当前位置:网站首页>Reading mysql45 lecture - self summary (part)
Reading mysql45 lecture - self summary (part)
2022-06-12 10:49:00 【Hurry to Friday】
sql Execution process
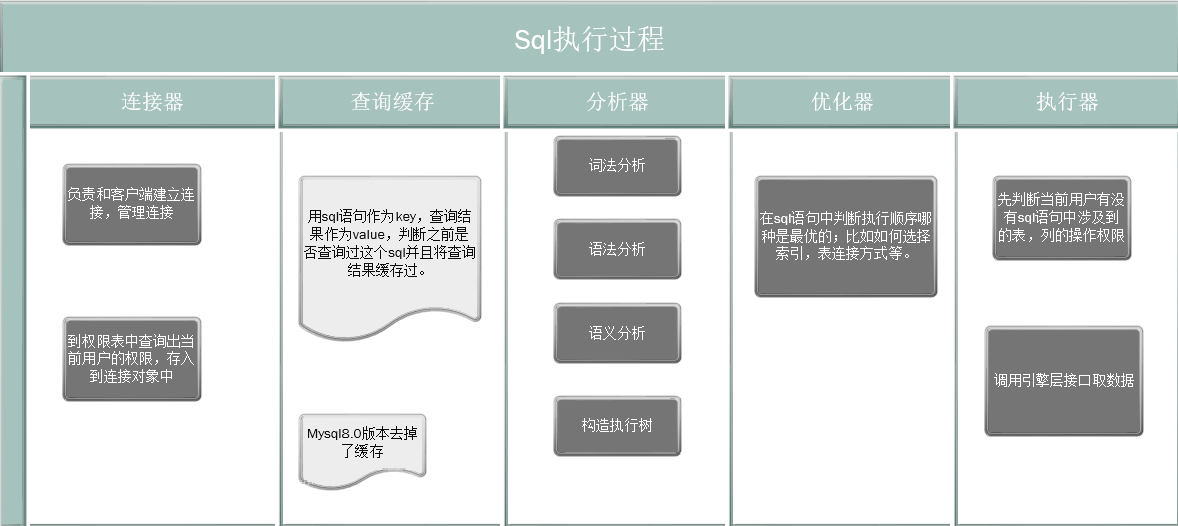
The connector
Responsible for establishing a connection with the client , After the connection is established, all the permissions of the currently connected user will be queried in the permission table , Put this permission set into the current connection object , after sql This permission set is used for all permission judgments involved in the process . If the connection is valid , Modify the permissions of the connected user with the super management account , It's not going to work , Only after reconnection will it take effect .
After the connection is complete , After execution sql after , The current connection will be idle ; Use show processlist; Command view is Command That column is Sleep value ;

The connection of the client has not been operated for a long time , The connection will automatically disconnect , The parameters for configuring this time are wait_timeout, The default is 2 Hours , The value of this parameter I query is 7200, In seconds, it is 2 Hours .
Long connection is after the connection is established successfully , Multiple query requests use this long connection ; Short connection is to disconnect after executing several query requests each time , Create a new connection the next time there is a query request .
Creating a new connection consumes resources , So long connections are preferred , However, long connections may cause insufficient memory . because MYSQL The memory used during execution is stored in the connection object , These resources are only released when the connection is disconnected .
More and more query requests , More and more memory will be used , If the long connection is kept open, the memory will be occupied all the time , Too much memory , It may be forcibly killed by the system (OOM).
The method to solve the problem that long connections occupy too much memory can be implemented after a resource consuming sql Then disconnect the connection manually ; Or use mysql_reset_connection To reinitialize the connection resources , This process does not require reconnection and re-authorization , But it restores the connection to the state it was in when it was created .
The query cache
MYSQL After getting a query request , I will check this first sql Is there any... In the cache ,key Is the statement of the query ,value Is the result of a query . Query cache failures are very frequent , As long as there is an update to a table , All query caches on this table will be cleared , So if the table has few update operations, it is suitable to use cache .
- query_cache_type=0(off) Indicates that the cache function is turned off
- query_cache_type=1(on) Indicates that the cache function is enabled
- query_cache_type=2(DEMAND) default sql No caching , If you want to use cache , stay sql of use SQL_CACHE Explicitly specify to use the cache , such as :select SQL_CACHE * from T where ID=10;
MySQL 8.0 Version of the query cache directly removed the entire block , in other words 8.0 At first, there was no This function .
analyzer
The analyzer will start with sql Sentences do “ Lexical analysis ”, That is, to identify keywords ,select Is a query statement ,select The next step is to query the column name ,from Later, it should be identified as table name, etc ; After lexical analysis, you have to do grammatical analysis , According to the result of lexical analysis , The parser will follow the grammar rules , Judge the one you typed SQL Does the statement satisfy MySQL grammar .
elect * from t Such a statement will report an error ; Less tips s; Such mistakes are grammatical mistakes , Then I understand that it is just not recognized in lexical analysis elect Should be select, But in the grammar analysis, it will be analyzed as select.
SQL Sentence analysis is divided into lexical analysis and grammatical analysis ,mysql The lexical analysis of is made by MySQLLex[MySQL Self realized ] complete , Grammatical analysis consists of Bison Generate . Well, except Bison Outside ,Java There are also open source lexical structure analysis tools, such as Antlr4,ANTLR Generate a parser from the syntax , You can build and traverse the parse tree .
Optimizer
In the real beginning sql Before , You also need to go through the optimizer . The optimizer is when there are multiple indexes in a table , Decide which index to use ; Or there are multiple table associations in a statement (join) When , Determine the join order of the tables . Like this sql:
select * from t1 join t2 using(ID) where t1.c=10 and t2.d=20;
- You can use first t1.c=10 Come first t1 Data fetching from table , And then use t1 Of ID and t2 Tables are associated , Retake t2.d=20 The data of
- You can also use t2.d=20 Come first t2 Data fetching from table , And then use t2 Of ID and t1 Tables are associated , Take it out again t1.c=10 The data of
The logical result of the two execution methods is the same , But the efficiency of the execution will be different , The role of the optimizer is to decide which solution to choose .
actuator
At the beginning of execution , Let's first judge what you do to this watch T Do you have permission to execute the query . For an ordinary sql such as :select * from t where id = 10,id There is no index , The execution is roughly as follows :
- Call the engine layer interface to query the first row of data , Judge id Is it equal to 10, If so, put it in the result set , No, just skip .
- Call the engine layer interface to get the next line , Because every record has next_record This attribute , You can quickly locate the next piece of data , Make the above judgment again
- Until the last piece of data in the database is queried .
In the slow query log of the database, there is a rows_examined Field of , Indicates that the statement is scanned during execution How many rows? . This value is accumulated each time the actuator calls the engine to get a row of data . In some cases , The executor is called once , Inside the engine, it scans multiple lines , So the number of lines scanned by the engine is not necessarily the same as rows_examined The values are equal .
journal
MYSQL It is often involved in WAL technology , All the way through Write-ahead logging, The implementation is to write logs first , Then operate the disk . When there is an update request , The operation will be recorded in the log first , Write to the disk in idle time or when the log is full . There is no need to operate the disk every time there is a request to update data , With logs, you can write requests for updating data to disk in batches , Increase of efficiency .
- binlog The journal is server Layer of ,redo log The journal is Innodb Engine layer ;
- binlog It is equivalent to logical log , The record is updated sql The logic of , But there are many different ways of recording , There are direct records sql Of the statement , There are also specific ways to update field values ;redo log Equivalent to physical log , It records what changes have been made on a data page ;
- binlog It is the method of additional writing , Is to write one file full and then write another file ; however redo log It's circularly written , That is to say redo log The size of is fixed , When it is full, it is necessary to erase what was written before it can be written .
Use how variables like '%innodb_log%' The command sees two files , The size of each file is 524288000KB( My guess is kb, Convert to a file 500M).


In the picture above write pos This is the location where the log is currently written ,checkpoint This is where the log needs to be erased , Clockwise according to yellow ,write pos To checkpoint The part between them is blank , You can continue to write , and checkpoint To write pos Between them are the logs that have been written ; When write pos and checkpoint After the overlap, a part of the contents of the log records will be updated to the disk , Then you can erase this part ,checkpoint You can go forward a part .
With redo log,Innodb You can guarantee mysql After an abnormal restart , Will ensure the integrity of the transaction , The submitted data will not be lost , Uncommitted data will be rolled back . This ability is called crash-safe.
Based on a simple update sql To draw a simple process of logging (update t set x = x +1 where id = 1):

stay redo log There are two operations in , This is the two-stage submission , Two phase commit is to ensure the logical consistency between the two logs .
- If it is written for the first time redo log And then there was a crash , Is that business or prepare state , And there's no writing binlog, Then roll back
- If you are writing binglog And then there was a crash , That means in redo log According to the XID Yes, you can. binglog Find the corresponding transaction in , Just commit the transaction .
Parameters innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit Set to 1 Represents... For each transaction redo log The logs will be persisted to the disk , Parameters sync_binlog Set to 1 Every time said binlog The logs will be persisted to the disk .
Brush dirty pages
Sometimes, we usually perform faster updates sql Suddenly the execution is slow , Probably because mysql Cleaning dirty pages . When the data page in memory is inconsistent with the data page in disk , Call this memory page dirty , After the data pages in memory are written to disk , The data pages of memory and disk are consistent , The data pages in memory are called clean pages , This process is called cleaning the dirty pages . The dirty page may be because :
- The update operation requires writing redo log;redo log It is limited. , When it is full, it cannot be written again , You need to brush dirty pages .
- The memory is full , When other queries need to read new data pages from disk to memory , If there's not enough memory , It is necessary to eliminate the data pages that have not been used for the longest time , At this time, if the dirty pages are eliminated , You need to brush dirty pages .
- mysql When the system is considered idle .
- mysql During normal shutdown .
If the performance of the machine is low , That is, the speed of cleaning dirty pages is slower than that of generating dirty pages , This will cause the entire database to be blocked .
Business
Four characteristics of transactions ACID(Atomicity、Consistency、Isolation、Durability, Atomicity 、 One Sexual nature 、 Isolation, 、 persistence )
SQL Transaction isolation boundary level in :
- Read uncommitted : Before a transaction is committed , Changes to the data can be seen by other transactions
- Read the submission : Before a transaction is committed , Changes to data are not visible to other transactions
- Repeatable : A transaction is in the process of execution , The data you see is always consistent with the data when the transaction is started , Changes to data are also invisible to other transactions before they are committed .
- Serialization : The read operation of the same row of records will be locked , Write operation will add a write lock , When there is a read/write lock conflict , Need to wait for the former to release .
Use command show variables like '%transaction_isolation%' You can view the currently set transaction isolation level .
The implementation of repeatable reading is to create a view when the transaction starts , It is equivalent to taking a snapshot of the data of the entire library , In this way, the data needed in the transaction process is seen from the entire snapshot , It can ensure that the data is consistent during the transaction process . At the read commit transaction isolation level , This view is in each sql Created during execution , Read uncommitted data is read directly every time , No concept of view ; Serialization is to avoid parallel access by locking .
There can be multiple records in the system A version , It's multi version concurrency control of database (MVCC)(multi version concurrency control)
start transaction / begin transaction Is not the starting point for starting a transaction , The real start of the transaction is the first one in the execution of the transaction sql When ; If you want to start a transaction directly , You can use commands start transaction / begin transaction with consistent snapshot;
Under the repeatable partition , When a transaction is started, a snapshot of the entire library will be taken , But this snapshot is not the data of all libraries copy One copy ; It is implemented by version number . Each transaction will apply for one when it is started transaction_id, This id At the beginning of the transaction InnoDB Of the transaction system , And in strict accordance with the order of application .
mysql Each row of data in is in multiple versions , The version of this row will be updated every time the transaction updates the data , And put the transaction_id Record in this row of data version , Record as row trx_id.
in other words , A row in a data table , There may be multiple versions (row), Each version has its own rowtrx_id.

v3 Is the latest version of the data ,v1,v2 Is physically nonexistent , But through redo log The operation of updating data recorded in to calculate the current data fallback data to v2 perhaps v1 edition .
There are three situations in which a data version can be invisible to a view that can be read repeatedly :
- Version not submitted , invisible .
- Version submitted , The transaction corresponding to the committed version is created after the view is created , invisible
- Version submitted , The transaction corresponding to the submitted version is created before the transaction is created , so .
The table used in the following figure t There's a piece of data in ,(id=1,k=1);

Sort out according to time :
- Business A Open consistency view , Start transaction
- Business B Open the one-time view , Start transaction
- Business C Open transaction , And update the data , Automatic submission (auto_commit=1)
- Business B Ready to update id=1 The data of , Although in business C The transaction was created before the data was updated B And open the consistency view , But the update operation is the current read , Otherwise, if the updated data of other transactions is not visible, the current transaction will lose data when updating ; So the business B The data read by the update operation of is k=2; After the update k=3; In the transaction B Medium select In operation , In the latest version of the read data row trx_id It's your own business id, So we can see , Read k=3.
- Business A Conduct select operation , Business A The view is created in a transaction B And transaction C Previous , So the data read is k=1.
If in select Add to statement lock in share mode perhaps for update It is also the implementation of the current read .( But I tried if I was directly in the business A In the query of lock in share mode It's blocked , It should be because the updated read lock will not be released until the entire transaction is committed , So it's blocked .)
The difference between read commit and repeatable read in creating a consistent view is :
- Read commit is in every sql The view is created only when it is executed
- Repeatable reading is to create a view when a transaction is started
Indexes
stay Innodb in , The data in the table is stored by index according to the primary key order , The tables in this storage mode are called index organization tables .Inndb Used B+ Tree index model , So the data is stored in B+ On the tree .

Innodb Indexes in are divided into primary key indexes and non primary key indexes ; The leaf node in the primary key index stores the entire row of data , It's also called cluster index ; The leaf node of a common index stores the value of the primary key , Also called secondary index .
The difference between a primary key index query and a normal index query :
- select * from t where id= 100, Primary key index query , Find directly in the primary key index tree id=100 The record of , Then directly round the data of the row .
- select * from t where c = 100, That is, the secondary index query , First in the index c Find... In the tree c=100 The record of , Then, according to the stored primary key value, go to the primary key index tree to get the data of the whole row . This process is called back to table .
Therefore, the query of non primary key index will have one more query tree process than the scanning of primary key index .
select ID from t where c = 100 Such a query will not return to the table , The primary key has been id The value of is already in c On the index tree , So you can directly provide query results , Indexes c Also called overlay index .
Leftmost prefix principle
This leftmost prefix can be the leftmost of the union index N A field , It can also be the leftmost of a string index M Characters .
If there are existing fields a And field b Joint query for , There are also fields a And field b Respective queries , Then build a joint index (a,b) Words , If the query criteria are only b Words , It does not conform to the leftmost prefix principle , And I won't go (a,b) Joint index of . Then you need to maintain a federated index (a,b), Maintain another index (b), Or you can maintain one (b,a) And a (a) Separate index ;
The different ways of indexing above can be based on the fields a And field b To distinguish , If the field a yes 8 Bytes of , Field b yes 16 Bytes of , Then you can consider building a federated index (b,a) And general index (a), In this way, the space occupied by the index can be smaller .
Index push down
select * from t where a >= 10 and b <= 100
There is a joint index (a,b); Then it will be based on a Index found all a A value greater than or equal to 10 Of , And because b It is also part of the union index , So it will be in a Filter out the records found in the index tree b Less than or equal to 100 The tree of , And then based on id Value to go back to the table to query the whole row of data , Because the query is *.
One of the important principles of index design is to access data as little as possible .
change buffer
When you need to update a data , If the data is in a data page in memory , Then update directly , If it is not in the current data page , The update operation will be recorded in change buffer in , This saves the need to write to the disk for each update . When you need to read data that is not in memory , And the data is in change buffer When there are records in , You need to read the data from the disk into the data page in the memory , And then change buffer The update operation in applies to the data , This ensures data consistency .
take change buffer The total process of applying operations in to data pages is called merge; Except that queries trigger merge, Database shutdown also triggers merge operation , The background thread will also go regularly merge.
however merge Operation does not apply to unique indexes , Because the unique index needs to judge that the inserted value cannot appear in the whole table , Then you need to read the data of the entire table into memory , There is no need to use it when it has been read into memory change buffer 了 .
Because querying the updated data will trigger merge operation , therefore change buffer The suitable scenario is to read less and write more .
stay explain sql In the process, if you find row There is a big difference between the number of scanned lines and the actual estimated number of lines , Can pass analyze table t To recalculate the index information .
Index a string
When quoting a string field , You can specify the length .alter table tableName add index idx_column(columnName(3));
Although this takes up less space than ordinary indexes , But the price is that the number of scanning lines will increase . The index tree of the ordinary index is stored name The value is xxyy; The index length of the referenced tree specified above name The value is xxy;
If there is a field dedicated to the ID card number , The current requirement is to query the corresponding date of birth , Then you can specify the length on this index , It will save some space .
We talked about overlay indexes before , For example, a sql:
select id,name from t where name = ‘xxx’
If name Field does not specify length , Is the full length , Then there's no need to go back to the table , You can get it directly id Value ; But if name The field is a prefix index that specifies the length , Then it needs to be based on id Index and then query name value , because name In an index entry name It's not complete .
count(*)
In the use of count(*) When querying how much data a table has ,mysql I will use the index to count the quantity , Because in the primary key index, the index entries store the entire row of data , The common index stores id, So the space occupied by ordinary indexes is relatively small , therefore mysql Will select normal index ; On the implementation mysql The optimizer will find the smallest index tree to traverse .
Sort
In general, you need to sort select In the sentence ,mysql Each thread will be allocated a memory block for sorting sort_buffer . such as :
select id,name,job_number ,entry_date
from myhr_user mu
where gender = 'FEMALE'
order by entry_date
limit 1000
If you sort according to the algorithm of full field sorting , The process is like this :
- initialization sort_buffer, Make sure that the field to put in is id,name,job_number,entry_date
- according to gender = ‘FEMALE’ Take out the qualified id
- And then according to id Query id,name,job_number,entry_date The value of the field is placed in sort_buffer in
- stay sort_buffer in , Yes entry_date Sort
- Take before 1000 Bar record
If select Fields in and order If there are many fields in . That is to say mysql Think put into sort_buffer There are too many fields in a single line , It takes up too much space , Will use rowid Sorting algorithm . The process is similar :
- initialization sort_buffer, Make sure that the field to put in is id,entry_date
- according to gender = ‘FEMALE’ Take out the qualified id
- And then according to id Query entry_date The value of the field is placed in sort_buffer in
- stay sort_buffer in , Yes entry_date Sort
- Take before 1000 results , And then use id Go back to the table again name,job_number,entry_date The value of the field returns
The difference between the two is that the fields to be placed in initialization are different , The former is to put all into , The latter is to put only the required fields , That is, sort fields and id, But the latter needs to be based on id Value is returned to the table for query select Required fields in .
lock
Global lock
Global lock is to lock the whole database instance .MySQL It provides a way to add global read lock , The order is Flush tables with read lock (FTWRL). After that, the following statements of other threads will be blocked : Data update statement ( Data addition, deletion and modification )、 Data definition statement ( Include Build table 、 Modify table structure, etc ) Commit statements for and update class transactions .
The official logic backup tool is mysqldump, When mysqldump Use command parameters -single-transaction When , A transaction will be started before importing data , Make sure you get a consistent view , because MVCC Support for , This process can update the data .-single-transaction Suitable for databases that support transaction engines ,FTWRL You can use libraries that do not support transaction engines .
Table lock
The syntax of table lock is lock table tableNameA read/write, tableNameB read/write…, The syntax for releasing locks is unlock tables .
lock table Syntax lock table , Will lock the access of other threads , It also limits how the current thread accesses the table .
lock table tableA read,tableB write; Other threads are not allowed to tableA Write operation , Not right tableB Read it ; alike , In the current thread unlock tables Before , The current thread cannot be used for tableA Write operation , Read only , But in the current thread tableB For reading and writing .
Another type of table level lock is MDL(meta data lock), This lock does not need to be added as shown , It is implicit and automatic . When adding, deleting, modifying, and querying a table , Will add a MDL Read the lock ; When modifying the table structure, a MDL Write lock .
- MDL Read lock and MDL There is no conflict between read locks , Multiple threads can add, delete, modify, and query the same table
- MDL Read lock and MDL There is a conflict between write locks , When modifying the table structure , You cannot add, delete, modify, or query ; alike , During addition, deletion, modification and query , It won't let you modify the table structure .
What I understand is MDL A lock is actually a lock added to a table structure modification .
If the data of a table is delete operation , Not completely released delete The amount of space occupied by data , part delete The space of the data will be marked as reusable . Can pass alter table t engine=Innodb Command to rebuild the table , To make delete The space occupied by data is completely released . Behind this command is to create a new temporary table with the same structure as the original table , Then insert the data of the original table row by row in the order of the primary key , So the data will be compact , There won't be spaces . Then replace the temporary table with the original table .
Row lock
Row locks are added when necessary , However, the row lock is not released immediately after use , Instead, the row lock will only be released when the transaction ends . This is the two-stage lock protocol .
If more than one row needs to be locked in a transaction , To put Most likely to cause lock conflicts 、 The lock most likely to affect concurrency should be put back as far as possible , In this way, the data time occupied by row locks that may conflict will be shorter .
Deadlock and deadlock detection
After a deadlock occurs, there are two strategies :
- Wait until the timeout , The timeout duration can be determined by modifying the configuration parameters innodb_lock_wait_timeout decision , This parameter defaults to 50s.
- Deadlock detection , After a deadlock is found , Rollback a transaction in the deadlock chain , Let other business continue , The parameter innodb_deadlock_detect Set to on, Indicates that the logic is turned on .
The second case will be used under normal conditions , Because in the first case, I have to wait 50s Your words have too much influence , However, you can't just set the timeout length to a small value , Some transactions may be executed a little longer , Easy to cause accidental injury .
The second method is deadlock detection when a transaction is locked , To consume cpu Does the resource computing itself fall into circular dependency , If the hot line is updated cpu The utilization rate of will soar .
边栏推荐
- A hundred secrets and a few secrets - Caesar encryption
- M-Arch(番外12)GD32L233评测-CAU加解密(捉弄下小编)
- Golang start service background daemon
- Wechat payment, wechat refund, Alibaba payment
- Get array median
- ID obfuscation
- Common tools download address
- Common methods of string class
- How to play the 618 super cat games on Taobao? Here comes the introduction to the overall activities of the Super Cat Games
- Tp6+memcached configuration
猜你喜欢
Grid layout

AcWing 135. Maximum subsequence sum (prefix sum + monotone queue to find the minimum value of fixed length interval)

How to refund the pre-sale deposit of JD 618 in 2022? Can JD 618 deposit be refunded?

k58.第一章 基于kubeadm安装kubernetes v1.23 -- 集群部署

How the ArrayList collection implements ascending and descending order
Malicious code analysis practice -- using apatedns and inetsim to simulate network environment

Create vite source code analysis

Leetcode2154. Multiply the found value by 2 (binary search)

Bug easily ignored by recursion

基于C#的安全聊天工具设计
随机推荐
Mysql5.6.24 installation free deployment method
M-Arch(番外13)GD32L233评测-来点音乐
Valentina Studio Pro for Mac(mac数据库管理软件)
Leetcode 2169. 得到 0 的操作数
PHP Apple internal purchase callback processing
卡鱼刺别再喝醋吞米饭了!教你2招,让鱼刺安全“跑出来”
How to play the 2022 Taobao 618 Super Cat Games? Playing skills of 2022 Taobao 618 Cat Games
[machine learning] practice of logistic regression classification based on Iris data set
Building 64 bit wampserver and DVWA in win7 virtual machine
Leetcode2154. 将找到的值乘以 2(二分查找)
Index query efficiency of MySQL
Binassii module - converting between binary and ASCII
M-Arch(番外12)GD32L233评测-CAU加解密(捉弄下小编)
PHP wechat red packet allocation logic
k53.第二章 基于二进制包安装kubernetes v1.22 --集群部署
基于C#的安全聊天工具设计
Failed to load resource: the server responded with a status of 413 (Request Entity Too Large)
AcWing 41. Stack containing min function (monotone stack)
Find the location of a function in PHP
【机器学习】基于鸢尾花(iris)数据集的逻辑回归分类实践