytoch notes
- Basic principle of Doppler effect
- LVS health state detection based on application layer
- arm各种交叉编译工具的区别
- MySQL45讲 01 | 基础架构:一条SQL查询语句是如何执行的?
- Clj3-100alh30 residual current relay
- Relatively rare exception records in UI automation test
猜你喜欢

K58. Chapter 1 installing kubernetes V1.23 based on kubeadm -- cluster deployment
信号继电器RXSF1-RK271018DC110V

Record the pits encountered when using JPA

Socket implements TCP communication flow

你需要社交媒体二维码的21个理由

Manuscript manuscript format preparation
当自己有台服务器之后

^34作用域面试题

scanf返回值被忽略的原因及其解决方法

无限生长,我们都将奔赴未来 | InfoQ中国成立15周年
随机推荐
读mysql45讲-自我总结(部分)
自然语言处理nlp 数据集下载地址
Signal relay rxsf1-rk271018dc110v
C# 35. Select default network card
scanf返回值被忽略的原因及其解决方法
ReentrantLock源码分析
Naming specification / annotation specification / logical specification
UML系列文章(31)体系结构建模---部署图
The difference between meta universe chain games and traditional games
架构训练模块 7
(三十七)Bee如何同时使用不同数据源实例
Logrotate log rotation method create and copyruncate principles
Deep learning and CV tutorial (14) | image segmentation (FCN, segnet, u-net, pspnet, deeplab, refinenet)
C# 35. 选择默认网卡
(37) How bee uses different data source instances at the same time
Unity connect to Microsoft SQLSERVER database
Don't swallow rice with vinegar! Teach you 2 moves to make the fish bones "run out" safely
VirtualBox virtual machine shut down due to abnormal system. The virtual machine startup item is missing
如何查看glibc版本
AcWing 1921. 重新排列奶牛(环图)